50+ Cybersecurity Stats in 2024: Market, Attacks & Tech

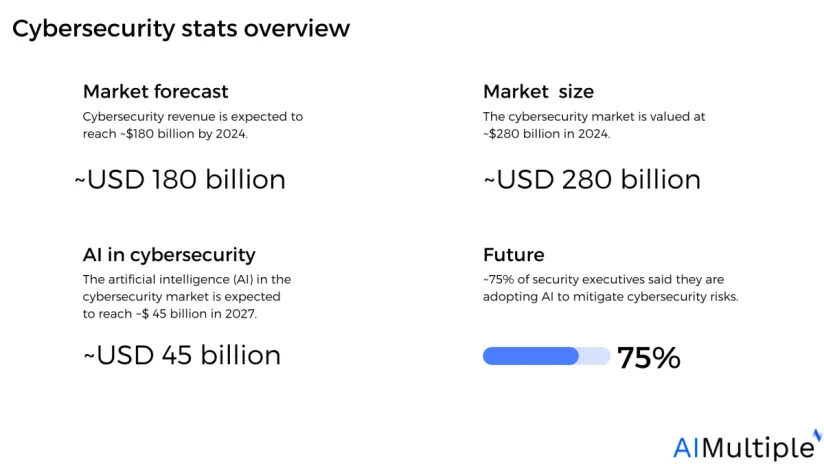
Figure 1: Cybersecurity stats overview
Network security statistics show that the average data breach cost in 2023 was ~$4 million (the highest value ever recorded, with a ~15% increase over 3 years).
Cybersecurity is becoming a major concern for individuals and businesses as more people are shifting to remote work and cloud use, creating new vulnerable environments susceptible to data breaches.
The cost of a data breach is rising along with the number of attacks, and businesses are trying to leverage privacy enhancing technologies, and other solutions such as network security policy management solutions, DLP software, RPA or ransomware tools to detect, manage, and mitigate cyber attacks.
In this article, we compiled important statistics about cybersecurity technologies, attacks, business spending, and the effects of COVID-19 on the landscape.
Cyber security market
Market size & forecast
The size of the cybersecurity market has been rising significantly over the past decade, and is estimated to grow even more:
1. The cybersecurity market was valued at ~$75 billion in 2015 (Forbes)
2. In 2024, the cybersecurity market is valued at ~$280 billion and is expected to reach ~$345 billion by 2026 (MarketsAndMarkets)
3. Cybersecurity revenue is expected to reach ~$180 billion by 2024.1
4. Cybersecurity market revenue is predicted to expand at an annual rate of ~10% (CAGR 2024-2028), with a market volume of $250+ billion by 2028.2
5. The U.S. will create the largest cybersecurity revenue (~$80 million in 2024).3
6. The artificial intelligence (AI) in the cybersecurity market is expected to reach ~$45billion in 2027. (GlobeNewsWire)
7. Global security and risk management spending is estimated to reach over $150+ billion in 2024.
Figure 2: Global security and risk management spending estimation (in billions USD)
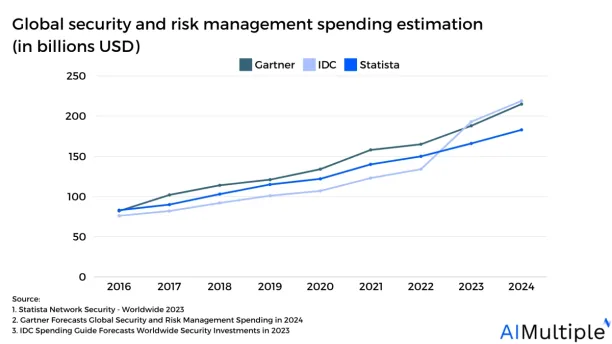
Source: 1. Statista42. Gartner53. IDC6
8. Microsoft (%16), IBM (%11), and Broadcom (%5) are the top three major players in the cybersecurity market, by brand share.
