The backbone of IoT ecosystem is connectivity. IoT devices can connect and exchange data with each other via communication protocols.
You need to know what the top IoT protocols are, and how they work if you are looking to establish an IoT system in your organization. Explore the top 10 IoT communication protocols and their characteristics!
Comparison of IoT Communication Protocols
| Protocol | Standard | Frequencies | Approximate Range | Data Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WiFi | Based on IEEE 802.11 (common in homes) | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands | 50 to 100 meters | 600 Mbps maximum; 150-200 Mbps the most common |
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth 4.2 core specification | 2.5 GHz | 50 to 150 meters | 1 Mbps |
| Zigbee | Zigbee 2.0 based on IEEE802.15.4 | 2.4 GHz | 10 to 100 meters | 250 Kbps |
| MQTT | ISO/IEC 20922 | -- | -- | Up to 256 Mbps in size |
| Cellular Data | GSM/GPRS/EDGE(2G), UMTS/HSPA(3G), LTE(4G) | 900/1800/1900/2100MHz | 35km max for GSM; 200km max for HSPA | 35-170 Kbps |
| Z Wave | Z-wave Alliance | Various | 30 meters | 0.3 to 50 Kbps |
| NFC | ISO/IEC 18000-3 | 13.56 MHz | 10cm | 100-420 Kbps |
| LoraWAN | LoRaWAN | Various | 2.5km (urban environment), 15km (suburban environment) | 0.3 to 50 Kbps |
| Sigfox | Sigfox | 900 Mhz | 30-50 km (rural environments), 3-10 km (urban environments) | 10-10000 Kbps |
What’s the best IoT communication protocol?
The best IoT communication protocol depends on the specific requirements and constraints of a given system. Factors that plays a role in choosing IoT protocols are:
- Geographic locations: These is physical distances between the two or more devices that form an ecosystem
- Power consumption needs: This is the amount of time for which the IoT devices are stayed on
- Physical barriers: These are the barriers that exist between the devices within the IoT ecosystem (e.g. walls, mountains, skyscrapers, etc.)
- Overall budget: Different protocols cost differently
Short-Range IoT Communication Protocols
1. Wifi
It is one of the IoT communication protocols, best suited for LAN environments, which are computer networks that interconnect computers within a limited area, allowing for fast data transfer. It uses the Internet Protocol (IP) to communicate between endpoint devices.
- Smart home devices (smart cameras, thermostats, and lighting systems)
- Industrial IoT (IIoT), where local networks require high-speed connectivity
- Healthcare monitoring systems
- Cloud-based IoT solutions that require frequent data transmission
2. Bluetooth
Bluetooth, particularly Bluetooth 4.2, is designed for short-range wireless communication and operates in the 2.5 GHz frequency band.
- Low energy consumption, suitable for wearables and medical devices
- Short-range communication (10-100 meters)
- Supports secure communication with AES encryption
- Compatible with smartphones and IoT hubs
- Ideal for fitness trackers, smartwatches, and beacons
3. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
HTTP is a high-level application-layer protocol used for web communication and is not a physical transmission protocol like WiFi. It operates over TCP/IP networks and is one of the most widely used protocols in IoT devices that interact with cloud-based platforms. HTTPS (secured with SSL/TLS encryption) ensures data security and integrity during transmission.
- Cloud-connected IoT applications (smart home hubs, industrial monitoring dashboards)
- RESTful API-based communication for sending and receiving IoT data
- Web-based remote control systems for IoT devices
4. Zigbee
Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate protocol that uses mesh networking for extensive coverage. It operates across multiple frequencies (868 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2.4 GHz).
- Low power consumption and short-range wireless communication
- Operates on IEEE 802.15.4 standard
- Mesh networking for better coverage
- Ideal for home automation, smart lighting, and healthcare devices
- Supports AES-128 encryption for security
5. MQTT
MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol using a publish/subscribe model, optimized for low-bandwidth and low-power IoT devices. It is widely adopted in IoT platforms and supports real-time communication between devices and cloud services.
