Worldwide annual revenue on IoT in 2033 is expected to be $934B.1 IoT enables a myriad of different business applications. Knowing those IoT examples and use cases can help businesses integrate IoT technologies into their future investment decisions.
Explore 40 IoT applications for business leaders to select the correct use case for their IoT implementation:
Smart Factories
1. Enterprise asset management
Enterprise asset management involves work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, supply chain management, and environmental, health, and safety (EHS) initiatives.2 Businesses collect real-time data from an asset with IoT sensors.
Businesses are rapidly adopting smart asset management systems into their businesses. Due to their asset-intensive environments, we mostly encounter IoT asset monitoring in industries such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing.
IoT-powered asset management increases real-time visibility of assets and helps businesses optimize their resource while providing benefits such as:
- Increased operational efficiency
- Better control over the sales lifecycle
- More efficient safety and compliance checks
- More responsive smart environment.
2. Predictive maintenance
Maintenance is conducted to prevent predicted problems. So over the lifetime of a machine, some components may never be checked if they are not predicted to cause problems.
For example, A robotics company that is working on reducing the downtime of machines with IoT technology uses sensors to predict when the failure of the component will happen.3
3. Industrial process automation/optimization
Organizations can keep a real-time record of the metrics of all the machines inside a plant using IoT and IP networks. Manufacturers can use this data to automate workflows and optimize production systems. Automation and optimization support industrial companies to reduce costs and increase the quality and volume of output.
The market for automated industrial robots is proliferating. The market size is expected to reach $165 billion in 2028.4
4. Energy management
Energy can be a costly input for industrial businesses. With fluctuating energy costs and strict government requirements for efficiency, managing energy distribution becomes important.
IoT devices can help manufacturers manage energy consumption based on real-time data collected from devices. Intelligent energy management systems reduce energy bills, operational expenditures, and the carbon footprint of the factory while increasing energy efficiency. Some IoT platforms provide IoT applications, including energy management, to optimize the energy consumption of businesses.5
Smart Cities
Kay Sharpington from Gartner, states “…Governments across the globe continue to use IoT technologies and solutions to improve citizen safety. At the same time, the falling endpoint and connectivity costs make smart city initiatives more viable”.6
With the growing interest in smart cities and the demand on IoT services, the IoT in Smart Cities Market is expected to expand from $230 billion in 2024 to ~$1,5 trillion by 2034. 7 Some of the use cases of IoT applications in smart cities are listed below:
5. Outdoor surveillance
IoT-enabled surveillance systems integrated with artificial intelligence and machine vision allow governments to automate monitoring of streets using connected devices such as IoT CCTV cameras.
These IoT systems collect data, process video feeds in real time, and provide actionable insights to law enforcement, enhancing public safety. However, as these devices process personal information, implementing robust data encryption, access control, and oversight mechanisms is critical to minimize risks of misuse while maintaining security.
6. Smart lighting
Smart lighting systems use IoT sensors to collect data on traffic and pedestrian conditions, optimizing energy usage and improving resource management. These systems automatically adjust lighting levels, saving up to 70% of energy and reducing costs for city infrastructure.8
Beyond public spaces, IoT-enabled smart lighting can also be extended to smart buildings and industrial IoT applications, providing scalable solutions for energy-efficient operations.
7. Electronic road toll collection and traffic management
IoT technology enhances traffic management by leveraging IoT networks and devices to monitor and analyze traffic flow in real time. Data collected by IoT sensors is processed through machine learning algorithms at traffic management centers to optimize traffic signal timing, reducing congestion. Additionally, automated systems for electronic toll collection streamline vehicle flow, improving fleet management and creating more efficient road networks.
8. Public transport optimization
IoT solutions in public transport leverage connected devices to provide passengers with real-time updates on schedules, delays, and estimated arrival times. IoT platforms also enhance fleet management by optimizing routes, schedules, and energy usage for buses, trains, and trams. By improving resource management, IoT systems create better commuting experiences and maximize the efficiency of mass transit infrastructure.
9. Smart parking
In cities like San Francisco, parking is a big problem. IoT solutions simplify parking by connecting IoT sensors to parking lots to detect vehicle presence and exchange data with mobile devices. IoT platforms process the data and share real-time updates on vacant spaces with drivers via mobile apps, enabling smoother parking experiences.
