4 Trends Fueling the Future of Process Mining in 2024
Recent findings show that more businesses will adopt process mining as a digital transformation driver and process automation and improvement by 2023. While process mining expands, change in customer demands impacts process mining tools’ capabilities and perspectives.
This research explains the top 4 factors that will affect the future of process mining.
1. Accelerate automation with process mining
The process mining consultants and vendors acknowledge the role of process mining in robotic process automation (RPA) projects. Process mining can discover tasks in processes that can benefit from automation. Process mining can:
- Identify steps in processes to be automated. This is also called robotic process mining (RPM). RPM obtains task data from the workers and IT systems and automatically includes it in the process model. Then, it uses this information to identify automation candidates.
- Assess the priority level among automation initiatives
- Track the entire automation journey
- Identify and predict the deviations and failure points in the project to ensure project success.
Surveys and industry analyst reports indicate that automation is one of the top 5 general use cases of process mining. For example, market leaders like IBM integrate process mining capabilities in their automation solutions.
Process mining is also being integrated with low code to discover and implement automation, surpassing traditional RPA. Such integrations have the potential to speed up process automation.
2. Generate value for customers with customer-oriented process mining
Process mining projects optimize an organization’s process management by discovering automation opportunities identifying inefficiencies and non-conformant cases. These are all initiatives to improve internal processes, which indirectly increase customer satisfaction. Yet, businesses can leverage process mining to advance their customer services by directly analyzing their external processes.
External processes are the operations and activities involving interaction with outside parties like customers or partners. For example, process mining can enhance customer journey mapping, boost marketing strategies, improve company websites, and prevent customer loss. Please read our article to learn more about how process mining augments customer journeys.
Thus, process mining vendors can integrate the capabilities of different customer service platforms to extract customer-related data such as customer feedback to enable businesses to compare such customer-oriented data with internal processes. Based on the analysis, business analysts can redesign their internal activities and change internal behaviour to transform their business while improving customer experience.
Gartner’s market guide report on process mining (2021) expects that “customer journey mining” is a new application that attracts more attention. 1 Such external process applications will bring more customer-oriented process mining software.
3. Adopt predictive and actionable process mining
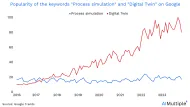
Process mining is being used descriptively to discover and explain processes based on historical data. However, this has been changing due to the users’ demand for predictive process mining. In a recent conference, Prof. Wil van der Aalst mentions that future process mining will be more predictive than descriptive. Today, vendors provide predictive process mining capabilities by integrating ML algorithms, predictive tools and digital twins of an organization technology with process mining platforms.
Following predictive process mining, there is increasing popularity of prescriptive process mining, also called actionable process mining, which aims to use predictions to generate actions. By applying causal machine learning techniques, academics work on causal process mining to discover processes and recommend the following steps. An example is developing rules that describe causal relations between problems and solutions.
For example, process mining can be applied to data from courier services to detect the delays in a delivery area and estimate the probability of customer satisfaction. This data can help the company understand if the customer is eligible for compensation or a discount due to delays or missed deliveries. The results of compensation or discount can also be analyzed by the process mining tool to generate rules about the positive or negative impact of the payment based on the customer’s demographics. Suppose a significant proportion of customers at a certain age would be satisfied with the discount. In that case, the company can generate such rules to connect the problem with a clear solution. Prof. Wil van der Aalst warns about the danger of such causal inferences from correlations. These causal pathways can be strong correlations based on a third-party factor and not a causality relation which can be misleading to build strategies upon.
However, if academics and process mining vendors can establish causal process mining, they can eventually reach automated process improvement. Automated process improvement would automatically generate recommendations on the higher and lower order causes of process performance.
To design automated process improvement, the vendors should combine these three technological developments:
- what-if scenario simulations
- causal process mining
- search-based optimization techniques (explore the space)
4. Power process mining with the Internet of Things (IoT)
Internet of Things (IoT) term refers to interconnected and physical devices, such as sensors, software or other relevant technologies. IoT sensors contribute to the collection of automated, real-time data. Therefore, these devices can serve as a data source for process mining. The data gathered by IoT devices include information on process execution. The relevant data can be extracted to apply process mining techniques.
Also, process mining typically deals with historical data since it relies on company IT systems as sources. However, IoT enables process mining to access real-time data because it collects the information while carrying out the process. By obtaining and analyzing IoT data, process mining will be able to identify deviations, errors or anything negatively affecting process performance in real-time and allow teams to optimize them.
For example, IoT devices integrated into manufacturing organizations can capture data that can be integrated into the process mining tools. The results of the process mining tool leveraging IoT data can identify performance differences among two different machines during production and warn manufacturers to prevent loss of money. Whereas process mining alone leverages historical data, thus, could help only after the production process is complete, leading to a lower cost cut than process mining empowered with IoT.
Given the benefits of IoT, it is expected that those process mining systems will be integrated with IoT platforms in the future. The IoT market is increasing, and we already see applications of IoT for process management through the smart city and port projects, generating more processes and workflows to be managed.
Further Reading
To discover more on process mining trends and process mining market, feel free to read our in-depth articles:
If you want to apply process mining, you can start checking vendors from our data-driven list.
Assess different vendors with a transparent methodology yourself by downloading our checklist:
And, if you believe you need help with finding the right vendor:
External Links
- 1. Kerremans, Marc; Searle, Samantha; Srivastava, Tushar; Iijima,Kimihiko (2020). “Market Guide for Process Mining.” Gartner. Revisited January 4, 2023.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.