Leveraging my 2 decades of experience as a cybersecurity practitioner, I selected top DLP software for securing sensitive information & complying with regulatory standards. I tested 6 of these DLP solutions over a month, focusing on key features like channel coverage, ease of deployment, and classification accuracy. See the results below:
| Product | Existing features | Missing features |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys | 17 | 0 |
| ManageEngine DLP Plus | 16 | 1 |
| Teramind DLP | 14 | 3 |
| Sophos Intercept X | 12 | 5 |
| Trellix DLP | 10 | 7 |
| Acronis Cyber Product | 6 | 11 |
See benchmark results below to see which features are provided and which are missing:
Benchmark results: Feature comparison
We compared these products across 4 dimensions, you can see the descriptions of these dimensions or check our benchmark methodology. To assist businesses in selecting the right DLP product, we conducted a comprehensive benchmark review of six popular DLP solutions, all offering free trials.
Channel coverage
| Products | Communication channels | Email* | Application** | Email/IP based exceptions | Active Directory (AD) Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sophos Intercept X | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Acronis Cyber Protect | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Teramind DLP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Trellix DLP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
* Attachments that are assigned as sensitive data can be blocked or audited, and internal & external users can be blocked by software.
** Allowance for certain applications to open, edit, or screen capture sensitive data by software.
Administration
| Product | Tamper Protection for agent file | Audit Trail/Client notifications | Files search/tags from hashes | Customizable data rules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sophos Intercept X | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Acronis Cyber Protect | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Teramind DLP | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Trellix DLP | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
Data classification
| Products | Effective data classification | Data classification customization | Data classification verification | OCR | Data Discovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sophos Intercept X | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Acronis Cyber Protect | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Teramind DLP | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Trellix DLP | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
Other capabilities
| Products | Deployment | Web filtering | Option to report false positive | User behavior analytics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys | Cloud, Virtual Appliance | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Sophos Intercept X | Cloud | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Acronis Cyber Protect | Cloud | ❌* | ❌ | ❌ |
| Teramind DLP | Cloud, VDI (Virtual desktop infrastructure) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus | On-premise | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Trellix DLP | On-prem, Cloud | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
* Acronis is offering a web filtering option as an add-on, categorized as ‘cloud-based URL filtering.’.
How to choose the right DLP for your business?
While all tested DLP tools effectively cover major data channels such as peripherals, email, and applications, data classification remains a persistent challenge. Accurate classification is critical for preventing data loss while avoiding false positives. Based on our findings, we offer the following best practices for testing DLP solutions safely and effectively:
- Simulate realistic data: Generate test datasets to mimic confidential information. This minimizes risk while allowing you to evaluate the tool’s capabilities without exposing sensitive business data.
- Leverage masked employee data: If test data creation isn’t feasible, use anonymized or masked datasets with controlled access. Build a separate database for this purpose, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Limit data scope: Test solutions on a small, controlled group of employee data rather than full production datasets to mitigate risks and maintain compliance.
- Avoid using production data in PoC environments: Proof-of-concept or trial systems can inadvertently expose sensitive information, so prioritize test environments free from live production data.
Our analysis also highlights that while off-the-shelf classifiers can provide basic functionality, their effectiveness is often limited. Customizing data classification policies to align with your organization’s unique needs is essential to achieve optimal protection and reduce false positives.
Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys
We tested Endpoint Protector by CoSoSys and looked at its DLP capabilities. Our findings are summarized below:
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Granular control over 30+ devices.
- Device monitoring through a control dashboard.
- Deep Packet Inspection for network file transfers.
- Predefined and custom policies.
- Effective rights for policy creation.
- eDiscovery for sensitive data detection.
- USB encryption.
- Notifications and alerts for blocked actions.
- Customizable client notifications.
- Audit trail.
- Tamper protection.
- Ineffective features:
- No device management.
Choose Endpoint Protector for a comprehensive DLP solution with strong device control capabilities.
1. Channel coverage
Endpoint Protector enables granular control over 30+ devices, including USBs, Bluetooth devices, smartphones, and more.
Peripheral devices
Device control
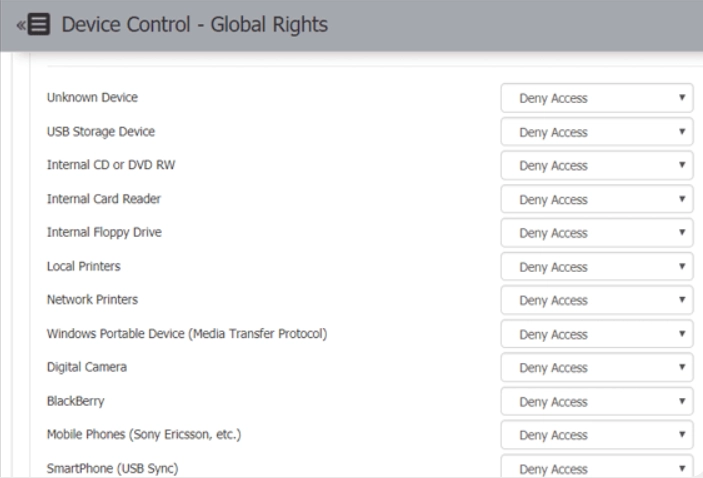
Administrators can set up access control for defined devices such that devices can be allowed or blocked from connecting to the clients’ computers.
Applications
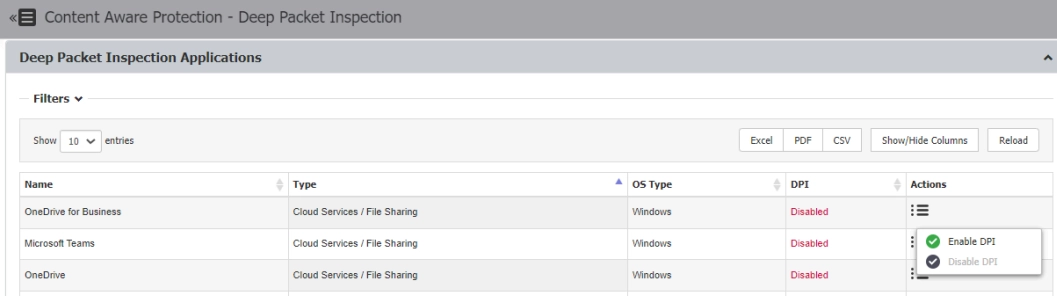
Deep Packet Inspection
It enables network file transfers to be managed by the administrator. Administrators can set up controls for webmail, drives, and third-party applications listed below. When enabled, CAP and device control settings work in compliance with DPI scans.
2. Data classification
Content Aware Protection (CAP)
Predefined policies
Predefined policies are available in 3 groups based on the client’s operating system: Windows, Mac, & Linux.
There are 86 predefined policies for Windows. These policies are, for example, as follows:
- File transfers: File transfers based on their content (graphic, archive, or programming) can be blocked.
- HIPAA: File transfers based on their content must comply with HIPAA, or else they are blocked.
- GDPR: File transfers based on their content must comply with GDPR, or else they are blocked.
Custom policies
Custom policies can be defined in accordance with policy exit points, users, and policy action of choice.
3. Administration
Access rights
Effective rights enable policy creation (access right control rule) based on a specific user/device/format (file type).
Global rights are the device control rights that apply in general. You can set different access rights for different devices.
Policy creation
To create a policy, the administrator can select from predefined or custom options.
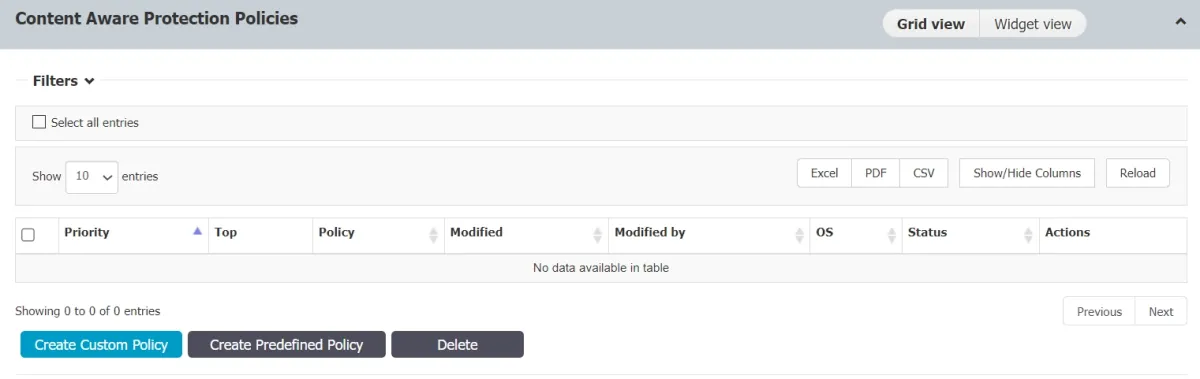
The administrator can order policies in accordance with their priority level (the administrator may prioritize one policy over another).
eDiscovery
Detects sensitive data at rest and enables encryption, decryption, and deletion at the target. You can create policies based on file types and file content. The policy defines the objects for scanning.

