Microsegmentation tools help IT teams divide their networks into discrete controlled parts, making it difficult for outsiders to breach the entire network. For example, thanks to network segmentation TeamViewer’s breach did not impact customer systems.1 Based on the key features and market presence, see the top 10 microsegmentation software solutions:
- Tufin for network security policy management
- Cisco Identity Services Engine for network access control
- AlgoSec
- Prisma Cloud (Cloud Workload Protection)
- Check Point CloudGuard Network Security
- VMware NSX for data center networking
- Illumio Zero Trust
- Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
- Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration)
- Flow Virtual Networking for network virtualization
Features
All providers offer common features and therefore can support typical microsegmentation use cases.
| Vendor | APT defense | Network topology mapping | Additional features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tufin | ✅ | ✅ | Policy orchestration |
| AlgoSec | ✅ | ✅ | Hybrid cloud management |
| Cisco Identity Services Engine | ❌ | ❌ | Medical network access control |
| Check Point CloudGuard Network Security | ❌ | ❌ | Hybrid cloud management |
| VMware NSX | ❌ | ✅ | Hybrid cloud management |
| Prisma Cloud (Cloud Workload Protection) | ✅ | ✅ | Runtime protection for cloud workloads |
| Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) | ✅ | ❌ | Not specified |
| Illumio Zero Trust | ✅ | ✅ | Hybrid cloud management |
| Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration) | ❌ | ✅ | Hybrid cloud management |
| Flow Virtual Networking | ❌ | ❌ | Network virtualization |
Vendors with:
- APT (advanced persistent threat) defense: Identify targeted threats by analyzing unusual traffic patterns
- Network topology mapping: Discover a network’s components and topology, creating a visual map of the network architecture.
Read more: Microsegmentation use cases, microsegmentation in cloud.
Market presence
| Vendor | Number of reviews* | Average rating* | Pricing driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tufin | 286 | 4.1 | Usage-based pricing |
| AlgoSec | 334 | 4.5 | Not specified |
| Cisco Identity Services Engine | 258 | 4.2 | Number & type of endpoints |
| Check Point CloudGuard Network Security | 194 | 4.3 | Usage-based pricing |
| VMware NSX | 190 | 4.3 | Rate-based pricing |
| Prisma Cloud (Cloud Workload Protection) | 134 | 4.1 | Usage-based pricing |
| Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) | 106 | 4.4 | Deployment size, options, and modules |
| Illumio Zero Trust | 34 | 4.4 | Number of workload units |
| Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration) | 22 | 4.2 | Deployment size and options |
| Flow Virtual Networking | 11 | 4.4 | Deployment size, chosen features, and support options |
See vendor selection criteria.
Tufin
Tufin is one of the market leaders supporting more than half of the Forbes Global 2000.2
Key features:
- Network change management: Monitor information about your organization’s network devices by documenting configurations.
- Microsegmentation: Divide a network into granular segments and implement security controls based on the needs of each segment.
- Network security policy management: Manage policies to secure firewalls, networks, and assets against unapproved access.
- Firewall orchestration: Execute a centralized security management layer to implement security policies across firewalls.
Why we like it:
One of its strengths is its broad compatibility across a wide range of devices and platforms, making it an ideal choice for multi-vendor environments. This vendor-agnostic approach ensures visibility and control over diverse network components.
We also appreciated its policy compliance and risk management features. Tufin effectively identifies and alerts on overly permissive rules or those that introduce unnecessary risk, making compliance audits far more manageable. The platform also correlates vulnerabilities with associated network policies. This helps operations teams to conduct proactive risk mitigation.
Additionally, Tufin provides robust API support, enabling seamless integration with both commercial tools and custom-built solutions, helping embed Tufin into their existing workflows. This is particularly beneficial for Managed Service Providers (MSPs), who often deal with hundreds of changes across multiple domains and require efficiency.
Choose Tufin for microsegmentation & policy management.
