Top 10 Endpoint Management Software in 2024: 12K+ Reviews
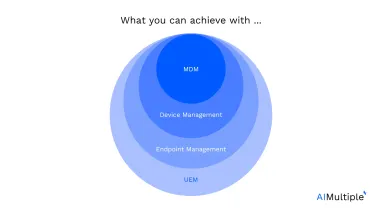
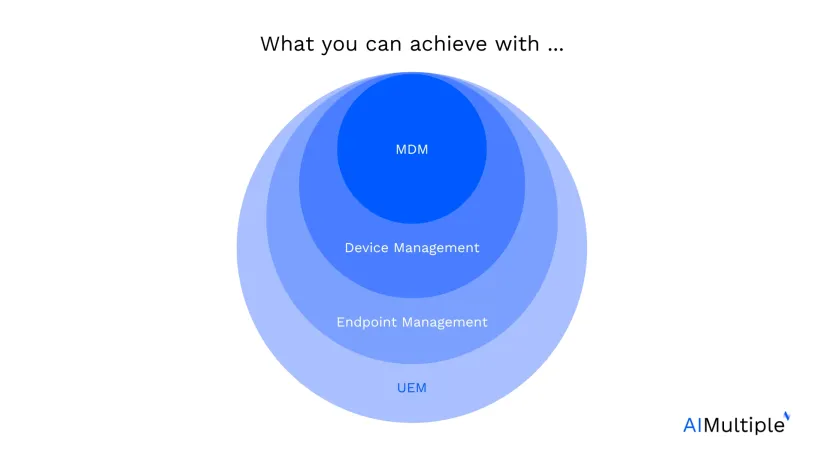
According to Microsoft’s Digital Defense Report, the most common case of cybercrime is unauthorized access to unmanaged devices, which compromises data security.1
With the rise of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) implementations and remote/hybrid work trends, businesses are strengthening their network security measures to prevent security compromises. Management software solutions provide IT professionals with the necessary tools to orchestrate network elements securely and efficiently. This article looks at endpoint management software solutions that aim at securing the endpoints of networked devices.
Table 1: Top endpoint management software comparison
| Endpoint management software | # of reviews* | Rating* | Price/year** | Pricing driver*** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symantec Endpoint Security Complete | 3,173 | 4.3 | N/A | N/A |
| ThreatDown | 1,598 | 4.6 | $109 | per-endpoint |
| Microsoft Intune | 1,418 | 4.3 | N/A | N/A |
| Webroot Business Endpoint Protection | 1,000 | 4.3 | N/A | N/A |
| FortiClient | 829 | 4.4 | N/A | flexible |
| VMware Workspace One | 779 | 4.3 | $113 | per-user |
| Checkpoint Harmony Endpoint | 550 | 4.4 | N/A | N/A |
| Cisco Meraki System Manager | 504 | 4.5 | $40 | per-license |
| Absolute Secure Endpoint | 373 | 4.6 | N/A | N/A |
| Citrix Endpoint Management | 326 | 4.3 | $216 | per-user |
* Based on the total number of reviews and average ratings (on a 5-point scale) from Gartner, G2, Capterra, and TrustRadius software review platforms as of 02/28/2024.
** Other licensing terms, such as the minimum quantity of licenses needed, are not taken into account.
*** Features and prices are in accordance with the selected tiers and packages as follows:
“Complete” for Symantec Endpoint Security; “Elite” for ThreatDown; “Suite” for Microsoft Intune; “Control” for Absolute Secure Endpoint; “UEM Essentials” for VMware Workspace One; “Workspace Premium” for Citrix Endpoint Management.
Vendor selection criteria
In order to provide an objective evaluation of vendors, we considered publicly verifiable data such as the number of reviews and user ratings on software review platforms. User reviews for pros and cons are selected only if multiple users report the same point.
- Number of reviews: We included the vendors with more than 300 total user reviews.
- Average rating: Above 4/5 rating on average across all software review platforms.
- Price: Endpoint management software products vary in price, and publicly available prices of products are added to the table. Potential users can compare products according to their price and pricing drivers.
- Pricing driver: The price of products depends on multiple aspects, such as minimum licensing or admin user quantity, device quantity, or domain quantity. Businesses can choose between pricing driver options in accordance with the quantity and admin user.
