RPA can automate repetitive tasks in the front and back offices. A use case-focused approach is critical to optimizing the value of technology investments.
We identify 100 use cases and real-life examples of Robotic Process Automation, illustrating its application in automating repetitive tasks across various business, industry-specific, and personal contexts.
RPA Software use cases with real-life examples
Fraud detection
Identifying suspicious transactions and behaviors to prevent financial loss and cybercrime.
Real Life Examples

John Lewis, a leading UK retailer, implemented Blue Prism's connected-RPA solution to optimize operational efficiencies and increase productivity. They automated various business processes, including fraud detection, price match requests, and handling returned goods. The implementation resulted in cost savings, improved customer experience, and time savings.

The Very Group, an online retailer in the UK, implemented Blue Prism's RPA solution to combat fraud. By using the automated parcel decision engine called 'GLITBot', the company quickly detects fraudulent purchases and issues credits to affected customers within 30 minutes. This has resulted in £4.2 million in cost savings associated with fraud and improved customer experience.

Patelco, a financial services company in the United States, partnered with Automation Anywhere to automate processes such as loan payoffs and fraud alerts. By implementing RPA solutions, Patelco achieved faster fulfillment, faster loan payoff calculations, efficiency gains, accuracy improvements, and cost savings. The company plans to expand automation to other areas such as mortgage applications and internal audit. The case study was created in 2020.
Web scraping
Extracting data from websites for analysis, research, and automation.
Real Life Examples

S&P Global, a financial services company, used AntWorks RPA solution to automate the retrieval and aggregation of data from multiple sources. By implementing QueenBOT RPA, the company achieved 100% data accuracy, reduced processing time by 50%, and expanded its range of services without adding staff. The streamlined process resulted in monetary savings, improved productivity, and reduced errors.
Document management
Streamlines the categorization, storage, retrieval, and version control of documents, enhancing accessibility and regulatory compliance.
Real Life Examples

A leading bank in India successfully deployed Nividous platform to automate their bank guarantee closure process, resulting in faster customer communication and a 45% reduction in process handling time. The platform connected multiple systems and eliminated manual operations, improving compliance and process visibility. The bank experienced cost savings, improved compliance, and time savings.

ANTstein™ Integrated Automation Platform helped this Fortune 500 Insurance company automate the Title Report Generation process, resulting in a 200% increase in productivity. The manual process of validating title documents was time-consuming and error-prone. By automating the process using AntWorks RPA, the company reduced processing time from 3 weeks to 3 days for a single case, improved accuracy and data quality, and achieved better productivity and quality control.

AutomationEdge helped a leading bank in India automate the process of providing loan moratorium to retail and corporate customers during the COVID-19 pandemic. The bank faced challenges such as staff shortage and high volume of moratorium requests. AutomationEdge's RPA bots and Hyperautomation solution enabled the bank to set up a new process flow within a short time, reducing the turnaround time for moratorium requests by 80%. The automated process resulted in cost savings, improved customer experience, and increased efficiency.
Data entry automation
Replaces manual data input with intelligent automation, reducing human errors and increasing the speed of data processing across systems.
Real Life Examples

Terreal, a European key player in clay building materials, leveraged Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate their pallet inventory tracking and integrate health insurance accounting with bank statements. The automation resulted in increased accuracy, efficiency, and saved 730 hours per year. Terreal plans to expand the use of RPA to other departments and company locations, recognizing its proven efficiency and scalability.

A leading bank in India successfully deployed Nividous platform to automate their bank guarantee closure process, resulting in faster customer communication and a 45% reduction in process handling time. The platform connected multiple systems and eliminated manual operations, improving compliance and process visibility. The bank experienced cost savings, improved compliance, and time savings.

ANTstein™ Integrated Automation Platform helped this Fortune 500 Insurance company automate the Title Report Generation process, resulting in a 200% increase in productivity. The manual process of validating title documents was time-consuming and error-prone. By automating the process using AntWorks RPA, the company reduced processing time from 3 weeks to 3 days for a single case, improved accuracy and data quality, and achieved better productivity and quality control.
Invoice processing
Automating the extraction, validation, and processing of invoices to streamline financial operations and reduce errors.
Real Life Examples

CNM LLP, an accounting advisory firm, automated its rate validation process for client invoices using the Nividous Hyperautomation Platform. The solution helped the customer save time and reduce manual efforts by standardizing the structure of client agreements and using smart bots to fetch and compare data from engagement letters with timesheets. The automation resulted in a reduction in manual efforts, improved process turnaround time, and reduced human errors.

A leading media company in India automated the processing of release orders using Nividous' Accounts Payable Automation Solution. This streamlined and automated the manual tasks, reducing manual efforts and turnaround time significantly. The company achieved higher accuracy and speed in processing payments, resulting in cost and time savings.

Dutch paving company De Krom implemented Workfusion Intelligent Automation Cloud to automate their time-consuming data entry process. The automation workflow created with RPA Express reduced processing time by 90%, improved document-handling accuracy from 60% to 98%, and increased employee satisfaction by reducing stress and overtime. The company experienced significant cost and time savings.
HR process automation
Automating HR tasks such as onboarding, payroll, benefits management, and performance tracking to improve productivity.
Real Life Examples

Terreal, a European key player in clay building materials, leveraged Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate their pallet inventory tracking and integrate health insurance accounting with bank statements. The automation resulted in increased accuracy, efficiency, and saved 730 hours per year. Terreal plans to expand the use of RPA to other departments and company locations, recognizing its proven efficiency and scalability.

Trelleborg Municipality in Sweden implemented UiPath RPA solution to automate administrative tasks in the Social Services and Labor Market departments. The implementation led to significant time savings, cost reductions, and improved citizen participation in labor market initiatives. Employees found the automation quick, painless, and satisfying, allowing them to focus on value-added services. The case study does not mention the creation year.