By reducing time spent searching for parking, smart parking systems enhance resource management, reduce traffic congestion, and improve overall city infrastructure efficiency.
- The working principle of smart parking is:
- Drivers check mobile apps to identify vacant parking spaces close to the location they aim to go to.
- Sensors are attached to parking lots to detect parked cars
- Measurements are periodically sent to the cloud by microcontrollers
- Mobile Apps use cloud data to identify empty parking spaces,
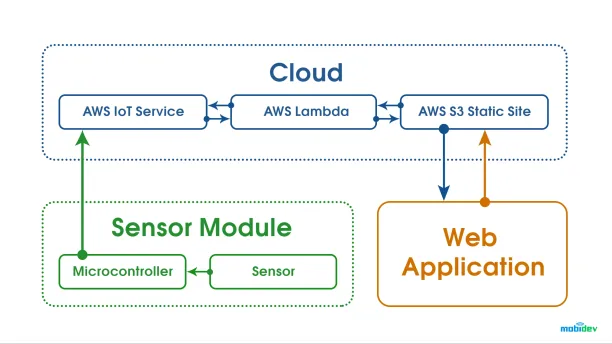
Source: Mobidev9
10. Noise Monitoring
Smart cities implement IoT devices for noise monitoring to maintain acceptable noise levels in urban areas. IoT systems continuously monitor sound levels, process data in real time, and alert organizations or businesses violating noise regulations. These connected devices help optimize urban environments and improve quality of life while ensuring compliance with local laws.
11. Structural health monitoring
IoT-enabled predictive maintenance systems facilitate continuous monitoring of buildings, bridges, and other critical structures. IoT devices collect real-time data on vibrations, material wear, and structural conditions, which is analyzed to predict potential failures. By using machine learning algorithms, these systems optimize maintenance schedules, enhance worker safety, and prevent costly structural damage.
12. Waste management
Traditional waste collections are complicated and costly since a fleet of trucks drives along busy streets using inefficient routes. Fill levels of garbage containers differ for each container, ranging from overflowing to partially filled to empty. IoT sensors can monitor fill levels for conventional bins and send the data to the relevant department of the city hall. With that information, the garbage truck routes can be optimized for trash collection.
Machine learning methods can also be implemented in IoT sensors (i.e. edge analytics) so that sensors can predict the fill levels of containers by learning from historical data.
Below the video, you can find how Proximus, an IoT solutions vendor, uses IoT to manage waste:
Water Management
Due to the drastic increase in urbanization levels and the importance of water quality in human health, water management is a key topic for cities. A water management system is based on real-time data collected from sensors. Water management can provide the following applications:
13. Water conservation
Sensors detect the water level in tanks and alert when the water level is lower than the threshold. Some smart home water conservation systems use IoT sensors to monitor water usage.10
14. Smart irrigation
IoT sensors determine the weather conditions and the soil moisture, which will help in getting the appropriate amount of water that the soil needs. For instance, A vendor that offers a sprinkler sensor optimizes its functionality based on the dryness of the soil.11

Source: Tech Hive12
15. Leakage management
IoT sensors play a crucial role in leakage management by continuously monitoring water tanks and pipelines for temperature fluctuations, pressure levels, and chemical leaks. These connected devices collect data in real time, enabling IoT systems to identify leaks early and prevent potential damage.
By integrating IoT technology with automated systems and predictive maintenance solutions, organizations can optimize resource management and enhance operational efficiency.
16. Water quality management
IoT-enabled devices enhance water quality management by analyzing key metrics such as total dissolved solids (TDS), bacterial content, chlorine levels, and electrical conductivity. These smart devices use IoT networks to collect and process data, providing actionable insights on chemical composition and ensuring safe water supply.
Through real-time monitoring and IoT software solutions, businesses and municipalities can maintain compliance with safety standards while improving sustainability efforts.
Learn more about IoT in agriculture.
Digital Health
17. Ultraviolet radiation monitoring
Sunlight consists of three major components:13
- Visible light: Wavelengths between 0.4 and 0.8 micrometers,
- Ultraviolet light: Wavelengths shorter than 0.4 micrometers,
- Infrared light: Wavelengths longer than 0.8 micrometers.