Figure 3: Key cybersecurity players in 2022 by brand share
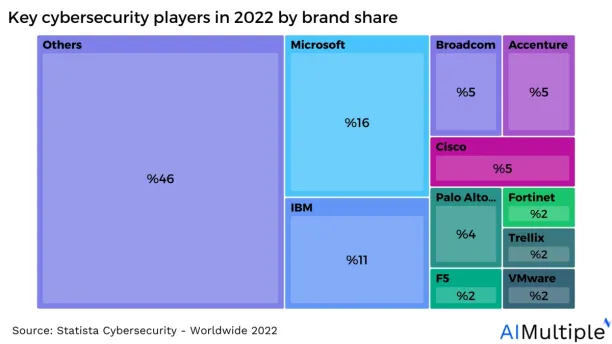
Source: Statista7
Market geography
9. Asia-Pacific is expected to have the highest market growth for cybersecurity solutions over the forecast period between 2020-2025 (Mordor Intelligence)
10. Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy, are leading European countries to adopt IoT and connected devices for cybersecurity purposes. (Business Wire)
11. The cybersecurity industry operates with 3 distinct mega-clusters: the San Francisco Bay Area (“SFBA”), metropolitan Washington, D.C., and Israel. (Mordor Intelligence)
12. The U.S. recorded ~75% of all global cybersecurity funding in 2020, at ~$6 billion. (CrunchBase)
13. Israel is the second leading country in the cybersecurity industry; over 20% of the country’s venture funding went to cybersecurity companies in 2020. (CrunchBase)
Funding
Figure 4: Cybersecurity venture funding between 2011-2020
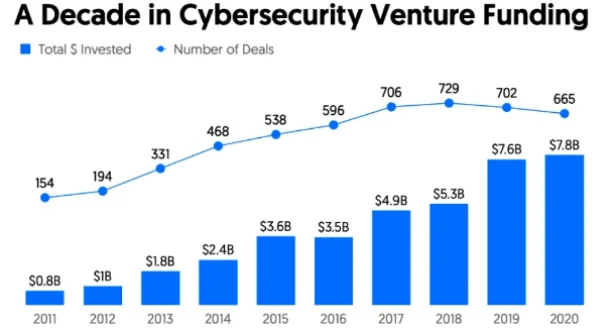
Figure 1. Cybersecurity venture funding
14. Global venture funding for the cybersecurity industry hit an all-time high in 2020, reaching ~$8 billion. (CrunchBase)
15. About 1,500 cybersecurity companies around the globe have received venture funding since 2017 and have not yet exited. (CrunchBase)
16. In 2020, global cybersecurity venture funding went to: (CrunchBase)
- angel and seed-stage deals (6%)
- early stage (39%)
- late stage (53%)
- tech growth rounds (2%)
17. Top 10 investors in the cybersecurity industry since 2010 are: (PitchBook)
- Accel
- Klein Perkins
- NEA
- Bessemer Venture Partners
- Intel Capital
- Paladin Capital Group
- GV
- Andreessen Horowitz
- Norwest Venture Partners
- Sequoia
Cybersecurity attacks
Number of attacks
Figure 5: Common mistakes by employees contributing to cyber incidents worldwide
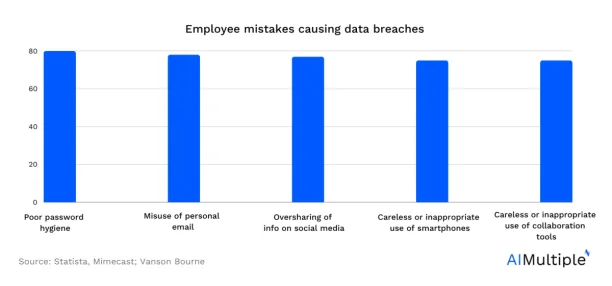
18. The number of annual malware attacks declined from ~10 billion in 2018 to 5+ billion attacks in 2020 (Statista*)
19. The most targeted industry by malware attacks is the professional sector with ~900 incidents in 2020, followed by manufacturing with ~300 incidents, public administration with ~250 incidents, and healthcare with ~200 incidents. (Statista**)
20. ~1.5 billion cyberattacks on IoT devices have been reported in 2020 (Kaspersky)
Causes of attacks
21. 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. (Cybint)
22. Ransomware is the #1 type of malware-threatening SMBs, followed by viruses, adware, spyware, and remote access trojans. (Datto)
23. The top 10 causes of ransomware attacks are: (Datto)
- Phishing emails
- Poor user practices/gullibility
- Lack of cybersecurity training
- Weak passwords/access management
- Open RDP access
- Clickbait
- Malicious websites
- Lost/stolen user credentials
- Lack of funding for IT security solutions
- Lack of executive buy-in for adopting security solutions
Read more: Most common cyber threat vectors.
