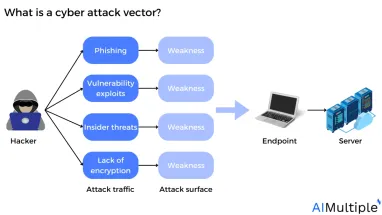
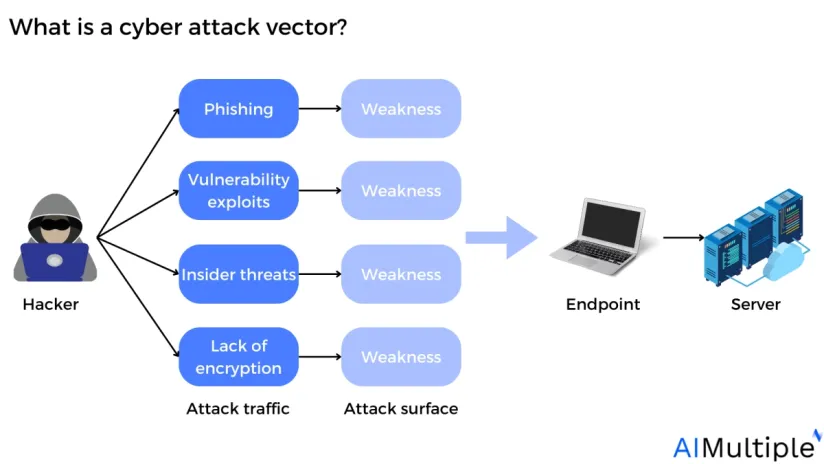
Network security statistics reveal that the cyber attack disruption levels have surged by 200% from 2019 to 2024, compared to a 4% increase from 2011 to 2016. The rise of cyber attacks is alarming since damage to information systems can harm processes, assets, individuals, and organizations. See the top cyber attack vectors, along with their effects, and types based on real-life cases:
1. Malware
Malware is malicious software that may make infected computers unusable. Malware can leak data, steal information, and delete files.
Figure 1: Annual number of malware attacks in selected countries in 2022 (in millions)
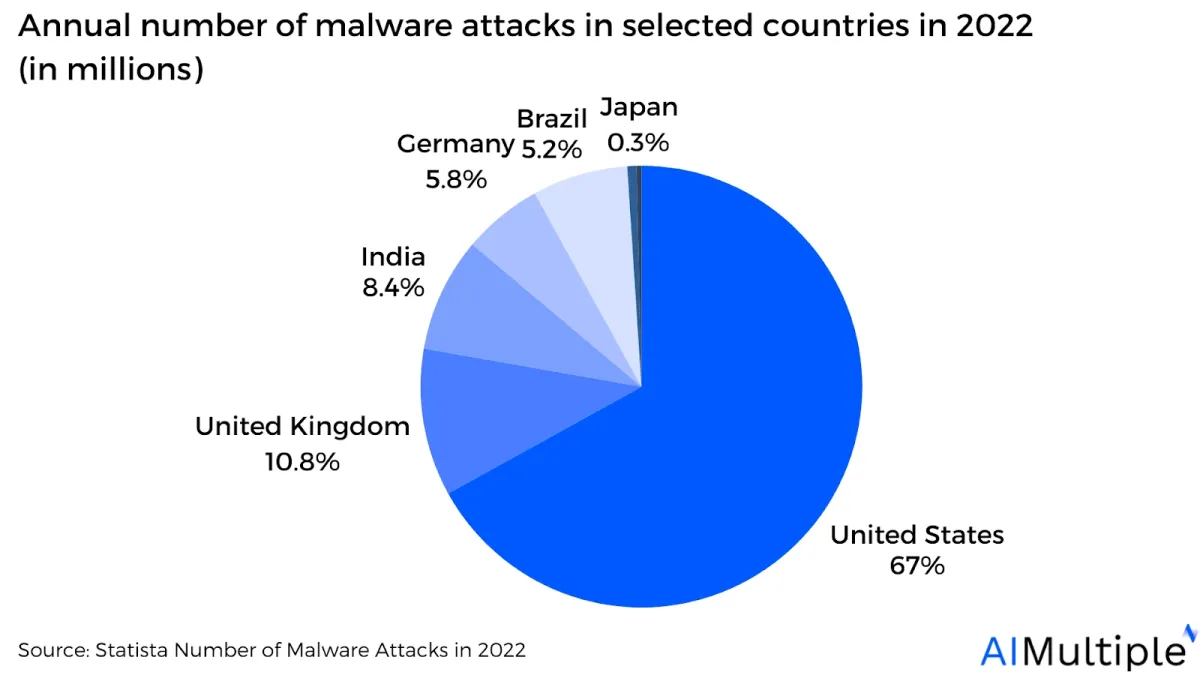
Source: Statista1
Malware takes numerous forms, including:
- Trojan horses pose themselves as beneficial applications or hide within legitimate software to mislead individuals into downloading them. A Trojan works by developing a hidden entry point on the targeted device and installing further malware once it has gained access.