The scan output helps the administrator see where sensitive data resides and take action.

Custom classes
Enables custom class creation and settings for devices such that administrators can assign “Trusted Device (TD)” based on device information such as its serial number and type.
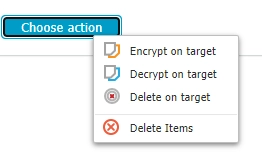
Deny & allow lists
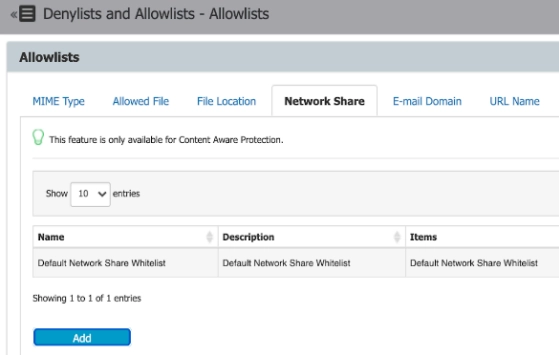
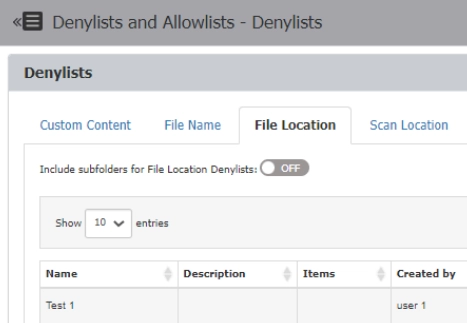
Helps with defining sensitive content. CAP and eDiscovery take it as their object for detection. It asks you to define which file types, custom content, file location, scan location, regex, domain, URL, and e-mail domain are allowed and which are disallowed.
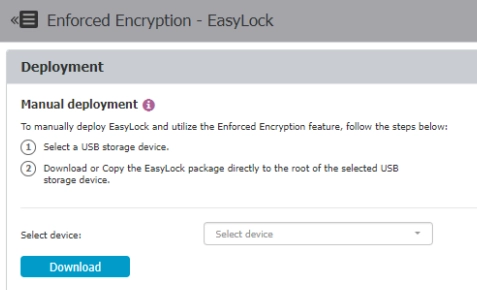
USB encryption
Endpoint Protector enables USB device encryption. The administrator can automate the action.
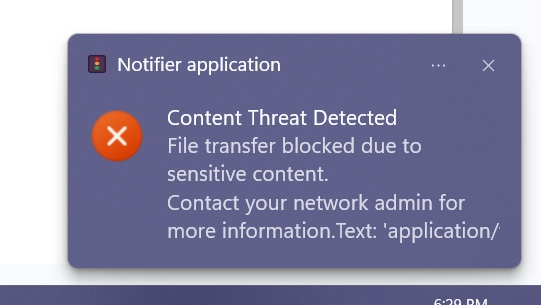
Notifications & alerts
When tried to attach an a.xlsx file type with the name “Confidential” and with social security number information inside in WhatsApp, Endpoint Protector blocked the action; it notified the administrator as below:
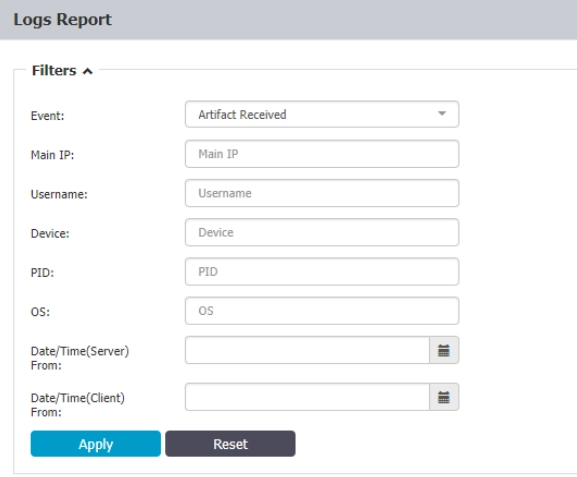
The administrator can see event logs in the Content-Aware Report window. The event log includes details such as event, time, user, device, destination, and file.
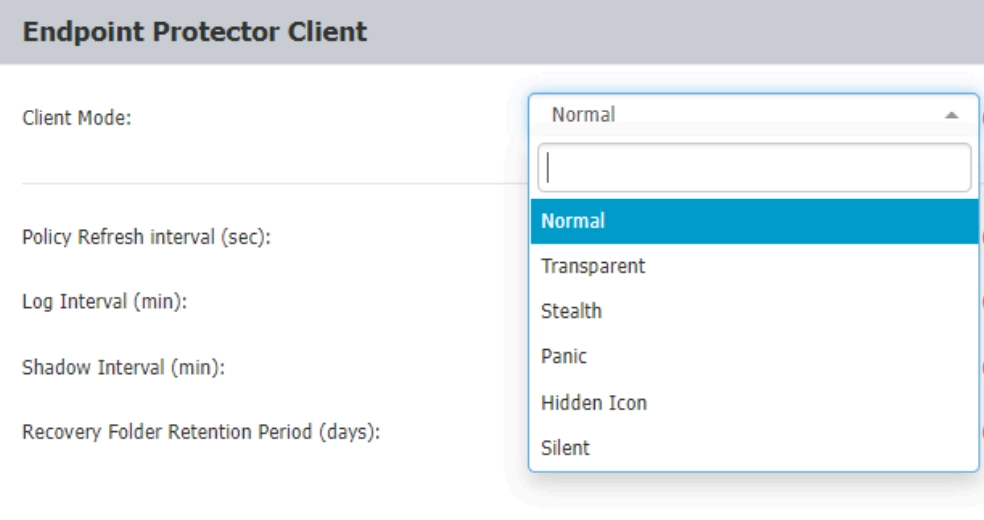
Other features
- Microsoft AD and Microsoft Entra ID synchronization is supported by the program.
- Client notifications can be customized.
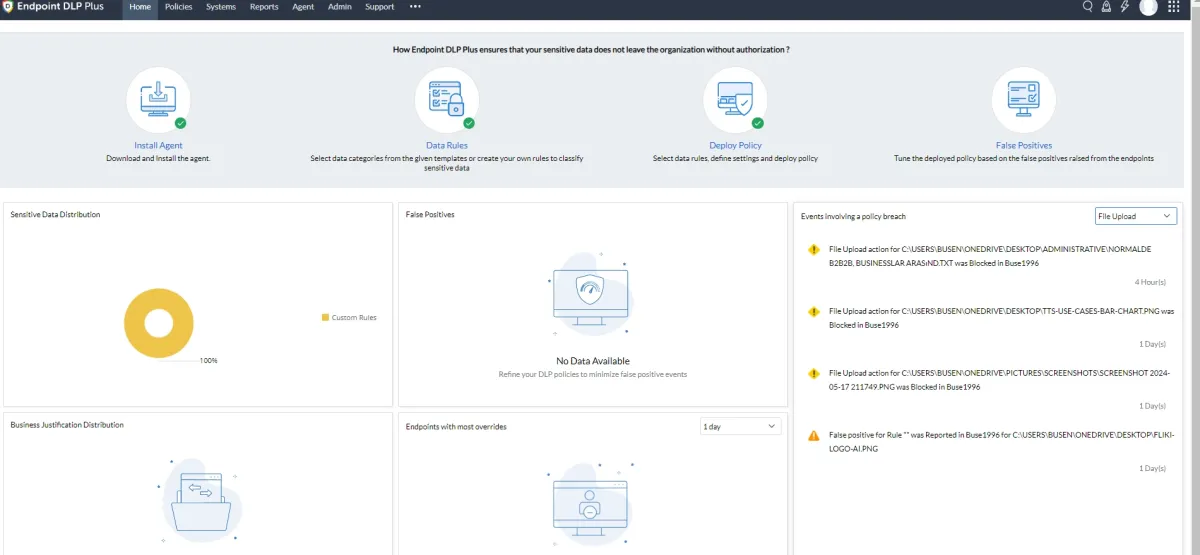
ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus
We leveraged ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus’ free trial. Enabling users to notify administrators about false positives was a helpful feature that not all other providers offer.
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Effective data classification.
- Effective email and application protection.
- Customizable data rules.
- Users can notify administrators about false positives.
- Option to report false positives.
- Offers active inventory integration.
- Offers tamper protection.
- Comprehensive audit trail.
- Ineffective features:
- No device management.
- No cloud deployment.
- No file search.