AutomationEdge helped a leading bank automate the user creation process, resulting in a 60% reduction in service cost, rapid delivery of new services, improved SLA compliance, and 100% customer satisfaction. The bank opted for AutomationEdge after the existing vendor suggested major architectural changes and high costs. AutomationEdge automated the user creation and role assignment for new joiners, improving accuracy and reducing manual effort.
Supply chain management
Managing and optimizing logistics, procurement, and distribution processes for efficiency and cost reduction.
Real Life Examples

Genpact partnered with Automation Anywhere to automate F&A processes for a trucking and logistics company. By utilizing the legacy system and implementing robotic process automation, they were able to reduce errors, increase productivity, and track trends in usage patterns and contract violations. The solution resulted in a 30% improvement in productivity, 25% increase in transaction speed, and zero errors. The company also saw benefits such as cost savings, increased visibility, and time savings.

Juniper Networks, a technology pioneer in the networking industry, used Automation Anywhere's Digital Workforce Platform to automate the billing portal process for its six largest customers. By automating invoice submission and improving accuracy, Juniper reduced process cycle time, improved cash collection, and decreased manual labor. The company now has a digital workforce of software robots working 24/7, allowing employees to focus on more challenging tasks and facilitating smoother cash flow.

Stant, a tier-1 automotive supplier, implemented Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate their accounts payable processes. This resulted in reduced invoice backlog, improved efficiency, and increased focus on strategic sourcing. Stant plans to automate more processes and expand the use of Automation Anywhere in their Finance and HR functions.
Sales and marketing automation
Enhancing lead generation, customer engagement, and campaign management through automated workflows.
Real Life Examples

Walgreens uses Blue Prism's Digital Workforce to improve HR shared service efficiency by 73%. The automation of transactional tasks allows employees to focus on enhancing the customer experience. Walgreens implemented a self-funding plan and collaborated with various teams for successful implementation. The RPA platform provided by Blue Prism enables Walgreens to deliver additional work and boost efficiency in the HR shared services group.

Juniper Networks, a technology pioneer in the networking industry, used Automation Anywhere's Digital Workforce Platform to automate the billing portal process for its six largest customers. By automating invoice submission and improving accuracy, Juniper reduced process cycle time, improved cash collection, and decreased manual labor. The company now has a digital workforce of software robots working 24/7, allowing employees to focus on more challenging tasks and facilitating smoother cash flow.

Prosegur, a private security company based in Spain, implemented Blue Prism's Connected-RPA solution to enhance speed, accuracy, and client experience. They created a Department of Automation and Robotics and utilized the Super Robot program to manage process discovery, analysis, and development. With over 300 processes automated, Prosegur achieved significant ROI and cost savings while optimizing operations.
Healthcare monitoring
Tracking patient vitals and health metrics to enable remote care and proactive healthcare interventions.
Real Life Examples

Kane Wound Care, a healthcare organization in the United States, automated their medical coding and billing process using Nividous' AI-powered RPA Bots. This automation improved coding accuracy, reduced manual work, and resulted in faster turnaround time. The company expects a significant increase in revenues and overall cash flow as a result.

Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust implemented Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate the monitoring of oxygen tank levels. This allowed for 24/7 monitoring without human intervention, freeing up 1,500 hours for staff and ensuring accurate data reporting. The solution improved compliance, saved costs, and saved time.
Inventory optimization
Managing stock levels using automated demand forecasting and replenishment strategies.
Real Life Examples

Terreal, a European key player in clay building materials, leveraged Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate their pallet inventory tracking and integrate health insurance accounting with bank statements. The automation resulted in increased accuracy, efficiency, and saved 730 hours per year. Terreal plans to expand the use of RPA to other departments and company locations, recognizing its proven efficiency and scalability.

Trelleborg Municipality in Sweden implemented UiPath RPA solution to automate administrative tasks in the Social Services and Labor Market departments. The implementation led to significant time savings, cost reductions, and improved citizen participation in labor market initiatives. Employees found the automation quick, painless, and satisfying, allowing them to focus on value-added services. The case study does not mention the creation year.

Walgreens uses Blue Prism's Digital Workforce to improve HR shared service efficiency by 73%. The automation of transactional tasks allows employees to focus on enhancing the customer experience. Walgreens implemented a self-funding plan and collaborated with various teams for successful implementation. The RPA platform provided by Blue Prism enables Walgreens to deliver additional work and boost efficiency in the HR shared services group.
Compliance
Ensuring regulatory compliance through automated monitoring, reporting, and risk assessment.
Real Life Examples

Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group, Inc. (SMFG) and Sumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation (SMBC) implemented UiPath RPA solution to increase productivity and efficiency. They achieved over 400,000 hours of annualized savings across 200 operations, with projected cost reductions of $450 million by 2020. The RPA implementation focused on compliance, routine operation center processes, and routine headquarter processes. The benefits included cost saving, increased visibility, and time saving.

A leading bank in India successfully deployed Nividous platform to automate their bank guarantee closure process, resulting in faster customer communication and a 45% reduction in process handling time. The platform connected multiple systems and eliminated manual operations, improving compliance and process visibility. The bank experienced cost savings, improved compliance, and time savings.

ANTstein™ Integrated Automation Platform helped this Fortune 500 Insurance company automate the Title Report Generation process, resulting in a 200% increase in productivity. The manual process of validating title documents was time-consuming and error-prone. By automating the process using AntWorks RPA, the company reduced processing time from 3 weeks to 3 days for a single case, improved accuracy and data quality, and achieved better productivity and quality control.
Service Level Agreement (SLA) management
Monitors SLA commitments, triggers alerts for potential violations, and automates escalations to maintain compliance and performance standards.
Real Life Examples

Cadence Design Systems, Inc., a multinational IT company based in the United States, enhanced their support experience with service desk automation using AutomationEdge. By automating processes such as employee onboarding and offboarding, self-service alias and group management, and security compliance improvement, Cadence achieved a 30% increase in resolution rate, 40% reduction in resolution time, and significant cost reduction. The automation efforts also improved operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and reduced the burden on IT staff.
Data migration
Automates the movement of large datasets across platforms while ensuring integrity, compliance, and minimal disruption.
Real Life Examples

Dentsu, a global digital marketing company, used UiPath RPA solution to build 60 robots in 6 days, saving 125K hours in the process. They successfully extracted and migrated over 2.8 million records, improving data analysis and business continuity. The project was completed within a tight timeline with the help of UiPath's Professional Services team, showcasing the power of teamwork and automation.
Document extraction
Extracting structured data from unstructured documents to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort.
Real Life Examples

Health Fidelity, a healthcare company based in the United States, used UiPath RPA solution to extract over 1.2 million records for its clients in a HIPAA-compliant manner. This helped them overcome internal bottlenecks and delays, while improving security and reducing costs. With UiPath, they were able to work with different EMRs based on Citrix technology and support clients they couldn't in the past. The solution provided visibility, control, and productivity, making the company more competitive.

