In-Depth Guide to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in 2024
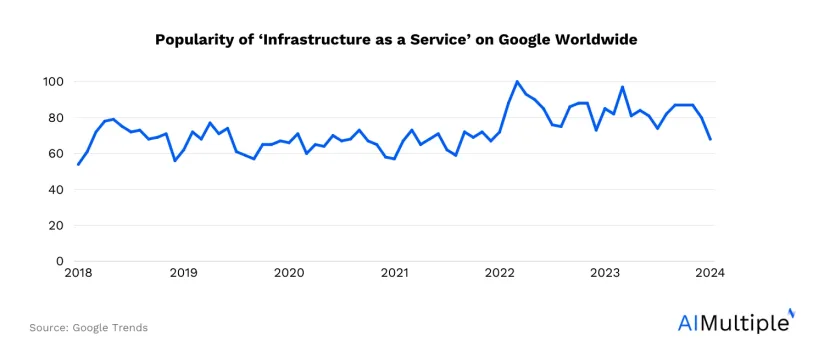
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a model of cloud computing that provides essential IT infrastructure components such as computing power, storage capacity, and networking resources through the internet on an on-demand basis. IaaS is a form of cloud service, alongside Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and serverless computing.
Cloud computing statistics shows that IaaS captures a significant interest; the IaaS sector in the cloud industry is projected to grow by approximately 30%in 2024 compared to its size in 2022.1 This could be the result of flexibility the model offers users to request and customize resources according to their specific application and IT system needs.
Even within IaaS, the cloud market is huge. In this article, we will provide you with detailed information on the subject and help you to make your choices more informed.
Top 5 IaaS providers
Amazon AWS dominated the worldwide infrastructure as a service (IaaS) software market. Microsoft follows AWS with around 25%.

Source: Gartner2
Figure 1. IaaS Market Share.
How does IaaS operate?
IaaS operates by virtualization; it mainly allows you to choose and configure the infrastructure types you need. In cloud computing, IaaS mostly refers to renting access to cloud infrastructure resources from a cloud service provider (CSP) like AWS. This service includes:
- servers
- virtual machines
- networking
- and storage.
Thus, in the IaaS model, each resource is offered as a separate service component. The IaaS platform automatically generates digital versions of this infrastructure and virtualized computing resources that simulate the physical one.
Provider & user responsibilities in IaaS models
In Iaas users can have specific responsibilities that include:
- Deployment: Users are responsible for deploying their applications, services, or workloads onto the virtual machines or other compute resources provided by the IaaS platform. This involves setting up the necessary software, applications, and configurations required for their business needs.
- Maintenance: Users must maintain the applications deployed. This includes regular updates and patches to ensure software is up-to-date and secure. Performance monitoring and optimization to ensure applications are running in an efficient manner can also be included in this phase.
- Support: Typically, users are responsible for providing end-user support for the applications running on the IaaS platform. The process can involve troubleshooting application issues & managing user access.
The IaaS provider, on the other hand, is responsible for the physical infrastructure and foundational technologies that support the IaaS, including:
- Hardware maintenance: IaaS providers are responsible for all aspects of the physical hardware maintenance, including servers, storage, and networking equipment. Regular hardware upgrades, repairs, and replacements can also be included under this title.
- Infrastructure Management: Providers manage the data center infrastructure. This can include power management, cooling systems, physical security, and disaster recovery measures.
- Network management: They are also responsible for managing the network infrastructure, ensuring robust and secure internet connectivity, network performance, and implementing network security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems.
- Virtualization and resource allocation: Providers should manage the virtualization layer that allows for the creation of virtual machines and resources.
- Compliance and security: Ensuring compliance with relevant data protection regulations and maintaining high-security standards to protect the infrastructure from cyber threats can be identified as some of the critical responsibilities of IaaS providers.
Key benefits of IaaS model
First, this model enables you to avoid the expenses and complexities associated with purchasing and managing physical servers and data center infrastructure. You only pay for the resources you use and for the duration you need them.
Second, with the exemption of need to purchase physical hardware, the CSP takes on the responsibility of managing and maintaining this infrastructure, which can spare more time for businesses to focus on software installation, configuration, and data security.
Third, IaaS providers can offer additional services such as:
- detailed billing
- management
- logging
- monitoring
- storage resilience
- security
Fourth is disaster recovery. Normally, disaster recovery can be costly due to the need for extensive technology and a sizable workforce. IaaS providers offer access to an unlimited infrastructure specifically designed for backup and disaster recovery purposes. You can replicate your applications across multiple servers which provides a fail-safe if one server fails, as another can immediately take over. Additionally, most of the IaaS providers enable the automatic and frequent synchronization of data backups.
Fifth is the global reach. IaaS providers often offer a global network of data centers.
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS
In the IaaS model, providers manage the backend infrastructure, including elements like computing power, storage, networking, and virtualization. The users are responsible for managing the operating system, middleware, data, and applications. In sum, IaaS offers the raw materials of IT infrastructure and leaves the details and operations to the user.
PaaS models offer the backend infrastructure similar to IaaS but additionally supply a suite of software tools and features necessary for application development. Users are responsible for coding and managing their applications and data. Yet, they are relieved from the burdens of managing the underlying software development platform.
SaaS models represent the most extensive service. This means providers handle everything from the application itself to the infrastructure required to host and run it. The user only accesses the application over the internet while the provider takes responsibility for maintenance, management, updates and other services.
| Service | Application | Data | Runtime or software that runs the application | Middleware or software that monitors the application | Operating systems on which the application runs | Virtualization technology | Server machines | Storage devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Paas | 🟡 | 🟡 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| SaaS | 🟡 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| User | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 | 🟡 |
* Yellow cells highlight the components you are responsible for managing.
* Green ticks indicate the elements managed by the cloud service provider.3
Key components of IaaS

