Guide to IIoT in 2024: 7 Benefits, 3 Challenges & Examples
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the use of the internet of things (IoT) across industrial sectors and applications.
Industrial IoT employs a network of sensors to:
- Collect critical production data,
- Store it in databases,
- Apply different algorithms and analytics to turn data into actionable insights,
About the efficiency of manufacturing operations.
In this article, we will explain in more detail the concept of IIoT, its benefits, use cases, and the industries that utilize it.
What is the industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the interconnected sensors, instruments, and other IoT devices networked together exclusively in an industrial environment (e.g. factory, warehouse).
IIoT is aimed at:
- Data collection,
- Exchange,
- And analysis,
To improve the quality control of the product, production analytics, and the overall economical efficiency of the manufacturing process.
What are the benefits of IIoT?
Benefits of IIoT include, but are not limited to, the following:
1. Efficient inventory management
IIoT can help optimize asset and inventory management. This can result in less downtime as the personnel will, ahead of time, be notified of a decreasing inventory. Much like a smart shelf that notifies a store’s staff of each diminishing item on the shelf, the same will happen in large-scale inventories.
Learn more about inventory management automation.
2. Transparent production process
Machinery, and production lines, equipped with sensors will make for a more agile and efficient production process, as outages will instantly be observable through real-time monitoring of IoT devices. Factors such as:
- Running time,
- Operating speed,
- Production output,
- Equipment depreciation,
- And capital erosion can signal areas where attention should be given.
3. Quality control
By monitoring the condition (speed, vibration, etc.) and calibration of machines responsible for the creation of a certain product, quality control assessment can instantly be undertaken following production.
4. Shorter time-to-market
A result of efficient inventory management and efficient production process is a reduced product cycle time, resulting in a quicker company-to-market delivery.
The American manufacturer company, Harley-Davidson, managed to reduce the lead time for producing customized motorbikes from 21 days to six hours. This happened through the quick gathering of data from customers and promptly leveraging it in the production process.
5. Improved safety
Given that employers are willing to invest in expensive, modern equipment, IIoT can potentially create a safer workplace for the workers. Wearable IoT healthcare devices can keep a constant track of workers’ vitals. This could lead to a reduction in the number of workplace health scares and emergencies.
Other sensors and IoT devices strategically placed around the workplace — air quality sensors, gas leakage alarm systems, safety-violation cameras, etc. — can further improve the safety of the workshops and the factories.
6. Shop floor transparency
IIot increases the constancy and consistency of record-keeping.
By providing the management with real-time, accurate, and insightful shop floor details — foot traffic, customers’ demographic, sales amount, etc. — they can gain accurate insights into the day-to-day business activities.

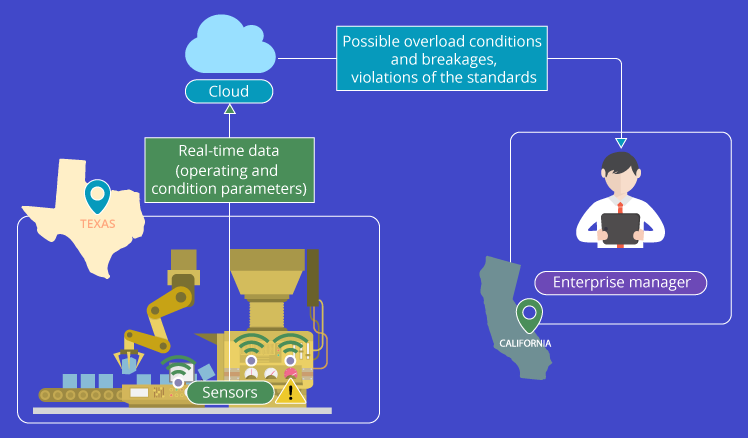
7. Remote operations’ transparency
In extension to the previous point, managers can also gain visibility into remote locations’ operations. Discontinuities and progress alike will automatically be recorded and monitored, allowing for preemptive, pragmatic adjustments (see Figure 1).
What are the challenges of IIoT adoption?
1. Large initial outlay
Although the numbers will vary for each business and the scope of the IoT ecosystem, adopting an IIoT network could cost, on average, a minimum of $50,000.
The specifics of the outlay would include:
- Hardware (e.g. sensors),
- Communication protocols,
- IoT cloud storage,
- Educated IT personnel,
- And sourcing technical support for IoT monitoring.
Note: Because each enterprise adapts to the implementation of new infrastructure at a different pace, the ROI to break even is difficult to predict.
2. Data security
Kaspersky, a cybersecurity provider, reported ~1.5 billion cyberattacks on IoT devices in 2020, an increase from 639 million in 2020. As long as the internet exists, IoT security is a challenge that needs counteracting via cybersecurity software.
3. Integration issues
Integrating different IoT devices, or overhauling old infrastructure with digitized systems, can present security issues (i.e. the network not having been stress tested adequately).
It could also cause business discontinuities (i.e. not having enough time to move most applications digital or make them “smart”).
Lastly, different IoT devices each using a different communication protocol might be challenging to bring under one umbrella.
What industries are using IIoT today?
Different industries are leveraging IIoT today, including:
1. The automotive industry
The interconnection of software, machines, and humans gives producers the agility to navigate the markets’ ever-changing climates.
1.1. Inventory management
For example, currently, there exists a shortage of computer chips to be embedded in automobiles. Theoretically, IIoT could have kept tabs on chips’ inventories to have given producers more time to think of substitutes as their stock of chips was lessening.
1.2. Personalization
Tesla buyers can personalize their cars — engine power, wheel-rim types, paint color, and interior details — to their individual preferences on the website (see Figure 2).
Each input that gets made (i.e. the wheel types) directly alerts the appropriate production segment responsible for making sure of on-time delivery. The direct, quick transfer of data from customers on their couches to inventory managers at the production site leads to faster manufacturing.
Learn more about IoT use cases in the automotive sector.

2. Utility companies
IIoT helps manage outages or identify heavy demands on resources (e.g. electricity grids and nuclear plants). It can also assist with resource distribution, fault detection, outage alerts, and repair suggestions.
Learn more about automation in utilities.
3. Oil and gas industries
3.1 Carbon footprint reduction
With IIoT technologies, the oil and gas industry can address leakages and environmental impacts. For instance, drones can be used to detect leaks or identify weak spots in pipelines. This vastly assists in environmental sustainability and carbon footprint reduction.
3.2. Demand forecasting
Data collected from IoT devices can be analyzed to enable businesses to adjust production levels based on real-time data of inventory, storage, distribution pace, and forecasted demand.
3.3. Data-driven extraction and drilling
The application of smart sensors and automated oil drillers allows companies to monitor reservoirs and understand how deep the extraction can still go.
4. Agriculture industry
IoT sensors can monitor the soil, crops’ leaves, and other factors of interest to inform the farmers of the time to harvest, the possibility of pest infestations, rainfall levels, and more.
Learn more about IoT in agriculture.
For more on IoT
To learn more about the Internet of things:
- Top 4 Use Cases of 5G IoT
- IoT Market Outlook For 2023 & Beyond
- Top 3 Benefits of IoT for Healthcare Providers
Finally, If you believe your business will benefit from an IoT solution or device, feel free to check our data-driven hub of IoT solutions and tools.
We can guide to through the process:

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.