- Rakhni Trojan: Infects devices by delivering ransomware or a cryptojacking program.
- Tiny Banker: Allows hackers to steal users’ financial information. It was detected after infecting at least 20 U.S. banks.
- Ransomware encrypts files on a device, making any files or programs that rely on them useless. Ransomware is the second most common type of cyberattack, accounting for ~15% of attacks.2
Real-life example: SolarWinds ransomware attack. A threat actor introduced test code into SolarWinds’ Orion software to leak high-value client data, including the US government.
The attacker sent malware into a test code file, which was then spread to SolarWinds’ Orion software during an update. Threat actors gained access to SolarWinds’ systems and cloud platforms, leaking massive amounts of sensitive data. 3 - Scareware manipulates people into visiting fake or virus-ridden websites or installing harmful software (malware). Scareware can take the shape of pop-up advertising that shows on a user’s computer or is propagated by spam email attacks.
Real-life example: Office Depot technical support scam. Malicious technicians at Office Depot ran fraudulent scans on clients’ laptops and used the findings to sell them unnecessary repair services. Thus, Office Depot billed customers for fake services.
When the dispute became public, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) ordered Office Depot to pay USD 35 million in fines.
- Spyware collects information about an individual or organization and sends it to another entity.
Real-life example: Apple device spyware. Hackers sent Mac spyware to target devices and stole passwords by leveraging keylogging and password phishing.4
- Worms absorb bandwidth, overwhelming infected computers and rendering them inefficient or unavailable.
2. Social engineering
- Phishing attacks utilize emails or SMS messages to get user passwords, steal private information, or transmit malware.
Phishing attempts persuade victims to click a link that leads to a malicious site or download a file that contains malware. Phishing is the second most prevalent source of breaches.5- Spear phishing attacks attempt to deceive a single individual, frequently by leveraging information from the victim’s accessible social media accounts to make the scam appear to be more credible.
- Whale phishing attacks are a spear phishing method that focuses on high-level business leaders.
Read more: Phishing vs whaling.
- Business email compromise (BEC) attacks attempt to mislead the target into completing a business function for a fraudulent purpose, like sending money. The attacker aims to pretend to be an executive to be persuasive or to generate a feeling of obligation in the targeted employee.
Real-life example: Minnesota BEC attack. A scammer posed as a senior official via email and persuaded the City’s accounting department to change payment information for a contractor. This resulted in the funds being transferred to a counterfeit account. Minnesota incurred a $1.2 million loss.6
3. Denial-of-service attacks
A denial-of-service (DoS) attack happens when a malicious threat actor prevents authorized users from accessing information systems (e.g. devices).
- A smurf attack involves the attacker impersonating the target machine and using its fake source IP address to send Internet messages to several hosts.
Real-life example: Amazon Web Services smurf attack. AWS was targeted by a significant DDoS attack. The attackers retrieved data from the AWS network and targeted an AWS customer. The assault lasted three days and reached a staggering 2.3 gigabytes per second.7
- A SYN flood happens when an attacker tries to gain access to the target server by sending a request but fails to finish the connection. Thus, due to the unfinished connection, all open ports will be flooded with requests from an attacker, making it impossible for authorized users to connect.
