Top 3 Alternatives to Using a VPN in 2024
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are useful for businesses that want to give their remote employees access to internal applications and data. However, VPN, as a tool, is full of flaws; when utilizing a VPN across networks, companies’ private information can become at risk of piracy. In this article, you can find the best alternatives to using a VPN for your corporation.
How does VPN work?
A VPN allows users to send and receive data over the internet with private networks. The information gets transmitted via an encrypted virtual tunnel that can only be accessed by authorized parties.
This is adequate when only a few users need permission. However, as the technology and needs change, users need to give access to contractors and third-party vendors in different locations which have threatened network security, allowing cybercriminals to intervene in the channel.
What are the risks of using a VPN?
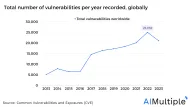
- VPN as an opportunity for hackers: With the enormous increase in the number of employees who are working remotely, VPN adoption and utilization have accelerated. Cybercrime has been on the rise since then. According to media reports, The use of VPN solutions has boosted the surface area of attack available to cybercriminals. This shows that if your 3rd party vendor can access your apps, servers, and applications, you are at risk of getting hacked.
- No accountability for 3rd party vendors: VPNs can’t provide any granular auditing, so you cannot control and track any VPN user actions. For instance, once an issue occurs, none will be able to determine who has caused this issue, allowing hackers to confidently steal private information.
- Policies to safeguard your credentials cannot be invented or implemented: 3rd party vendors may engage in a variety of practices over which you have no control, this will allow hackers to access your data and share your credentials.
- Slow connection: VPNs take a long time to encrypt data, and the higher the encryption level is, the longer it will take to access the network. This proves that VPNs slow application speed, resulting in a decrease in the quality of performance delivered.
- High costs: Since VPN doesn’t provide the feature of controlling and managing connections remotely, businesses may require to add more resources to support users. As a result, VPN will cost lots of money which will augment business expenses.
- Desktop sharing issues: For collaboration, businesses may use the desktop sharing feature without being aware of its risks:
- During a 3rd party access, this feature may force vendors to circumvent their authentication structure, which threatens the security of networks.
- This feature doesn’t provide any screen recording or even a detailed list of participants’ actions. Therefore, participants can easily take action against the security.
- The audit trail for desktop sharing is limited since it doesn’t include any detailed information about the chats, the files transferred, or any oth
- er relevant data.
- Desktop sharing can’t control or limit access to apps, web servers, and databases. This will allow cybercriminals to exploit these security flaws.
What are VPN Alternatives?
Software Defined Perimeter (SDP)
SDP is a security approach that transmits access to internal apps based on a participant’s identity, using context-aware trust.
This cybersecurity solution differs from traditional network-based security in its approach. Whereas traditional security is concentrated in the data center, SDP is distributed throughout the cloud. Instead of concentrating on the network, SDP concentrates on protecting the user, the application, and the connectivity between them.
SDP technologies are distinguished by four core principles:
- Trust is never implicit
- No inbound connections
- Application segmentation, not network segmentation
- Secure internet leverage
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
It permits extra security for a VPN. Instead of just tapping your username and password, IAM provides a trustworthy verification process to ensure the legitimacy of all login attempts. This method allows you to add multi-factor access control to your VPN connection.
IAM also shows each user’s activity and which access privileges he has, allowing network administrators to track and monitor individuals’ actions on each network to ensure that each user has the right access.
Privileged Access Management (PAM)
Privileged Access Management tools concentrate on managing sensitive network information and data within systems and applications.
PAM solutions include developed security features including user activity and data access control, password rotation and obfuscation. These features save risks by helping IT managers identify suspicious and risky activities, control actions on apps and systems, and make sure that all users have the right permissions and can use them only when it is required.
Privileged Access Management helps you with:
- Password and authentication management.
- Secure system communication.
- Implementing least privilege policies.
- Privilege accounts control and monitoring
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
It is one of the secure service edge approaches. ZTNA assumes that all participants are untrustworthy, thus, every user should prove that they are not a threat before accessing any network.
ZTNA investigates who are the users, whether they are internal or external, and what access they require. Network managers must take into consideration those data to allow permissions only to those who are trusted.
ZTNA has special features since it helps provide cloud-based and high availability security services, as it offers easy and quick access to private applications.
Figure 1. How IAM, PAM, and Zero Trust differs from VPN
The age of remote working has arrived. VPNs’ limited capabilities have put end-users in front of the urgency of adopting VPN alternatives as the most efficient cyber security tools.
Security is constantly changing as cyber risks appear, to find best practices that will enhance your cybersecurity posture you can check our Top 8 Cybersecurity Best Practices for Corporations article.
Further reading
- Secure Access Service Edge: The New Norm for Cybersecurity
- Software Defined Perimeter: Definition, Importance & Use Cases
Please contact us if you have any additional information about cybersecurity solutions:

Cem is the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per Similarweb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
Sources:
AIMultiple.com Traffic Analytics, Ranking & Audience, Similarweb.
Why Microsoft, IBM, and Google Are Ramping up Efforts on AI Ethics, Business Insider.
Microsoft invests $1 billion in OpenAI to pursue artificial intelligence that’s smarter than we are, Washington Post.
Data management barriers to AI success, Deloitte.
Empowering AI Leadership: AI C-Suite Toolkit, World Economic Forum.
Science, Research and Innovation Performance of the EU, European Commission.
Public-sector digitization: The trillion-dollar challenge, McKinsey & Company.
Hypatos gets $11.8M for a deep learning approach to document processing, TechCrunch.
We got an exclusive look at the pitch deck AI startup Hypatos used to raise $11 million, Business Insider.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.