Top 10 Endpoint Security Best Practices For Avoiding Incidents
Endpoint security has been a growing concern for businesses. The rise of hybrid and remote work impacts cybersecurity in different ways. The increasing number of users and endpoints, the diversity of work devices, and remote work put more pressure on IT teams to keep the network elements, such as endpoints, secure and reliable.
In this article, we present the top 10 best practices for endpoint security by identifying its risks and challenges.
Top 10 best practices for endpoint security
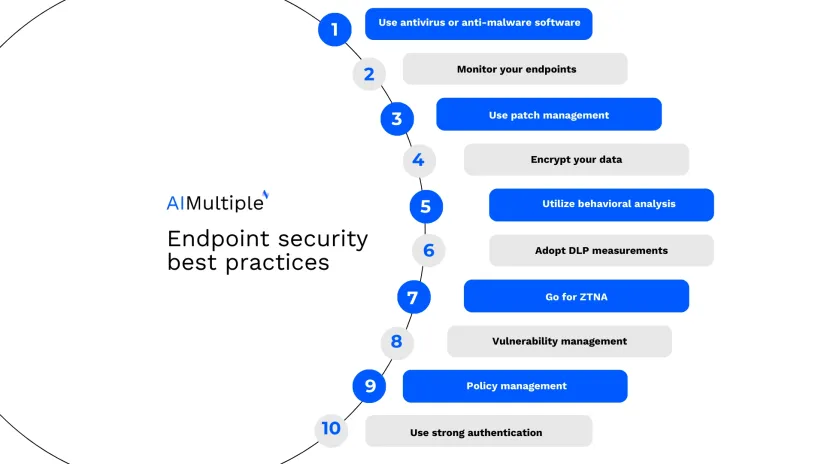
Implementing effective endpoint security practices is essential for safeguarding sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, and mitigating the risk of cyber attacks. Top 10 best practices are:
1. Use antivirus or anti-malware software
Antivirus software takes security measurements against signature based threat actors such as viruses, trojans, and worms. Endpoint security works robustly when combined with antivirus and helps mitigate the spread of malware. For more, explore how antivirus collaborates with endpoint security.
2. Monitor your endpoints
Monitor your endpoints against unauthorized use of applications or web browsing. Making your endpoints visible helps with endpoint detection, threat intelligence, and behavior analysis. Most of the endpoint protection suites come with monitoring features. For more information on endpoint management software: Top 10 Endpoint Management Software
3. Use patch management
Patch management helps to keep your endpoints up-to-date and healthy. Apply the latest security patches; vulnerabilities result from unfixed bugs, and old versions of software are evaded so that most endpoint management software comes with a patch management feature. For more information on endpoint management software: main components of endpoint protection solutions
4. Encrypt your data
Utilize encryption technologies to protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Implement full-disk encryption on endpoints to safeguard data in case of device loss or theft. Additionally, use encrypted communication protocols such as HTTPS for secure data transmission over networks.
5. Utilize behavioral analysis
Use behavioral analysis to detect and respond to suspicious or malicious activities on endpoints. Behavioral analysis involves monitoring and analyzing patterns of behavior exhibited by users, applications, and processes to identify deviations from normal or expected behavior that may indicate a security threat.
6. Adopt DLP measurements
Adopting Data Loss Prevention (DLP) practices can significantly enhance endpoint security by helping organizations prevent the unauthorized disclosure or exfiltration of sensitive data from endpoints. Data encryption, encryption of removable storage, such as USB devices, are practices DLP solutions assimilate. For more: Complete Guide to Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and Top 10 USB Blocking Software
7. Go for ZTNA
The Zero Trust Network Approach ensures security by providing access per user based on policy rules, meaning the access control check is done for each user when access rights are requested for applications, websites, or network connections. In comparison to VPN, which permits access to users when they are inside the network, ZTNA controls granular access requests so that users inside the network are subject to continuous security verifications. For more information: Differences between ZTNA and VPN
8. Vulnerability management
Manage your vulnerable endpoints and vulnerable data, such as your critical files, by proactively scanning and monitoring. Adopting vulnerability management practices is essential for strengthening endpoint security by proactively identifying, prioritizing, and addressing security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
9. Policy management
Create intelligible and succinct policies for endpoints. Policies build a security posture by enforcing rules such as access control and device control. For more about device control rules: Device Control Policy: Features, Benefits & Challenges
10. Use strong authentication
Enforce the use of strong passwords or implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance authentication security. MFA requires users to provide additional verification factors, such as biometrics or one-time codes, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Most common endpoint security risks
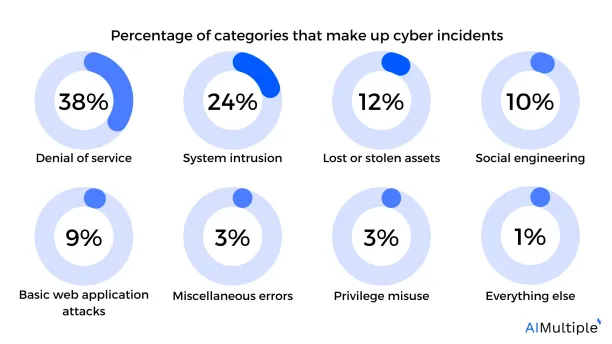
According to the report, Data Breaches Investigations 20231 , published by Verizon, an American multinational telecommunications conglomarate2, incidents that lead to data breaches are classified into 7 (excluding the subcategory “everything else”) subcategories: system intrusion, social engineering, basic web application attacks, miscellaneous errors, denial of service, lost and stolen assets, and last but not least, privilege misuse.
The most frequent top three actors in order are denial of service, system intrusion, and lost or stolen assets, with system intrusion having the highest probability of resulting in data breaches (2 in 5 data breaches belong to the subcategory of system intrusion). System intrusion is the general title for incidents such as malware and ransomware, which leverage sensitive information to achieve their ends.
Why is endpoint security so important?
As described above, endpoint security best practices help businesses overcome endpoint security risks that have become more frequent in the last few years. For more: Why is it important now?
FAQ
What is BYOD, and what does BYOD policy aim for?
The trend of employees using their personal devices for work purposes is called Bring Your Own Device.
BYOD policies must balance the benefits of employee flexibility with the need to maintain security and compliance standards. Ensuring that personal devices meet security requirements and segregating personal and corporate data is essential to mitigating the risks associated with BYOD. For more: BYOD policy
Further reading
- Top 10 Hexnode Alternatives Based on 10,800+ Reviews
- Top 10 Device Control Software: Review-based Analysis
- Top 10 Endpoint Management Software: 12K+ Reviews
If you need help finding a vendor or have any questions, feel free to contact us:
External resources
- 1. “2023 Data Breach Investigations Report”. Verizon. Accessed: 22/March/2024.
- 2. “Verizon”. Wikipedia. Accessed: 22/March/2024.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.