NFTs and smart contracts are an intriguing blockchain technology. However, most people do not fully understand how these concepts overlap.
- NFTs, like cryptocurrency, can only be owned by one person at a time (e.g., artwork, collectibles).
- Smart contracts are self-executing digital contracts that control NFTs.
What is the difference between NFTs and smart contracts?
| Aspect | NFT | Smart contract |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Represents ownership and authenticity of digital assets. | Facilitates, verifies, and enforces digital transactions and agreements. |
| Uniqueness | Each NFT is unique, with its own token ID and metadata. | Not unique to a specific asset; it’s a program that can be used for various purposes. |
| Ownership | Ownership is connected to a unique token and can be transferred. | Does not represent ownership itself; it manages the transfer or creation of ownership. |
| Functionality | Proof of ownership for digital goods and assets. | Automates processes like minting, transferring, and managing assets. |
| Interaction | Can be bought, sold, or traded by individuals. | Used to govern the creation, management, and transfer of NFTs and other assets. |
What are NFTs?
NFT stands for Non-Fungible Token and has similar features to other types of tokens, such as ERC 20 tokens. NFTs are tokens with smart contracts, but this varies depending on the type of blockchain being used.
- On the Ethereum blockchain, NFTs are primarily implemented as smart contracts with specific functions for compatibility. For example, the ERC 721 (EIP-721: Non-Fungible Token Standard) is a standard created to define actions, such as Transfer() and balance_of(), in case the owner has multiple NFTs.
- On the Cardano blockchain, NFTs are treated as specialized entities with unique properties, rather than smart contracts.
Other blockchains may also implement NFTs as native entities with distinct characteristics, differing from the smart contract-based approach seen on Ethereum.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are codes that run on the Ethereum VM. The Ethereum blockchain includes a mechanism for running code triggered by transactions.
Smart contracts eliminate the middleman
For example, say A (the girl in the image) bets $5 with B on a soccer game. If A’s team loses, B doesn’t need to pay anything.
A smart contract is written and deployed on the Ethereum blockchain to automate this process. When the transaction occurs, the smart contract executes, verifies contract terms, and takes the necessary action based on the outcome of the game.
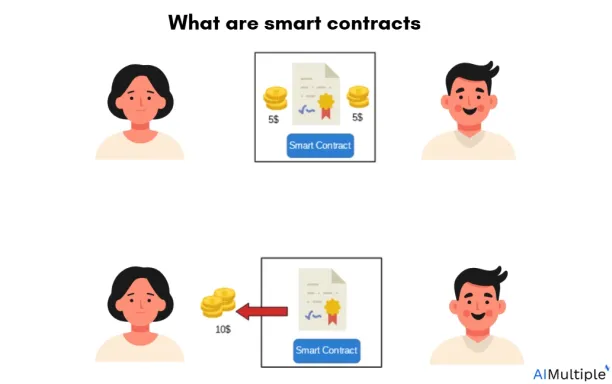
Do NFTs have smart contracts attached to them?
Yes, NFTs are inherently related to smart contracts. Smart contracts are what make NFTs functional on blockchain networks.
A smart contract can own an NFT; they are created through these contracts and are responsible for delegating ownership and reassigning it when resold or transferred.
Simply put, smart contracts are tools that enable the implementation of a sales agreement. They verify the transactions without a central authority and emphasize that NFTs cannot be divided, making them unique and non-replicable.
The purpose of an NFT smart contract is to manage and improve NFTs and digital assets.
The role of smart contracts in NFT
1. Minting of NFTS
Minting an NFT refers to creating a unique digital asset on a blockchain, making it publicly verifiable and transferable. This process involves turning a digital file, such as artwork, music, videos, or even virtual items, into a non-fungible token (NFT).
Once NFTs are minted, the smart contract defines their properties and functionality, allowing them to be legally connected to the blockchain. The smart contract transfers ownership to the first buyer, establishes rules for future transfers, and defines what the NFT represents.
2. Creation and management of NFT ownership
NFTs are unique digital assets whose creation, management, and transfer rely entirely on smart contracts. The contract automatically records each NFT’s ownership on the blockchain, ensuring secure and verifiable transactions.