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are electromagnetic waves that account for about 10% of solar light. When overexposed, UV rays have harmful effects such as skin cancer, premature aging, cataracts, and immune system suppression. IoT sensors measure UV sun rays to warn people not to be exposed during certain hours.
18. Fall detection
Falling to the ground and not being able to get up or request help can be a scary experience for senior citizens. IoT sensors can detect falls using geolocation data and summon help so that it reduces the time the elderly remain on the floor after a fall which could lead to lethal consequences.
19. Companion robots
A companion robot is a robot that is designed to create companionship mostly for elderly and single children. IoT sensors are essential for robotics and it is the same for companion robots as well. Sensors detect objects that surround the robot and enable the robot to move.
People have become more receptive to companion robots during the pandemic.14 Social isolation may lead people to loneliness, anxiety, and frustration, especially the elderly.
20. Medical fridges
Medical fridges monitor the temperature of vaccines, medicines, and organic elements for clinics and health centers. Medical fridges provide an opportunity to follow all safety standards and national regulations of the pharmaceutical market using IoT sensors. They prevent medicines and vaccines from spoiling.
Efento is an IoT sensor and IoT platform vendor that has a variety of temperature measurement products and wireless temperature monitoring in medical refrigerators.15
21. Patient surveillance/remote patient monitoring
20% of patients who had surgery are readmitted to the hospital within just 30 days.16 Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems use wearables to monitor the condition of patients who are resting at home after surgery. RPM enables real-time data collection about patients’ body temperature, which is the main indicator of infections.
With RPM, doctors can observe patients’ data and provide early diagnoses without requiring patients to be physically present at the hospital.
Telit is an IoT solution vendor and offers its customers a remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution that enhances patient monitoring capabilities and patient satisfaction.17 Telit’s offering can reduce:
- Patients hospital stay duration thanks to early diagnosis of complications
- Hospital readmissions
Smart Retail
22. Supply chain control
IoT devices have transformed supply chain management. Sensors, which are attached to storage containers or products themselves,
- show the location of goods using GPS,
- track the speed of movement, providing an accurate estimated time of arrival (ETA) for goods,
- monitor warehouse conditions such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and other environmental factors
23. Near-field communication (NFC) payment
NFC enables contactless payments. POS vendors include NFC support in their systems, and customers are adopting contactless payments via their smartphones.
24. Layout optimization
Sensors in the store collect data like voice, image, or video to better understand customer habits and preferences. Retailers can get insights to redesign the layout of their stores. The optimized layout can enhance sales.
25. Smart product management
IoT sensors enable retailers to control the rotation of products on shelves and warehouses to automate merchandising decisions. We have already written about retail analytics use cases, feel free to check it out if you want to learn more.
Smart Workplace
26. Sociometric badges
Sociometric sensors are wearable IoT devices that measure the amount of face-to-face interaction, conversational time, physical proximity to other people, and physical activity levels using social signals derived from vocal features, body motion, and relative location.
For example, Humanyze is a vendor that uses sociometric sensors to perform people analytics.18 The company helps organizations understand how their teams interact to increase performance.
Smart Homes
27. Remote control appliances
IoT-powered home appliances let residents remotely switch on and off devices using smartphone apps to avoid incidents and save energy. Additionally, these devices can make autonomous decisions based on sensor inputs, such as preparing fresh coffee when a resident is identified to wake up. Other examples of autonomous or remote-controlled actions include:
- Turning on lights,
- Starting the coffee maker,
- Setting temperature,
- Open up a music playlist,
- And locking doors.
Home Intrusion Detection Systems:
IoT-based home security applications give users capabilities such as smart locks and security cameras that detect motions and send alerts to their smartphones so that they can monitor the safety conditions of their homes from anywhere.
28. Smart locks
Smart locks enhance security by allowing remote access control and real-time monitoring through connected networks. Eyelock is a security provider vendor that offers its clients an iris-based authentication solution.19
29. Motion detection
Motion detection devices are also IoT applications used in security. Manything is another vendor in the IoT-based home security market.20 It streams home/office videos and lets users receive alerts when it detects any activity.
