process mining market revenue is estimated to grow by 40% last year, increasing the competition amongst leading process mining vendors. Such competition pushes the discipline to offer more precise and less complex process analysis and visualization.
Object-centric process mining is one recent development in the field of process mining. Since it is a new specification, business leaders and process analysts might have questions regarding:
- What object-centric process mining is
- How it differs from traditional process mining and multi-level process mining
- Why does it matter in the first place?
This article will respond to these questions with examples.
What is process mining?
Process mining is a process technology and an analytical field that provides data-driven process intelligence. Process mining architecture involves process discovery, conformance checking and process enhancement. Process mining software:
- Integrates with company systems (e.g. ERP, CRM) and collects the event logs data.
- Analyzes the data and discovers activity sequences for each case from the event logs.
- Merge these sequences into a complex process model.
Process mining employs ML driven process mining algorithms to do these steps automatically.
Learn more about process mining by reading our comprehensive article.
What are the limitations of traditional process mining?
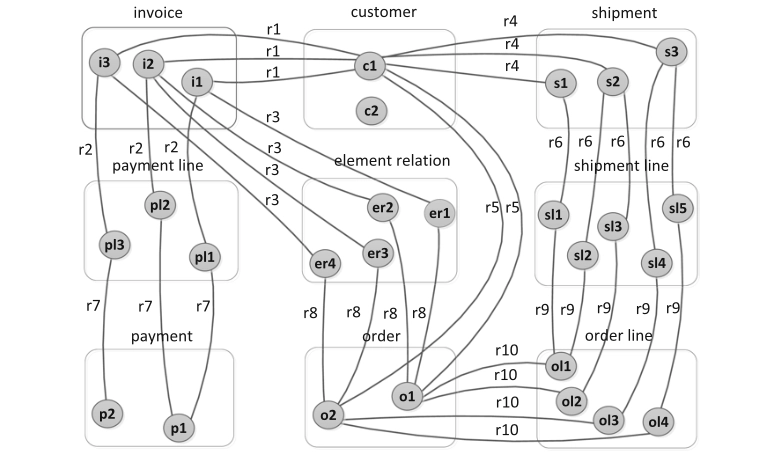
Traditional process mining tools assume that there is a single case identifier, known as case notion assumption (See Figure 1). A case is the collection of events to execute a specific process. However, an event can be related to several objects, such as customers, location, and multiple items ( See Figure 2).
For instance, In a sales order system, a case refers to all events to create and confirm an order, collect, pack, deliver and invoice order items. Each of these events is related to several objects.
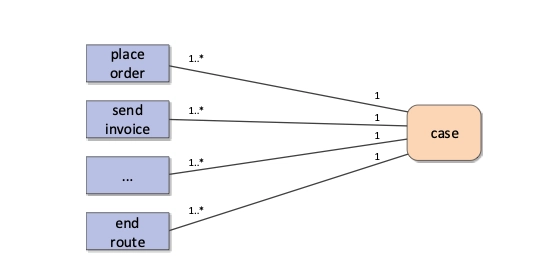
Challenges
Classical process mining focuses on the order of the events inside log cases. Yet, the process analysis might be affected by 2 major issues:
- Convergence: When the same event is related to different cases. In such cases, process analysis may replicate the same event.
- Divergence: When a case contains different independent instances of the same activity. One example is the sales order activities, such as collecting and packing items, which may include other instances.
