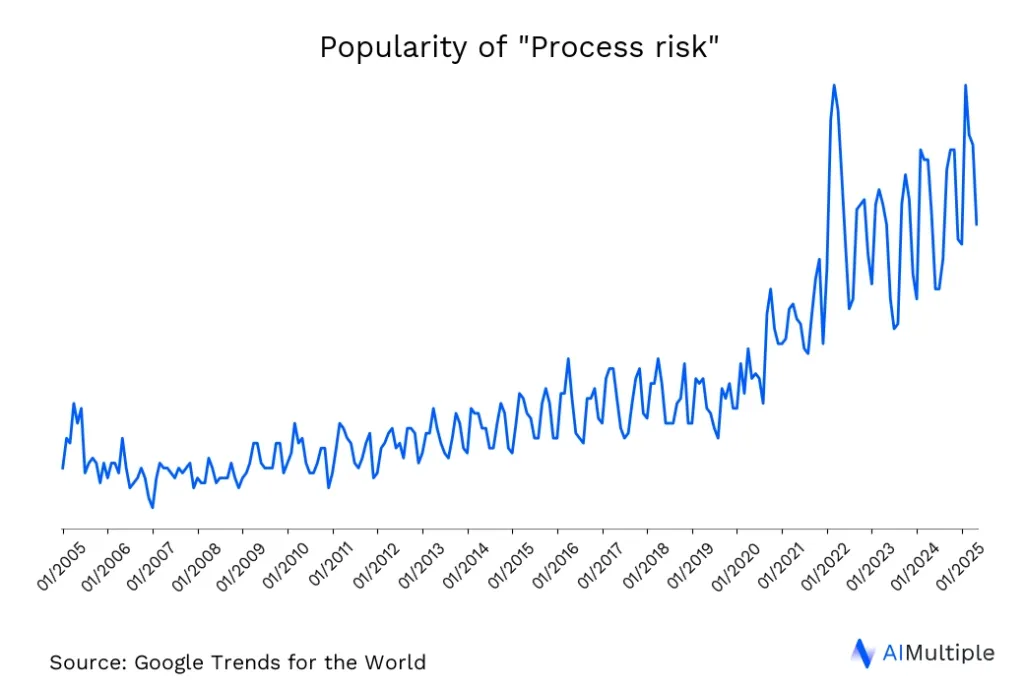
Processes may underperform, go over budget , or increase the lead-time because of process risks, such as malfunctioning equipment or human errors. Such process risks incur cost on the company and lower customer satisfaction, harming a business’ reputation and finances in the process. This is why interest over process risk has gradually increased over the last 20 years (Figure 1).
To overcome these risks and their consequences, leaders should know how to identify and mitigate them.
Explore the different types of process risk, give examples of them , and offer 7 process risk management best practices:
What is business process risk?
Process risk, a sub-component of operational risk, refers to inefficient and ineffective business processes that lead to higher costs and lower customer satisfaction. These “ineffective business processes” can stem from:
- Actual failed processes
- Inadequate policies systems
- And disrupting events, such as employee errors, fraudulent activities, or other physical events
For example, an error in the order fulfillment process reflects poorly on the quality control process and lowers customer experience.
Therefore, process risk can also be explained to be a result of a lack of proper process management.
What are process risk types?
Process risk types are harmful scenarios that stem from different departments/entities and can cause inefficient, ineffective, and non-compliant processes.