Smart Logistics
30. Fleet tracking
IoT fleet tracking systems improve security and provide precise and complete reports that give the fleet managers full transparency regarding the fleet’s activities. Through GPS monitoring and geo-location tools, companies can track the location of their trucks, optimize routes, and monitor their fleet utilization in detail.
For instance, Canadian delivery service Sure Track Courier saved 6-10% per month on fuel costs by optimizing routes using IoT data from trucks.21
31. Platooning
Platooning involves a group of self-driving trucks that follow a lead truck at high speed safely and efficiently. Trucks use IoT sensors so that each truck communicates with the other trucks to adapt its speed and braking accordingly.
32. Connected vehicles
Sensors are enhancing vehicles along with AI and analytical capabilities. These sensors provide communication with the driver to supply useful information about other cars on the road and roadside infrastructure to the driver to help the driver make safer or more informed decisions. For example, these vehicles provide GPS-enabled location detection features that help them detect traffic congestion.
Autonomous vehicles are also applications of IoT devices. Though it is not commonly used in logistics yet, we will witness this approach soon. For instance, the Mercedes-Benz prototype of the semi-autonomous truck is scheduled for release in 2025.22
Smart Metering
33. Smart grid
With the increasing attention regarding climate change and carbon emissions, utilities focus on reducing energy consumption. For utility companies, IoT enables remote data management and monitoring capabilities to manage better power flows into and out of their grids, and give users the insights needed to understand their energy infrastructure investments.
34. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of physical entities such as devices, people, processes, or systems that help businesses make model-driven decisions. With the help of IoT sensors, businesses collect data that is needed to create a digital twin.
Digital twins enable businesses to gain a deeper understanding of real-world conditions so that they make necessary adjustments to their products & services.
Healthcare
35. IoT devices in healthcare
In healthcare, the ecosystem of IoT-enabled devices such as wearables (smartwatches, rings, vests, etc.), monitors (heart monitors, sleep monitors, temperature monitors, etc.), and trackers (medication refill reminder, drug effectiveness tracking, etc.) can be used for:
- Constant monitoring of patients’ vitals (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature rate, etc.),
- And more accurate diagnoses of patients, thanks to real-time data from IoT devices, thus reducing the possibility of readmission and rising hospital bills.
Banking industry
36. Wearables and smart devices

Source: 7 Ring23
IoT-enabled wearables and smart devices are enhancing banking experiences through contactless payments and financial habit monitoring:
Devices like NFC-enabled smartphones, fitness trackers, rings, and smartwatches provide easy access to credit/debit cards and checking accounts for secure, on-the-go transactions. 7 Ring is an example of a contactless wearable IoT payment device.
Clients can set spending limits on their wearable devices, which track daily transactions. When spending approaches the set limit, the device sends alerts, helping users manage their finances and reduce overspending.
37. IoT-enabled ATMs
Modern ATMs leverage IoT technology to optimize customer service and reduce operational costs:
IoT-enabled ATMs can self-diagnose maintenance needs and automate cash replenishment, ensuring operational efficiency. IoT sensors monitor foot traffic around ATMs, providing banks with data to optimize placement or branch locations. Some ATMs offer live-stream video consultations, enabling customers to interact with bank advisors in real-time.
38. Blockchain-based banking services
The integration of IoT and blockchain technology is transforming financial transactions and data management:
Blockchain enhances security and transparency, enabling participants to conduct direct transactions without intermediaries. IoT-powered blockchain solutions, such as smart contracts, simplify international trade transactions, reduce maintenance costs, and address infrastructure challenges.
Financial institutions are investing in blockchain startups and developing their own IoT-driven blockchain solutions to modernize services.
39. Indoor navigation solutions

Source: PARTTEAM & OEMKIOSKS24
IoT enhances customer service efficiency within smart bank branches:
IoT devices monitor queues, provide estimated waiting times, and direct customers to free counters, minimizing delays. Mobile apps allow clients to book, manage, and monitor appointments, enabling a more streamlined experience. IoT facilitates seamless interaction between branches in different locations, reducing staffing needs and operational costs.