- Common features (minimum requirements): We selected the vendors that deliver its users policy management, authentication, compatibility, integration, deployment, endpoint detection and response (EDR), MDM, patch management, backup, and recovery features.
Analysis of the endpoint management software
1. Symantec Endpoint Security Complete
Symantec is a cybersecurity product suite owned by Broadcom Inc., which provides a wide range of hardware and software solutions.
Pros
- Security: The user likes the product’s security features. Specifically, real time threat identification and protection are mentioned.2
- Centralized management: The reviewer praises the centralized control panel, which enables users easy access to different tools such as monitoring and controlling endpoints.3
Cons
- False positives: Some users mention they face false positives, which result in the blocking of unwanted data.4
- System performance: Scanning inhibits system speed, according to multiple users.5
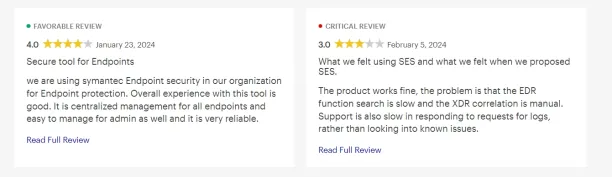
Source: Gartner.6
Figure 1 . The above screenshot captures two reviews, one favorable and the other critical.
2. ThreatDown
TreatDown is an IT security solutions brand founded by Malwarebytes. It offers IT security solutions focused on endpoint security.
Pros
- Patch management: The patch management is found to be easy to implement. User reviews mention that it is very useful for updates.7
Cons
- User experience: The software portal/dashboard needs to be more organized because the structure leads to complexities.8
Source: G2.9
Figure 2. The above screenshot captures ThreatDown’s dashboard.
3. Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Corporation is a technology company founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen. The company is best known for its Windows line operating systems and software applications such as Microsoft 365.
Pros
- Easy use: The remote monitoring and management abilities of the product are praised by the reviewer.10
- Integration: The product is claimed to be seamlessly integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem.11
Cons
- App management: The app management tool is found to be problematic by the reviewer. The tool is time-consuming because it demands unnecessary tasks.12
- Operating system compatibility features: The product is found to be less efficient on macOS than on Windows.13
4. Webroot Business Endpoint Protection
Webroot produces security solutions for endpoints and e-mails, as well as DNS protection.
Pros
- Resources: The product necessitates modest hardware resources without putting extra weight on it by slowing the system down.14
Cons
- Setup: According to reviewers, the configuration at the start of using the product and, in general, the setup process are cumbersome.15
Source: Webroot.16
Figure 3. The above screenshot captures Webroot’s management console.
5. FortiClient
Forticlient is headquartered in California, United States. The company offers endpoint security systems, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Pros
Cons
- System abruption: Many users claim that the system gets disconnected all of a sudden.18
6. VMware Workspace One
VMware is a cloud computing company that is headquartered in California, United States. The company produces app management tools, and cloud-based security and networking software solutions. VMware was acquired by Broadcom Inc. .
Pros
- MDM: According to multiple reviewers, the Airwatch feature makes mobile device management practical.19
Cons
- Learning curve: Many users claim that the product demands a steep learning curve.20
Source: VMware.21
Figure 4. The above screenshot captures Workspace One UEM’s dashboard.
7. Check Point Harmony Endpoint
Check Point produces security solutions for networks, cloud systems, internet based applications, developers, and e-mails.
Pros
- Alerting and notifications: Users define alerts as proactive.22
- Security: Real-time protection involving actively monitoring drives is found to be an effective tool for cyber security.23
Cons
- System performance: According to multiple users, the system may get slow when installing a client.24
- False positives: Multiple users dislike the occurring false positives and alarming notifications following them.25
8. Cisco Meraki System Manager
Cisco is headquartered in California, United States, and produces hardware, software, and telecommunications equipment.
Pros
- Device configuration: The configuration of devices is found to be practical.26
Cons
- Cost: According to multiple users, the total cost is found to be expensive.27
Source: Documentation Meraki.28
Figure 5. The above screenshot captures Meraki’s MDM common page.
9. Absolute Secure Endpoint
Absolute produces cybersecurity solutions focused on endpoint protection.
Pros
- Device management: The product provides the user with easy access to display and oversee connected devices.29
Cons
- System performance: According to the multiple reviewers, the product takes too much time to respond.30
Source: G2.31
Figure 6. The above screenshot captures Absolute’s dashboard.