Best practices:
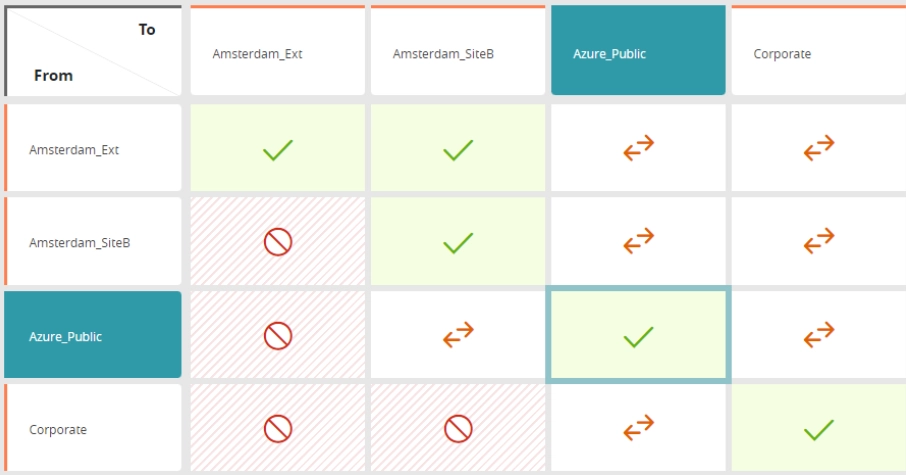
Implement and monitor network microsegments: Users can identify access violations across microsegments by using a corporate matrix, and choose to delete them or mark them as temporary deviations.
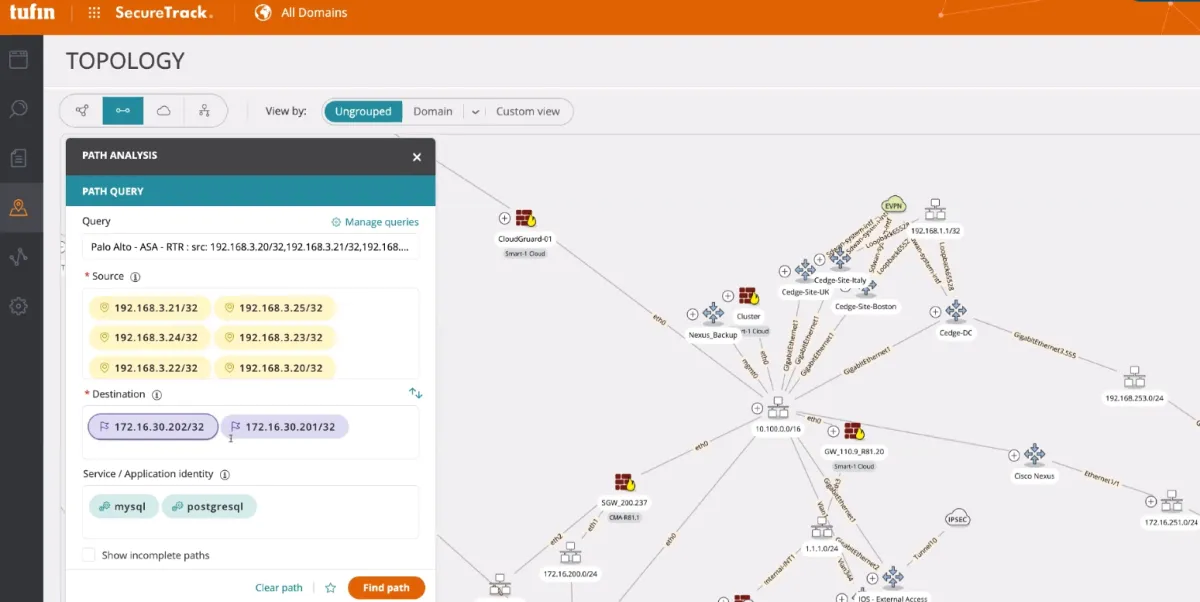
Navigate network topology maps: Gain network visibility by leveraging the topology map, allowing security policy management across cloud and hybrid environments.
Define zero-trust zones: Users can enable zero-trust cloud network access with Tufin—keep close track of what can talk to what, and who can communicate to whom on your network.
