Top 7 Open Source Firewall Audit Tools in 2024: Analysis & Comparison
Ensuring robust network security is paramount for businesses of all sizes. Open source firewall audit tools offer solutions for assessing and managing firewall configurations, rules, and policies. However, mid-market and enterprises companies may explore closed source firewall audit software for more comprehensive solutions.
This article discusses the key players in open source firewall audit tools, providing a comprehensive overview of their features and capabilities.
Top 7 open source firewall audit tools reviews
Table 1. Open source firewall audit tools
| Vendor | User Rating* | Number of Reviews* | License | Platform Compatibility** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pfSense | 4.8 | 383 | Permissive | MacOS |
| Nmap | 4.6 | 121 | Strongly protective | MacOS, Linux |
| CrowdSec | 4.7 | 89 | Permissive | Linux |
| OpenVas | 4.3 | 62 | Strongly protective | MacOS, Linux |
| Snort | 4.2 | 39 | Strongly protective | Linux |
| Scuba | 3.2 | 13 | Weakly protective | MacOS, Linux |
| OSSEC | 4.6 | 11 | Strongly protective | MacOS, Linux |
*Data was obtained from review platforms such as G2, Gartner, TrustRadius, and Capterra.
** All analyzed software packages are compatible with Windows
Inclusion criteria:
- This table is constructed using publicly accessible and verifiable data.
- Only vendors with over 10 reviews across all review platforms were considered.
- The companies are ordered based on the total count of reviews.
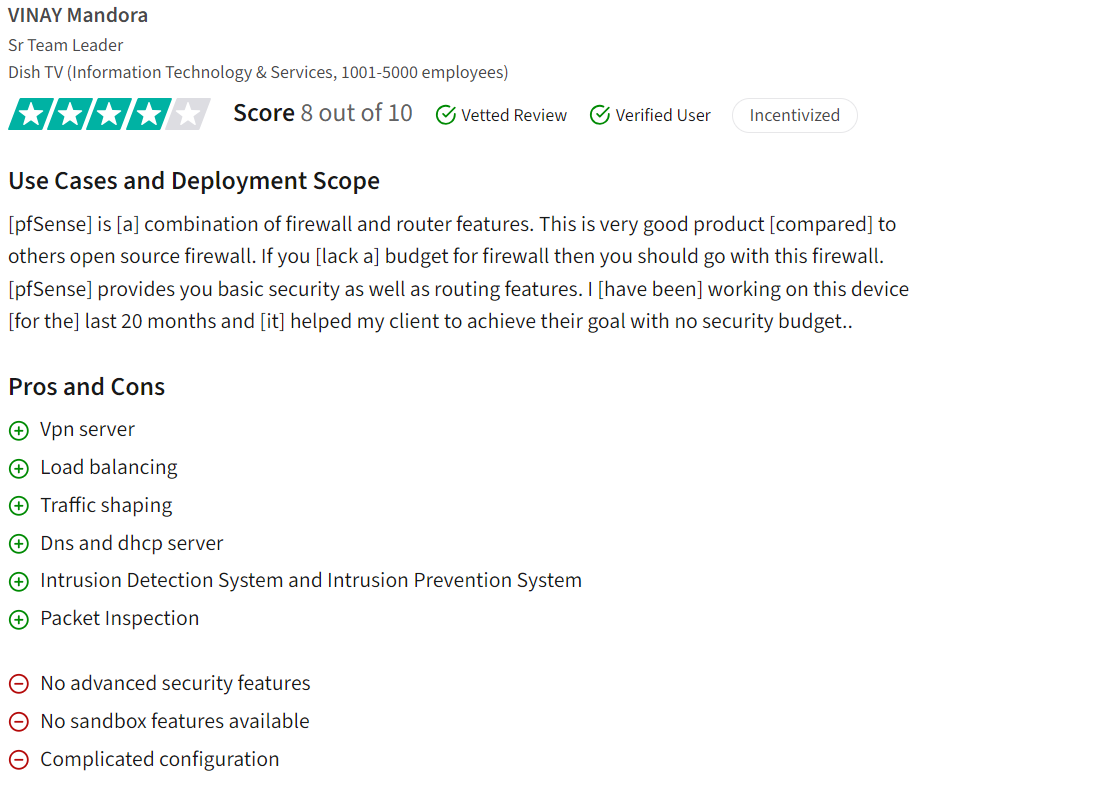
1. pfSense
As one of the open source firewall audit software, pfSense is known for its intuitive user interface and robust firewall capabilities. The software, developed by Netgate, claims to provide comprehensive firewall management and auditing functionalities.
pfSense utilizes PHP programming language and operates under the Apache 2.0 license. It is developed by Netgate and is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros
pfSense receives positive feedback for its open-source nature, large community support, and flexibility in creating fine-tuned firewall rules. Users appreciate its stable firewall rules, powerful control mechanisms, and advanced features like VPN management, load balancing, and traffic shaping. The user-friendly web interface and responsive support community are also highlighted as strengths.
