Difference Between Permissioned and Permissionless Blockchain
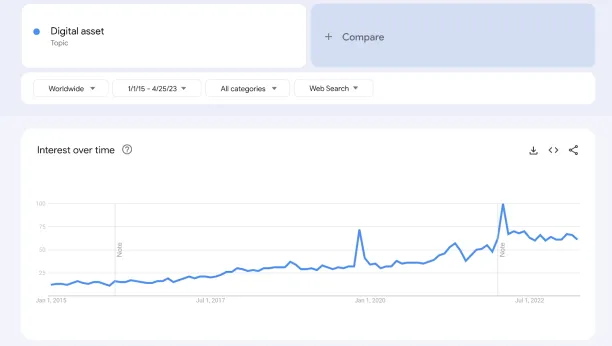
In recent years, digital assets have experienced a rise in popularity (Figure 1). To take full advantage of their capabilities, we should better understand the underlying blockchain technology that powers them.
Difference between permissioned and permissionless blockchain mainly boils down to accessibility. Permissionless blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are accessible to anyone who wishes to participate in them, fostering a decentralized, trustless environment where innovation flourishes.
The recent development of Ordinal Inscriptions which brings NFTs to Bitcoin, thanks to inscription tools that create these digital artifacts, is an example of such democratized innovation.
Permissioned blockchains, on the other hand, are not open to the public and are mostly used by companies and governments.In this piece, we’ll learn the differences between permissioned and permissionless blockchains so that we can use them better in our businesses, for personal trading, and in our quest to learn more about the digital asset ecosystem as a whole.
What is a permissioned blockchain?
A permissioned blockchain, or a private blockchain, is a type of distributed ledger with only a selected group of users and organizations having access to it. These users, often referred to as validators or nodes, have explicit authority to:
- Participate in the network
- Read the data
- Execute various functions, like adding new transactions or validating blocks
Permissioned blockchains are typically favored by enterprises and organizations seeking control, security, and privacy.
What are key features of a permissioned blockchain?
Popular permissioned blockchain networks, like Quorum, Hyperledger Fabric, and R3 Corda, typically have the following features:
1. Controlled access
Only authorized users who pass identity verification can access the network, reducing the risk of data breaches. This maintains a higher level of security and privacy.
2. Defined roles
A central authority – an organization, a consortium of organizations, a governmental body, or a trusted entity – defines specific roles, responsibilities, and permissions for the users of a permissioned network. This ensures accountability, security, and compliance.
3. Governance
Permissioned blockchains have a centralized governance structure, allowing the central authority to enforce rules, update the network, or intervene in case of disputes. This reduces its transparency because the consensus algorithms are controllable.
4. Low transaction latency
Permissioned networks have higher throughput and faster transaction speeds than permissionless ones due to the reduced need for consensus protocol.
5. More energy efficient
A permissioned blockchain network utilizes more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), Proof of Authority (PoA), or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms don’t rely on computational power for validation, but on predetermined validators, which consume less energy.
What are permissionless blockchains?
A permissionless blockchain, also known as a public blockchain, allows all users to join, read, and participate in the decentralized network without prior authorization.
In a permissionless system, users can create and validate transactions, run nodes, and mine blocks. Permissionless blockchains are typically decentralized, relying on consensus mechanisms to maintain the network’s security and integrity.
What are the key features of permissionless blockchains?
Popular permissionless blockchains, like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, have the following features:
1. Open access
Anyone can participate in permissionless blockchain networks without a verification process. The liberal accessibility, promoted by decentralization, fosters innovation.
2. Anonymity
Users can interact with the network pseudonymously and with public addresses. This ensures their privacy and helps them bypass institutional censorship.
3. Consensus-based security
Permissionless systems rely on consensus algorithms to verify transactions, prevent double-spending and other fraudulent activities, network updates, and dispute resolution.
4. Immutability
Public blockchains’ transparency and decentralization makes them more immutable than permissioned blockchains. That’s due to permissioned blockchains’ consensus mechanisms’ centralization.
5. High energy consumption
Although this varies based on the specific implementation and consensus mechanisms of the blockchain, permissionless blockchains are generally more energy-consuming than permissioned ones.
That’s because permissionless blockchains require a more complex mechanism to validate transactions and maintain network integrity, which translates into higher energy consumption.
However, it’s worth noting that some permissionless blockchains, particularly those using Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus – like Ethereum, Cardano, Polkadot, and Solana – are designed to be more energy-efficient than traditional Proof of Work (PoW) based blockchains.
6. Expanded use cases
Both permissioned and permissionless blockchains support digital assets. But those on permissioned networks are more enterprise-oriented, like supply chain management, interbank transactions, or private tokenized securities.
Permissionless blockchains, on the other hand, allow open access and validation by a decentralized consensus mechanism. This design enables “permissionless” use and trade of digital assets like cryptocurrencies. In addition, permissionless blockchains enable the creation of various decentralized applications and tokens, providing a wider range of possibilities and innovation.
Permissionless Digital Assets & Their Connection to Permissionless Blockchains
Blockchain technology, and a distributed ledger technology, allow users to hold and trade digital assets without an intermediary.
Digital assets that are specifically traded on permissionless blockchains are called permissionless digital assets. That’s due to the key factors that contribute to the permissionless nature of a digital asset, such as:
- Open accessibility
- Decentralization
- Anonymity
- Censorship resistant
- Programmability
Permissionless digital assets are digital assets that operate on decentralized blockchain networks without requiring authorization from a central authority. Users can access, transfer, and interact with these assets freely and without restrictions. As an example, this is the case of NFTs traded on the Stacks blockchain, as well as on blockchains such as Ethereum.
For more on NFTs and blockchain
To learn more about NFTs and blockchain, read:
- What are NFT Royalties & How Bitcoin Ordinals Can Help
- 4 Benefits, 15 Use Cases of RPA and Blockchain Integration
- Top 3 Blockchains for NFTs
Transparency statement
AIMultiple works with multiple companies including Gamma.io mentioned in this article.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.