1. Channel coverage based on selected policy enforcement or audits
Printers, USB devices, applications, etc., can be added to a trusted devices or applications list. You can specify a device by entering the device instance path.
Network printers and USB printers are the two types of printers available. Disk drivers and CD-ROM are the two options available for removable storage devices.
If a device or application is not trusted, communication with it will be blocked. You may also choose to audit devices or applications.
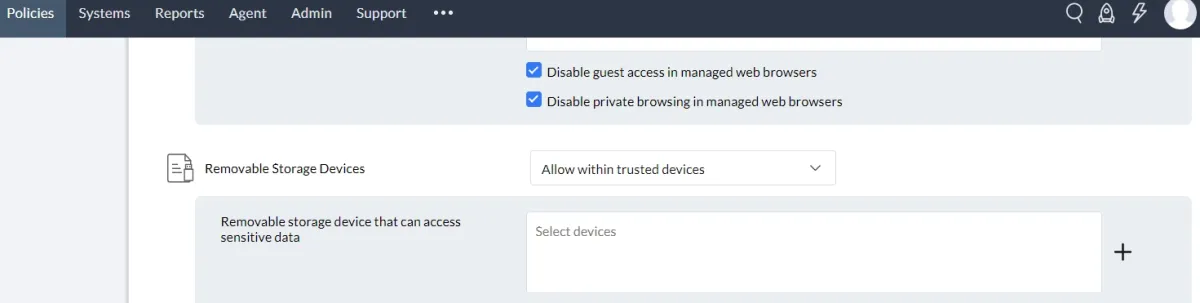
ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus can be configured to protect assigned sensitive data by blocking its upload to the designated browser.
How does ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus block files?
Once sensitive data has been assigned in the data rules section, ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus applies the specified policies.
The option to report false positives to the administrator was included for the user. This functionality is not provided in all DLP solutions.
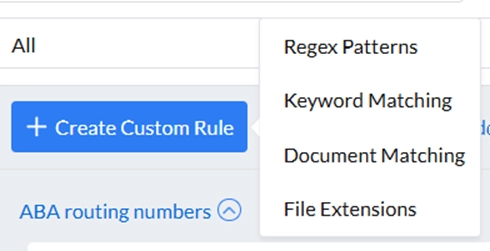
2. Data discovery & classification
The solution enables users to choose established rules from the rules library or lets them create custom rules for sensitive data discovery.
Step-by-step guide on the configuration of data rules for sensitive data discovery:

Data classification is based on regular expressions. AIMultiple hasn’t come across any semantic classification capabilities.
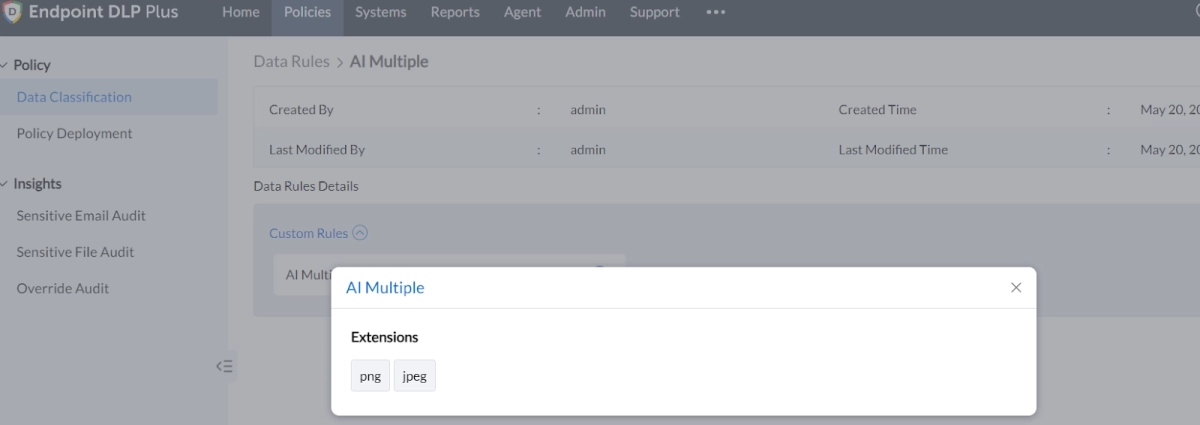
Custom rule based on file extension: It is offered to assign files ending (for example) in PNG and JPEG to the sensitive data category.
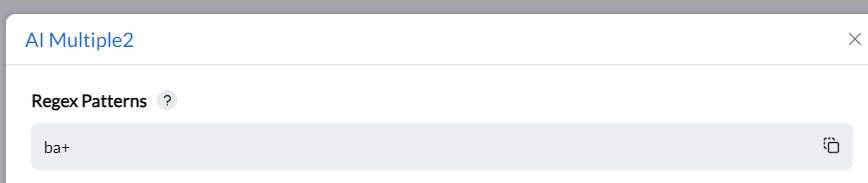
Custom rule based on regex (regular expression): It is offered to assign files with the expressions, like expression “ba” as sensitive data.
3. Administration experience
Users with different access levels:
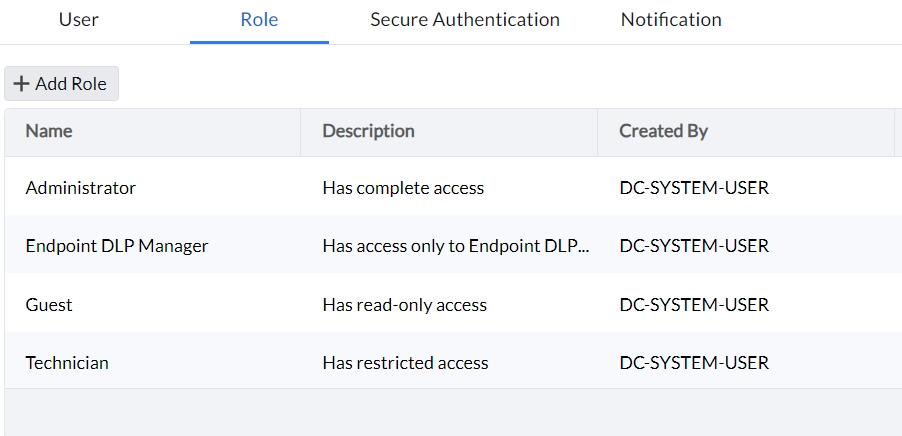
After the installation of agents, custom groups of agents can be leveraged to associate policies based on agent groups. Policy deployment asks the user to provide a custom group of agents, policy of choice, and data rules.
Data rules and policy associations work in collaboration. Sensitive data is defined by data rules, and as a result, it is assumed that the related policies should protect this object.