Cons
Users noted the absence of certain advanced security features and sandboxing capabilities, along with a perceived complexity in configuration1. While pfSense is powerful, it may require advanced networking skills for optimal utilization.
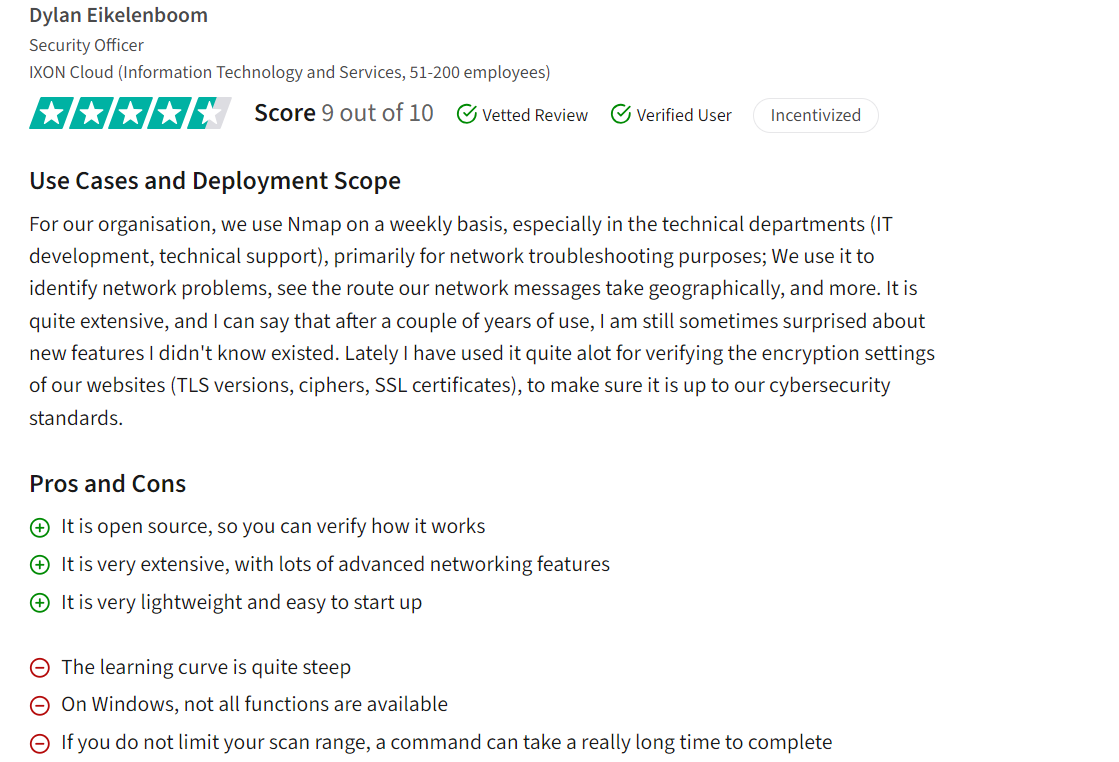
2. Nmap
Nmap is an open source firewall audit software for network discovery, mapping, and security auditing, available for free. Its key functionalities encompass port scanning, detecting unknown devices, evaluating security vulnerabilities, and pinpointing network problems.
Nmap, developed by Gordon Lyon, is written in Lua and distributed under the GPL-2 license. It is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros
Nmap has garnered positive feedback for its user-friendly interface and effective vulnerability scanning capabilities2. Users appreciate its simplicity in selecting targets and conducting scans, particularly for identifying open ports, services running on them, and potential vulnerabilities requiring patching. The tool’s lightweight nature, advanced networking features, and real-time topology view are also highlighted as strengths.