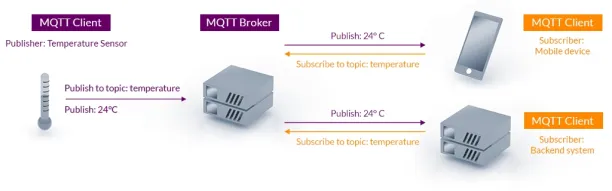
Source: MQTT
- Lightweight and efficient for low-bandwidth networks
- Publish-subscribe messaging model
- Supports Quality of Service (QoS) levels for reliable message delivery
- Secure communication using TLS encryption
- Ideal for industrial IoT, smart homes, and remote monitoring
6. Z Wave
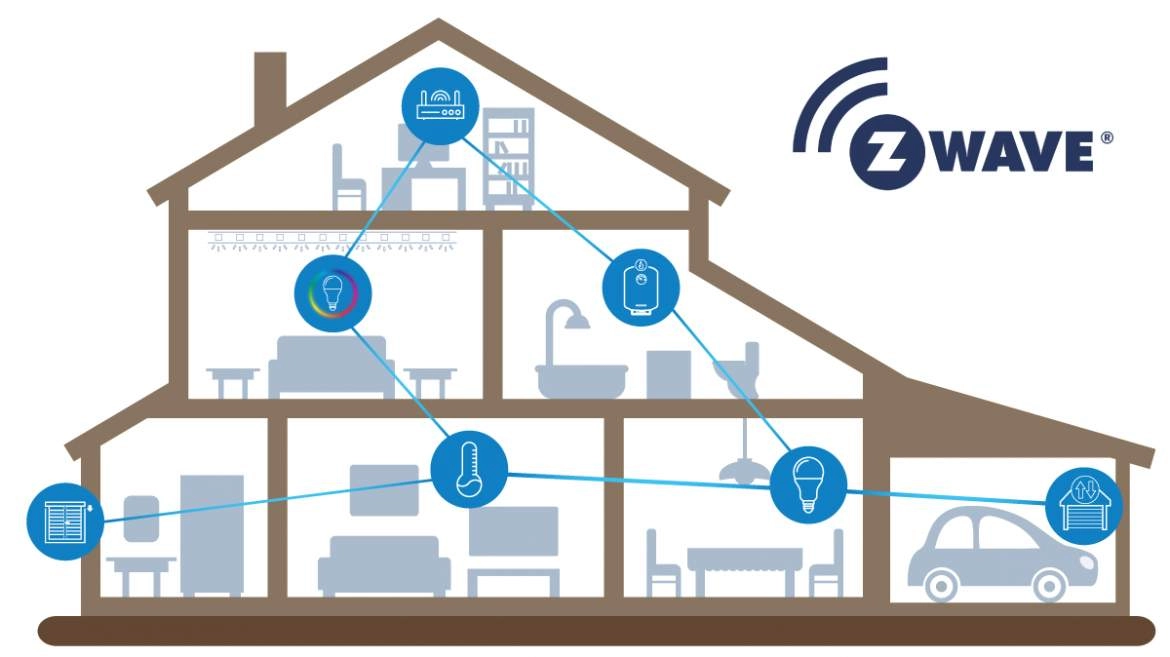
Z wave is based on low-power radio frequency (RF) communication technology. It’s highly preferable for smart home products such as lamp controllers, door locks, electronic kettles, etc.
- Optimized for smart home applications
- Uses sub-1 GHz frequencies for better range
- Low power consumption, ideal for battery-powered devices
- Mesh networking improves device connectivity
- Supports up to 232 devices per network
7. NFC (Near Field Communication)
NFC (Near Field Communication) is a short-range wireless communication technology based on the ISO/IEC 18000-3 standard. It operates at 13.56 MHz and has a minimal range of up to 10 cm, making it one of the shortest-range IoT communication protocols.