Dentsu, a global digital marketing company, used UiPath RPA solution to build 60 robots in 6 days, saving 125K hours in the process. They successfully extracted and migrated over 2.8 million records, improving data analysis and business continuity. The project was completed within a tight timeline with the help of UiPath's Professional Services team, showcasing the power of teamwork and automation.

PwC partnered with UiPath to reshape its workforce for the digital age. They implemented citizen-led innovation and upskilled their global workforce using RPA. With the help of UiPath's platform, they automated about five million hours of non-value-added work, leading to improved productivity and employee satisfaction. PwC plans to expand RPA globally and continue enhancing its support for their own work and their clients' digital transformations.
Document processing
Automating document handling, classification, and validation to enhance workflow efficiency.
Real Life Examples

Health Fidelity, a healthcare company based in the United States, used UiPath RPA solution to extract over 1.2 million records for its clients in a HIPAA-compliant manner. This helped them overcome internal bottlenecks and delays, while improving security and reducing costs. With UiPath, they were able to work with different EMRs based on Citrix technology and support clients they couldn't in the past. The solution provided visibility, control, and productivity, making the company more competitive.

Dentsu, a global digital marketing company, used UiPath RPA solution to build 60 robots in 6 days, saving 125K hours in the process. They successfully extracted and migrated over 2.8 million records, improving data analysis and business continuity. The project was completed within a tight timeline with the help of UiPath's Professional Services team, showcasing the power of teamwork and automation.

Patelco, a financial services company in the United States, partnered with Automation Anywhere to automate processes such as loan payoffs and fraud alerts. By implementing RPA solutions, Patelco achieved faster fulfillment, faster loan payoff calculations, efficiency gains, accuracy improvements, and cost savings. The company plans to expand automation to other areas such as mortgage applications and internal audit. The case study was created in 2020.
Email marketing
Delivering targeted marketing messages via email to increase engagement and conversion rates.
Real Life Examples

Husch Blackwell, a law firm based in the United States, implemented Automation Anywhere's RPA solution to automate processes specific to their legal practice. By automating tasks such as conflict checks and potential litigation alerts, the firm saved hours annually and increased efficiency. They are also exploring the use of IQ Bot for processing courthouse documents. With 13 automation ideas in the pipeline, Husch Blackwell continues to leverage RPA to improve inefficiencies and retain/win new business.

AutomationEdge helped one of the largest banks in India automate their NPCI Mailer Process, resulting in an 800% reduction in Turnaround Time (TAT). The solution involved downloading and emailing reports for multiple sub member banks, saving time and reducing manual efforts. The automation also improved accuracy and eliminated the possibility of manual errors.
Issue resolution
Managing and resolving issues efficiently through tracking, prioritization, and automation.
Real Life Examples

Mashreq Bank, a leading bank in the United Arab Emirates, modernized its service desk using AutomationEdge. They achieved end-to-end modernization by automating over 100 use cases in various areas. The automation resulted in significant improvements in turnaround time, customer satisfaction, and cost reduction.

Cadence Design Systems, Inc., a multinational IT company based in the United States, enhanced their support experience with service desk automation using AutomationEdge. By automating processes such as employee onboarding and offboarding, self-service alias and group management, and security compliance improvement, Cadence achieved a 30% increase in resolution rate, 40% reduction in resolution time, and significant cost reduction. The automation efforts also improved operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and reduced the burden on IT staff.
Report automation
Generating reports automatically to save time, improve accuracy, and enhance decision-making.
Real Life Examples