Cons
Users review also point out some areas for improvement, such as the readability of scan results, limited functionality on Windows, potential slowdowns with certain scan profiles, and the need for automated updates and patch installations3. Performing scans without proper range limitations is criticized since it can result in long command execution times, affecting overall efficiency.
3. CrowdSec
CrowdSec is an open-source security solution designed to identify and block aggressive behaviors that could compromise system security. It promotes community collaboration by notifying all members whenever an IP is blocked, allowing them to take proactive measures.
CrowdSec is developed in Go programming language and licensed under MIT. It is compatible with Windows and Linux platforms.
Pros
Users praise CrowdSec for integrating well with various tools like fail2ban, Cloudflare, WordPress, NGINX, and Linux Firewalls, enhancing overall network security4. It also provides flexibility in attack remediation, allowing users to apply tailored responses based on the severity of the security risk.

Cons
Reviews point to challenges that may arise when running CrowdSec on OPNsense due to OS limitations, requiring additional effort for implementation5. Open source CrowdSec is claimed not to address more sophisticated threats or adequately cover well-configured servers since it predominantly focused scenarios on protecting against scanners, brute force attacks, and bots.
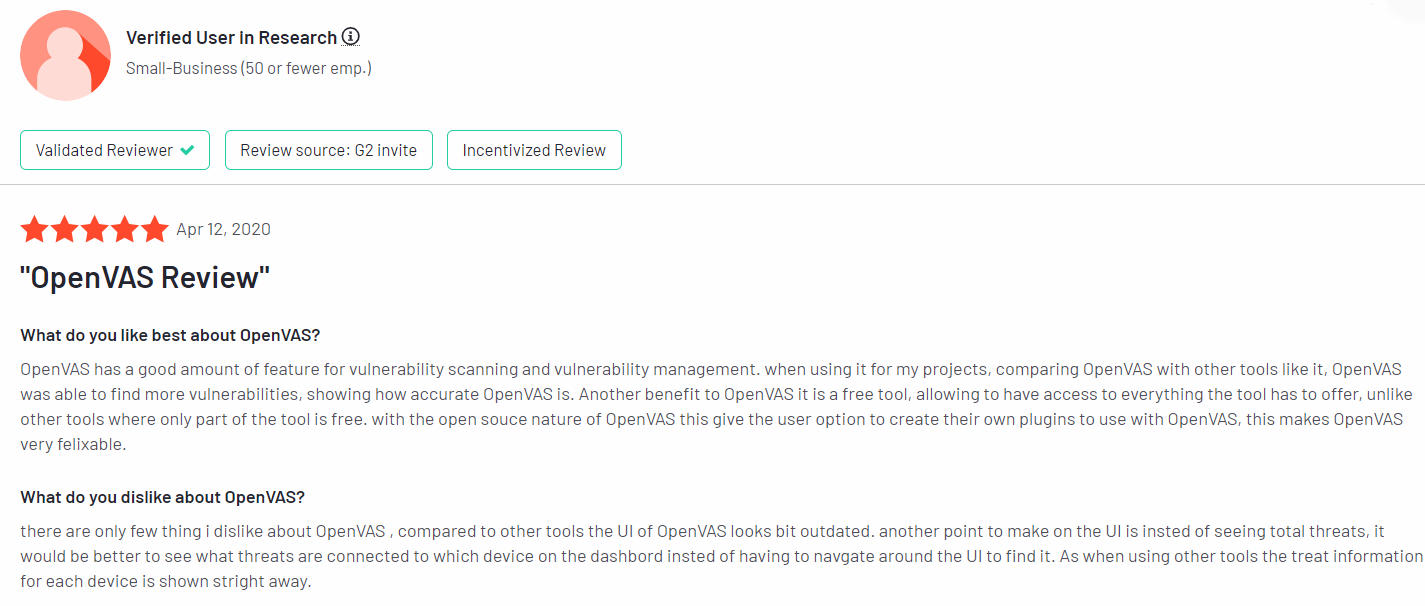
4. OpenVas
OpenVAS, an integral part of the Greenbone Vulnerability Management framework, serves as a scanner for detailed risk assessment and management. The vendor claims to be particularly useful for non-profit organizations seeking compliance with standards such as HIPAA and PCI.
OpenVas, developed by Greenbone, is written in C and distributed under the GPL-2 license. It is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros
Users appreciate OpenVAS’ accuracy in finding vulnerabilities, especially when compared to other tools, and value its open source nature that allows for plugin customization. The crawler feature and result presentation are commended for their usefulness in managing security issues effectively6.