40. Mobile banking chatbots
IoT has enabled the proliferation of AI-powered chatbots in banking, offering round-the-clock customer service:
Chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to deliver tailored interactions and improve with every customer query. By automating common support requests, chatbots reduce response times and operational expenses and free staff to focus on more complex tasks.
Text-based chatbots are accessible via preferred communication channels, enhancing customer satisfaction and engagement.
Learn more about IoT in banking industry.
FAQs
How does IoT work?
There is not a single IoT architecture; however, the most basic and commonly agreed format is the three-layer architecture.
Perception Layer: It refers to the physical layer of the architecture. It involves sensors, actuators, and edge devices that are embedded in ‘things’. They collect data from the environment in which they operate.
Network Layer: It handles the transmission and processing of all collected data. Through routers and gateways, IoT devices could be connected to other smart devices, servers, and network devices.
Application Layer: It performs end-user services and consumer applications. It is the layer where consumers interact with the devices.
What are the challenges of IoT applications?
Security
As the number of IoT devices grows, security control over each device becomes harder. Also, many IoT devices do not share encrypted data with servers. This problem could be prevented with new machine learning approaches such as federated learning. This is especially important for healthcare applications since data privacy has greater importance in that industry.
Compatibility
As the number of IoT devices are expected to increase to 3 per capita, it becomes challenging to achieve interoperability between different devices and servers. However, world-leading technology companies including Apple, Amazon, and Google have formed the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) to increase adaptation and standardization in the IoT industry.
Further reading
We have written articles about IoT technologies before, feel free to read our other articles on:
- Increase Speed to Market Using an IoT Platform
- Edge Analytics: What it is, Why it Matters & Use Cases
- IoT Testing: Framework, Challenges, Case Studies & Tools
We also have some in-depth articles on other use cases of IoT in different industries:
- Top 6 Use Cases of IoT in Manufacturing
- 5 Use Cases of IoT in Automotive
- 7 Ways IoT Will Improve Your Banking Experience
Finally, if you believe your business could benefit from implementing an IoT solution, we have a data-driven list of vendors prepared.
External Links
- 1. Worldwide IoT revenue 2034| Statista. Statista
- 2. What Is Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)? | IBM. IBM
- 3. Installation - Find more information on field and maintenance.
- 4. Global Industrial Robotics Market by Type, Application, Industry & Geography - Forecast to 2024. Cision PR Newswire
- 5. Zoho IOT | A low code IOT platform and tailored solutions.
- 6. Gartner Says Government IoT Revenue for Endpoint Electronics and Communications to Total $15 Billion in 2020. Gartner. Accessed: January/23/2025.
- 7. Iot Smart Cities Market Size, Share & Trends [2034].
- 8. Swiss cities leverage smart lighting to save energy - Cities Today. Cities Today
- 9. IoT-based Smart Parking System Development - MobiDev . MobiDev
- 10. Well - Home Water Conservation System - The Index Project.
- 11. GreenIQ Smart Garden Hub Gen 3 review: A pricey sprinkler with some unique add-ons | TechHive. TechHive
- 12. GreenIQ Smart Garden Hub Gen 3 review: A pricey sprinkler with some unique add-ons | TechHive. TechHive
- 13. Sunlight | Definition, Wavelengths, & Facts | Britannica. Encyclopedia Britannica
- 14. Researchers find people are more receptive to social robots during the pandemic | VentureBeat. VentureBeat
- 15. Efento. GetEfento. Accessed: January/22/2025.
- 16. How IoT Can Improve Data Access for Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions | IoT For All.
- 17. Health Monitoring Solutions and Devices | Telit Cinterion. Telit
- 18. Drive Performance & Retention with A.I.-Powered Workforce Analytics.
- 19. Eyelock. Eyelock. Accessed: January/21/2025.
- 20. Monitor anything with Manything - Videoloft.
- 21. Sure Track Courier drives down costs and accelerates business with mobile solutions from Bell. Bell. Accessed: January/21/2025.
- 22. Please make a U-turn. Mercedes-Benz. Accessed: January/23/2025.
- 23. 7 Ring – India’s first contactless payment wearable ring.
- 24. Queue Management | PARTTEAM & OEMKIOSKS. OEMKIOSKS


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.