The below image provides a summary of the program’s process units:
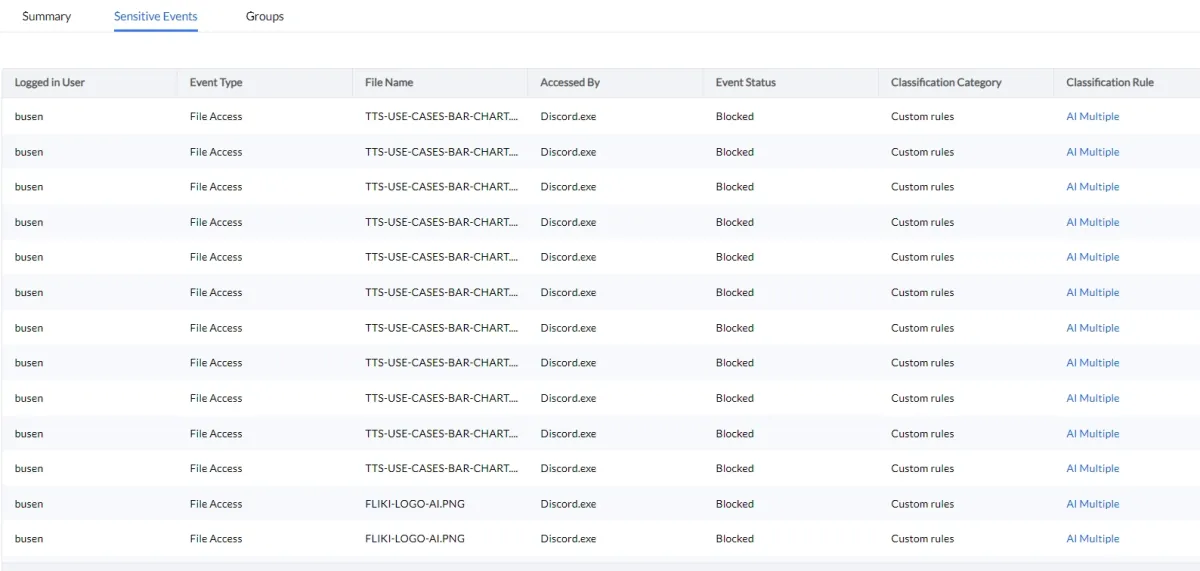
Based on agent audit requirements, ManageEngine prepares audit reports based on the desired frequency:
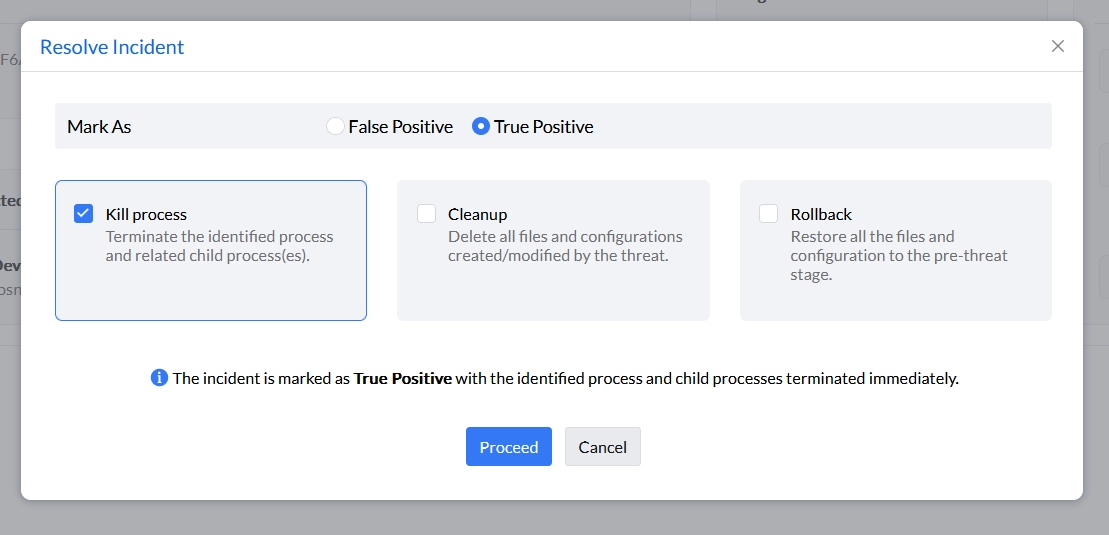
The program’s user interface keeps the administrator informed about events involving a policy breach in the home segment and in the reports segment.
False positive notifications
The program allows users to notify the admin about false positives. This allows the admin to adjust policies in light of false positives.
Deployment
The free version of ManageEngine Endpoint Control Plus is limited to 30 days of use and cannot be deployed on the cloud; it needs to be deployed on the admin’s device.
Sophos DLP platform
In this section, we offer a summary of our findings and detailed findings categorized into channel coverage, data classification, and administration.
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Effective email, peripheral, and application protection.
- Tamper protection works effectively.
- Offers active directory integration.
- Customizable data classification.
- Offers files search/tags with hashes.
- Comprehensive audit trail.
- Supports peripherals.
- Ineffective features:
- Some features, like peripheral protection, require custom policies.
- No user behavior analytics.
- No device management.
1. Channel coverage
In both Peripherals and email, while default base policies did not stop file transfers, we were able to block them with custom policies, as seen in the image below.
Custom policy:
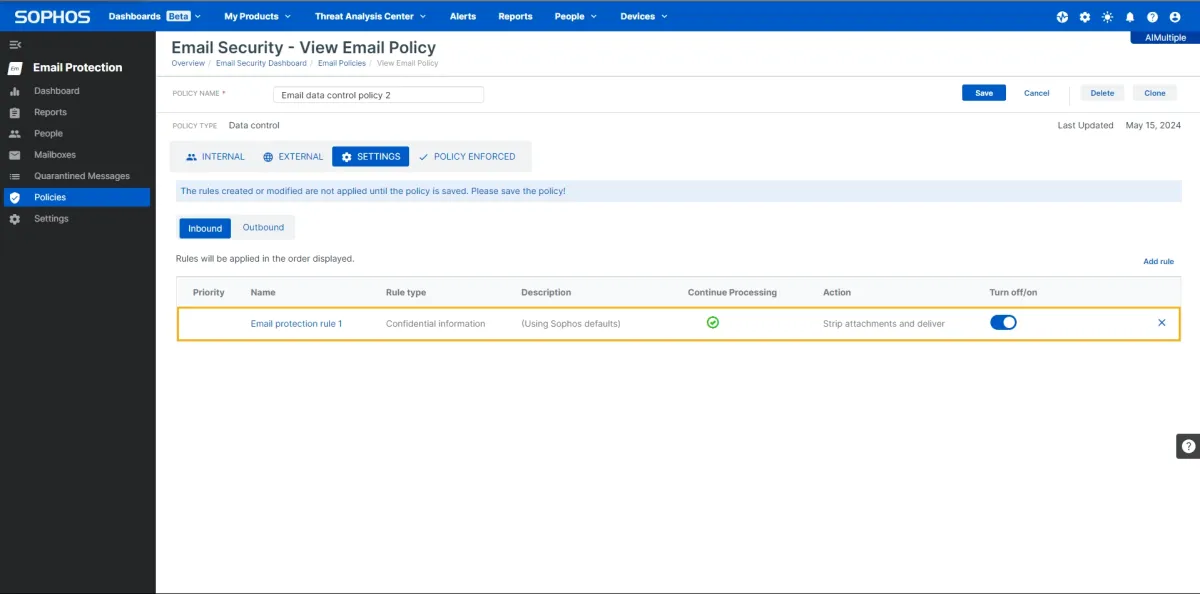
- Application: The application control feature restricted file transfer to other platforms such as Google Drive.
- Email/IP-based exceptions: Users can be directly included or excluded from the policies.
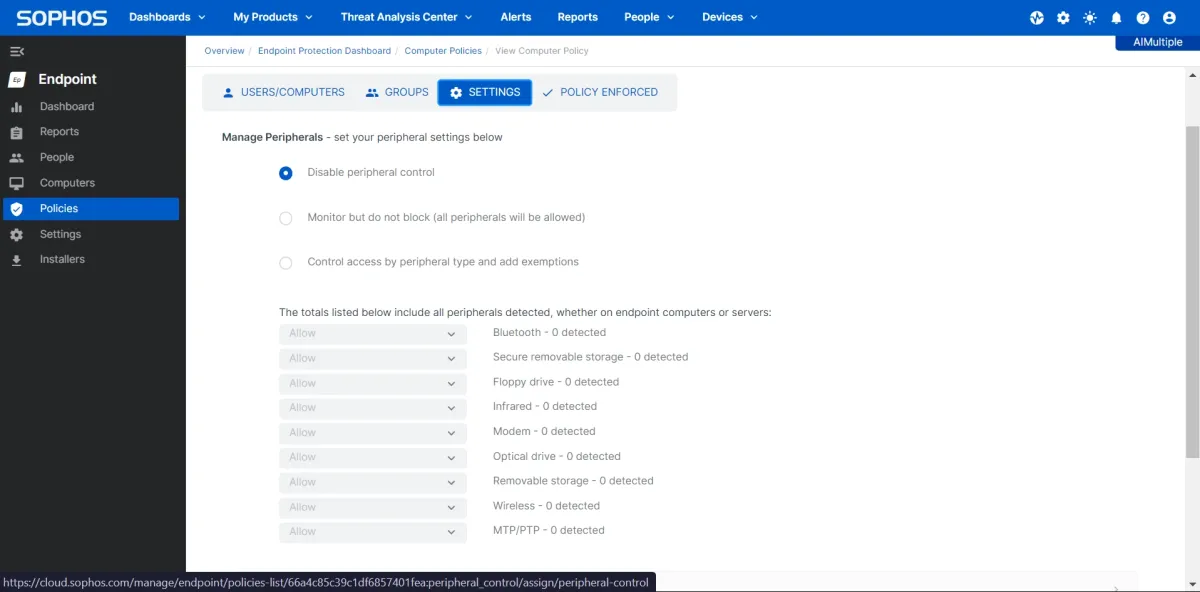
- Peripherals: 9 types of removable devices can be monitored and controlled, which is fairly less than other competitors like Endpoint Protector.
2. Data classification
- Automated data classification was not effective since it classified risky emails as having low severity.
- Customized data classification: You can customize the data classification parameters. The following options are available for customization.