Cons
Some users find the user interface (UI) of OpenVAS to be outdated compared to other tools, suggesting improvements for better visual representation and device-specific threat information7. Like many vulnerability scanners, OpenVAS may generate false positives at times, highlighting the ongoing need for tool refinement and accuracy validation.
5. Snort
Snort represents another free and open source solution for network intrusion detection and prevention, developed under the guidance of Cisco.
Snort, developed by Cisco Systems, is an intrusion detection system written in C++ and licensed under GPL-2+. It is compatible with Windows and Linux platforms.
Pros
Snort is appreciated for its open-source nature, providing users with a network intrusion detection system capable of capturing and analyzing network packets for potential threats. It can be integrated into existing firewall setups to enhance network security and aid in meeting compliance standards like PCI DSS8.

Cons
Users note that Snort’s setup and configuration can be complex, requiring a deep understanding of network concepts and manual configuration in the snort.conf file. Lack of a user-friendly interface and potential false positives are also mentioned, although extensive documentation and example configurations are available to mitigate these issues.
6. Scuba Database
Scuba is a free and open source tool designed to scan enterprise databases for security vulnerabilities, configuration weaknesses, and patch status, enabling the identification of potential security threats within the database infrastructure.
Scuba, developed by Imperva, is a security tool written in Java and licensed under LGPL-2.1. It is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros
Scuba is praised for its user-friendly interface and the ability to customize scans extensively. It offers easy and insightful reporting, providing a quick overview of security postures related to databases. Additionally, users appreciate its lightweight scanning capabilities9.
Cons
Some users find that Scuba’s data exploration features are limited, requiring users to be intentional and knowledgeable about their queries. The learning curve is steep, leading to challenges in adoption by stakeholders who may struggle with complex queries or navigating the explorer view. Loading times can be slow, although the tool offers powerful capabilities for reading log data and performing surface-level analysis.
7. OSSEC
OSSEC is a host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS) available as open-source software. It conducts log analysis, file integrity checking, policy monitoring, rootkit detection, and process monitoring.
OSSEC, developed by Atomicorp, is a host-based intrusion detection system written in C and distributed under the GPL-2 license. It is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros
Users appreciate that the firewall audit tool provides robust monitoring capabilities for point-of-sale systems, aiding in intrusion detection and ensuring compliance with PCI-DSS standards10. They find it easy to deploy across multiple clients and manage centrally, leveraging the tool’s free and open-source nature. The tool’s installation process is also commended for its simplicity and effectiveness in log monitoring and intrusion detection.
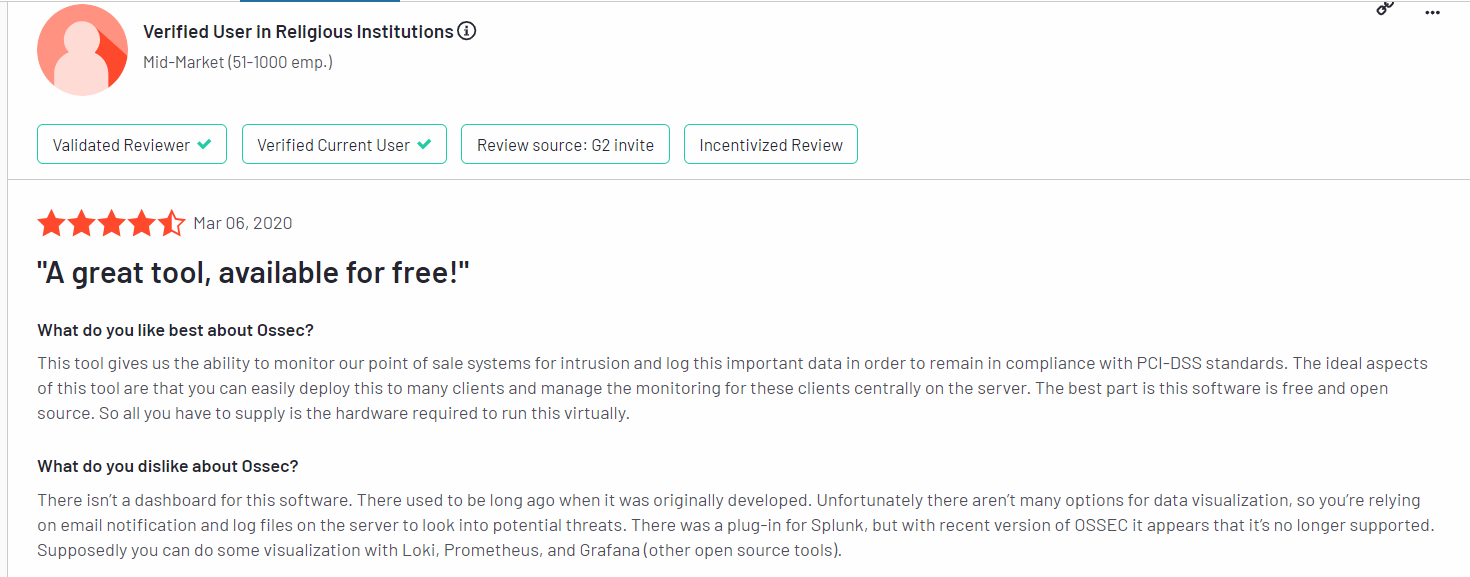
Cons