Real-life example: Panix – SYN Flood and domain hijacking. The assault targeted mail, news, name, and Web servers. A SYN flood was sent to disconnect network connections, preventing legitimate users from connecting to servers.8
4. Man-in-the-middle attacks
A man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack, also known as an in-path attack, is a type of cyberattack that occurs when an attacker secretly sends communications between two parties that assume they are speaking with each other directly.
- Email hijacking enables hackers to access email accounts. Once inside, attackers can view transactions and interactions between the company and its clients.
For example, an attacker may impersonate the company’s username and password and send clients emails urging them to retrieve their credentials to an account owned by the hackers.
- Wi-Fi eavesdropping involves hackers convincing victims to connect to a local wireless network with a legitimate-sounding name.
For example, the wireless network may have an innocent name, such as “Free Wi-Fi”, However, once users log in to the infected Wi-Fi, the attacker has two options: monitor the user’s online behavior or extract login credentials.
- Domain name system (DNS) spoofing injects malicious data into the DNS cache. Thus, traffic is subsequently redirected to the attacker’s preferred computer.
5. Other types of cyber attack vectors
- Structured query language (SQL) injection manipulates the connection between a webpage and the database that supports it. Usually, the goal is to induce malicious code to run on the database’s server. 9
- Fileless malware (in-memory malware) is an attack vector that doesn’t require traditional file storage because it lives only in a computer’s memory (e.g. RAM).
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) inserts malicious scripts into resources that are hosted on legitimate websites. After that, the content with malicious code is sent to the victim’s browser.
- Zero-day exploits focus on an undetected or unresolved security vulnerability in hardware or software. “Zero day” describes a software or hardware issue where malicious parties can immediately access it, giving the vendor zero days to remedy it.
Cyber attack prevention tools
- Identity and access management (IAM) tools help administrators regulate user access to vital information.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) helps prevent unauthorized or risky sharing, transferring, or using sensitive data. Read more: Top 10 data loss prevention or DLP software.
- Firewalls block network traffic from threats gaining access to a device. Firewalls can filter traffic by modifying the source and destination IP addresses, IP protocols, and source and endpoint port numbers. Read more: Firewall assessment.
- Vulnerability prevention can help block vulnerabilities before attackers execute them. Read more: AI pentesting tools.
- Attack surface management (ASM) software can detect, list, and fix potentially unsecured assets before cyber attack vectors identify them. Read more: Open source ASM software.
- Unified endpoint management (UEM) technologies can apply security controls and guidelines to all endpoints on the business system. Read more: Top 10 endpoint management software.
Cyber attack detection tools
It is challenging to prevent cyber attack attempts, thus businesses may also utilize early detection methods to identify cyber attack vectors.
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems collect and track communication from various internal cybersecurity technologies (e.g. intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPSs), endpoint detection and response systems (EDRs)).
- Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) platforms enhance security alerts to assist administrators in comprehending the types of threats they may encounter.
- Antivirus programs may scan machines for risky applications and automatically remove malware.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) technologies can help administrators organize diverse security products into automated protocols for intrusion prevention in real-time.
- Data breach incident response systems can assist in limiting and eliminating cyber attacks, maintaining damaged networks, and identifying the underlying causes to prevent further attacks.
Key motives behind cyber attack vectors
1. Criminal
Criminally motivated attacks seek financial benefit by stealing funds, and information, or disrupting business operations. Hackers can either break into a bank account to take funds directly or use social engineering scams to mislead individuals into transferring money to them. Hackers may steal personal information and use it to execute identity theft, trade it on the dark web, or keep it as a hostage.
2. Personal
Personally motivated criminals, such as upset current or past workers, seek revenge for a perceived injustice. They may steal assets, confidential information, or destroy a company’s infrastructure.
3. Political
Politically motivated attackers are frequently associated with electronic warfare and “hacktivism.” In cyber warfare, nations frequently attack their adversaries’ government agencies or key infrastructure. Activist hackers, known as “hacktivists,” may not damage their victims significantly. Instead, they try to draw attention to their causes by publicly exposing their attacks.