For example, a smart contract determines how an NFT can be transferred from one owner to another, ensuring all parties follow the pre-defined rules.
3. Interoperability
Smart contracts enable NFTs to be recognized and used across various platforms and marketplaces, provided they follow standard protocols such as ERC-721 or ERC-1155 on Ethereum.
4. Automating NFT transactions
Smart contracts automate NFT transactions. For example, when someone buys an NFT, the contract can automatically transfer ownership, handle payments (via cryptocurrency), and trigger any other necessary actions, like royalties to the original creator.
5. Rule enforcement
Smart contracts eliminate intermediaries by automatically enforcing terms when certain conditions are met.
Think of a smart contract as a vending machine. When you insert a dollar, you get a Soda. The machine follows built-in rules. When one party meets their obligation (by inserting a dollar), the following action (dispensing a Coke) starts.
Best 8 real-world NFT smart contract use cases
NFTs represent ownership of assets, while NFT smart contracts ensure transparency, enforce verification, and manage the sale, transfer, and distribution of funds, etc.
1. NFT-based loyalty rewards
Companies use loyalty systems with NFTs, offering customers rewards that can be traded, sold, or exchanged for products or discounts. Customers earn NFTs through purchases or engagement, which can be stored in their digital wallets.
Examples of NFT-based loyalty rewards:
- Taco Bell – Taco NFTs:
Taco Bell NFTs1
Taco Bell released a limited-edition collection of 25 taco-themed NFTs on the Rarible marketplace, rewarding customers with special perks and collectible digital assets. The NFTs featured taco-themed GIFs and images.
The tokens, which were initially priced at 0.001 ETH (just under $2 at the time), sold out in approximately 30 minutes. Resale prices quickly surged on NFT markets, with some reaching over $180,000.
- RTFKT and Nike CryptoKicks:
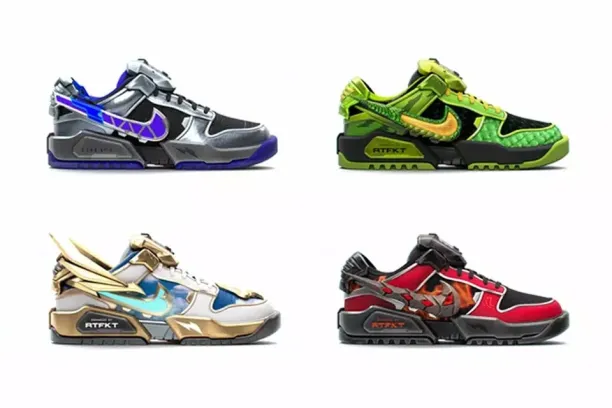

Nike, Rtfkt launch digital ‘Cryptokick’ sneaker2
Nike’s debut NFT campaign, CryptoKicks, was launched on the Ethereum blockchain in partnership with RTFKT (a digital art studio). CryptoKicks offers digital sneakers inspired by the iconic Nike Dunk. This initiative marks a notable step for Nike in the growing space of digital fashion and NFTs.
2. Ticketing & access control

NFT ticketing3
Although NFTs are primarily associated with digital artwork, they can also represent other assets, like tickets.
By tokenizing tickets on the blockchain (with the ticket’s QR code for admission kept private), every transaction—from issuance to transfer—is securely recorded, creating a transparent ownership history accessible to anyone.