Some users note the absence of a dashboard in the software. This lack of data visualization options limits visibility into potential threats, relying primarily on email notifications and log files. Although there was a plug-in for Splunk previously, it is no longer supported, leaving users to explore visualization options with other open-source tools like Loki, Prometheus, and Grafana.
Key features of firewall audit software
When it comes to choosing the best firewall audit tool, several key factors warrant consideration to ensure optimal functionality and alignment with organizational needs. Here are essential aspects to evaluate:
1. License
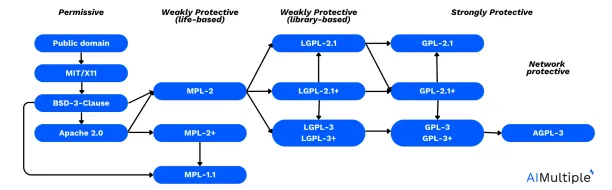
Source: David A. Wheeler (2007)11
Another aspect that you need to choose best firewall audit software for your organization is the license of the tool. The software’s license determines its usage rights, redistribution policies, and whether it aligns with organizational requirements and compliance standards. Understanding license compatibilities is essential for developers, as it enables them to make informed decisions about incorporating third-party code into their projects while complying with legal requirements and fostering collaboration within the open-source community.
Apache 2.0 is known for its permissive nature, allowing users to modify and distribute derivative works under certain conditions. GPL-2, GPL-2+, and LGPL-2.1 are licenses that prioritize open-source principles, requiring derivative works to also be open source and adhere to specific distribution terms. MIT is another permissive license, granting users the freedom to use, modify, and distribute software with minimal restrictions, making it compatible with a wide range of projects and licenses.
2. Platform compatibility
Considering the platform compatibility of the software ensures seamless integration with existing infrastructure, network devices, and cloud service providers. Compatibility with Windows, MacOS, Linux, and other operating systems is crucial for widespread deployment and management convenience.
Reasons to use an open source firewall auditing tool
1. Continuous compliance
Firewall audit tools open source enable regular firewall audits, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards like PCI DSS and GDPR and fostering a secure network environment.
2. Enhanced security management
Through detailed security audit reports and customizable audit capabilities, open-source firewall auditing solutions empower network security teams to proactively identify and address vulnerabilities, bolstering network security posture.
3. User-friendly interface
With intuitive user interfaces and customizable reports, open source firewall auditing tools offer a seamless user experience, simplifying the management of firewall configurations.
Benefits and drawbacks of working with open source firewall audit software
Benefits
1. Cost-effectiveness
Open source software is typically free to use, eliminating licensing fees and reducing overall costs associated with firewall audit software procurement. This cost-effectiveness is particularly beneficial for organizations with limited budgets or those seeking cost-efficient solutions without compromising on quality.
2. Customizability and flexibility
One of the key strengths of open source firewall audit tools lies in their customizability. Users have the freedom to modify and adapt the source code according to their specific firewall configurations, network security policies, and compliance requirements. This level of flexibility allows organizations to tailor the tool to their unique security management needs, ensuring a more robust and tailored approach to firewall auditing.