Create a policy with Tufin:
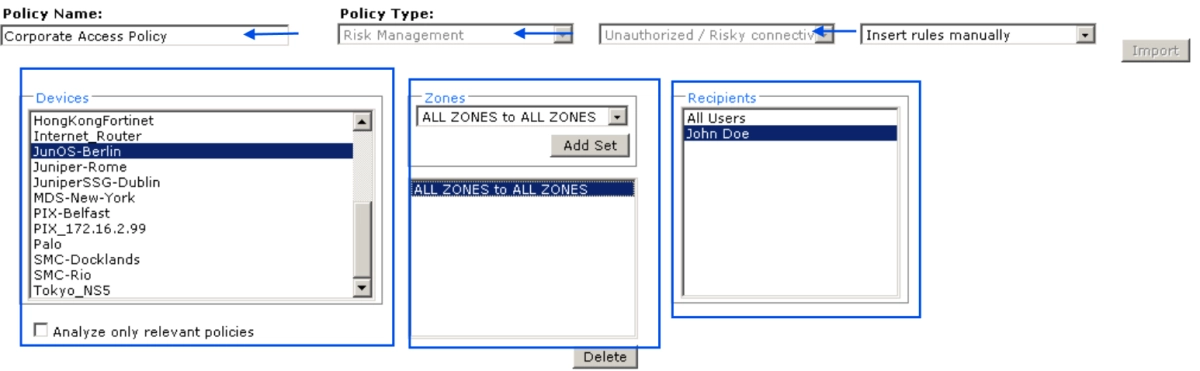
Users can type a “policy name”, and select the following:
- Compliance policy type
- Devices to which the compliance policy will apply
- Recipients to receive alerts when installed policy conflicts with this compliance policy
Pros✅
- Microsegmentation: Customers note that when a hacker breaches traditional firewalls and attempts to move laterally, Tufin plays a critical role by isolating the whole network to guarantee there is no damage to the sensitive data.3

- Firewall management: User comments reflect that Tufin is one of the most effective firewall management tools, allowing users to execute in-depth rulesets analysis, and create accurate network mapping.
- Firewall auditing: Users say they can efficiently verify the company’s rules across several secure web gateways, and configure firewalls based on internal auditing guidelines.
- Automated policy management: Reviewers say that the product is an efficient instrument for automated policy analysis and optimization across several firewalls, allowing them to understand the impact of policy changes in advance.
Cons❌
- Integrations: Layer 2 device integration can be improved since it requires manual scripting.
- Ease-of-use: Some users say that firewall management is complex for beginners.
- Customization: Users note that custom dashboarding customization should be more straightforward.
Cisco Identity Services Engine
Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE) is a microsegmentation tool with network security policy management capabilities. The product also provides NAC (network access control) solutions.
Video: Cisco ISE in action: Apply micro-segmentation at scale to block common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE)
Source: Cisco4
Pros✅
- Installation and cost: ISE’s ease of deployment and low cost (especially in long-term plans) are valued positively by some users.
- Authentication: Users say that Cisco ISE with the dot1x feature is an effective solution since it successfully provides an authentication framework that requires a username, password, or digital certificate before allowing access.
- Policy sets: Users compliment the policy sets, stating that they are powerful and dynamic.
Cons❌
- Integrations: Some users point out that errors and bugs are frequently encountered during third-party integrations.
- Upgrades: One major concern that users articulate is that the upgrade process is vulnerable and frequently fails.
- Migration from old systems: Some users who backed up with the new version, which needed licensing argue that migration could be improved since choosing a product is challenging and the system requires them to meet numerous requirements for each feature.
AlgoSec
AlgoSec is a microsegmentation and firewall analyzer tool that offers security visibility by monitoring the network, connecting firewall rules with business apps, and detecting compliance anomalies using its IP engine.
Pros✅
- Firewall rules – ChristopherWalsh Vice President Head of Information Security – The most valuable is helping us determine where our rules are too permissive.
- Intelligent automation: Reviewers express that AlgoSec’s automation capability can effectively simplify difficult processes, such as firewall policy management, and detect obsolete rules.
- Integrations: Some users indicate that integration with numerous vendors is simple. Firewalls, network devices, data center switches, and web proxies can be seamlessly integrated into the product.