NFT tickets can be used for:
- Concerts
- Sports events
- Online events
Examples of NFT ticketing platforms:
- Ticketmaster:
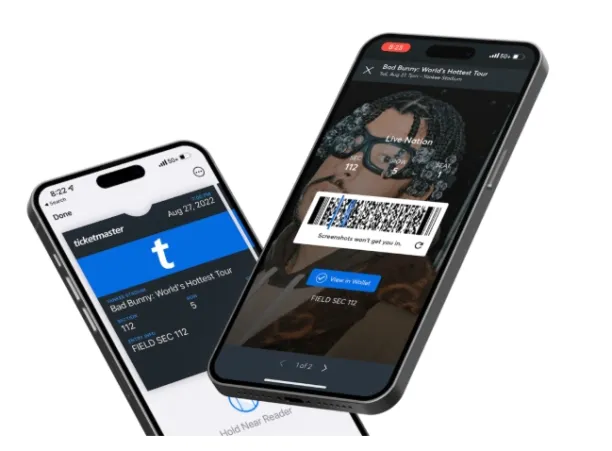
NFT-based ticket sales with Ticketmaster4
Ticketmaster is an NFT-based ticket sales platform that allows fans to buy, sell, and transfer event access through NFTs. Ticketmaster’s platform is compatible with tokens minted on Ethereum and stored in decentralized app (dapp) wallets like MetaMask or Coinbase.
- SeatLabNFT: Offers NFT-powered tickets.
- YellowHeart: Offers NFT ticketing for live events and concerts.
- Wicket: Targets the Italian music market. Connects tickets to buyer’s phone number, limiting resale to the platform at original prices.
- DeFy Tickets: Combines ticketing with NFTs for transparent transactions.
3. Digital art & copyright protect

Beeple’s Human one – sold for ~$29M5
NFTs are y used to establish ownership and authenticity of digital art, providing a transparent and secure way for creators to protect their intellectual property.
It works by tokenizing digital art as an NFT, with the smart contract behind it containing key details about the artwork’s provenance, creator, and ownership history.
Examples of NFT platforms for digital art:
- OpenSea – One of the first established NFT marketplaces:
Covers all types of digital assets, and accepts over 150 cryptocurrencies.- Blockchain network: Ethereum, Polygon, Klatyn, Solana
- NFT types: Art, Music, Collectibles, Sports Assets, Crypto Domain Names, Photography, Trading Cards, Virtual Worlds, Utility
- Rarible – Community-owned NFT marketplace:
Offers 3 blockchain networks to choose from.- Blockchain network: Ethereum, Flow, Tezos, Polygon
- NFT types: Art, Gaming Collectibles, Photography, Metaverse, and others
- SuperRare – Art-focused NFT marketplace:
An NFT marketplace specializing in digital art, offering curated and unique artworks. It provides resources and content for artists through its blog.- Blockchain network: Ethereum
- NFT types: Digital Art
Examples of the most expensive NFTs ever sold:
From digital art pieces to collectibles, NFTs are rapidly gaining recognition for their value. For example, In March 2024, CryptoPunk #3100 sold for 4,500 Ether, equivalent to approximately $16 million at that time.
The CryptoPunks collection, created in 2017 by Larva Labs and subsequently acquired by Yuga Labs, is now one of the most popular NFT collections. CryptoPunk #3100 was originally bought for just over US$2,000 in 2017.6
Below are some examples of the most expensive NFTs ever sold:
| NFT name | Company | Collection | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| The Merge | Pak | The Merge NFT | $91million |
| Everydays: The First 5000 Days | Beeple | N/A | $69 million |
| Clock | Pak and Julian Assange | N/A | $52 million |
| HUMAN ONE | Beeple | N/A | $29 million |
| CryptoPunk #5822 | Larva Labs | Crypto Punks | $24 million |
| CryptoPunk #3100 | Larva Labs | Crypto Punks | $16 million |
| CryptoPunk #7523 | Larva Labs | Crypto Punks | $12 million |
| TPunk #3442 | Mondiblo & Bastardber | Tpunks | $11 million |
| CryptoPunk #4156 | Larva Labs | Crypto Punks | $10 million |
4. Real estate & property ownership
NFT Marketplace for real estate7
NFT real estate involves representing physical or virtual properties as unique NFTs on the blockchain.
These NFTs serve as the digital equivalent of a traditional title deed, capturing ownership and provenance. NFT real estate can include physical properties such as houses and land as well as virtual properties within metaverses and digital environments.
The world’s first real property sale by NFT occurred in Ukraine in 2017 when an apartment was sold for 36 ETH (~ $93,000 at the time). The transaction involved transferring ownership of shares in a US company, registered in the Ukrainian land registry, as the apartment’s owner.8
Why people and companies invest in NFT real estate:
- Ownership and provenance: NFT real estate offers a transparent and immutable record of ownership, helping to eliminate disputes and fraud.
