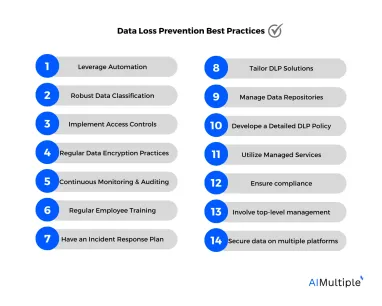
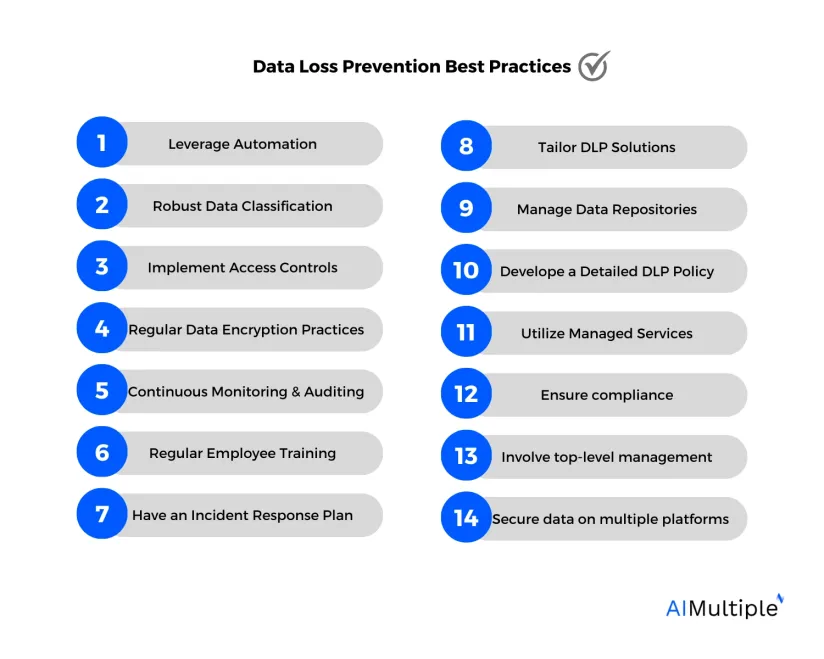
14 Data Loss Prevention or DLP Best Practices in 2024
In today’s increasingly digital era, safeguarding sensitive information has become paramount for organizations worldwide as the costs of data breaches rise (Table 1). Companies must use the right data loss prevention tools to protect sensitive data and minimize such losses. This comprehensive guide dives into Data Loss Prevention (DLP), offering the top 14 DLP best practices for protecting critical organizational data against loss, theft, and unauthorized access.
Table 1. Average total cost per data breach worldwide 2020-2023, by industry1
| Industry | May/20-Mar/21 | Mar/21-Mar/22 | Mar/22-Mar/23 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | 9.2 | 10.1 | 10.9 |
| Financial | 5.7 | 5.9 | 5.9 |
| Pharmaceuticals | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.8 |
| Technology | 4.8 | 4.9 | 4.6 |
| Energy | 4.6 | 4.7 | 4.7 |
| Professional services | 4.6 | 4.7 | 4.4 |
| Industrial | 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.7 |
| Global average | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Research | 3.6 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Education | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Consumer | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Entertainment | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Communications | 3.6 | 3.6 | 3.9 |
| Transportation | 3.7 | 3.5 | 4.1 |
| Retail | 3.2 | 3.2 | 2.9 |
| Media | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.5 |
| Hospitality | 3.0 | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| Public sector | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.6 |
Source: Statista, IBM
1. Leverage automation
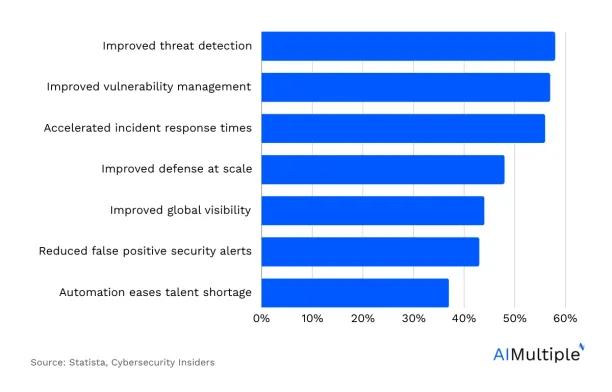
AI-powered solutions are offering various benefits to businesses trying to improve their cyber security (Figure 1). Leveraging an automated tool can be one of the most efficient ways to implement data loss prevention. Automated DLP solutions play a pivotal role in preventing data breaches by monitoring, detecting, and controlling data usage across an organization’s network. They offer real-time protection against both internal and external threats.