InsurTech Probus Insurance leverages Nividous Platform's Robotic Process Automation (RPA) solution to automate the manual task of report generation and policy distribution. This automation resulted in an 85% faster turnaround time, improved productivity, and increased accuracy in process automation. The company plans to further integrate RPA, cognitive, and analytics to enhance customer experience.
Common Business Processes
1. Customer onboarding
The customer onboarding process is critical in reducing customer churn and getting new customers to start using the product.
OCR and RPA can help companies deliver intelligent automation in customer onboarding. Most customer onboarding processes, like contract generation, can even be done in companies relying on legacy systems.
Real-life example: Finastra, a financial software company, has leveraged automation to streamline its contact center operations. Before automating, the onboarding process for new employees took 8-12 weeks. With the automation, this time has been significantly reduced, allowing new hires to become proficient faster.1
2. Extracting data from PDFs & scanned documents
Screen scraping, OCR, and basic pattern recognition technologies enable data extraction from almost any format. This reduces the need to extract and input data manually. Explore our data-driven list of the top document-capturing applications.
This use of RPA gains importance in processes such as accounts payable, where document management and document capture should be together. There are examples where the accounts payable process in ERPs is developed by technologies that also use RPA:
- Dynamics 365 in Accounts Payable Automation
- Blackbaud Accounts Payable (AP) Automation
- Sage Accounts Payable (AP) Automation
- NetSuite AP Automation
Real-life example: Carglass automated its manual PDF data import process, saving around two hours daily that were previously spent correcting data entered by field technicians. By streamlining administrative tasks, Carglass empowered its field teams to focus on customer service and sales.2
The automation significantly improved employee satisfaction, with 99% of technicians reporting positive experiences.
3. Data updates
Most departments, including HR, customer service, and marketing, routinely need to update their ever-changing customer or personnel data.
By setting up bots to automatically update relevant data from forms and emails, departments will always have access to the most recent and correct information.
4. Data validation
Most data validation controls can be embedded in databases. However, RPA is suitable for other validation tasks, such as cross-checking data against publicly available data. That’s because RPA is easy to program, scalable, and integrable with different systems.
Real-life example: Protelindo leveraged automation to enhance data validation and reconciliation tasks through its employee-driven “ProAction” event. Employees across various departments developed automated solutions, significantly reducing the time required for data validation, improving operational accuracy, and enabling the company to manage high data volumes.3
Employees developed 29 automation projects, enabling the company to process large data volumes 75% faster.
5. Periodic report preparation and dissemination
Businesses need regular reports to inform managers and teams of their progress. However, manual report preparation and sending are time-consuming.
RPA can auto-generate reports, analyze their contents, and based on the contents, email them to relevant stakeholders. This automates periodic reporting.
For example, telecom operators need to send reports on connectivity issues to the correct personnel. For instance, a CTO should be copied on reports with critical issues, and the head of the network on major issues.
RPA bots can analyze reports to modify recipients according to the provided criteria. Learn more about RPA use cases in reporting.
6. Data migration and entry
Legacy systems still perform critical functions at companies. For example, legacy billing systems need to interface with other systems, which may not have the capability to pull relevant data from APIs. In such cases, employees manually migrate data using formats like CSV.
Real-life example: Encova Insurance automated its policy intake process and reduced manual data entry from approximately 650 hours per month to just 12.5 hours per year with a productivity increase of over 99%.4
7. Generating mass emails
Personalizing emails, newsletters, and other forms of marketing outreach can lead to more successful campaigns. But personalization relies on data inflow from different systems (e.g., CRM or ERP systems), which can be time-consuming if done manually.
RPA can help businesses:
- Gather customer data from different systems
- Put them onto pre-approved email templates
- Send them to customers/potential leads
Real-life example: HUB International’s automated email processing enables the automatic extraction and classification of customer data directly into their NetSuite policy management system. By automating this previously manual workflow, HUB International reduced costs associated with third-party labor and scaled its operations to manage thousands of diverse documents and communications.5
Automation has supported HUB International’s rapid growth by streamlining over 60 processes company-wide, allowing them to integrate new acquisitions faster.
8. Quote-to-cash
Businesses need to sell to survive. Quote-to-cash issues can result in late receivables, delayed invoice generation, selling at reduced prices (due to clerical errors), etc.
By streamlined data extraction and transportation from different order forms and systems, quote-to-cash automation enables:
- Manual error reduction
- Faster B2C/B2B services
- Reduction in accountancy costs
9. Procure-to-pay (P2P)/Source-to-pay (S2P)
The procure-to-pay process involves creating a purchase order and extracting invoice and payment data from multiple systems:
- Supplier emails
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Customer relationship management (CRM)
- Banks
- Vendors
- Logistics companies.
The data coming in can be in different forms, such as emailed vendor invoices. Invoices need to be captured, validated, and enriched. For example, companies need to assign general ledger (GL) accounts to invoices without purchase orders (POs).
Learn more about RPA use cases in the procurement process.
Commercial Functions (Marketing & Sales)
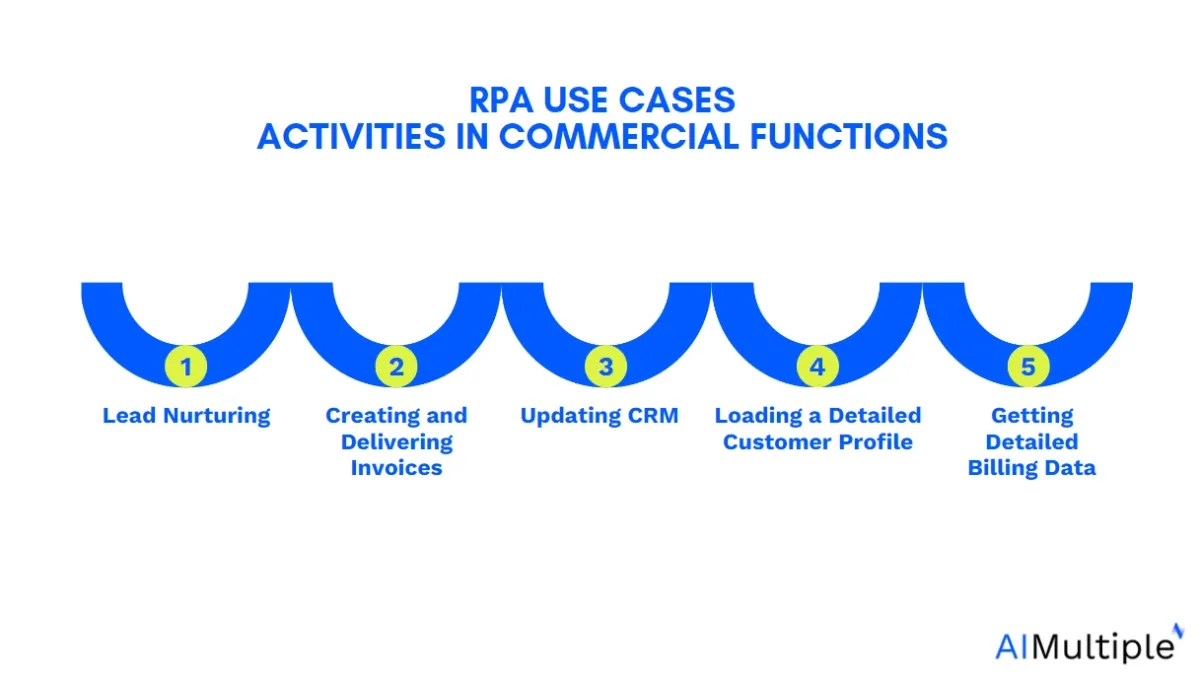
Marketing:
10. Lead nurturing
Leads arrive through a myriad of channels such as LinkedIn, lead collection forms, and vendors. RPA bots can extract them and put them in a single location.
Real-life example: Habib Bank Limited (HBL) automated its sanction screening process for new customer onboarding using 15 digital workers, which now handle over 80,000 cases monthly with 98% accuracy. Previously, a manual task requiring significant effort, automation reduced processing time from hours to minutes, enabling compliance teams to focus on complex tasks.6