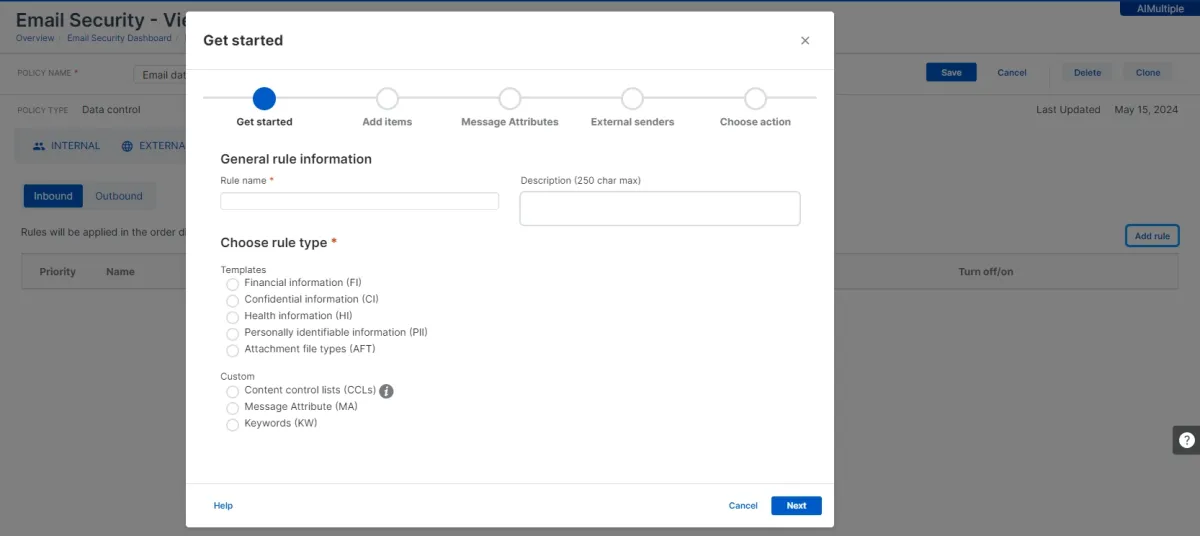
- Data classification verification: Our team could reach a comprehensive list of files and their classification status.
3. Administration
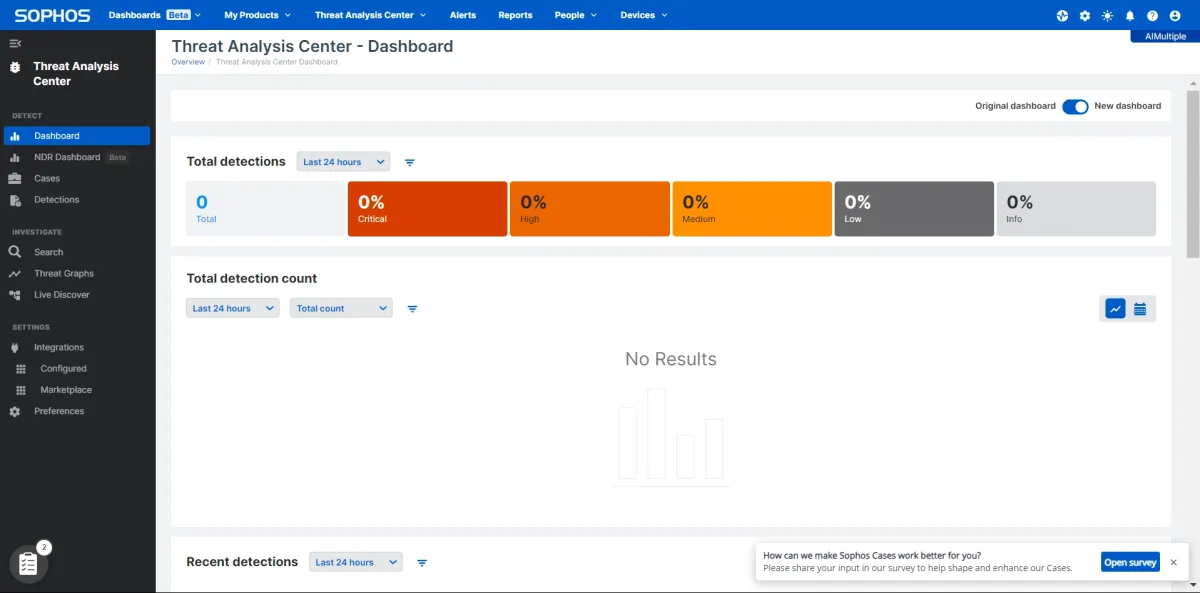
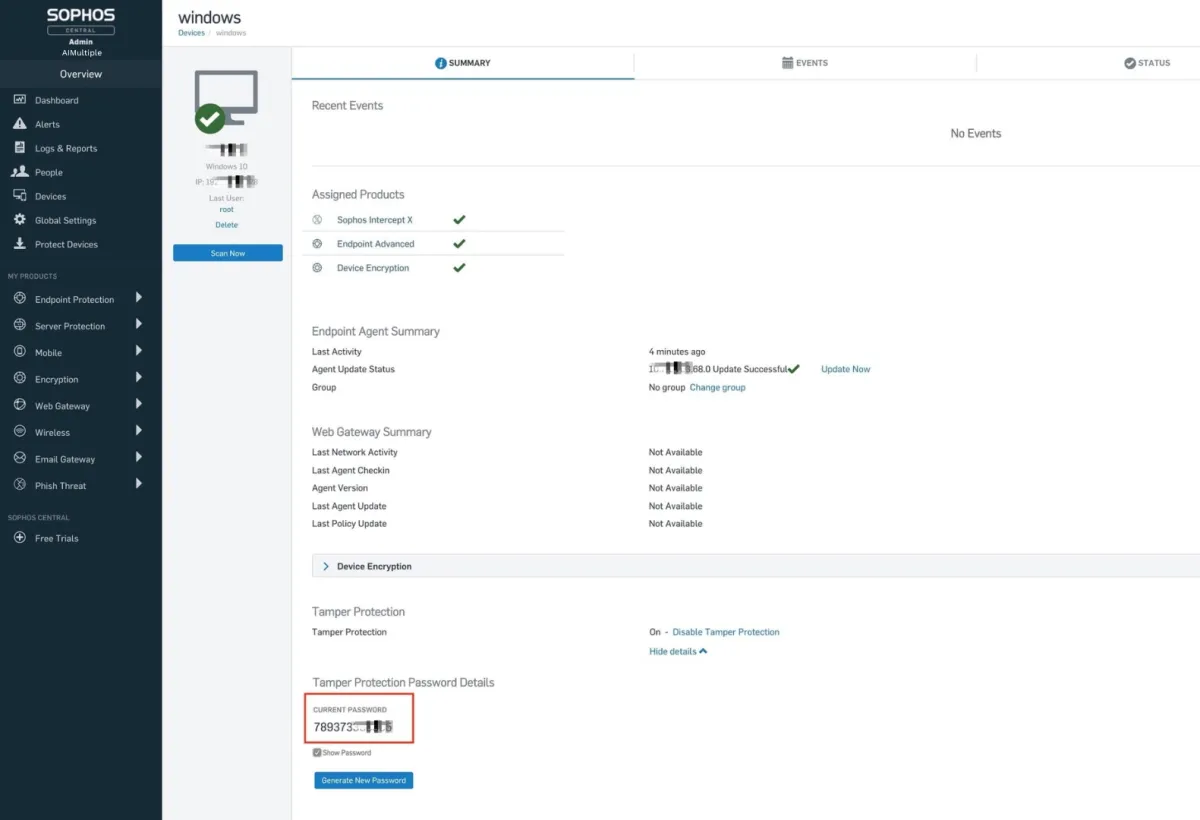
- Tamper protection: Restricted devices from tampering with the agent software and required a password share to uninstall the agent file. This feature worked during our test (see image below).
- Audit trail: Sophos Central successfully recorded audit logs on user activities.
- Files search/tags with hashes: Sophos offers this through its discovery features to identify risky files.
Teramind DLP platform
In this section, we offer a summary of our findings and detailed findings categorized into channel coverage, data classification, and administration.
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Effective peripheral, email, and application protection.
- Detailed data classification customization.
- Comprehensive audit trail.
- Offers active directory integration.
- Offers file search.
- Ineffective features:
- Ineffective data classification.
- Custom policies are difficult to manage.
- No tamper protection.
- No OCR.
1. Channel coverage
- Peripherals: USB blocking policies were effective, but they also blocked non-confidential files from being copied to peripheral devices.
- The types of devices were not mentioned in the removable devices policies.

- Email: Email policies are effective; however, they also prevent internal users from sending emails.
- Application: The application protection policy restricts all data from being transferred to applications such as Google Drive.
- Email/IP-based exceptions: You can exclude specific emails or domains from policies.