10. Citrix Endpoint Management
Citrix delivers its customers IT solutions focused on hybrid/remote work settings, such as employee work performance analytics, remote connection services, network access solutions, and endpoint management.
Pros
- Mobile access: The reviewer is pleased with mobile access to the product.32
- Easy use: Most of the users are satisfied with easy setting of the product.33
Cons
- Updates: The updates run on the product are found to be slow.34
- System performance: Some users describe deployment as time costly because of the multiplicity of features the product offers.35
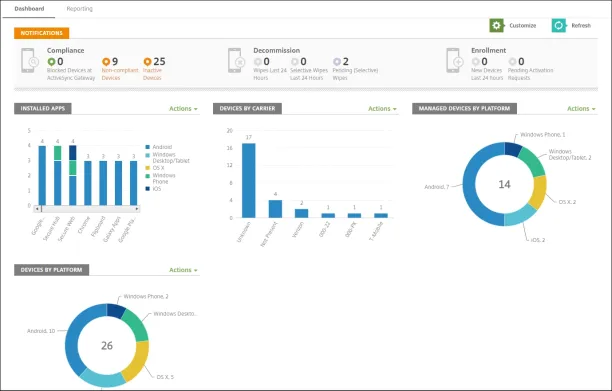
Source: Citrix.36
Figure 7. The above screenshot captures Citrix Endpoint Management’s dashboard.
How does the remote working trend affect the IT industry?
The fastening development of network and remote connection technologies is correlated with hybrid and remote working hype around the world. Employees and employers prefer remote working over traditional on-prem work because of its promising advantages, such as enhanced productivity and decreased costs for each side.
According to the data summarized by Forbes, remote working in the US will rise and make up 22% of the workforce by 2025.37 Data indicates that remote working is becoming more common, and this will put additional pressure on IT security systems to maintain adequate and secure network systems.
IT teams and managed service providers (MSPs) will make use of qualified software solutions for endpoint management and security. Device management and endpoint security, with a focus on network security solutions, will be in high demand. According to Statista, the global market for endpoint security is expected to rise to $27 billion by 2027. 38
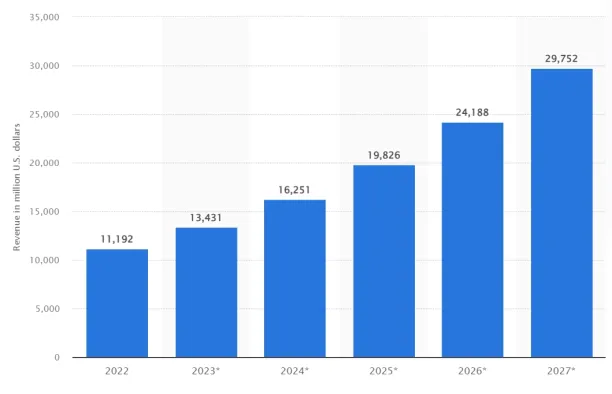
Source: Statista.39
Figure 8. The above column graph shows the projected revenue values of the endpoint security market from 2023 to 2027.
What does endpoint management software do?
Endpoint management software protects network devices, including mobile phones, PCs, USBs, and other hardware, against data loss and malicious attacks that aim at data theft. Endpoint management software also ensures the efficiency of the network system by regularly monitoring and managing it.
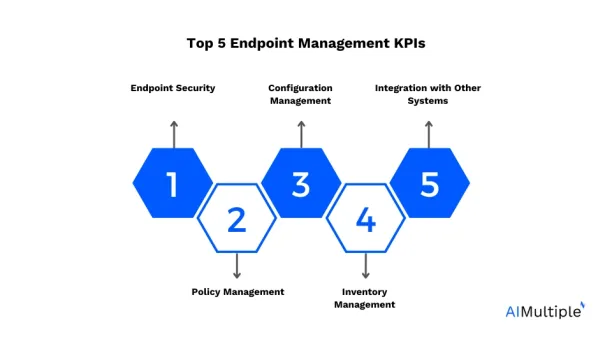
What are endpoint management software capabilities?
Endpoint management software typically offers a wide range of capabilities to help organizations efficiently manage their endpoint devices. Here are some common capabilities:
1. Inventory management: Keep track of all endpoint devices connected to the network, including hardware specifications, software inventory, and network configurations.