Automation saved HBL approximately 341,000 working hours annually, driving the bank’s wider digital transformation and improving service quality for its 37 million customers.
11. Bid adjustment
Automated bid adjustment tools use RPA-API integration to monitor your ads’ performance, assess it, and automatically adjust the bid.
Although you should keep monitoring the bot’s performance, the need to manually adjust the bid decreases.
Real-life example: Sopra Steria leveraged automation by integrating RPA with AI/ML technologies to fully automate its bid adjustment processes. This resulted in processing bids three times faster, reducing manual effort to zero, and eliminating errors. This automation allowed Sopra Steria to achieve ROI within just six months, significantly streamlining operations and enhancing competitiveness in bidding processes.7
12. Price monitoring
RPA bots can monitor competitor prices on e-commerce retail websites to track and implement price changes in real time.
13. Product and service monitoring
The R&D department can use RPA bots to track competitors’ products/services on competitor websites and online retail platforms. The gained insights can shape the company’s offerings.
14. Customer review monitoring
Companies can use RPAs to track, extract, and structure users’ sentiment analysis about their products.
Sales:
Though sales personnel should focus on building relations and selling, most of their time is spent on operational activities in most organizations. RPA can automate the interactions between the data systems and the CRM.8
15. Creating and delivering invoices
This is a case of data replication. Both the CRM and the accounting systems should have identical sales data. Bots can update accounting records, prepare, and deliver invoices from the right email accounts to ensure data consistency between systems.
Real-life example: FlySafair automated its invoicing processes to streamline billing airline partners for shared journeys, significantly reducing manual work hours and protecting income. This automation reduced the billing time per invoice from hours to minutes.9
16. Updating CRM
Adding interactions with prospects to the CRM is time-consuming but critical.
Modern solutions help companies integrate their email, call, and other communication data into a CRM system. But they require integration into your company’s CRM to work. When such integrations are not available, companies can build bots to update CRM records with customer contact information.
17. Updating scorecards
RPA bots can ensure that CRM changes are uploaded to scorecards. This allows sales reps to see their progress in real time.
Customer Relationship Management
18. Loading a detailed customer profile
RPA bots can load customers’ profiles (Figure 1) on demand.
Figure: Example of a customer profile template.
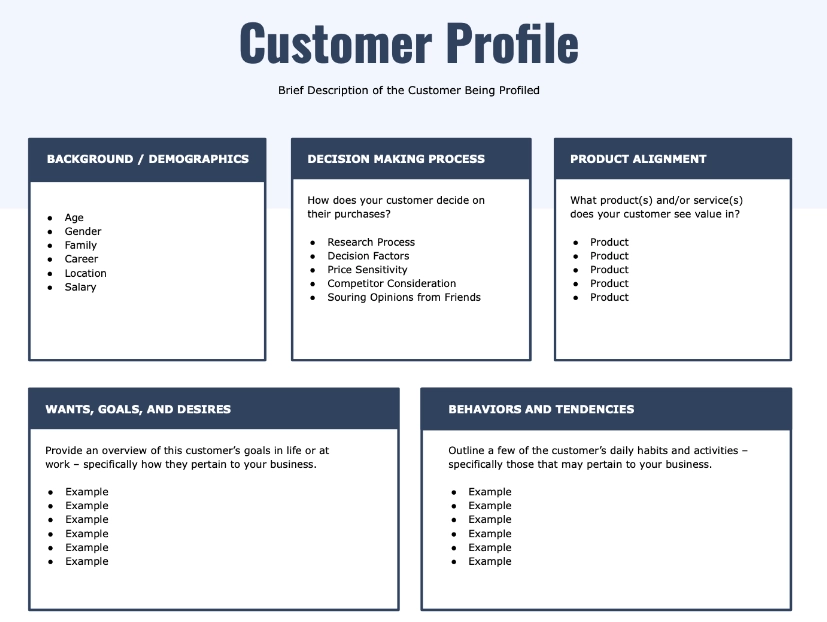
Source: 10
19. Getting detailed billing data
When you call customer service about your most recent payment, you need to stay on the line while the rep pulls your record and reviews it.
With RPA bots, reps can load billing data much quicker.
20. Updating user preferences and other user information
RPA chatbots can update user preferences, addresses, contact/personal information, and more. This replaces the need to connect to a live agent.
21. Resolving simple, yet common customer issues
RPA bots can reset a customer’s broadband network or fix simple connection issues without a rep interacting with multiple windows.
22. Automating multi-step complex tasks that require little decision-making
Some legacy systems require customer service reps to navigate a lot of steps for simple tasks. If these do not require human judgment, they can be automated, saving significant time.
23. Answering FAQs
Companies can build RPA-enabled FAQ chatbots to answer customers’ most frequently asked questions without human intervention.
24. Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
RPA bots can be used to automatically generate SLAs, monitor conformance, give breach notifications, and orchestrate troubleshooting. Learn more about service-level agreement automation.
25. Automating multi-step complex tasks that require little decision-making
Some legacy systems force customer service reps to complete numerous steps to complete some common tasks. If these steps do not require human judgment, they can be automated, saving significant time.
26. Spam detection
Approximately:
Companies can use NLP-driven RPA bots to read incoming emails, documents, and online reviews to notice those that are likely to be spam and flag them as such.
Real-life example: Leaf Home leveraged automation to overcome spam filter issues that prevented them from reaching potential customers, causing daily losses of up to $3 million. By automating the rotation of their contact phone numbers, Leaf Home successfully bypassed spam detection systems, significantly improving customer communication and protecting vital revenue.13
27. Automated translation
Especially for international companies, customer complaints, emails, and other forms of correspondence can come in different languages, making it harder for customer reps to understand them.
RPA bots can automatically translate the content’s language to allow customer agents to resolve them quickly. Learn more about RPA & NLP integration.
IT, Security & Technology Operations
IT Support & Security:
28. Regular diagnostics
Regular diagnostics are running preemptive screening of processes. This puts the tech support teams one step ahead and allows them to respond to possible failures before regular users can notice them.
This improves user satisfaction and saves support personnel from wasting time on calls about problems they already know about. There are workload automation (WLA) tools that can be scheduled to run regular diagnostics on the processes to notify users of possible failures.
29. Fault remediation
In fault remediation, conversational AI-enabled RPA bots can leverage responses from command catalogs to troubleshoot users’ problems.
For instance, a user might say the application “keeps crashing.” The chatbot would understand the query, search the database for the appropriate answer, and give it to the user.
30. Incident management
IT incident management is identifying, solving, and minimizing disruptive incidents in the IT ecosystem.
RPA bots can send a notification to the IT staff automatically when an IT outage is detected. Or they can put all the support tickets in one location, enabling the IT staff to access them easily.
Real-life example: PostNord automated its regression testing, continuously testing and monitoring 20 critical end-to-end logistics processes overnight. This automation enabled the immediate detection and rapid resolution of software issues, resulting in a reduced time for incident identification and resolution.14
31. Server monitoring