Figure 3. Key Components of IaaS
The key components of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) that are fundamental to its operations include:
- Compute Resources: Compute resources can include GPUs, virtualized servers or Virtual Machines (VMs) that provide computing power for running applications and services.
- Storage: IaaS storage can include different types such as file storage, block storage and object storage.
- Networking: Networking capabilities related to IaaS can encompass cloud services including virtual networks, load balancers, and VPNs (Virtual Private Networks).
These three components – compute resources, storage, and networking – are considered the pillars of IaaS. The other components can be counted as:
- Load balancing
- Firewalls and security
- Physical infrastructure (data centers)
- Management and automation tools
Successful real-world examples & use cases of IaaS
Netflix
Netflix works with Amazon Web Services (AWS), an IaaS provider. This allows Netflix to handle massive amounts of data and streaming traffic, scale up or down depending on demand. AWS allows Netflix to rapidly deploy thousands of servers and terabytes of storage.4
Dropbox
In 2018, Dropbox used AWS’s S3 storage service to manage its massive amount of data. Although Dropbox later migrated most of its storage in-house, its initial growth and scalability were significantly supported by the IaaS model.5
Cleveland Clinic
Hospitals and healthcare providers have used IaaS to manage patient records and data securely. Cleveland Clinic is one of the examples that uses cloud services to analyze patient data for research and treatment.6
Etsy
Many e-commerce companies utilize IaaS to handle their traffic loads, particularly during peak seasons. Etsy, an e-commerce website focused on handmade or vintage items, can be a representative example. Etsy uses IaaS to scale its infrastructure during high traffic periods like holiday seasons. Google claims that through the use of GCP, Etsy was able to:
- Save 50% + computing energy
- Reduce 42% percentage of compute costs
- Migrate 5.5 petabytes of data.7
Zynga
Zynga used AWS to carry out several proof of concept (PoC) tests to evaluate their analytics platform infrastructure with the latest Amazon EC2 instances. This led to the development of an analytics management solution that initially halved the size of their 230-node zCloud cluster to a 115-node cluster within AWS. Further efficiency and performance enhancements achieved through additional PoC efforts allowed the solution to operate effectively on clusters as small as 70 nodes.8
Steps to implement IaaS

Figure 4. Steps to implement IaaS
- Assessment and planning:
- Businesses should evaluate their current IT infrastructure & identify which components can be moved to an IaaS model.
- Determine the specific requirements for compute, storage, and network resources.
- Choose the right IaaS provider:
- Compare various IaaS providers based on factors like cost, scalability, security and more.
- Consider the provider’s geographical coverage for latency and legal compliance.
- Architecture Design:
Design the cloud architecture that best fits your needs. This includes deciding on the type of VMs, storage options, and networking setup. - Data Migration:
Develop a data migration plan that guarantees an efficient transfer of data to the cloud. This may involve the use of migration tools provided by the IaaS provider or third-party tools.
Further reading:
- Cloud GPU Platforms
- Top Cloud Collaboration Tools of 2024
- 40+ Cloud Computing Stats From Reputable Sources in 2024
- Cloud GPUs for Deep Learning: Availability & Price / Performance
- Cloud Deep Learning: 3 Focus Areas & Key Things to Know in ’24
- Amazon Web Services Alternatives with focus on Compute & AI
External Links:
External Links
- 1. “Public cloud services growth 2022-2024 | Statista”. Retrieved on January 16, 2024.
- 2. “Gartner Says Worldwide IaaS Public Cloud Services Revenue Grew 30% in 2022, Exceeding $100 Billion for the First Time” Gartner. Retrieved on January 16, 2024.
- 3. “What is IaaS? – Infrastructure as a Service Explained – AWS” AWS. January 16, 2024.
- 4. “Netflix Case Study” January 16, 2024.
- 5. “ Dropbox migrates to Amazon S3 analytics data lake” January 16, 2024.
- 6. “Cleveland Clinic and Oracle Shape the Future of Healthcare” January 16, 2024.
- 7. “Etsy Case Study | Google Cloud” January 16, 2024.
- 8. “Zynga Case Study” January 16, 2024.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.