CMMS vs EAM in 2024: What are the differences?
Up to 10% of a company’s production time and 20% of productivity can be lost due to unplanned downtime, which can cost $50 billion for manufacturers each year. To prevent such losses due to maintenance-related problems, companies in asset-intensive industries such as manufacturing, construction, or mining appeal to asset maintenance management solutions such as EAM and CMMS. In this article, we will present CMMS and EAM and explore the differences between them.
What is CMMS?
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software that facilitates asset maintenance processes by centralizing maintenance-related information. CMMS was first adopted in the manufacturing sector in the 1960s and has since evolved and expanded into other industries including communication, education, healthcare, and transportation. In their business processes, around 40% of companies use CMMS and 30% of them are planning to implement it.
With its database, a CMMS enables streamlining maintenance inventory management by automating stock control, keeping track of the work orders, providing the organization with preventive maintenance solutions, and recording the list of assets in detail.
What are the benefits of CMMS?
- Centralizing maintenance information: CMMS centralizes all the necessary information about asset maintenance, from asset details to repair guide and maintenance histories. This makes maintenance-related information accessible to all relevant employees.
- Managing preventive maintenance effectively: CMMS allows businesses to keep track of the condition of assets, compare the actual data with historical data about their maintenance, and predict repair times and costs. It facilitates planning maintenance for each asset, keeping a list of actions to be taken, recording data about the condition of assets and their malfunctions, and providing access to these records through an application.
- Saving energy: With a preventive maintenance approach, organizations can save %18 of energy, whereas %30-%60 of energy can be wasted in a reactive approach. As a result, organizations can lower energy costs and increase energy efficiency by using CMMS in their business processes.
Check our article on the benefits of CMMS for a more comprehensive account.
What is EAM?
Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) is a tool that is created to centralize the management and maintenance processes of assets. An EAM system can be used through both on-premise and cloud infrastructure.
Source: SAP
EAM is used for improving the quality of asset lifecycles, improving health and safety conditions, and optimizing asset performance through the development of effective strategies from the planning phase to the replacement phase. In asset-intensive sectors such as transportation and manufacturing, EAM is used to facilitate the operations and asset maintenance processes. According to a report, the global EAM market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7%, and reach $5.5 billion in 2026.
What are the benefits of EAM?
- Improving decision-making: With its ability to provide accurate and real-time data, EAM gives organizations the ability to make data-driven decisions about their assets.
- Enhancing worker safety: Integrating EAM with Environmental, Health, and Safety solutions allows creation a safe working environment through predictive maintenance, its ability to detect possible risks, and the collection of security weaknesses and failures.
- Centralizing asset information: With EAM, asset information is collected in a centralized manner, enabling easier monitoring, maintaining, and planning.
- Decreasing operational costs: By providing information about the performance of physical assets and their maintenance status, EAM can decrease operational costs and ensure savings for organizations.
What are the differences between EAM and CMMS?
EAM and CMMS can be confused due to their overlapping qualities. Both tools are preferred by companies in asset-intensive industries and both of them provide organizations with tools to facilitate inventory management, preventive maintenance, work order planning, and also purchasing management. The key differences between them are their:
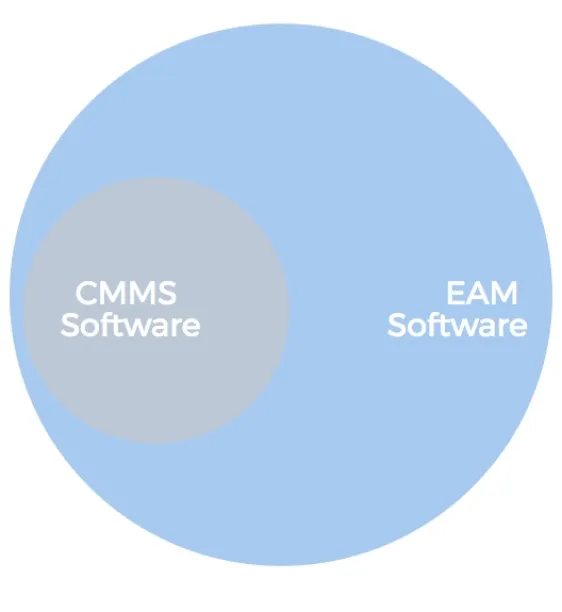
Source: Comparesoft
- Scope: CMMS only focuses on assets that are in use by an organization. EAM, however, focuses on the entire asset lifecycle, from planning to disposal.
- Focus area: CMMS is primarily concerned with asset maintenance, whereas EAM has a broader range of functions. Supply chain and human capital management processes, as well as health and safety processes, are also of interest to EAM.
- Users: The differences between their scope and functions also differentiate their users. CMMS offers functionality to maintenance and operations professionals, whereas EAM’s user portfolio includes other departments (such as finance and compliance teams) as well.
- Complexity: Finally, since EAM has a more advanced structure, it is better suited to larger organizations with a large number of assets in different locations.
If you have questions about EAM, CMMS and how to get started with them, we can help:

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.