3. Community support and collaboration
Open source projects thrive on community-driven support and collaboration. Users can leverage the collective expertise and contributions of a diverse community of developers, security professionals, and enthusiasts. This collaborative environment fosters continuous improvement, innovation, and the rapid development of new features and functionalities, enhancing the overall quality and effectiveness of open source firewall audit tools.
4. Transparency and security assurance
The transparency of open source tools provides organizations with greater visibility into the tool’s codebase, security mechanisms, and data handling practices. This transparency fosters trust and confidence in the tool’s security posture, as users can independently review and audit the source code for vulnerabilities, compliance with security standards, and adherence to best practices. Additionally, the open nature of the software allows for timely security updates and patches, further bolstering network security and resilience against emerging threats.
5. Integration and compatibility
Open source firewall audit tools are designed to integrate seamlessly with a wide range of network infrastructures, firewall devices, security controls, and cloud service providers. This compatibility ensures smooth integration into existing security architectures, simplifying deployment, management, and monitoring processes. Moreover, open source tools often support various industry-standard protocols and formats, facilitating interoperability and data exchange with other security tools and management platforms.
Drawbacks
1. Limited support
While open source communities can offer valuable assistance and resources, the support may not always be as comprehensive or timely as what closed source firewall vendors provide. This can be a concern for organizations that require immediate assistance with complex firewall configurations, troubleshooting security incidents, or resolving technical issues promptly.
2. Complexity
While customization allows organizations to tailor firewall configurations and security policies according to their specific needs, it can also lead to complexity, especially for users with limited technical expertise. Configuring and managing open source tools effectively may require a deeper understanding of network security principles, firewall policies, and audit processes, which may not be easily accessible to all users.
3. Integration challenges
Compatibility issues with cloud service providers, network infrastructure, or other security tools may require additional development efforts or workaround solutions, adding complexity to the implementation process. Organizations need to carefully evaluate the compatibility of open source tools with their existing infrastructure and assess the level of effort required for seamless integration.
How much do firewall audit software tools typically cost?
Generally, open-source firewall audit tools are available for free or at a relatively low cost, as they are community-driven and do not involve licensing fees. On the other hand, proprietary firewall audit tools may have pricing structures that include one-time licensing fees, subscription models based on monthly or annual payments, or usage-based pricing for cloud-based solutions. It’s essential to research and compare different firewall audit tools to determine the most suitable option based on your organization’s needs and budget.
Can firewall audit software automatically recommend optimizations to firewall rules based on industry best practices?
Firewall audit software can automatically recommend optimizations to firewall rules based on industry best practices. These recommendations are often generated through the analysis of network traffic patterns, security policies, and known vulnerabilities. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and rule-based engines, firewall audit software can identify redundant or ineffective rules, detect potential security gaps, and propose optimizations to enhance the overall security posture of the network.
These recommendations may include suggestions such as:
Removing redundant or unused firewall rules to reduce complexity and improve performance.
Consolidating overlapping rules to streamline firewall policy management.
Identifying and addressing overly permissive rules that may expose the network to security risks.
Implementing rule optimizations based on specific compliance requirements, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
Prioritizing critical rules or traffic for more effective threat prevention and mitigation.
External Links
- 1. A user review on pfSense. TrustRadius. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 2. A user review on Nmap. TrustRadius. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 3. A user review on Nmap. TrustRadius. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 4. A user review on CrowdSec. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 5. A user review on CrowdSec. TrustRadius. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 6. A user review on OpenVas. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 7. A user review on OpenVas. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 8. A user review on Snort. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 9. A user review on Scuba. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 10. A user review on OSSEC. G2. Accessed: 20/March/2024.
- 11. David A. Wheeler. Open Source Software (FLOSS) License Slide. Accessed: 22/March/2024.

Cem is the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per Similarweb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
Sources:
AIMultiple.com Traffic Analytics, Ranking & Audience, Similarweb.
Why Microsoft, IBM, and Google Are Ramping up Efforts on AI Ethics, Business Insider.
Microsoft invests $1 billion in OpenAI to pursue artificial intelligence that’s smarter than we are, Washington Post.
Data management barriers to AI success, Deloitte.
Empowering AI Leadership: AI C-Suite Toolkit, World Economic Forum.
Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU, European Commission.
Public-sector digitization: The trillion-dollar challenge, McKinsey & Company.
Hypatos gets $11.8M for a deep learning approach to document processing, TechCrunch.
We got an exclusive look at the pitch deck AI startup Hypatos used to raise $11 million, Business Insider.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.