2. Configuration management: Remotely configure settings and policies on endpoint devices, such as security configurations, network settings, and software configurations.
3. Patch management: Automate the deployment of software updates and security patches to ensure that all endpoint devices are up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities.
4. Security management: Enforce security measures such as antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, and compliance with security policies and standards.
5. Remote donitoring and troubleshooting: Monitor the health, performance, and security status of endpoint devices in real-time and troubleshoot issues remotely.
6. Remote deployment and software distribution: Remotely deploy new software applications, updates, and patches to endpoint devices without the need for physical access.
7. Policy enforcement: Define and enforce policies governing device usage, data access, and security practices across the organization.
8. Asset tracking and reporting: Track the usage, performance, and status of endpoint devices over time and generate reports for auditing, compliance, and optimization purposes.
9. Integration with other systems: Integrate with other IT systems such as identity management, ticketing systems, and network monitoring tools to provide a comprehensive IT management solution.
10. Mobile device management (MDM): Manage mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, including security, application management, and data protection.
11. User and access management: Manage user access to endpoint devices, applications, and data, including user authentication, authorization, and access control.
12. Backup and recovery: Provide backup and recovery capabilities for endpoint devices to protect against data loss and enable quick recovery in the event of hardware failures or security incidents.
13. Compliance management: Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and industry standards by enforcing security policies, tracking compliance status, and generating compliance reports.
Top 3 challenges for endpoint management software
Implementing endpoint management can come with its own set of challenges. Here are three common ones:
1. Device diversity: One challenge is managing the diversity of endpoint devices within an organization. Companies often have a mix of devices running different operating systems (Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android), each requiring unique management configurations and tools. Ensuring consistency and compatibility across this diverse landscape can be a significant challenge for IT administrators.
2. Security risks: With the increasing number of endpoints connected to corporate networks, security risks multiply. Endpoint devices are often the target of cyberattacks, including malware, ransomware, and phishing attempts. Implementing effective endpoint security measures, such as antivirus software, firewalls, encryption, and patch management, while ensuring compliance with security policies and regulations, is a constant challenge for IT teams.
3. Remote workforce management: The rise of remote work has further complicated endpoint management. With employees accessing corporate resources from various locations and devices, IT administrators need to ensure secure remote access, enforce security policies, and manage endpoint devices outside the traditional corporate network perimeter. Balancing security and usability for remote workers while maintaining visibility and control over endpoint devices poses a significant challenge for IT teams.
Top 3 best practices for endpoint management software
Implementing endpoint management effectively involves following best practices to ensure smooth operation, security, and efficiency. Here are three key practices:
1. Inventory and asset management: Begin by establishing a comprehensive inventory of all endpoint devices within the organization. This includes desktops, laptops, servers, mobile devices, and any other network-connected devices. Maintain detailed records of hardware specifications, software inventory, network configurations, and ownership information. Regularly update the inventory to reflect changes in the IT environment, such as new device deployments, retirements, or replacements. Having a complete understanding of the endpoint landscape is crucial for effective management, security, and compliance.
2. Centralized policy management and automation: Implement centralized policy management and automation to streamline configuration, security, and compliance management across all endpoint devices. Define and enforce standardized policies governing device configurations, security settings, software installations, and user access controls. Leverage automation tools and scripts to deploy and enforce policies consistently across the organization, reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of configuration errors. Regularly review and update policies to align with evolving security threats, regulatory requirements, and business needs.
3. Continuous monitoring and remediation: Implement robust monitoring and remediation processes to detect and address security threats, compliance violations, and performance issues across endpoint devices. Utilize endpoint management software to monitor device health, security status, and compliance posture in real-time. Set up alerts and notifications to promptly identify and respond to security incidents, system errors, or policy violations. Establish proactive remediation workflows to address identified issues swiftly, such as deploying security patches, quarantining malware-infected devices, or initiating user education and awareness campaigns. Regularly conduct vulnerability assessments, security audits, and compliance checks to ensure the effectiveness of monitoring and remediation efforts.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between endpoint management and endpoint security?
Endpoint management is a compact IT solution that gives its users control over devices by administering policies that set access and authorization rules in order to keep endpoints managed, and it also delivers automation on IT tasks that help IT administrators gain control over updates, system failures, and configuration changes.