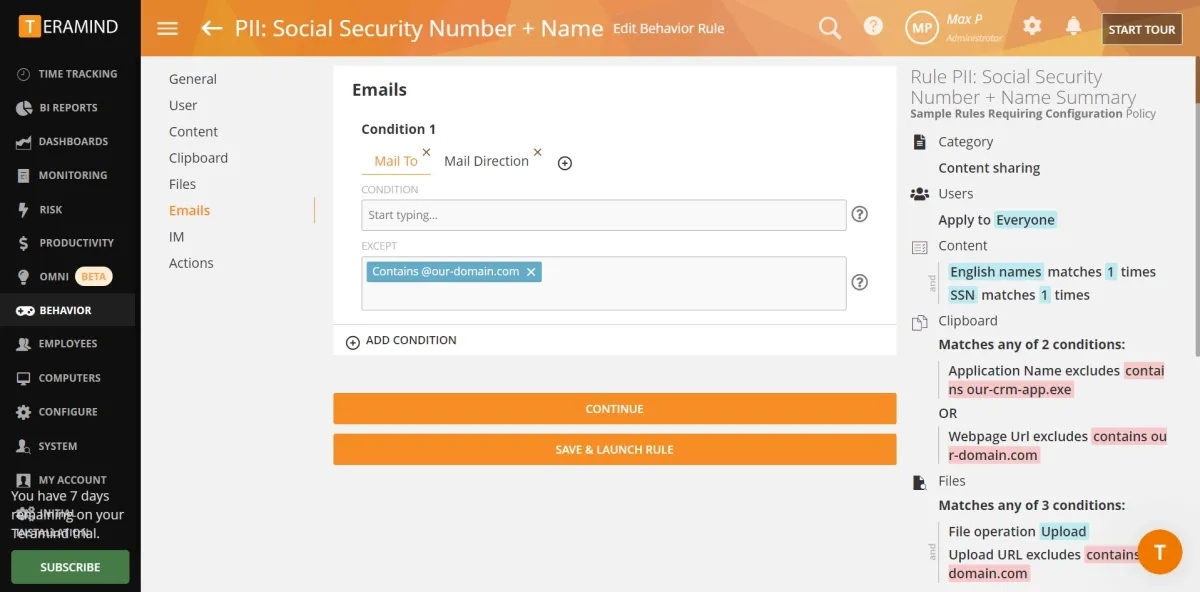
2. Data classification
- Data classification was not effective since it could not differentiate between confidential and non-confidential data.
- Customized data classification: Detailed customization options are available for its data classification feature. However, some familiarity with the platform is required to use them.
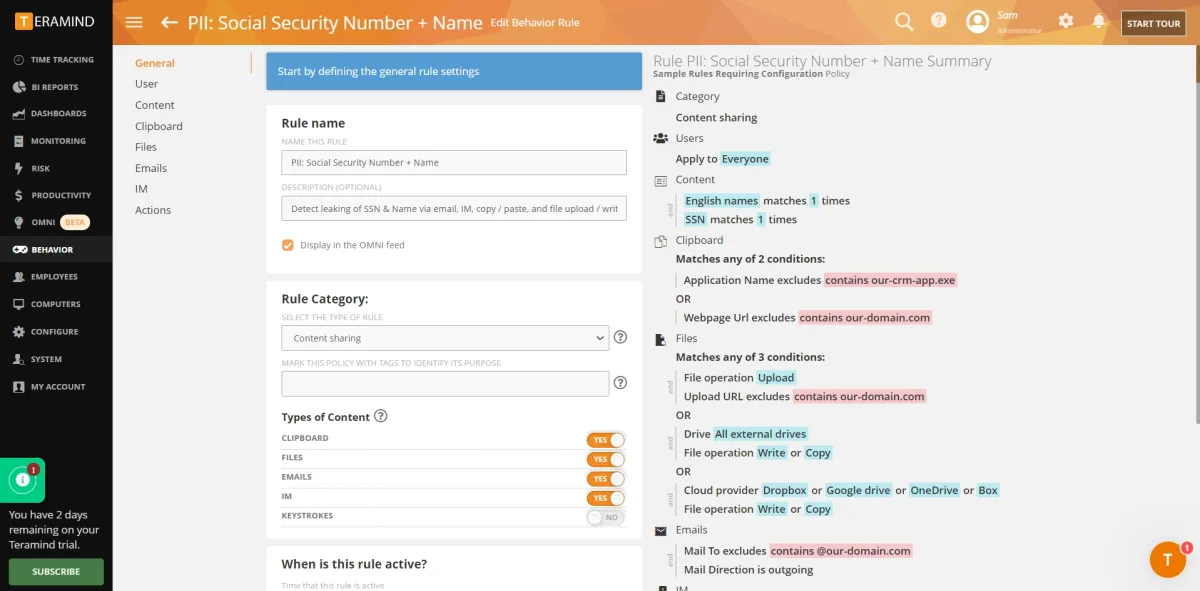
- Data classification verification: Our team was able to verify the details of the classified data.
3. Administration
For behavior policies, see the image below:
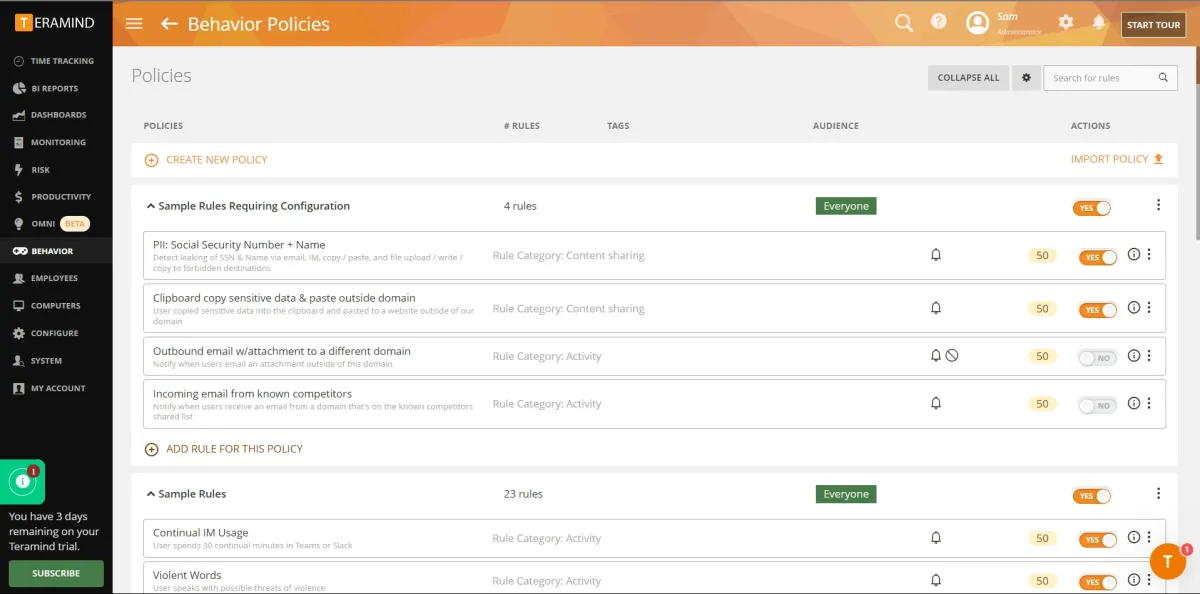
- Tamper protection: Tamper protection was not effective since it allowed the user to easily tamper with the agent file.
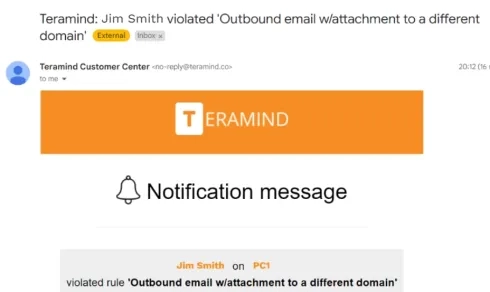
- Audit trail: We were able to monitor each user’s activities trail. Alerts were also sent to the admin’s email (see image below).
- OCR data identification: Teramind lacks OCR support for the web in the free trial.

Acronis Cyber Protect
In this section, we offer a summary of our findings and detailed findings categorized into channel coverage, data classification, and administration.
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Supports USB devices in its device control policy.
- Effective data classification.
- Effective application protection.
- Comprehensive audit trail.
- Offers active directory integration.
- Ineffective features:
- Ineffective email protection policies (has problems with some file formats)
- No data classification customization.
- No tamper protection.
- No files search/tags with hashes feature.
- No comprehensive web filtering.
1. Channel coverage
- Peripherals & email: The base policy worked fine on blocking USBs for agents. However, emails with confidential data were not blocked. Email-specific policies were also not found. 10 types of removable devices are covered in its device control policy.