Cons❌
- Usability: Some reviews show that navigating the features might be difficult for users who are unfamiliar with a network security solution or a firewall control system.
- Integrations: While some users compliment AlgoSec’s integration capabilities, a few state that its integration with other security systems is difficult.
- Log management: Log management and processing is challenging for some users.
Read more: See AlgoSec alternatives.
Prisma Cloud (Cloud Workload Protection)
Prisma Cloud (Cloud Workload Protection) offers cloud-native security to build cloud-native applications for hosts, containers, and serverless activities. The product protects infrastructure, applications, information, and licenses throughout the clouds (public, private, and hybrid) and also on-premises.
Pros✅
- Detailed compliance alerts: Users say that the product displays data compliance (SoX, LGPD, GDPR, and CIS) and network security alerts in detail.
- Granularity: Customers say that the granularities that the container defender feature extracts from the container layers are efficient.
- Visibility: Some users conclude that visibility and a dashboard for multi-cloud security status using custom compliance are extremely beneficial to their organization.
Cons❌
- Customization: Some reviewers comment that investigations and security policies are difficult to customize.
- Analytics engine: The analytics engine might be improved in terms of creating customized queries for data extraction.
- Setup and learning curve: Some users argue that the product has a complex setup and a steep learning curve for beginners.
Check Point CloudGuard Network Security
Check Point CloudGuard Network Security offers microsegmentation, threat mitigation, and automated cloud network protection via a virtual security terminal across multi-cloud and on-premises environments.
Pros✅
- Deployment: Users appreciate how simple it is to deploy the product in a large-scale environment without any difficulties and in a short time.
- Logging: Users express that the solution provides the most efficient logging experience in the industry.
- Centralized console: Some users say that the centralized management console is convenient for administering and monitoring security rules and events, making the security team’s work smoother.
Cons❌
- Costs: Some users state that the cost needs improvement as it is quite expensive for them.
- Threat scanning system: Some comments argue that the threat scanning system should categorize threats to improve data interpretation.
- Technical operating requirements: Some user reviews say that the operations require a skilled workforce with extended experience working with networking systems to achieve successful results.
VMware NSX
VMware NSX is used for microsegmentation, network security, software-defined networking, and private cloud deployment.
It assists in the transition from physical to virtual infrastructure by ensuring network virtualization and production workload security.
Pros✅
- Microsegmentation: Users state that the VMware NSX environment (vSphere) provides an effective solution for adding microsegmentation and firewall rules.
- Flexible microsegmentation configurations: Users say that VMWare NSX provides flexible microsegmentation configurations. Implementing the technology across four sites, each with its own VMware NSX installation is convenient.
- Scaling: IT specialists argue that VMware NSX facilitates large-scale configurations.
Cons❌
- Technical requirements: Network engineers express that technical knowledge is required to properly operate VMware NSX.
- Deployment: Some analysts convey that more deployment modules can be added (e.g. customized web-based deployment models).
- Documentation: Some reviews show that documentation is still lacking in terms of implementation manuals for various scenarios.
Illumio Zero Trust
Illumio Zero Trust is a microsegmentation technology that assists enterprises in protecting their data centers and apps from cyber threats, by segmenting cloud workloads into virtual machines (VM) or containers.
Pros ✅
- Implementation: Users express how easy it is to implement and configure Illumio Zero Trust.
- Traffic visualization: Reviewers note that Illumio Zero Trust effortlessly visualizes application network traffic across complicated and ever-changing networks.
- Learning curve: Some users express that the platform can be used with minimal knowledge of firewall rules.
Cons ❌
- Application-level security support: Some users state that Illumio is incompatible with network-based security solutions, application-level security support can be improved in a way that works with other host-based security solutions.
- Granularity: Some users say that there is a lack of granularity for the shared services of Illumio Zero Trust.
- Integrations: Some reviews remark that Integration is more difficult in large and complex IT settings, particularly when integrating with current infrastructure.
Zscaler Private Access (ZPA)
Zscaler founded in 2007 with 7,500+ customers, including 30% of the Forbes Global 2000, offers Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) product, an automated microsegmentation solution, that can reduce harmful application-to-application accessibility in your network.5
Pros✅
- VPN solutions: Users say that with Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) they were able to consolidate several different VPN solutions and improve end-point security effectively.