Suppose a financial firm handles sensitive client information. An automated DLP system flags an unusual attempt to transfer financial data to an external server. The system automatically blocks the transfer and alerts the IT department, averting a potential data breach.
Figure 1. AI benefits in cyber security
2. Robust data classification
Data classification is essential for understanding what constitutes sensitive, confidential, and public data. Classifying sensitive data, or confidential data ensures that proper controls are in place to safeguard it.
A healthcare provider classifies patient records as highly confidential. The DLP system then applies stringent access controls to these records, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify them. This way, different data types are treated with different protective measures.
We recommend using DLP software that has data classification features.
2.1- Data discovery and identification
Identifying and cataloging the data that needs protection is a critical first step in data loss prevention. Data discovery tools can help locate and classify sensitive data across an organization’s network.
For instance, a law firm can use data discovery tools to locate all instances of personally identifiable information in its network, ensuring that these sensitive data points are adequately protected under its data loss prevention program.
3. Implement access controls
Access controls play a pivotal role in ensuring the security and integrity of confidential data. They are designed to regulate who can view and manipulate such data, thereby safeguarding against unauthorized access and breaches. Key components of access controls include:
- User authentication: To verify the identity of individuals accessing the system.
- Authorization levels: To determine the extent of access and privileges granted to each user.
- Auditing of user activities: This involves monitoring and recording actions taken by users to ensure compliance with security policies and to detect any potential security violations.
These measures collectively help in maintaining a secure and controlled data access environment.
Her is our guide to role-based access control (RBAC)
4. Regular data encryption practices
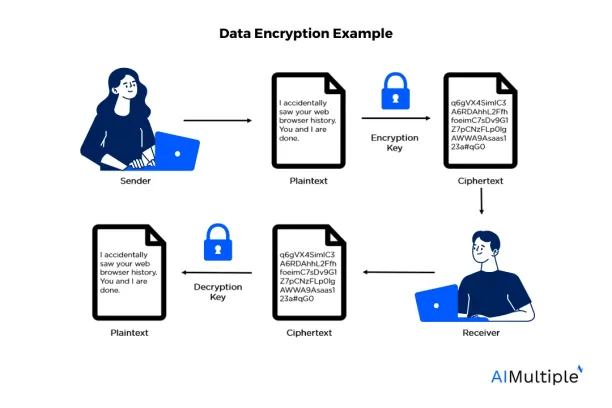
Regular data encryption practices are essential for enhancing the security of sensitive company information. Data encryption involves converting sensitive data into a coded format (See the image below), making it unreadable to anyone who does not have the key to decrypt it. This process is crucial for protecting data both at rest, such as files stored on a server or a hard drive, and in transit, like information being transferred over a network or the internet.
For instance, a bank encrypts customer financial data. Even if hackers manage to intercept this data during transmission, the encrypted data format renders it useless to them.
Here is our guide to encryption key management.
5. Continuous monitoring and auditing
Continuous monitoring and auditing are indispensable strategies for detecting and responding to data loss incidents in a timely manner. These practices involve regularly reviewing and analyzing system logs, user activities, and network traffic to identify any unusual or suspicious behavior that might indicate a security breach or data loss. By maintaining constant vigilance through these methods, organizations can quickly identify and address vulnerabilities, prevent potential data breaches, and mitigate the impact of any incidents that do occur.