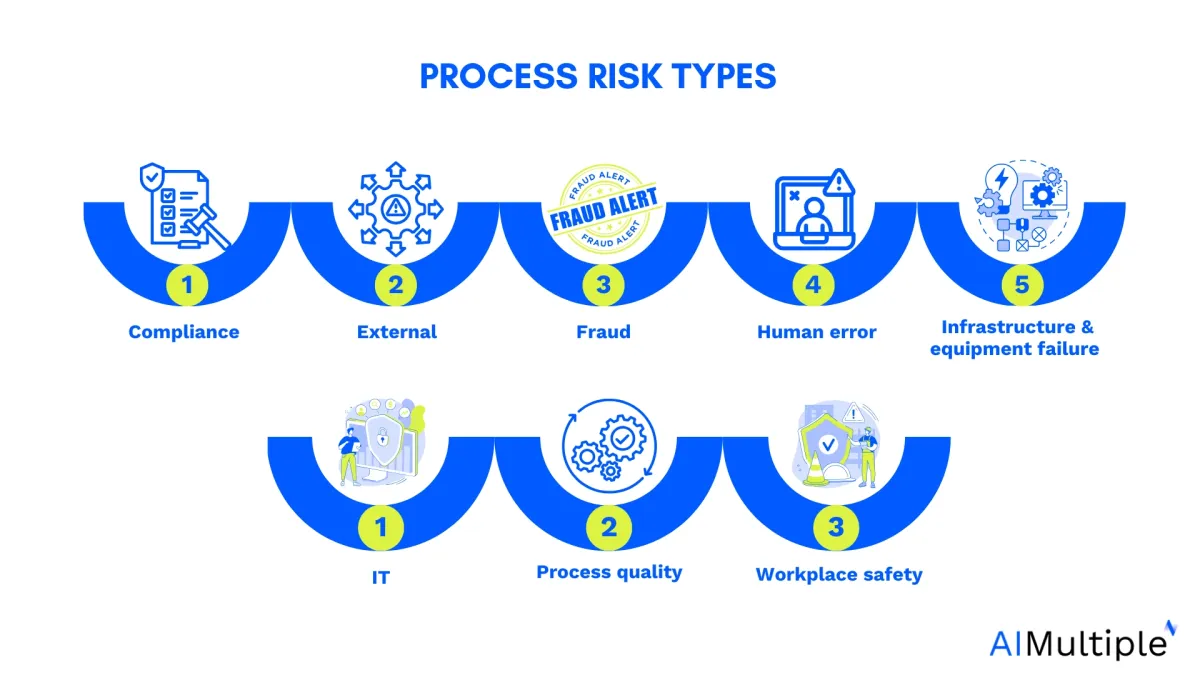
These risk types can be an external problem, an internal error, or both. These types include:
1. Compliance risk
Compliance risk arises from the failure to adhere to laws, regulations, or industry standards. Changes in legislation or enforcement can amplify this risk.
For example, a healthcare provider that neglects to update processes to comply with new patient privacy laws may face regulatory fines and reputational harm.
2. External Risk
External risks stem from factors outside the company’s control, such as natural disasters, political instability, or economic shifts.
For instance, a company located in a region prone to hurricanes may experience disruptions in supply chains and facility operations, leading to significant losses.
3. Fraud risk
Fraud risk involves intentional deception, manipulation, or exploitation of company processes for personal or organizational gain. Weak internal controls or oversight can exacerbate this risk.
For instance, an employee exploiting expense reimbursement systems could result in financial losses and damage to organizational trust.
4. Human error risk
Errors that are resulted from manual work, including challenges like employee turnover, lack of skills, or misconduct.
For instance, an accountant might enter the wrong number accidentally, which is a minor yet common mistake, and due to miscalculations’ ripple effect, can cause significant loss for the company.
Another example is losing a key employee without a succession plan can disrupt operations. Similarly, an untrained employee might mishandle a critical task, leading to inefficiencies or compliance issues.
Embedding safety principles into training programs and operational guidelines can significantly reduce the occurrence and impact of human errors.
Real-life example
A process mining case study shows how process intelligence can overcome human risk error. EDEKA Minden-Hannover used a process mining tool to improve IT service management and reduce human error. With real-time process visibility, the IT team enhanced issue prioritization and diagnosis, leading to faster ticket resolutions and reduced frustration for retailers, improving overall process efficiency.