- Visibility and log features: The visibility and log availability provided are highly valued by customers.
- Performance: Users say that Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) has robust performance, shifting between networks seamlessly and rapidly.
Cons❌
- Web server security: Some users claim that the reliability of their UAE servers is unstable, prompting the use of the Paris server instead.
- Learning curve: Some reviews reflect that the learning curve for Zscaler Private Access (ZPA) is steep, beginner administrators should expect to spend a significant amount of time learning the platform.
- Crashes: Some users claim that the system was vulnerable to malfunctioning frequently.
Cisco Secure Workload (Tetration)
Cisco Secure Workload (previously Tetration) is a zero-trust microsegmentation technology that secures workloads in virtually any setting from a single interface.
Secure Workload assists companies in securing their application environment by establishing a software-defined micro-perimeter at the load level throughout the whole infrastructure on virtual machines, bare metal servers, and containers.
Pros✅
- Data encryption: Some users state that Cisco Secure Workload effectively assisted them in managing large-scale data and automating many of our company’s operational operations.
- Zero trust network: Users appreciate the customized zero-trust paradigm which shows microsegmentation of different workloads.
- Vulnerability scanning: Users say that it is convenient to monitor the security posture of apps across environments, and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) vulnerabilities can be accurately identified.
Cons❌
- Ease-of-use: Some users claim that Secure Workload is difficult to use, and the dashboard is not simple, it requires some time to get used to it.
- Learning curve: Some users emphasize that Tetration is a complex tool that requires a specialized skill set to learn how to operate the product.
- Latency: Sometimes users encounter latency issues between applications.
Flow Virtual Networking
As an optional add-on to the Nutanix Acropolis platform, Nutanix sells Flow software. Microsegmentation is one of Flow’s major functionalities, allowing for granular management and control of all traffic within and outside of a VM or set of virtual machines.
With Flow Virtual Networking administrators may combine policies to construct custom protection systems. Flow also has a unique test function for ensuring that policies are appropriately established before implementing them in microsegments.
Pros✅
- Microsegmentation: Some users claim that Nutanix Flow improves at microsegmentation by separating particular databases from apps.
- Ease-of-use: Users highlight that Nutanix Flow has an easy-to-use interface.
- Network visibility: Some users believe that the platform makes it simple to monitor network traffic flowing between multiple systems.
Cons❌
- Data transfer: Some user reviews indicate that not every port receives a data transfer through Flow Virtual Networking.
- UI: Some users expect to have a visual upgrade for the user interface.
- Cloud connection: Users express that connecting to the cloud with Flow Virtual Networking can be challenging.
What is microsegmentation?
Microsegmentation is a security solution process designed to intuitively divide data based on workload within an organization’s operating systems. Security architects can create protocols that define how all traffic flows in your ecosystem, north-south and east-west.
Benefits of microsegmentation tools
1. Reduced attack surface
- What it does: By isolating individual assets, microsegmentation minimizes the risk that an attacker can access multiple resources.
- Real-life example: Illumio helped the retail company Hi-Temp Insulation reduce its attack surface by applying segmentation policies that protected sensitive customer data.6
2. Compliance with regulatory standards
- What it does: Microsegmentation helps companies meet regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, by ensuring that sensitive data is not breached.
- Real-life example: Cisco enabled Frankfurter Bankgesellschaft a Zurich-based Swiss private bank, to maintain compliance with data protection laws by securing their cloud environment with detailed segmentation rules.7
3. Granular policy control
- What it does: Microsegmentation provides detailed control over network policies, allowing businesses to define security policies based on user, application, or workload.
- Real-life example: VMWare enabled the California Department of Water Resources to implement granular controls for their healthcare applications, reducing the risk of data breaches.8
4. Enhanced cloud security
- What it does: In cloud environments, microsegmentation ensures that workloads in different virtual machines or containers are isolated, improving cloud security.