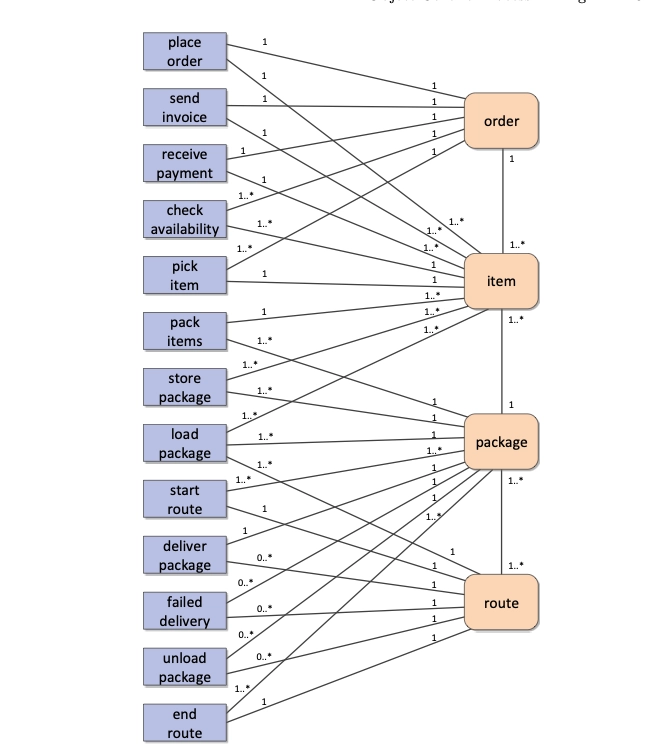
What is object-centric process mining?
Object-centric process mining (OCPM) is a type of process mining that particularly analyzes the behavior of individual objects or entities (See Figure 3). OCPM does not follow the case notion logic. It assumes that multiple case notions can coexist, and these cases (objects) can correspond to different object types (See Figure 2).
Also, it aims to overcome convergence and divergence issues by biasing process analysis. Thus, this technique assumes that:
- Events can relate to multiple objects
- Each event may contain various cases
- A single case may include independent and repeated activities
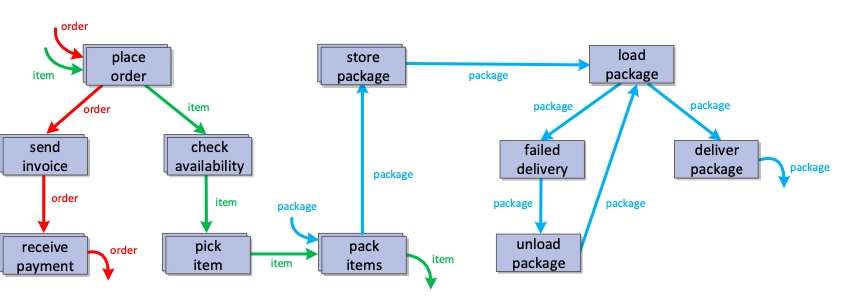
As a result, OCPM provides a more detailed analysis of the individual-level object behavior, including:
- Interaction between different objects with the process
- Impact of objects’ behavior on the process performance KPIs.
Learn more about OCPM by watching the video below:
How does object-oriented process mining work?
Object-centric process mining works similarly to classical process mining. However, it extracts and analyzes object-specific data from event logs by:
- Employing specialized algorithms and techniques, such as:
- Data pre-processing
- Data enrichment
- Data analysis methods, such as:
- Clustering
- Classification
- Association rule mining.
Multi-level process mining vs object-centric process mining
Object-centric process mining is not the only approach to prevent divergence and convergence problems. One major approach is multi-level process mining, also known as hierarchical process mining. MLPM defines multiple different entities and tracks their interaction in a given process.
On the other hand, MLPM simplifies by associating each activity with one case notion. However, the same event may refer to many case notions. By choosing one, the model becomes misleading, specifically regarding frequency statistics.
What are the benefits of object-centric process mining?