RPA bots can monitor network and server usage data and send the reports to employees.
Improve tech support by learning other IT automation technologies, such as
- Top 10+ Data Center Automation Software
- Top 12 IT Automation Software: Vendor Benchmarking
- Top 10 Batch Scheduling Software: Vendor Benchmark
- TOP 5 SAP Job Scheduling Software: Vendor Benchmarking
32. DevOps Management
Real-life example: TriNet streamlined its DevOps change management process, transforming manual workflows into automated, real-time processes. By automating code deployment tasks, they eliminated manual hand-offs and human errors, reducing cycle time from 15 minutes to under one minute.15
Technology Operations:
33. Opening internal tools to customers or employees
Almost all customer service or tech support departments have internal tools with advanced functionality. Service reps use them for internal and external needs. For example, they may be used to approve payments to vendors even when a 3-way match is not reflected in the systems, or enable employees to take additional days off.
If those tools are in legacy systems, it is difficult to expose them directly to customers or employees without training. RPA offers a solution.
The usage frequency of functionalities follows the Pareto principle. A few functionalities (80%) are quite commonly used; the rest (20%) aren’t. After identifying the most popular functionalities of an internal tool, it is possible to write simple web interfaces that leverage bots to complete them.
This saves users time while reducing the burden on support teams. In addition, the functionalities that the internal tools provide would be more targeted, enabling more efficient usage.
34. Software installations
RPA can enable single-click installations of complex systems with interdependent components
35. Automated software testing
RPA tools evolved from testing tools that mimic user interactions. The tests can be built into the software, but testing from a user perspective is equally important.
Manual testing is time-consuming; automated RPA testing is fast and can:
- Boost digital transformation of businesses
- Speed up software development
- Produce more reliable outcomes
- Be run after each deployment to ensure new bugs aren’t introduced
Creative manual tests are required for specific scenarios. But no-code RPA solutions are good for common tests that need to be repeated.
36. Product update automation
Companies can automate their product updates to notify their customer base of added capabilities of their product/service line in real-time.
The benefit of product update automation is that companies do not have to dedicate manpower to notify customers by email, message, or phone call.
Finance & Accounting
Planning & Accounting:
37. Financial planning & budgeting
Financial planning involves processing and merging financial statements from numerous departments in a Financial Planning & Analysis (FP&A) system. Intelligent RPA bots with OCR features can automate this via data extraction and ETL.
Real-life example: A large U.S. financial services firm used RPA to enhance customer interactions and internal efficiency within its loan underwriting processes. By automating 60% of customer inquiries and 80% of complex calculations through generative AI-powered automation, the firm achieved a reduction of over 99% in Service Level Standard (SLS) times. Additionally, overall response times decreased by 67%.16
38. Bank statement reconciliation
RPA bots can automate data extraction and reconciliation against ledger entries.
Specifically, RPA can:
- Check for incoming bank statements
- Download and extract the file content
- Reconcile them against entries
- Flag exceptions and notify accountants
- Close the books
Learn more about how account reconciliation is automated.
39. Treasury management
RPA in treasury management can automate processes such as:
- Accounts reconciliation
- Forecasting risk factors
- Debt collection
- Investment decisions (for low-risk investments)
- Balance sheet preparation
40. Daily P&L preparation
Large financial institutions, especially those in trading, need to track their profit & loss (P&L) and risk exposures daily.
Real-life example: A global financial services company automated its daily profit and loss (P&L) report preparation. Previously, employees manually combined multiple Excel and legacy-system reports, a process prone to errors and taking up to an hour each day. After automation, robots now automatically populate, validate, and distribute these reports, improving accuracy to 100% and reducing handling time from 60 to 20 minutes.17
Automating daily P&L reporting reduced manual handling by 70%, saving approximately 150 productivity hours annually.
Learn more about RPA in finance.
Banking & Loan:
41. Loan processing
As with most rules-based, document-processing tasks, loan processing automation is doable with RPA. Business engine rules embedded in bots can:
- Extract applicant info
- Validate it
- Assess the submitted business plan
- Ask users to fix incorrect issues
- Make a preliminary evaluation
- Generate confirmation/rejection letters
Real-life example: The Loan Store (TLS) automated various mortgage lending processes, including loan setup, disclosures, underwriting, and servicing. This automation resulted in a 100% increase in productivity, 60% cost savings, over 80% straight-through processing, and a reduction of mortgage loan turn times by more than 25%. The automation allowed TLS to scale operations while maintaining high levels of customer service, leading to faster loan processing and cost savings.18
42. Trade execution
In cases where legacy systems are not capable of storing complex limit orders, RPA bots can automate the processing of complex orders.
43. Same-day funds transfers
The Cooperative Bank completes payments using the Clearing House Automated Payment System (CHAPS), which offers same-day funds transfers.
The manual process, which took 10 minutes per request, was automated. The steps included:
- Checking for fund availability
- Making a purchase order
- Performing transfers to where the funds are needed manually
Real-life example: The Co-operative Bank automated its CHAPS payment transfer process. Previously, each transfer required around 10 minutes of manual effort, but automation reduced this time to approximately 20 seconds. The automated workflow includes verifying fund availability, performing the transaction accurately until manual authorization, charging the customer, and updating the account notes.19
44. Account closure
Real-life example: The Co-operative Bank automated its account closure process. Previously, closing an account involved multiple manual tasks, including canceling direct debits and transferring funds. Now, customer service agents simply fill out an electronic form during a call, and the RPA system processes these requests automatically, eliminating manual intervention.20
45. Validating and processing online loan applications