Negligent threats: While negligent users could harm their organizations, a cyber attack occurs when an individual purposefully utilizes their privileges to carry out threatening conduct. An employee who negligently keeps sensitive information on an insecure drive is not conducting a cyber attack; an upset employee who intentionally copies secret material for personal gain is.
What are the targets of cyber attack vectors?
Threat actors usually breach IT systems because they’re seeking specific items.
Common targets of cyber attack vectors are:
- Business financial data
- Client data (may include personally identifiable data)
- Contact information and login credentials
- Intellectual property (e.g. trade secrets and product ideas)
In some circumstances, cyber attackers are hesitant to acquire anything at all. Rather, they just seek to disrupt computer networks or IT infrastructure that negatively impact a business, authority, or another target.
5-stages of a cyber attack
Figure 3: 5 stages of a cyber attack
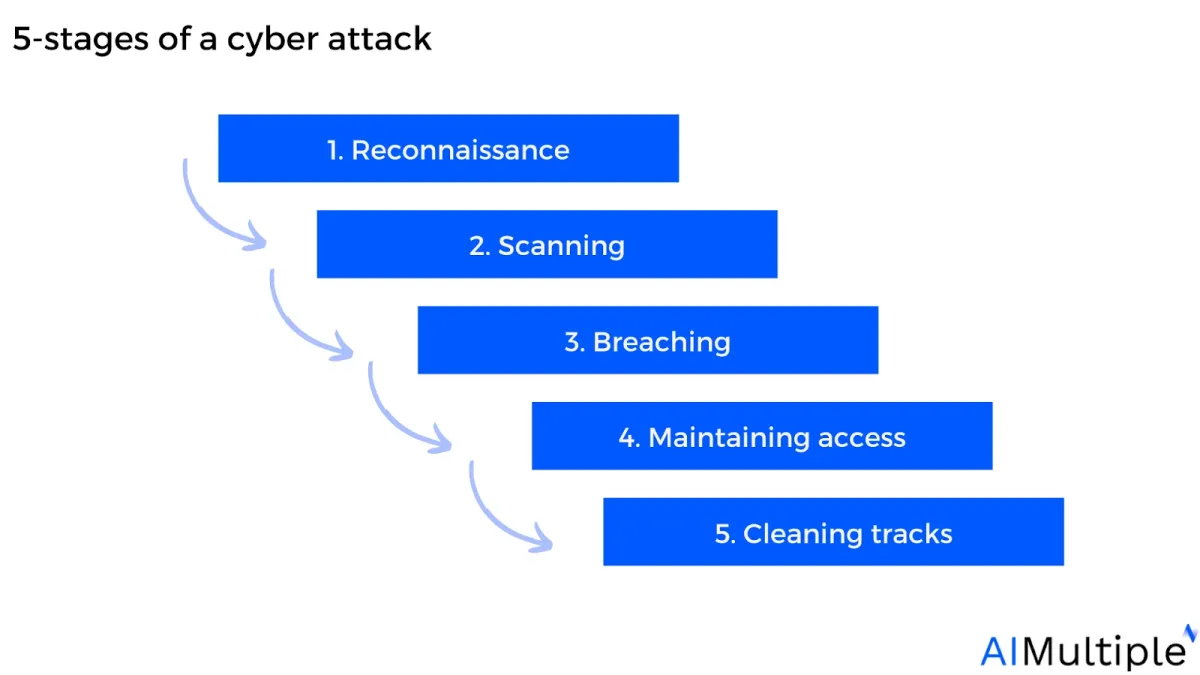
1. Reconnaissance
During the reconnaissance phase, attackers seek to gather precise information about the target employee or organization, including identifying key online actions.