- Scarcity and value: Similar to physical real estate, the rarity and uniqueness of NFT properties can increase their value over time, making them appealing to investors.
- Fractional ownership: Fractional ownership of NFTs allows more people to invest in high-value properties, making it accessible to a broader range of investors.
Examples of NFT platforms for real estate & property ownership:
| NFT platform | What is it | Real-life example |
|---|---|---|
| Propy | A real estate platform that enables property transactions through NFTs, tokenizing ownership. | Propy facilitated the first NFT-based real estate transaction in the U.S. with a Florida home sold for 210 ETH (~$650,000).9 |
| Decentraland | A virtual metaverse where users can buy, sell, and trade virtual land represented by NFTs. | A virtual land parcel in Decentraland was sold for $913,000, marking one of the largest sales in the metaverse.10 |
| The Sandbox | A virtual metaverse allowing users to buy, sell, and develop virtual land using NFTs. | A virtual land NFT in The Sandbox sold for 4.3 million SAND tokens (~$4.3 million).11 |
5. Fractional ownership of assets
Fractionalization can eliminate the cost barriers that limit demand for specific tokens and high-value assets, making them accessible to a broader range of investors.
For example, an NFT representing a digital artwork valued at $1 million could be divided into 1 million shares, with each share worth $1. This allows multiple individuals to collectively own a portion of the original asset, each holding a fraction.
Note that, NFT platforms for real estate and property ownership can also offer fractional ownership of assets.
Examples of fractional ownership of assets:
- Shared ownership in physical assets: Fractionalized NFTs enable shared ownership of physical assets such as real estate, artwork, and collectibles.
- Example: A valuable artwork can be tokenized into an NFT and then divided into fractional shares, with each share representing a portion of the artwork.
- Shared ownership in digital assets: Fractionalized NFTs also allow for shared ownership of digital assets like virtual land, digital art, and virtual goods.
- Example: A plot of virtual land in Decentraland could be tokenized and divided into fractional shares, allowing multiple users to own a part of the virtual land.
- Shared investment funds: Fractionalized NFTs can be utilized to create shared investment funds, where a group of individuals pools their resources to invest in valuable NFTs.
- Example: A group of investors could set up a fund to buy fractional shares of high-value digital art, giving each participant ownership of a portion of the artwork collection.
- Collectibles: Ownership of collectibles, ranging from rare items to cherished memorabilia, can be divided into units through fractional NFTs.
- Example: The rare Honus Wagner baseball card was sold through fractional ownership.12
6. Gaming
NFTs are used in gaming to represent in-game assets like skins, weapons, and characters, allowing players to own, sell, or trade their digital items.
Examples of smart contracts in gaming:
- Fan token rewards: A fan engagement platform issues tokens through a smart contract. Fans can earn tokens for watching matches, attending events, or purchasing merchandise. These tokens are redeemable for exclusive perks, such as in-game items, VIP passes, or direct interactions with players.
- Real-life example: NBA Top Shot is a blockchain-based marketplace where fans can buy, sell, and trade officially licensed NBA collectibles as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens).
- Transfer and ownership of digital assets: Smart contracts manage the buying, and selling of virtual goods like in-game skins or collectible items.
- Example: A player may want to sell a rare skin to another player; the smart contract will ensure the transaction is completed only if the conditions are met (e.g., the player receives the agreed cryptocurrency or in-game currency).
- Player transfers and contracts: A football club can use a smart contract to automatically process a player’s transfer.
- Prize payout in esports tournament: In a large esports tournament smart contract can calculate and distribute the prize pool across winning teams and players without manual intervention.
7. Product tracking
Large corporations can use NFTs to represent products within their supply chain, enabling real-time tracking of product locations and ensuring data transparency.
Tokenization of products:
- Each product gets a unique NFT, representing its digital twin.
- NFT contains product details: origin, manufacturing date, batch, and serial number.