- Real-life example: Illumio used microsegmentation to help a leading hospital network in Brazil secure its cloud infrastructure, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.9
Network segmentation vs microsegmentation
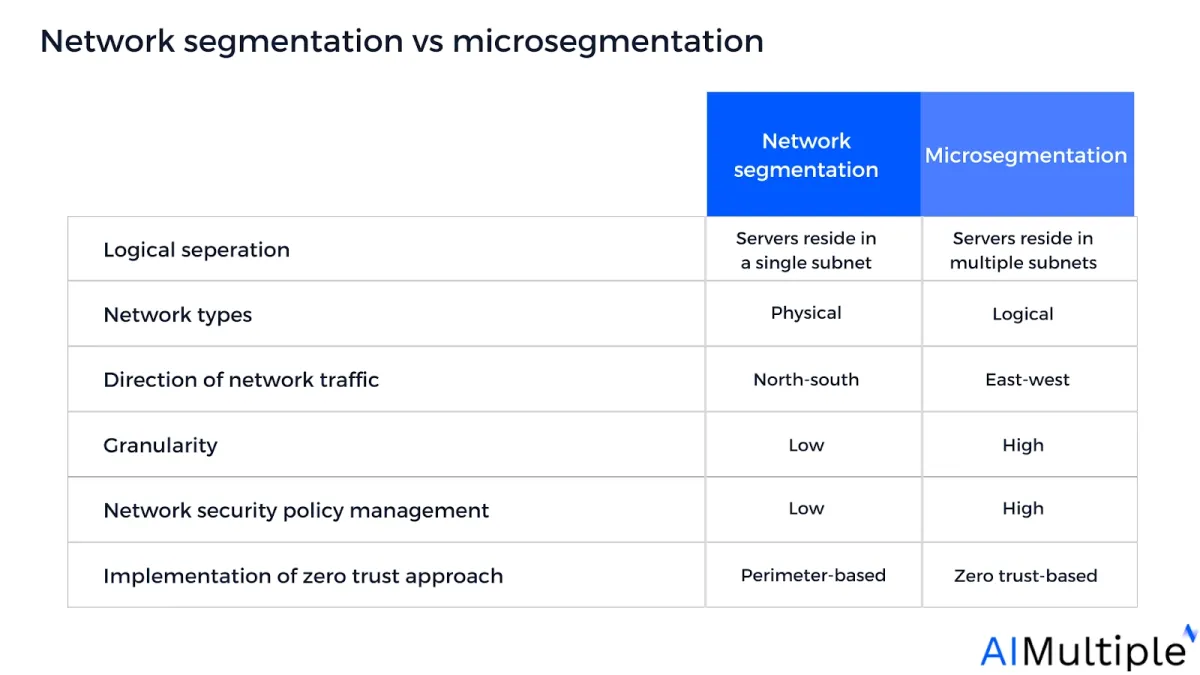
- Network segmentation enforces traditional castle-to-moat policies that leverage firewall rules at network boundaries
- Microsegmentation creates security zones that can be configured down to the host (computer) level across individual subnets.
Comparison between network segmentation and microsegmentation – using VLANs –
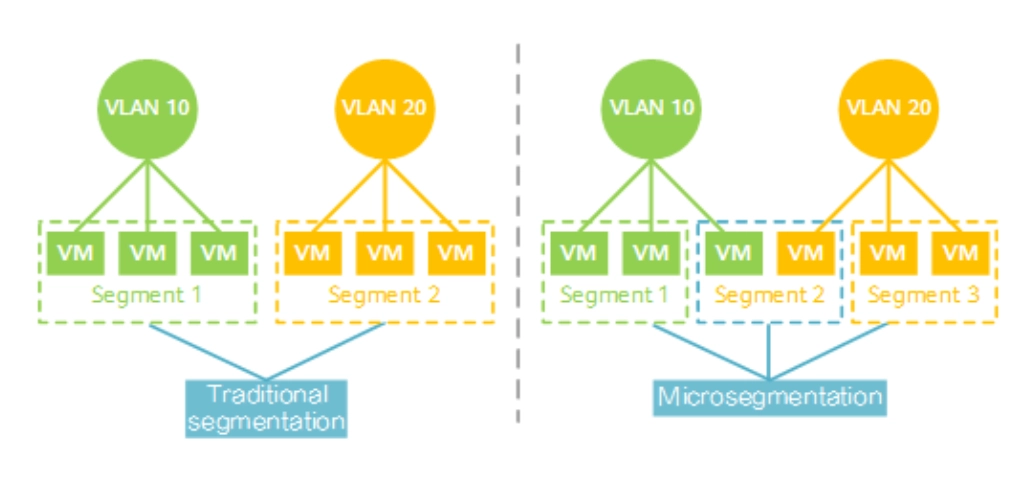
Source: Huawei10
Who should use microsegmentation?