Automated solutions can offer continuous monitoring and tracking of data. When unusual data transfer is detected, an alert is triggered, allowing for quick investigation and response.
Here is our guide to the top firewall audit software on the market
6. Regular employee training
Training employees about the importance of data protection, security policies, and recognizing potential threats is vital for preventing accidental data loss and data breaches. This training should encompass educating staff on best practices for handling sensitive information, understanding the organization’s specific security protocols, and identifying various forms of cyber threats such as phishing, malware, and social engineering attacks. By equipping employees with this knowledge, they become the first line of defense, capable of detecting and averting potential security incidents.
Additionally, regular refreshers and updates on these trainings ensure that the workforce stays informed about the evolving nature of cyber threats and the latest security measures, further reinforcing the organization’s overall data protection strategy.
7. Have an incident response plan
A well-structured incident response plan ensures quick and efficient action during a data loss incident, minimizing potential damage. This plan typically includes predefined procedures for identifying, containing, and resolving security breaches, as well as clear lines of communication to swiftly engage all relevant parties, such as IT staff, management, and external cybersecurity experts.
A software company faces a data breach. Their incident response team quickly isolates the affected systems, assesses the damage, and communicates with stakeholders, mitigating the impact of the breach.
Here is how to use RPA for indecent management and response.
8. Tailor DLP solutions
Every organization has unique data protection needs. Customizing DLP solutions to align with specific business processes and data types is essential for effective and robust data loss prevention.
For instance, a manufacturing company will have to customize its DLP policy to focus on protecting intellectual property and design documents, crucial for its competitive advantage.
9. Manage data repositories
To manage data repositories (e.g., data lake & warehouse) and storage effectively for Data Loss Prevention (DLP), a company should secure data across all storage locations, including cloud storage, on-premises servers, and mobile devices. This involves implementing appropriate security measures like encryption, access controls, and regular audits of the data stored in each of these environments to protect the data from unauthorized access or breaches.
10. Develop a detailed DLP policy
A well-defined and comprehensive data loss prevention policy sets the standards and procedures for handling sensitive data, serving as a guideline for employees and the DLP system. It outlines what is considered as sensitive data, the protocols for processing and storing this data, and the responsibilities of employees in maintaining critical data security, thereby ensuring a consistent and effective approach to data protection across the organization.
11. Utilize managed services
For many organizations, especially small to medium-sized businesses, utilizing a managed service provider for data loss prevention can provide access to expertise and technology that might otherwise be unavailable.
12. Ensure compliance
Adherence to legal and regulatory requirements such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), or PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is essential for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining customer trust.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that an organization is handling sensitive data, like personal information, health records, or credit card details, in a secure and lawful manner, which not only prevents costly legal ramifications but also reinforces the organization’s reputation as a trustworthy entity in the eyes of its customers and partners.
13. Involve top-level management
Involving executive and senior leadership in the development and implementation of DLP strategies ensures organizational commitment and resource allocation. The CEO of a corporation, for instance, takes an active role in developing the DLP strategy, signaling its importance to the entire organization and ensuring adequate resources are allocated.
14. Secure data on multiple platforms
A robust DLP strategy must account for a variety of operating systems and platforms used within the organization to ensure consistent data protection. This is crucial to prevent vulnerabilities in one system from compromising the overall security of the organization’s data.
Final recommendations
While this guide does not encompass every aspect of DLP, it provides a comprehensive overview of best practices for data loss prevention. By understanding and implementing these strategies, organizations can significantly enhance their data protection efforts, safeguarding their most critical and sensitive data from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats.
Further reading
External resources
- 1. IBM. Average cost of a data breach worldwide from May 2020 to March 2023, by industry (in million U.S. dollars). Statista. Accessed: 15/January/2024.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.