Real-life example: The Co-operative Bank automated its online loan application process. Previously, loan applications required significant manual intervention for data validation and preliminary decision-making. Automation enabled the bank to process 99% of loan applications on the same day they were submitted, greatly improving customer service by reducing delays.21
46. Audit preparation
Banks need to reply to requests by the auditors for company audit reports. Bots can be used to retrieve all customers’ year-end balances and return the audit to the audit clerk in the form of a Word document.
This can reduce the time it takes to run an average audit from days to minutes.
Real-life example: The Loan Store, Inc. (TLS) implements automation across several mortgage processes, including audits and loan documentation. By automating processes like loan document classification and disclosures, TLS increased productivity by over 100% and compressed mortgage loan turn times by more than 25%.22
47. Trade finance logistics
Trade finance involves multiple parties coordinating and ensuring the delivery of goods and payments.
For instance, the banks and the trading company communicate through letters of credit and other documents, which need to be processed (see diagram below from IBM).
Figure: Automation of trade finance workflow
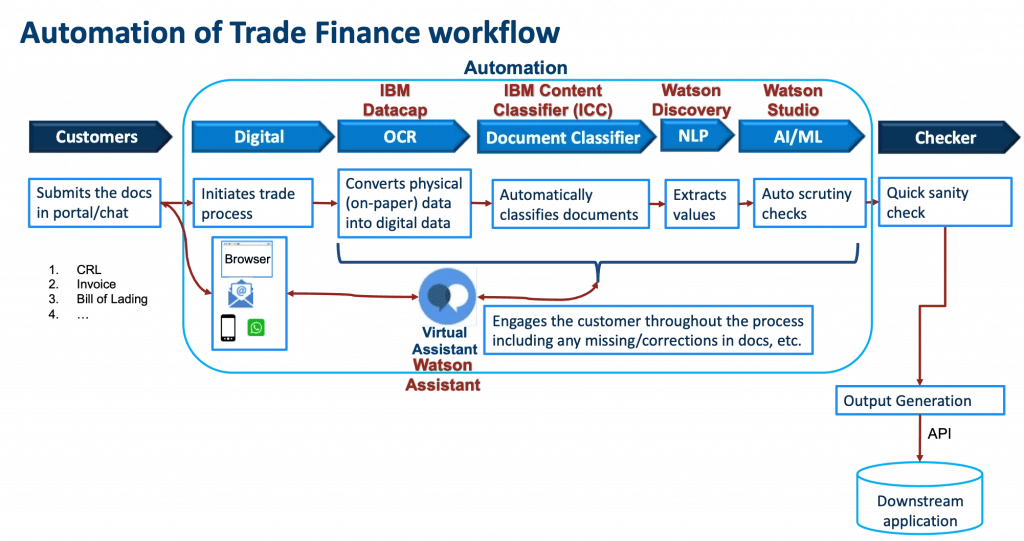
To learn more about finance automation, read RPA in finance.
Human Resources (HR)
48. Candidate sourcing
Companies relying on legacy HR systems can use bots to automate aggregating CVs, assessment results, and interview notes.
Businesses can leverage web crawlers which can pull data from platforms such as Glassdoor/LinkedIn to create talent pools, compare candidate data, and understand the job market. Learn more about web scraping use cases in recruiting.
Real-life example: ManpowerGroup improved its candidate validation process. This led to a 500% increase in candidate processing capacity and reduced the average handling time per candidate from 5-7 minutes to just 1 minute. The automation saved the team approximately 200 hours per month.23
49. Employment history verification
Real-life example: A candidate verification service provider automated its employment history verification. Previously, manual tasks such as arranging candidate interviews, contacting previous employers, and managing records consumed significant time and resources. After implementing automation within just 8 weeks, the company successfully reduced manual labor by 40%, allowing employees to concentrate more on direct interaction with candidates.24
50. Employee onboarding
Efficient onboarding and offboarding can reduce the burden on the HR staff and ensure continuity, especially in fast-growing or shrinking firms. In employee onboarding, the bot can schedule introductory meetings to speed up orientation.
51. Employee offboarding
In employee offboarding, the RPA bot can automatically restrict the outgoing employee’s access to confidential company data, calculate compensation packages, and more.
52. Payroll automation
Payroll requires repetitive payroll processing, taking into account myriad regulations and company rules.
While modern payroll software provides a good solution for this process, some companies rely too much on legacy systems to be able to make the switch to modern payroll software.
RPA bots can, at least partially, automate the payroll process, such as:
- Automating payroll reports,
- Automating payroll taxes,
- Calculating commissions,
- Collecting timesheets and more.
53. Absence management
Manual absence management is difficult because:
- Employees might forget to log their days off
- Deductibles for unaccounted vacation days are employee-specific
- The process is time-consuming and prone to human error
Inefficient absence management costs companies ~ $4K/year and $3K/year for each hourly and salaried employee, respectively.
To remedy this, RPA bots can:
- Cross-check employees’ absence reports against their logged-in time in the corporate system
- Alert other team members when an employee adds their info to the vacation calendar.
54. Claims management
Real-life example: Walgreens, a leading U.S. pharmacy chain, automated its workers’ compensation and leave-of-absence processes. Before automation, managing approximately 2,000 employee leaves per day required extensive manual data handling between internal databases and claims service providers. With RPA, leave types (paid or unpaid) are automatically recorded, and data exchanges occur seamlessly. As a result, payroll accurately reflects employee leaves without manual input.25
Automation improved Walgreens’ HR shared services efficiency by 73%.
55. Expense management
Companies can use RPA tools to automate their expense management. The bot would extract the amount, date, location, and other info from the receipts and log them into the system.
This eliminates the need for employees to hold and submit paper receipts. Moreover, entries will be automated, fast, and accurate. Learn more about expense management automation.
56. HR virtual assistants
An HR virtual assistant can handle most HR processes. For instance, recruiting chatbots can automate parts of the hiring process.
HR virtual assistants can also help employees:
- Register sick leave/vacation time
- Ask about their employee contract stipulations
- Submit expense reports
Learn more about HR technology trends that are shaping the future of HR management.
57. Change management
RPA bots can:
- Gather employees’ change requests’ data
- Screen them
- Evaluate them
- Send them to the department heads
- Communicate the results to employees
Learn more about RPA in HR.
Operations & Procurement
58. Updating inventory records
Inventory management typically involves reconciliation across multiple systems, as companies find it challenging to bring all inventory management features under one system.
RPA bots can automate such intersystem reconciliation and communication with ease.
Real-life example: Eletrobras implemented an AI-powered solution to automate the review of 65,000 technical documents annually, saving 9,360 hours per year. The automation, combined with generative AI, improved document review accuracy from 50% to 92%, significantly reducing manual effort by 90%. The solution also freed up five full-time employees (FTEs) to focus on strategic initiatives, ultimately saving $277,377 annually and enhancing the company’s ability to lead in the renewable energy sector.26
59. Issuing refunds
Unoptimized refund issuance leads to delays and customer dissatisfaction.
This is a concern because customers requesting refunds are already dissatisfied customers. Making them more dissatisfied can lead to severely negative online reviews, which can harm a company’s reputation.
60. Compliance
Changing business, regulatory, or tax requirements requires businesses to validate internal and external records, such as constantly scraping government websites for policy changes.
Learn more about RPA in compliance.
61. Updating vendor records