Consequences of attacks
24. Data breaches exposed 36 billion records in the first half of 2020. (RiskBased)
25. Personal data was involved in ~60% of breaches in 2020. (Verizon)
26. It takes ~280 days to find and contain an average cyberattack. (IBM)
27. A threat hunt, which is the process of repetitively searching through networks to detect and isolate advanced threats, is estimated to take 170 days to detect an advanced threat, 39 days to mitigate, and 43 days to recover. (Wikipedia)
28. The cost of a data breach rose from ~$3.8 million to ~$4.2M in 2020. (IBM)
29. The average cost of a ransom in ransomware attacks was ~$5,500 in 2020 whereas the cost of the downtime caused by the attack was ~$270,000 (~50x the ransom) (Datto)
30. The overall amount paid by ransomware victims increased by ~300% in 2020 reaching ~$350 million worth of cryptocurrency. (Chainalysis)
31. 21 out of 40 breaches result in worse stock performance versus the NASDAQ in the six months after a breach than they did in the six months prior. (Comparitech)
32. After 2 years of a company experiencing a breach, the average company share price is estimated to decrease by ~10% (Comparitech)
33. Only 70% of organizations successfully got their data back following a ransomware payment, whereas 20% paid the ransom and never got access to their data, and 10% paid the ransom but faced additional ransom demands. (ProofPoint)
Effects of COVID-19 on cybersecurity
34. In the first 2 months after the beginning of the pandemic, the FBI reported a 300% increase in reported cybercrimes (IMC Grupo)
35. In April 2020, the first month after the beginning of the pandemic, Google blocked ~18 million daily malicious coronavirus messages to Gmail users. (Business Insider)
36. Coronavirus scams cost Americans $7 million in the first 9 days of April 2020 (Business Insider)
37. ~25% of COVID-19 cyberattacks target banks or healthcare organizations (Fintech News)
38. ~50% of legal and compliance leaders are concerned about third-party cyber risks due to remote work since COVID-19. (Gartner)
Read more: Third party cyber risk management.
Cybersecurity technology
Data encryption
39. Some of the most common privacy enhancing technologies are:
- Cryptographic algorithms such as homomorphic encryption and differential privacy
- Data masking
- Synthetic data generation
- Federated learning
40. The main causes for using data encryption technology are: (Entrust)
- protect customer personal information
- protect information against specific, identified threats
- limit liability from breaches or inadvertent disclosure
- avoid public disclosure after a data breach occurs
41. 50% of surveyed companies have a consistent data encryption plan implemented across the entire enterprise to protect privileged data. (Entrust)
42. ~40% of respondents say encryption is performed on-premise before sending data to the cloud using keys their organization generates and manages. (Entrust)
Cloud migration
Figure 6: Impact of cloud-breaches
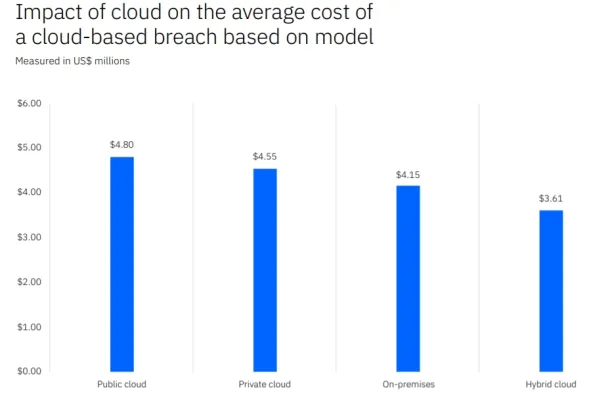
43. COVID-19 and remote work have driven businesses to migrate their work to cloud share points, increasing security risks. (IBM)