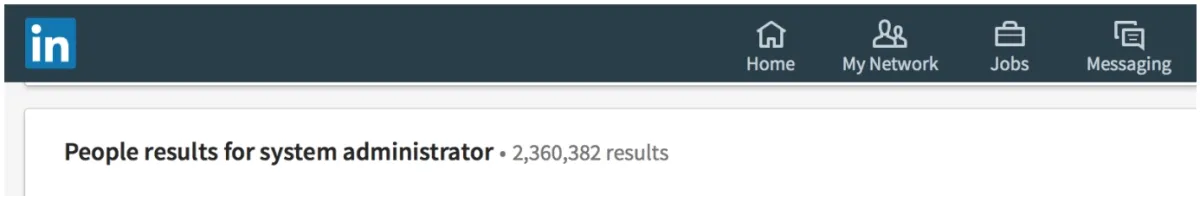
The attacker can simply search for “system administrator” on social media sites like LinkedIn To obtain the employee names and roles (see below).
Figure 4: People results for system administrator
2. Scanning
Scanning entails using the information gathered during reconnaissance to investigate the network. Attackers search for any information that may assist them in carrying out the “breach,” including machine names, IP addresses, and login credentials.
During the scanning phase, the attackers also scan the target’s network for weaknesses. For example, the attacker may attempt to identify the target’s system specifications (e.g. whether it uses antivirus software).
3. Breaching
During the breaching phase, an attacker will achieve one or more of the following goals to breach the organization’s network:
1) Gaining unauthorized entry to one or more targeted databases.
2) Conducting application-level attacks against web-based services.
3) Launching denial-of-service attacks against services operating in the system under attack.
For instance, a malicious individual could spoof the e-mail address of the employee on vacation and then send the spoof e-mail to HR, claiming that he or she demands access to specific records but has forgotten their login credentials. If the HR submits the account and password without suspecting the fake email, the attacker will obtain the necessary credentials to breach the network.
4. Maintaining access
Once an attacker has acquired access, they intend to maintain it to prevent further attacks. Attackers may protect the system against other hackers or security employees by using Trojans to ensure exclusive access. Once the attacker has taken control of the system, they might utilize it as a base of operation to launch more attacks.
5. Cleaning tracks
Covering tracks implies that the attacker should eliminate any evidence of detection. Attackers may hide their activities to evade discovery by security staff and continue to use the hacked system. Attackers may try to remove all signs of the attack, including data logs and intrusion detection alerts.
Overlapping between stages: There is an overlap between the five phases; for instance, an attacker who breached the organization’s network in stage 3 can then use that access to keep scanning in stage 2 and perform reconnaissance in stage 1.
Cybersecurity risk management

Implementing cybersecurity risk management into business initiatives has become imperative since ~60% of risk executives continuously ranked cyber threats as one of the top five threats for the current and upcoming three years.10
See how organizations can implement cybersecurity risk management to prevent cyber attack vectors:
1. Risk framing
- Identify assets and threats.
- Define scope (resources and investigation timeline).
- Understand legal standards.
2. Risk assessment
- Assess impact and likelihood of risks.
- Prioritize risks using a risk matrix.
3. Responding to risk
- Reduce risk likelihood, remediate vulnerabilities, or transfer risk (e.g., cyber insurance).
4. Monitoring
- Continuously monitor for new threats.
- Conduct audits and test incident response readiness.
Further reading
- Top 10 Microsegmentation Tools
- Intrusion Prevention: How does it work? & 3 Methods
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Network Segmentation: 6 Benefits & 8 Best Practices
- Network Security Policy Management Solutions (NSPM)
External Links
- 1. Number of malware attacks by country 2022| Statista. Statista
- 2. X-Force 2025 Threat Intelligence Index | IBM.
- 3. SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack | Fortinet.
- 4. New ‘Dangerous’ iPhone Spyware Attack Warning Issued To iOS Users.
- 5. Cost of a data breach 2024 | IBM.
- 6. Federal investigation underway into sham emails that led to city of Cottage Grove losing $1.2M. Yahoo Finance
- 7. ”Threat Landscape Report” AWS Shield. 2020. Retrieved March 25, 2024.
- 8. New York's Panix Service Is Crippled by Hacker Attack.
- 9. ”Understanding Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)“. (PDF). CISA. 2009. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- 10. Risk and resilience priorities, as told by chief risk officers | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.