Web 3.0 in 2024: Promises & Challenges
Web3 or Web 3.0 is a term that has attracted a lot of attention recently. Binance has announced a $500 million fund to invest in Web3. In this article, we will explore the promise of Web3 and its current limitations.
What is Web3?
Web3 was first used in 2014 by Gavin Wood, the co-founder of Ethereum and creator of the Polkadot blockchain. Web3 is a new version of the web that is built, operated, and controlled by its users and it is not managed by centralized parties like technology companies. Cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) are all part of Web3.
Evolution of the web
- Web1 was read-only, the pages were static and there was close to no interaction between users.Web1 started in 90s and ended in early 2000.
- Web2 is read, and write only. Users are able to interact with each other. User generated contents start to appear and social media platforms rise. This is the current version of the web .
- Web3 is labeled as read, write and own. In Web 3, users own their data.
Figure 1. Evolution of the web
The main point behind Web3 is “trustless”. In Web3, there is no centralized network so there is no need to trust in a counterparty. Everything is run on a blockchain system with the help of AI and machine learning. In contrast, the service providers (e.g., Google, and Facebook) control the system in Web2.
Pillars of Web3
Decentralization
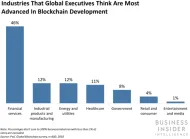
The current state of the internet is being dominated by a few companies. Figure 2 shows that almost 57% of global application traffic went to 6 companies. In Web3, ownership is not in the hands of a few entities and it is distributed among users. An algorithm provides the services which are hosted by all of the participants.
Figure 2. Global application traffic in 2021
Permissionless
Anyone who has access to the network can utilize the services, no one can be banned or excluded because the network is decentralized and there is no centralized authority to verify data transmission, verification happens at the user level with the thousand of nodes participating.
Trustless
It means that there is no centralized network which means there is no need for a trusted third party to facilitate interactions between two pirates. The only trust that is needed is in the underlying algorithm.
Native payment
Instead of relying on a slow and bureaucratic banking system, payments will be done in cryptocurrencies. No limitation can be imposed on money transfers as cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ether are decentralized, meaning no one can impose limitations on tokens transfer.
Ownership
Users own their data and can decide how much of it they want to share. If a user owns an NFT from a game and the game manager removes their account, the user still owns the NFT which is a major change from the Web2 ownership system. NFTs will play a major role in Web3 as they will function as proof of ownership.
Censorship resistance
All data is stored in the blockchain which means it is tamper-proof and immutable. No one can delete them or censor them.
Limitations & problems of current Web3 infrastructure
Performance
Speed
Major blockchain networks are slow when compared to centralized networks. There is always a trade-off between decentralization, scalability, and security. This situation is commonly referred to as the blockchain trilemma. Web3 needs to provide all of these at the same time to be able to shift people from Web2. However, solutions such as layer 2 and sidechains have been developed to tackle this trilemma but they are far from perfect.
Storage
Storing data on the blockchain is not cheap. For instance, storing 1GB of data on the Ethereum blockchain costs thousands of dollars.
Too much decentralization
No one can censor or ban a user on Web3. This means that illegal content cannot be taken down as there is no centralized power.
Traceability
Crypto wallets theoretically provide anonymity since all transactions are public and recorded on the blockchain. However, this means that anyone can see, analyze, and trace them back to an individual. For example, the FBI has traced and retrieved the ransom paid to criminals in the Colonial Pipeline attack. For non-criminal activities, this means that anyone that you have ever made a transaction with that knows your identity can check and track all of your transactions. It was pointed out in the Bitcoin whitepaper that a new key pair should be used for each transaction so the transactions won’t be traced back to a common owner.
Speculation in the cryptocurrencies
If cryptocurrencies are to be used as a payment mechanism in Web3, they must function as real money. This means that they should have the store of value function which they currently lack due to their volatility. Stablecoins are also not a good substitute as stablecoins like Tether are centralized stablecoins that are supposedly backed by US Treasuries and dollars. Algorithmic stablecoins are also not a good option as they can lose their value easily as happened in the case of Terra.
Further reading

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.