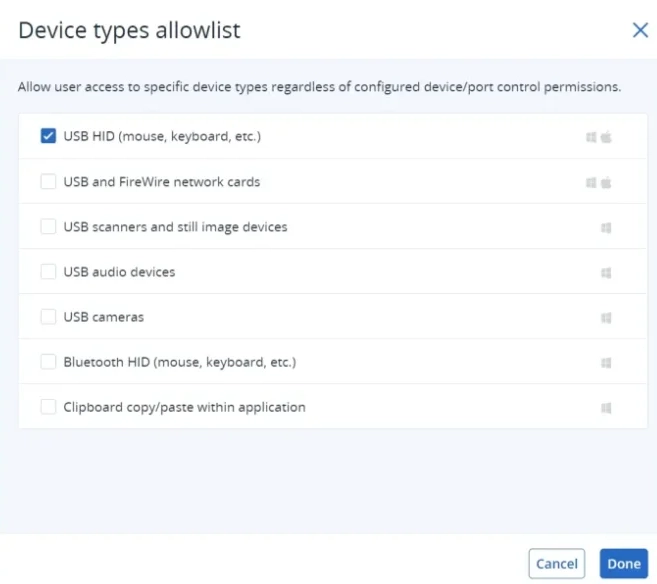
- Application: The data protection policy restricted confidential data from being transferred to cloud storage, such as Google Drive.
2. Data classification
- Effective data classification: The data classification feature worked on confidential data being copied on removable storage devices.
- Customized data classification: While the DLP features include data classification capabilities, the predetermined classifications cannot be edited.
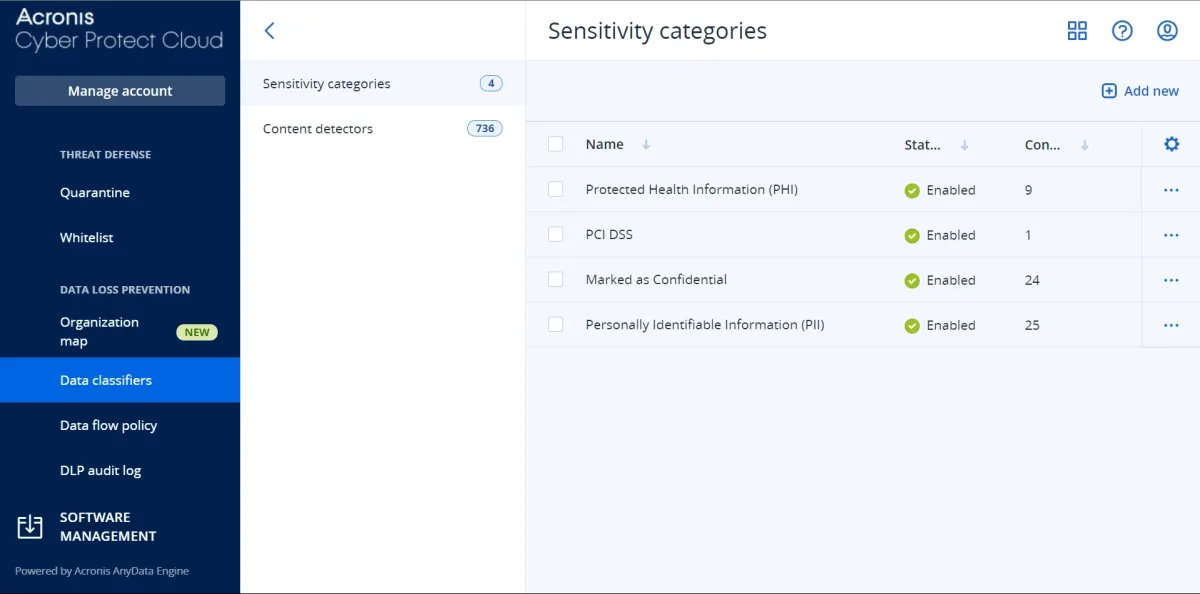
- Data classification verification: Our team could not verify the data that was classified by the set policies.
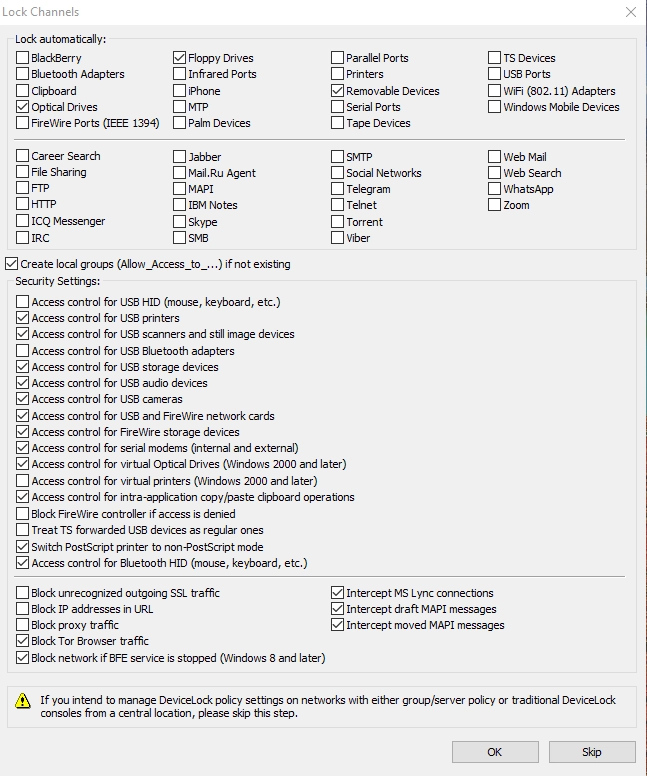
3. Administration
- Tamper protection: Our team did not find any tamper protector options on Acronis Central.
- Audit trail: Each user’s activities are recorded, and there is a separate audit log for all devices.
- Files search/tags with hashes: Our team could not find any features to tag files with hashes.
Trellix DLP
In this section, we offer a summary of our findings and detailed findings categorized into channel coverage, data classification, and administration.
Summary of findings:
- Effective features:
- Wide channel coverage
- Comprehensive email and application protection.
- Customizable data rules.
- Offers audit trail.
- Offers tamper protection.
- Offers web filtering.
- Ineffective features:
- No active directory integration.
- No file search.
- No user behavior analytics.
- No OCR.
1. Channel coverage
Trellix DLP covers a wide range of endpoint and network channels but lacks uniformity across certain critical areas.
Email Protection
- Trellix can detect when a user configures Outlook to send sensitive files through personal email accounts and can quarantine emails containing sensitive information.
- However, the release of quarantined emails can be cumbersome, requiring manual approval from the sender, sender’s manager, or data owner through email notifications rather than a streamlined, automated process.
- Additionally, Trellix does not fully support filtering sensitive data from being synchronized to mobile devices via ActiveSync for certain user groups.
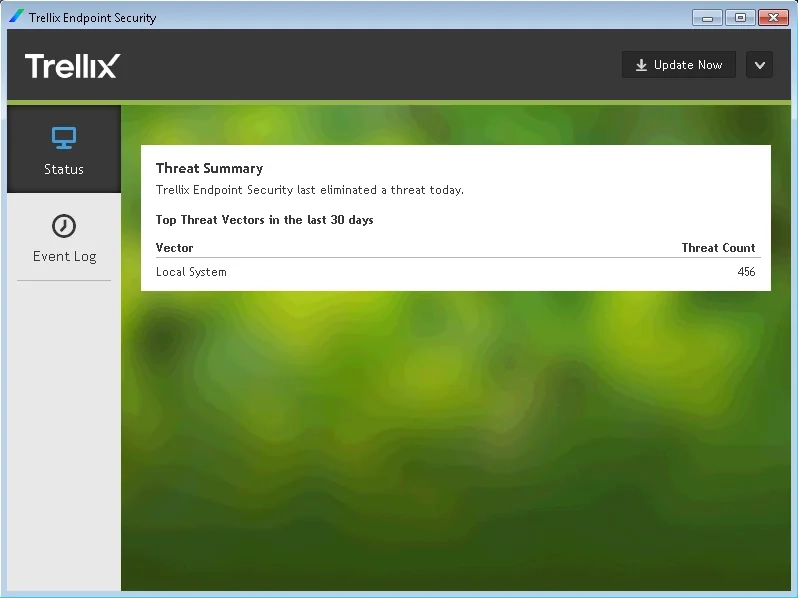
Device control / peripheral devices
- Monitoring and control of peripheral devices are possible.
- Trellix does not support a unified policy (single set of rules) for all channels, which limits flexibility in environments where multiple peripheral devices are used.
- Administrators can set up access controls for USB devices and other peripherals.
- Policy implementation can sometimes be inconsistent, especially across newer channels such as mobile devices.
- Advanced support, like encryption for USB devices, requires additional subscriptions.
Applications
- Trellix supports DLP policies for various applications.
- Chrome, for instance, is not fully supported, allowing users to bypass DLP policies in certain scenarios, like while uploading files from a public Wi-Fi.
2. Data classification
Predefined policies
Trellix’s predefined policies cover a range of common regulatory frameworks, such as PCI-DSS and GDPR.
- The policy templates are not as comprehensive or accurate compared to competitors, leading to potential gaps in detection.