- Very short-range (up to 10 cm), ensuring secure communication
- Low power consumption, ideal for passive (battery-free) tags
- Fast data exchange, but low data transfer speeds compared to WiFi or Bluetooth
Long-Range IoT Communication Protocols
8. LoRaWAN

LoRaWAN is designed for long-range, low-power applications, making it ideal for smart cities, agriculture, and supply chain management. It can cover up to 15 km in rural areas and has excellent battery life, typically lasting several years.
- Long-range communication up to 15 km
- Low power consumption, ideal for battery-powered devices
- Uses unlicensed radio spectrum (ISM band)
- Suitable for smart agriculture, asset tracking, and remote sensing
- Supports bidirectional communication
9. Sigfox
Sigfox is a long-range network for machine-to-machine (M2M) applications, featuring lower power consumption compared to other networks. That makes it a good choice for connecting remote devices that have to run on batteries for long periods without charging.
- Ultra-narrowband technology for long-range communication
- Low data rate and ultra-low power consumption
- Uses unlicensed spectrum, reducing operational costs
- Best suited for asset tracking, agriculture, and environmental monitoring
- Provides global IoT network coverage
10. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IoT leverages existing cellular infrastructure to provide low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) capabilities. It is highly scalable, supporting millions of nodes with a battery life of over 10 years, making it perfect for smart metering and environmental monitoring.
- Cellular-based LPWAN technology
- Provides excellent coverage in urban and underground areas
- Very low power consumption for long battery life
- Ideal for smart cities, utility metering, and industrial IoT
- Supports high device density per network cell
For more on the Internet of things
To learn more about the Internet of Things and its use cases in different sectors, read:
- In-Depth Guide to IoT Monitoring: Pros, Cons, & Importance
- Ultimate Guide to IoT Security: Challenges & Tools to Tackle Them
- Edge Computing: A Better Alternative Than Cloud for IoT
If you believe your business will benefit from an IoT solution, feel free to check our data-driven hub of IoT solutions and tools.
FAQ
What are IoT communication protocols?
IoT communication protocols are the rules and standards that define how devices within the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem exchange data and communicate with each other. These protocols manage the connectivity, data transmission, and interactions between IoT devices, enabling them to work together and share information efficiently. They can be categorized into two main types:
Network Communication Protocols: These protocols manage the connectivity and communication over networks, including the transmission of data between devices. Examples include WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN. These protocols typically operate at the physical and data link layers of the network stack and are responsible for ensuring that data packets are transmitted across networks.
IoT Data Protocols: These protocols facilitate the transmission of data between devices and are designed to operate on low-power, resource-constrained devices. Examples include MQTT, CoAP, and AMQP. These protocols often work at the application layer and handle the actual exchange of messages, commands, and data.
Why are IoT communication protocols important?
IoT protocols are crucial because they ensure interoperability and efficient data exchange between various devices in an IoT ecosystem. Without standardized protocols, devices might struggle to connect and share information, leading to compatibility issues, security vulnerabilities, and inefficient data transmission.
Which IoT protocol is best for long-range communication?
For long-range communication, LoRaWAN and NB-IoT are top choices. LoRaWAN is optimized for long-range, low-power applications and can cover distances of up to 15 km in rural areas. NB-IoT leverages existing cellular networks to provide wide coverage with low power consumption, suitable for large-scale IoT deployments.
What is the difference between Zigbee and Z-Wave?
Both Zigbee and Z-Wave are iot communication protocols used in home automation, but they differ in frequency and range. Zigbee operates on 2.4 GHz and supports mesh networks with a higher data rate but shorter range. Z-Wave operates on sub-GHz frequencies (e.g., 868 MHz) and offers a longer range with lower data rates.
This article was originally written by former AIMultiple industry analyst Bardia Eshghi and reviewed by Cem Dilmegani.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.