Endpoint security aims to keep endpoints secure by utilizing security tools such as VPNs, firewalls, antivirus programs (AVs), and encryption. In order to succeed at keeping endpoints secure, endpoint security solutions work in hand with endpoint management tools such as endpoint monitoring and policy management. The two security solutions focus on endpoints to sustain a safe network system by utilizing endpoint detection and response tools, automation tools, and connection tools.
2. What is the difference between device management and mobile device management (MDM)?
Device management solutions, and likewise endpoint management solutions, maintain the security of the network by controlling access to a broad range of devices, including mobile devices, printers, USBs, HDDs, CDs, Bluetooth devices, USB modems, card readers, memory cards, webcams, and more. Supplementary data loss prevention tools with content protection may be offered with device management tools.
While networked devices can be tracked within the scope of the network, mobile devices, when not connected to the network, are still able to transfer sensitive data. Using mobile devices outside of network range increases the risk of malware attacks and data breaches for bring your own device (BYOD) deployments. Endpoint management, by utilizing mobile device management functionalities, can limit access to sensitive data and applications of choice.
Further reading
- Top 10 Hexnode Alternatives Based on 10,800+ Reviews
- Device Control Policy: Features, Benefits & Challenges
- Top 10 USB Blocking Software: Based on 3.9K+ Reviews
- Top 10 Device Control Software: Review-based Analysis
- Top 10 RMM Software: Analysis From 7,700+ Reviews
If you need help finding a vendor or have any questions, feel free to contact us:
External resources
- 1. “Microsoft Digital Defense Report 2023”. Microsoft. Accessed: 27/Feb/2024.
- 2. “Crowdstrike Falcon review”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 3. “Robust and Reliable Protection”. Capterra. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 4. “Symantec Endpoint Security”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 5. “Symantec Endpoint Security”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 6. “Overall experience with Symantec Endpoint Security Complete”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 7. “It’s almost a set it and forget service.”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 8. “Malwarebytes Is A Very Solid Product For Networks. Don’t Overlook It!”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 9. “ThreatDown Reviews”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 10. “Empowering Hybrid Workforce Management and Security”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 11. “Say Goodbye to Chaos: Streamline Your Device Management with Intune”. Capterra. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 12. “A Very Useful MDM With Its Easy Onboarding, Management, Monitoring, And Security Features.”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 13. “Control your employee devices seamlessly!”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 14. “A low resource useful virus scanner”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 15. “Excellent Tool For Endpoint Management With Huge Source Data”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 16. “Webroot® Endpoint Protection”. Webroot. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 17. “great security software, av, vpn and more”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 18. “Review for Forticlient”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024
- 19. “Endpoint management tool and UEM solution”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 20. “Unified endpoint management.”. G2. Accessed: 1/March/2024.
- 21. “Managing Devices with Workspace ONE UEM”. VMware. Accessed: 1/March/2024.
- 22. “Very Good And Easy To Get Into Business”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 23. “Check Point AV the solution you can trust!”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 24. “Very Good Product And Ease To Use Of Centralized Management.”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 25. “Harmony Endpoint is EDPR”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 26. “Amazing & Easy to use”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 27. “meraki on the fly”. Capterra. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 28. “MDM Commands in Systems Manager”. Documentation Meraki. Accessed: 1/March/2024.
- 29. “Efficiency Enhanced: Simplifying Device Management with Absolute”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 30. “Exactly what I hoped it would be!”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 31. “Absolute Secure Endpoint Reviews”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 32. “Citrix Endpoint Management- Best For Security And Control .”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 33. “Citrix And Is Facilities”. Gartner. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 34. “Unified endpoint management software”. G2. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 35. “Citrix Endpoint Management review 2023”. Capterra. Accessed: 29/Feb/2024.
- 36. “Monitor and support”. Citrix. Accessed: 1/March/2024.
- 37. “Remote Work Statistics And Trends In 2024”. Forbes. Accessed: 27/Feb/2024.
- 38. “Forecast revenue from endpoint security market worldwide from 2022 to 2027”. Statista. Accessed: 27/Feb/2024.
- 39. “Forecast revenue from endpoint security market worldwide from 2022 to 2027”. Statista. Accessed: 27/Feb/2024.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.