5. Infrastructure and equipment failure risk
These are breakdowns in primary building blocks of a process, such as communication breakdowns, network shutdowns, transportation fragmentations or the breakdown of the machinery or tools that are used to complete processes, which result in process failures. Such failures can delay the production, assembly, and delivery of products and harm order fulfillment as a result.
For example, a bakery’s oven malfunctions in the middle of a large order, causing the bakery to miss delivery deadlines and leading to spoiled goods and financial losses.
6. IT risk
Cyber risks
They include hardware and software failures, spams, viruses, malwares, and cyber attacks that infect a company’s digital infrastructure.
For example, an online retailer’s website crashes due to a server failure during a high-traffic sale event, preventing customers from making purchases and resulting in lost revenue.
Real-life example
DUO implement an event-driven process to improve student finance request handling. Using process mining, they identified and resolved IT risks, such as technical errors in the pilot phase, while gaining transparency in key business metrics to reduce costs by 25%.1
System failures
System risk refers to operational disruptions caused by failures or vulnerabilities in interconnected systems. These risks include software glitches, system crashes, or data breaches.
For example, a manufacturing company experiencing a system-wide failure in its inventory management software could face delays in production and fulfillment.
7. Process quality risk
This risk occurs when processes are not well designed and planned. For example, a car manufacturer schedules its production based on the time and complexity of tasks, like prioritizing seat installation before seat cushion installation.
However, if the manufacturer can’t accurately predict the processing time for each step—such as seat cushions being delayed due to supply chain issues—the installation phase may be delayed, risking the delivery timelines promised to customers and dealerships, leading to lost time and money.
8. Workplace safety risk
It refers to any accidents or injuries that may threaten human health and safety. Promoting and applying safety principles in workplace design and daily operations is essential to minimizing these risks.
For instance, a factory worker slips on an unmarked wet floor and injures their back, resulting in medical expenses, production downtime, and potential legal action against the company.
What are some real-life business process risk examples?
Commonly, there are h two forms of process risks:
Process risks in banking
These risks mostly result from documentation issues.
For example, during the KYC process or loan processing stage, a bank filling the wrong information on the documents will slow down processes, such as loan/credit card approvals, and financial statement generation and can suffer from high audit and compliance fees.
Explore how to benefit from process mining in banking and reduce such risks.
Process risks in supply chain
In the supply chain, process risks in the order fulfillment stage are common and cause inefficiency.. For instance, mistakes in establishing the correct amount of inventory can slow down delivery time or even fail to finalize the fulfillment of the orders.
Explore how to use process mining in logistics/supply chain firms to mitigate these risks.
What are the 7 best practices to mitigate process risks?
We may not eliminate all the risks but we can minimize them by improving the operations, activities, and task management.
Here are 7 recommendations to manage your process risks:
1. Develop a data-driven process risk assessment
The first important step is to identify the risks in your processes.
To achieve this, you should leverage your event logs data where information about the process executions is stored. By analyzing such data, you can evaluate your risk exposure in a data-driven manner.
To extract and analyze process data, you can benefit from process mining, which is a tool that can automatically extract and analyze your event logs data.
2. Map your processes
Process maps and visuals can paint a picture of the complexity of a process.
Therefore, you should map your processes including each task, activities, sub-processes, and employees. Mapping your processes can streamline the identification of risky areas so that you can specifically implement changes where they are needed to hedge against the risks.
To do so, you can use process mining since it automatically maps the discovered process model. You can zoom into each step or activity to check its impact on process performance.
3. Increase automation level
Once the process is mapped and the event log data is analyzed, you can assess your automation level to discover new automation opportunities.
Automation increases efficiency because it can reduce the risk that comes with manual errors. But choosing the right area to implement automation and to choose the right tool is not easy. Learn how to choose the correct automation tool.
You can also deploy process mining to assess your automation level and detect areas that require automation. Some process mining vendors offer a digital twin of an organization‘s capability which can help you to calculate ROI for each automation initiative and decide accordingly.