Object-centric process mining allows analysts and business leaders to:
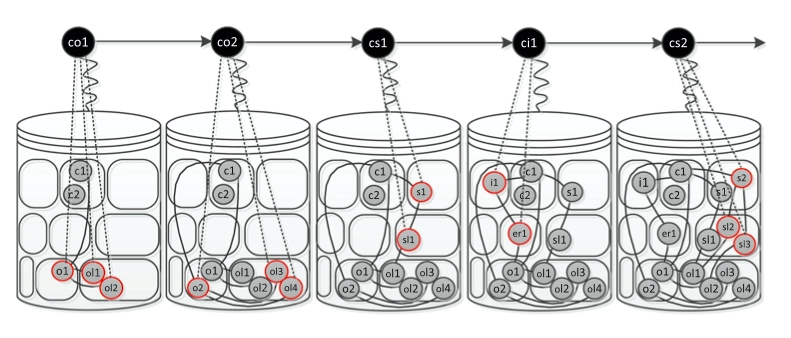
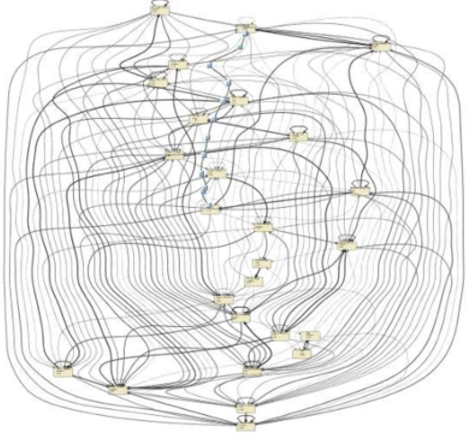
- Generate simple graphs: In the traditional approach, a case ID is attributed to each order, generating loops for every item at other steps. This would lead to complicated spaghetti-like charts as in Figure 6. With object-centric process mining, it is possible to avoid such models without losing valuable information (See Figure 5).
- Improve accuracy for process KPIs: Single case notion duplicates events, leading to bias in important performance indicators such as automation rate or the number of process steps. OCPM improves the accuracy of the analytics by tracing many-to-many relationships.
- Display correct delivery time: Traditional process mining analytics aggregates the delivery time for orders with multiple packages. However, object-centric process mining shows the respective time for each delivery case, allowing analysts to monitor their processes closer to reality.
- Align sales and production: By obtaining correct and accurate insights, businesses can align their sales and manufacturing departments. This reduces delayed shipments and the costs associated with them.
- Capture behavioral patterns: Traditional process mining concentrates on generating an end-to-end process flow. OCPM focuses on specific objects’ behavior in the process, such as the customer, service or product. For example, OCPM can analyze customer behavior and identify purchasing patterns to improve sales operations.
Further reading
Learn other developments in process mining by reading:
- Top 6 Applications of Machine Learning in Process Mining
- Predictive Process Mining: Top 3 use cases & case studies
- 4 Trends Fueling the Future of Process Mining
Check out our data-driven and comprehensive vendor list to benefit from process mining software.
If you have more questions, let us help you:
External Links
- 1. van der Aalst, W. M. (2019). Object-centric process mining: Dealing with divergence and convergence in event data. In Software Engineering and Formal Methods: 17th International Conference, SEFM 2019, Oslo, Norway, September 18–20, 2019, Proceedings 17 (pp. 3-25). Springer International Publishing. Revisited February 24, 2023.
- 2. van der Aalst, W. M. (2019). Object-centric process mining: Dealing with divergence and convergence in event data. In Software Engineering and Formal Methods: 17th International Conference, SEFM 2019, Oslo, Norway, September 18–20, 2019, Proceedings 17 (pp. 3-25). Springer International Publishing. Revisited February 24, 2023.
- 3. van der Aalst, W. M. (2019). Object-centric process mining: Dealing with divergence and convergence in event data. In Software Engineering and Formal Methods: 17th International Conference, SEFM 2019, Oslo, Norway, September 18–20, 2019, Proceedings 17 (pp. 3-25). Springer International Publishing. Revisited February 24, 2023.
- 4. Extracting Object-Centric Event Logs to Support Process Mining on Databases | SpringerLink. Springer International Publishing
- 5. Extracting Object-Centric Event Logs to Support Process Mining on Databases | SpringerLink. Springer International Publishing
- 6. ResearchGate - Temporarily Unavailable.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.