- Tracking shipping and storage: Oracles, third-party services, or systems that bridge the blockchain and the outside world:
- Upload real-time data to the blockchain (e.g., product location, origin, manufacturing date, batch, serial number, etc).
- Provide updates on product status as it moves through the supply chain.
Example of product tracking NFT
De Beers blockchain-backed diamond tracking:
De Beers leverages blockchain and NFTs to track the provenance of its diamonds Each diamond is tokenized as a unique NFT, which stores product details such as its origin, cut, and carat.13
8. Insurance contracts
NFTs can be used to tokenize insurance policies, making them more transparent, tradable, and customizable. Smart contracts ensure that claims are processed automatically, increasing efficiency and reducing fraud.
Examples of platforms that use smart contracts in the insurance industry:
- Etherisc: A decentralized platform providing parametric insurance products, such as flight delay insurance, using smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain
- ChainThat: Specializes in using blockchain to optimize reinsurance, risk management, and policy administration.
- Insurwave: A blockchain-based platform developed by EY (Ernst & Young) in collaboration.
- Teambrella: A decentralized insurance platform that uses smart contracts to manage mutual insurance.
Examples of smart contracts in insurance:
- Parametric insurance
- Insurance pricing
- Contract and policy management
- Claim processing
- Regulatory reporting
- Fraud detection
Other topics about NFTs and smart contracts
Traditional contracts versus smart contracts
Traditional contracts, such as rental agreements, require third-party supervision for enforcement and dispute settlement. For example, a renter must pay rent on the first of each month, and if a dispute arises, a governmental authority must step in.
Smart contracts eliminate intermediaries by automatically enforcing terms when certain conditions are met. Like a vending machine, when you insert a dollar, you receive a Coke. The machine follows preset rules, similar to if-then statements in code, ensuring that agreements are executed precisely without needing third parties.
Non-fungibility: The heart of NFTs
Non-fungibility is a difficult concept with a straightforward definition. In finance, an asset is fungible if it can be swapped one for one with another of the same type.
For example, one Bitcoin may be traded for another, making it fungible. NFTs, on the other hand, contradict this paradigm. Because of their distinct characteristics, they cannot be substituted like-for-like.
Each NFT is unique, including the information and qualities that differentiate it. This non-fungibility is what makes NFTs valuable.
NFTs vs cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are fungible, meaning they can be exchanged on a one-for-one basis. In contrast, NFTs are non-fungible, each being unique and carrying distinct attributes.
For example, two NFTs representing digital art by the same artist cannot be exchanged directly because each piece is one-of-a-kind.
For more on NFTs
To learn more about NFTs, read:
- NFT Loans: Unlocking Liquidity for Collectible NFTs?
- 20+ NFT Stats: Market Size, Companies, Users, & More
- Top 5 Differences Between Ordinal Inscriptions vs NFTs
External Links
- 1. De Beers group introduces world’s first blockchain-backed diamond source platform at scale – De Beers Group .
- 2. De Beers group introduces world’s first blockchain-backed diamond source platform at scale – De Beers Group .
- 3. 10 Innovative NFT Ticketing Platforms Revolutionising Events. AmplifyWorld Resources
- 4. Our Solutions - Ticketmaster Business IE. Ticketmaster Business
- 5. Most expensive NFT Art | StadioPlus.
- 6. Rare CryptoPunk NFT sells for US$16 mln, signaling market revival. Yahoo Finance
- 7. NFT real estate marketplace platform — Aetsoft.
- 8. Real Property NFTs – Bricks-and-mortar to blockchain-and-token | Herbert Smith Freehills Kramer | Global law firm.
- 9. ”NFT house sells for $654k in historic auction". Tampa Bay Times. 2022. Retrieved March 2025.
- 10. ”People Are Paying Millions For Land in the Metaverse". CNET. 2022. Retrieved March 2025.
- 11. ”A plot of virtual land that went for $4.3 million in The Sandbox". Business Insider. 2021. Retrieved March 2025.
- 12. World's Rarest Baseball Card Set on Deck For NFT Experience. Cision PR Newswire
- 13. De Beers group introduces world’s first blockchain-backed diamond source platform at scale – De Beers Group .


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.