Process mining can also be helpful to manage the automation project. Learn how process mining helps you discover and manage automation projects.
4. Monitor and measure process performance
To ensure that your processes follow time, cost, quality, and compliance objectives, you should set performance metrics and monitor your all transactions, such as onboarding, sales, service or product delivery.
Monitoring and measuring your processes will allow you to pinpoint risks and intervene in time. Also, you can enhance your predictions by constantly monitoring your processes, ensuring early anticipations and improving process controls.
Several process mining tools include KPIs for business analysts to track their performance easily. Some vendors also allow users to personalize their KPIs. These solutions also come packed with predictive analytics capabilities on their platforms so that you can predict whether the selected process will result in the desired outcome or not.
For instance, process mining users can estimate if the loan application will be approved on the promised date or not. Estimating the date and taking precautions, such as setting reminders, can prevent high-cost risks.
5. Comply with best practices and regulations
Following the best practices and complying with regulations, including established safety principles, can help reduce workplace safety or IT security risks. Also, you can standardize your processes by ensuring that each process follows best practices.
Suppose a bank monitors its loan processes and identifies idiosyncrasies in employees’ execution behavior. Lack of standardization, and each employee beating on their own drum, can affect the bank’s reputation negatively while increasing lead time and cost.
This can result in the bank being slapped with high fees due to non-compliance. The bank should standardize its processes around best practices and regulations.
Process mining’s core feature conformance check allows you to assess your compliance level by comparing your processes against best practices, ideal models, and regulations.
For instance, Piraeus Bank analyzed its loan processes and detected variations in the application processes with the help of process mining. As a result, they shortened their application processes from 35 minutes to 5 minutes on average.
Check out for more process mining case studies.
6. Improve communication channel
Different parties that co-function and collaborate on mazy processes should be in constant communication with each other to be on the same page and avoid an infrastructure failure.
For example, when a test manager notices that hiring inexperienced developers might lower the software quality. Therefore, the manager is expected to increase the number of re-tests. Yet, such a solution prolongs the time to launch the product in time.
In such a situation, the manager should either communicate with the HR team to ensure that the right developers are in the team or improve the onboarding of young developers to prevent such problems.
Process mining maps can determine relevant parties. Thus, these visuals can streamline the communication among these different teams.
7. Consider process inter-dependency
In many cases, processes are complex and interdependent like procure to pay (P2P) so various processes or sub-processes might affect each other. It is important to consider such inter-process relations while looking for inefficiencies or measuring the impact of a change in your operations.
Imagine an improvement for requisition activities can increase efficiency for this process while creating bottlenecks at the invoice level.
Multi-level process mining (MLPM) can help you understand inter-dependency and complexity by defining different entities in a given process and tracking interactions among them. By offering a more comprehensive model, the MLPM can ensure you can find out the risks and tackle them in-time.
What is process risk analysis?
Process risk analysis involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks within business processes to prevent inefficiencies, errors, and disruptions. It includes evaluating potential threats, analyzing their impact, and implementing controls or improvements to ensure process reliability and compliance with standards or regulations.
FAQs
What is the process control risk?
Process control risk occurs when internal controls fail to prevent errors, fraud, or non-compliance within a process. This can result from weak oversight, poorly designed workflows, or inadequate monitoring systems, leading to financial losses, operational disruptions, or reputational damage.
Further reading
Explore how process mining can enable process improvement and management:
- 3 Ways Process Mining Streamlines Process Management
- Pair Methodology with Technology for Process Improvement
- What is Process Technology & 3 Reasons to apply it?
If you believe your business can benefit from process mining, do not hesitate reviewing our data-driven comprehensive process mining vendor list.
To mitigate process risk, manage and improve your business process. Check out objective lists of process management and improvement tools:
- Workflow management software
- Business process management software
- Low-code/No-code development platform
- Onboarding software
And, if you are left with more questions, we are happy to help:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.