Enterprises (e.g. Fortune 1000, global banks, leading insurance companies, and enterprise SaaS) with complex network security use cases are recommended to adopt microsegmentation. Traditional network segmentation methods might not be effective for large organizations with numerous network security use cases since these tools are not built for highly granular, application-level security permissions.
Cloud-native organizations that use several software, cloud, and SaaS platforms are recommended to adopt microsegmentation technologies. These organizations are more vulnerable to cloud-related threats and need to secure application workloads at a high granular server-to-server level.
Who should use traditional network segmentation?
SMEs: Traditional perimeter-based network segmentation is an easy-to-implement solution for organizations that:
- Require overarching security for their entire infrastructure without detailed application-level or agent-based policy configurations.
- Have less complex networks with low-security needs.
- Have limited technical labor.
- Have limited network security budgets.
Key parameters for choosing between network segmentation and microsegmentation:
If you want a more detailed answer than these high level recommendations, these parameters can help determine the right approach for your company:
- Business scope: Implementing microsegmentation across core business areas can significantly reduce the lateral flow of a ransomware attack.11 Companies with numerous branches and departments seeking may choose microsegmentaton to enhance intra-network traffic.
- Level of security needed: Organizations with high network security needs such as Fortune 1000, global banks, insurance companies, or multinational corporations (MNCs) may select microsegmentation technologies to use finer-grained management and application-level security.
- Level of granularity needed: Microsegmentation provides far more granular control and is significantly more effective to implement and administer at scale. Large-scale private or public companies may use microsegmentation to execute strong network traffic control.
- Level of identity-based zero trust security needed: The zero trust model employs the “never trust, always verify” principle rather than defending the network perimeter. This ensures that only verified users can access specific content. Companies that need rigid identity verification for employees and devices may implement microsegmentation with zero trust architecture.
- Level of granularity needed: Microsegmentation provides far more granular control and is significantly more effective to implement and administer at scale. Large-scale private or public companies may use microsegmentation to execute strong network traffic control.
- Network complexity: 35% of IT specialists say that network complexity is an obstacle they encounter when segmenting their network.12 Organizations with less complex networks may utilize traditional network segmentation.
- Number of network components: Companies that use several hardware, software, cloud, or SaaS platforms across their network can use microsegmentation to eliminate unnecessary network zones. For example, a CISO of a 300-employee company states that microsegmentation enhanced network visibility in their organization, enabling them to identify and eliminate 15 no-longer-needed zones with license costs.13
- Scope of network security policy configurations: Network security policy management statistics show that the rate of all cyber incidents caused by security misconfigurations is 35%. Companies with thousands of complex security rules and firewalls might leverage microsegmentation technologies to manage misconfigurations at scale.
- Scope of network traffic: Organizations with extensive east-west data transfer within the internal network may select microsegmentation technologies to divide their data centers or cloud environment into logical units.
- Numbers of employees: Companies with hundreds of employees may choose microsegmentation technologies since microsegmentation allows host-level segmentation that enables administrators to set user-based rules.
- Number of network components: Companies that use several hardware, software, cloud, or SaaS platforms across their network can use microsegmentation to eliminate unnecessary network zones. For example, a CISO of a 300-employee company states that microsegmentation enhanced network visibility in their organization, enabling them to identify and eliminate 15 no-longer-needed zones with license costs.13
- Financial budget: Microsegmentation integration with a security stack is expected to cost between $40K to $100K on average.14 Companies with lower finances and older infrastructure may choose network segmentation technology.