44. Cloud misconfiguration was the third most common threat, accounting for 15% of breaches (IBM)
45. In 2020, public cloud-based breaches cost an average of $4.8M, whereas breaches in hybrid cloud-based models cost $3.61M. (IBM)
46. Organizations further along in their cloud modernization strategy contained the breach on average 77 days faster than those in the early stage of their modernization journey. (IBM)
AI and automation
47. Companies with no security AI and automation averaged a cost of ~$7 million per breach, whereas an organization with a fully deployed system saw costs averaging ~$3million. (IBM)
48. ~75% of security executives said they are adopting AI to mitigate cybersecurity risks. (Capgemini)
49. ~30% of respondents are using security products with AI embedded, with 30% using proprietary AI algorithms, and ~40%, currently either use (or plan to use by next year) both proprietary solutions and embedded products. (Capgemini)
50. When asked the question: “Do you use AI in cybersecurity in these areas”, respondents said: (Capgemini)
Figure 7: Percentage of organizations using AI in cybersecurity
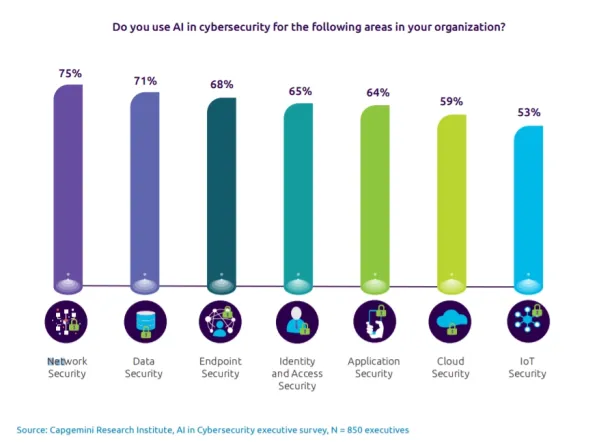
51. ~50% of the executives surveyed say they make extensive use of AI in cyber threat detection, ~35% use it extensively for prediction, and ~20% use it for a response. (Capgemini)
52. AI reduces the time taken to remediate a breach or implement patches in response to an attack by ~10% (Capgemini)
Businesses can also leverage RPA bots as well as workload automation tools to mitigate cybersecurity risks by automating privileged data transfers and other sensitive tasks. To learn more, feel free to read our in-depth article about RPA for cybersecurity and our workload automation guide for tech buyers.
If you believe your business will benefit from a cybersecurity solution, feel free to check out our hub for data-driven lists of cybersecurity products and explore the ecosystem.
External links
- Business Wire
- Business Insider
- Capgemini
- Chainalysis
- Comparitech
- CrunchBase
- Cybint
- Datto
- Entrust
- Fintech News
- Forbes
- Gartner
- Kaspersky
- IBM
- IMC Grupo
- MarketsAndMarkets
- Mordor Intelligence
- PitchBook
- ProofPoint
- RiskBased
- Statista*
- Statista**
- Verizon
- Wikipedia
- 1. ”Cybersecurity – Worldwide“. Statista. September, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 2. ”Cybersecurity – Worldwide“. Statista. September, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 3. ”Cybersecurity – Worldwide“. Statista. September, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 4. “Cybersecurity – Worldwide“. Statista. October, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 5. “Gartner Forecasts Global Security and Risk Management Spending to Grow 14% in 2024“. Gartner. September 28, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 6. “New IDC Spending Guide Forecasts Worldwide Security Investments Will Grow 12.1% in 2023 to $219 Billion“. IDC. March 16, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.
- 7. “Cybersecurity – Worldwide“. Statista. October, 2023. Retrieved April 4, 2024.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.