Custom policies
- The administrator can create custom policies using keywords, regular expressions, and file fingerprinting.
- However, Trellix does not support more advanced features like machine learning or behavioral risk-based protection.
OCR data identification: Trellix lacks full OCR support for web detection and prevention, as it can only inspect graphical documents like PDFs with scanned content for discovery purposes, not for prevention.
3. Administration
Trellix DLP’s administration capabilities offer basic features, but some essential functionalities are missing or underdeveloped.
Access rights: Administrators can assign rights based on users or groups, but Trellix lacks role-based delegated administration, limiting the ability to assign specific roles for policy management and incident handling.
Other features: Trellix offers standard features such as USB encryption and endpoint DLP policy enforcement. However, advanced options like risk-adaptive protection and native behavioral analytics are either limited or require third-party integration, which adds complexity to deployment.
Notifications & alerts: Alerts are generated for incidents such as sensitive data transfers via email, but the lack of customization in reporting and limited incident management capabilities may require additional manual oversight by administrators.
Focus points of benchmark testing
1. Channel coverage
Data communication can take place across different channels, which need to be secured.
- Peripherals: DLP technology makes use of device control to prevent the unauthorized movement of data to removable storage devices like USBs or other peripherals like printers.
- USB Devices/drives/memory cards
- Printers(policy based control)
- Webcams
- iPhone/Android phones
- Bluetooth Devices
- Communication channels like Discord, WhatsApp, etc.
- Email: Including message body and attachments
- Applications: Certain applications that may not involve communication (e.g., Word) may need to be blocked or allowed to operate on sensitive files with the help of data classification. Especially critical applications include Microsoft Office, Google Docs, Google Drive, Zoom, and Skype.
- Email/IP-based exceptions: Testing to see if users or agents are excluded from the policy through email or IP address.
- Active Directory (AD) integration: Active Directory integration in DLP software enables centralized management of user access and policies based on directory services.
- Device management: Device management and DLP are essential components of a comprehensive mobile security strategy. Device management focuses on device-level management and control, while DLP ensures data protection and prevents unauthorized disclosure.
All of the providers offer MDM as an add-on. The free trial versions didn’t offer device management.
2. Administration / other
Deployment: Some solutions only offer on-premises or SaaS options for the administrator. With the SaaS option, DLP product companies must provide a fully isolated environment and a written guarantee to the customer about the safety of their data.
Audit trail: DLP solutions need to record user actions to maintain an audit trail about sensitive information. This was provided by all benchmarked solutions. It was provided by all benchmark solutions, but it does change from one to another.
For example, the detailed version contains detailed traces of administrative activities surrounding policies, users, and roles, service configurations, incident access, remediation, and structured and unstructured configuration profiles. The basic version contains user logins and activities only.
Tamper protection for agent files: This prevents the uninstallation or other tampering with the software on agent devices. Additionally, DLP agents should be protected by long and complex passwords to prevent unauthorized uninstallation or stopping of their services.
Agent/group rule assignment: We checked if policies and rules can be assigned to individual agents/users and agent/user groups.
Files search/tags with hashes: We checked if the ‘search’ or ‘discovery’ features have the option of tagging files with hashes.
Built-in data security policies: Many DLP tools come with built-in policy templates for common types of sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information, protected health information, and IBAN/crypto wallet ID detection.
Device monitoring through a control dashboard: The DLP Dashboard lets you view the data and content-related activity in your network based on the data control policies. The screen contains several widgets that provide visibility for the different data violation criteria. The screen also lets you filter according to a specific time frame to drill down and focus on the relevant data violations and events in your account.
Notifications and alerts for blocked actions: The DLP alerts provide detailed information about each alert, including the type of policy violated, the user involved, and the data that was attempted to be shared or leaked, allowing security teams to quickly identify potential data breaches and take action.
Option to report false positives: When a user performs an action that is restricted by the DLP policy, a block event triggers an alert message. Sometimes, the alert event is for an action that is legitimate but, for some reason, is considered forbidden by the DLP policy. Such incidents are false positives. To overcome this issue, the block can be marked as a false positive, allowing the user to then access the sensitive file.
Customizable data rules: DLP allows users to create custom data rules, offering flexibility for tailored data protection to navigate specific needs.
3. Data classification
Automated data classification
Classifying data into designated sensitivity levels helps ensure that sensitive information is protected with appropriate measures. DLP products enable the automatic detection of sensitive data based on predefined data categories (data discovery).
These categories are determined by pre-established policies after identifying and defining the company’s data and critical data assets. Data classification can be coordinated with the predefined policies provided in the “Policies” section.
All benchmarked providers offer automated data classification capabilities.
Effective data classification
AIMultiple tested the correctness of auto data classification with a few files, including:
- Personal health record
- Confidential due diligence document, which included the statement “private and confidential” at the bottom of every page
- Trade secret (i.e., source code for a website function)
Customized data classification
Data classification can be customized with regex, file extensions, etc.
Data classification verification
Classified data needs to be verifiable by administrators and members of the GRC team to ensure that the classification works correctly. During the testing or proof-of-concept (PoC) phase, personnel from the GRC team should participate alongside administrators.
They can legally check and confirm the data classifications. Typically, solutions provide lists of files that are classified in a certain way (e.g., financial data, healthcare data.
OCR
We checked if the vendors offer OCR data identification from images or visuals.
The providers that don’t have the OCR feature in the free trial have it as an add-on.
Benchmark methodology
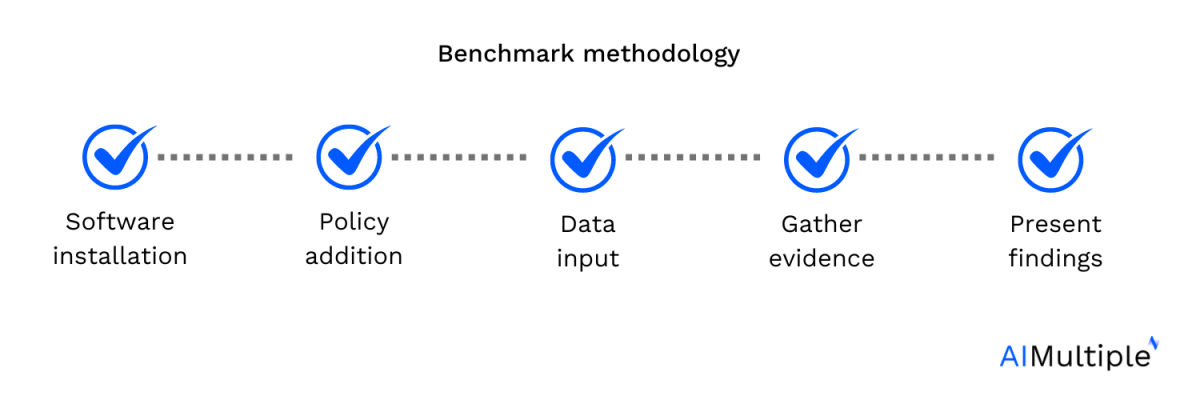
- Software installation: We installed admin and agent modules on separate PCs.
- Policy addition: Additional policies were added to compare the effectiveness of basic policies with the custom ones.
- Data input: Various files containing different levels of confidential and financial data were shared through different channels, each with distinct security settings.
- Gather evidence: Screenshots were taken of relevant parts of the platform.
Findings: The findings are presented and summarized in this benchmark.
FAQ
What is DLP?
Organizations face growing challenges in safeguarding private data and personally identifiable information (PII). Preventing unauthorized access and mitigating data breaches are critical to minimizing reputational and financial risks. This is where Data loss prevention (DLP) solutions come in, helping businesses secure sensitive information and comply with regulatory standards.
Data loss prevention is a technology solution that aims at the prevention of incidents that may end with data breaches or data losses. DLP solutions come in a bundle of tools, such as data classification, device control, encryption, and user authentication tools. The main purpose of data loss prevention is to minimize the risk of unauthorized data leakage and disclosure.
Data leakage prevention requires a security strategy that oversees the identification of sensitive data, the classification of sensitive data, and the effective protection of sensitive data. The classification of sensitive data can be automated thanks to machine learning technologies. Likewise, the protection of confidential data can be enhanced with the integration of next-generation protection solutions directed at endpoint and network security.
What is a DLP software benchmark?
A DLP software benchmark is a test that collects verifiable data to outline the performance of DLP software products. The output collected by the DLP benchmark sheds light on the products’ administrative and technical aspects.
At the outset, available features offered by DLP software products are registered as test objects. Registered features are tested for effectiveness and compared with what they claim to promise. The sum of the gathered data is ordered under test aspects and constitutes the conclusive evaluation.
Why should businesses adopt DLP solutions?
Organizations face growing challenges in safeguarding private data and personally identifiable information (PII). Preventing unauthorized access and mitigating data breaches are critical to minimizing reputational and financial risks.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.