- Skilled labor availability: ~40% of IT specialists state that lack of skills and expertise for segmentation is their main issue for implementing microsegmentation.15 Companies with low-skilled labor or resources may select network segmentation since segmenting physical network VLANS and access control lists requires less technical knowledge compared to developing logical microsegments.
Read more: Microsegmentation tools, network security audit tools, SDP software.
Vendor selection criteria
- Number of reviews: 10+ total reviews on Gartner, G2, PeerSpot, and TrustRadius.
- Average rating: Above 4.0/5 on Gartner, G2, PeerSpot, and TrustRadius.
- Sorting: Vendors are sorted by the total number of reviews in descending order.
Microsegmentation software features
Unique features
These are offered by one or a couple of vendors:
- Firewall orchestration helps to manage and optimize firewalls with centralized management and configuration capabilities.
- Day 2 network operations can authenticate the health of application-focused network traffic/routes, firewalls, and Access Control Lists (ACLs) for applications and Virtual Machines (VMs).
- Hybrid cloud management can manage and regulate the segmentation of cloud and on-premises infrastructures into smaller security segments.
- Medical network access control detects medical devices as they connect to an organization’s network to safeguard medical devices and patient records against security risks.
- Runtime protection for cloud workloads offers instant security for cloud-based tasks, web applications, and APIs.
- Multi-tenancy solution provides multi-tenant isolation, self-service provisioning, and IP address preservation using VPCs, enabling a secure setting in which multiple tenants can operate together without compromising the accessibility of their applications.
Transparency statement: AIMultiple works with numerous emerging tech vendors including Tufin.
Common features of vendors
Each included vendor provides the following common features:
- Network visibility and discovery: Provides instant insight into security changes and breaches.
- Automated policy enforcement: Automatically detects and rectifies policy violations or non-compliance issues.
- Zero trust: Maintains access controls that do not trust anyone by default, including those already within the network perimeter.
- Threat detection and response: Monitors data from different sources within an organization’s environment using technologies such as machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify security threats.
- Compliance and regulatory support: Maintains policies and procedures that govern the integrity of IT systems.
For guidance on choosing the right tool or service for your project, check out our data-driven lists of software-defined perimeter (SDP) software and zero trust networking software.
Further Reading
- Microsegmentation examples
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA): Definition & Benefits
- 10 Cybersecurity Best Practices for Corporations
- Firewall as a Service: Definition & Top 8 Benefits
- Data Compliance: Best Practices & Challenges
External Links
- 1. Network Segmentation Saved TeamViewer From APT29 Attack. Dark Reading
- 2. SIX Case Study | Tufin.
- 3. ”Tufin Reviews“. G2. October 2, 2022. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- 4. ”Cisco Zero Trust in Action: Apply micro-segmentation at scale“. YouTube. 2023. Retrieved September 13, 2024.
- 5. ”Zscaler“. Zscaler. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- 6. “Hi-Temp Insulation Launches Microsegmentation Security in 30 Minutes“. Illumio. 2024. Retrieved September, 2024.
- 7. Securing, Virtualizing, and Micro-Segmenting Private Banking Infrastructure with Cisco.
- 8. “CASE STUDY INSIGHTS: MICRO-SEGMENTATION TRANSFORMS SECURITY“. VMWare. 2024. Retrieved September, 2024.
- 9. Leading Hospital Network Secures Rapid Growth with Illumio | Illumio Customers. Illumio
- 10. ”What Is Microsegmentation?”.
- 11. ”The State of Segmentation 2023”. Akamai. 2023. Retrieved April 23, 2024.
- 12. ”The State of Segmentation 2023”. Akamai. 2023. Retrieved April 23, 2024.
- 13. ”Building A Business Case for Microsegmentation Part |: Put Zero Trust At The Core“. AIRGAP, a Zscaler Company. 2024. Retrieved April 24, 2024.
- 14. ”Building A Business Case for Microsegmentation Part |: Put Zero Trust At The Core“. AIRGAP, a Zscaler Company. 2024. Retrieved April 23, 2024.
- 15. ”The State of Segmentation 2023”. Akamai. 2023. Retrieved April 23, 2024.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.