Keeping vendor master files up-to-date to streamline vendor payments.
Updating such files with bots can relieve procurement professionals from simple tasks to focus on managing vendor relationships.
Industry-specific processes
According to our experience and research, financial services, including insurance and BPO (business process outsourcing), seem to be the top users of RPA technologies.
Insurance:
62. Claims processing automation
Claims processing is at the heart of every insurance company. Since customers make claims at times of misfortune, a fast and efficient customer experience is crucial.
Some factors that make claims processing biased, delay it, and reduce visibility are:
- Manual/inconsistent processing: Claims processing often involves manual analyses completed by outsourced personnel/claims adjusters.
- Input data of varying formats: Customers send in data in various formats
- Changing regulation: Insurance companies should keep in line with regulation changes through constant staff training and process updates
RPA bots enable claims processing transformation by:
- Taking the unstructured data in forms, structuring, extracting, and assessing them
- Automating claims verification with rules
- Ensuring compliance by changing rules in line with regulatory changes, without the need for re-training staff
- Increasing fraud detection percentage
- Claims Bots can take in unstructured data in various forms, structure it, extract it, and finally assess it based on predefined rules.
Real-life example: A large commercial property and casualty insurance company automated its workers’ compensation claims processing with RPA, significantly reducing the time taken for each claim. By deploying bots to handle policy audits, endorsements, and payroll updates, the company cut the claims processing time by 60% and achieved error-free documentation.27
63. Appeals processing
Some claims might result in appeals because of mismatched dates or other documentation issues. End-to-end appeals processing enables:
- Reading the claims by OCR
- Extracting the complaint and applying the relevant rule with RPA
- Managing the exception with BPM
64. Responding to partner queries
Industries such as telecom or insurance rely on brokers to sell their products and services. It is crucial to serve these partners promptly to maximize their sales.
South African insurance company, Hollard, automated responses to partner queries by building bots that interpreted incoming emails and either resolved them or passed the complex ones to humans.
Automotive:
65. Automotive telematics
Cars leveraging Android Automotive OS are on the rise. RPA can allow automated:
- Over-the-air software updates
- Location data exchange
- Anti-theft protocol updates
- Navigation features updates
Learn more about RPA use cases in the automotive sector.
Aviation:
66. Air traffic control processes
RPA bots can improve air traffic control (ATC) through a constant exchange of data between airplanes’ flight schedules and real-time locations, weather reports, and fueling times.
67. Informing travelers
Airports, airlines, or travel agencies can use RPA to send travelers real-time notifications via apps or emails. Use cases include:
- Informing them of flight schedule changes and gate changes
- The estimated walking time from their specific location to a boarding gate
- Boarding time, etc.
68. Automated traveler check-ins
The check-in kiosks at airports leverage OCR-enabled RPA bots to:
- Scan the travelers’ passport barcode
- Cross-match their info with the ticket info
- Load up their specific accommodation requests
- Print their luggage and boarding tickets
Real-life example: FlySafair, has integrated automation into several core operational areas. One of the areas was the traveler check-in process. The airline streamlined check-in tasks, speeding up the process and enhancing customer experience. By automating repetitive tasks like large booking entries, invoicing, and flash sales processing, the airline improved customer satisfaction and reduced time per transaction.28
Agriculture:
69. Soil preparation
RPA-IoT integration allows IoT agricultural sensors to extract soil data, such as:
- Soil type
- Nutrient levels
- Moisture levels
RPA bots can structure the data and present the information for data-driven soil preparation.
70. Irrigation
RPA can be one of the technologies to start the smart irrigators whenever IoT sensors indicate a drop in soil moisture level. Moreover, by accessing weather data through agricultural APIs, RPAs can plan irrigation schedules based on predicted precipitation levels.
71. Yield prediction
RPA bots can extract soil and crop data from the IoT sensors, and the weather report from databases, along with other variables, to feed into ML algorithms to predict the yield amount.
Note: This is a reductive explanation of how yields can be predicted.
Education:
72. Course registration
RPA bots can create personalized registration semester plans for each student based on their:
- Majors and minors
- Remaining needed credits for graduation
- Available seats in each class
- Expressed interest in elective subjects
73. Exam grading
For multiple-choice exams, RPA bots can automatically grade each entry by comparing it against the exam key.
For long answer questions, RPA bots can use NLP and OCR to figure out what the student said and compare it to the possible answers the professor gave.
74. Booking advising sessions
Students need constant advising sessions. These could be meetings with:
- College advisor to see the student’s possible college candidates
- Academic advisors in college see students’ progress
- Immigration advisors in college/high school to ensure international students’ legal status
- Career advisors in college help students browse job opportunities after graduation
RPA bots, on school portals, can automatically create meeting time slots between the student and the relevant advisor based on the student’s current status.
75. Shortlisting admission candidates
Schools and universities can use RPA for the initial screening of applications to eliminate those that do not meet the basic requirement criteria, such as missing documents, and spam applications.
The benefit is that the admission personnel can then spend more time on applications that have made it to the next round.
76. Attendance management
RPA bots can be used by teachers to track each student’s attendance. For example, if answering live quiz questions in class is a sign of attendance, RPA bots can match each student’s answer on the day with their name. Alternatively, in virtual classrooms, they can manually enter each student’s name into the attendance sheet for that day. Then, they can figure out how many points each student has.
Hospitality:
77. Room reservation
RPA bots can reconcile users’ online payments, extract their information from the website’s database, and reserve their rooms automatically.
78. Automated check-ins & check-outs
RPA bots can send periodic notifications or emails to guests to remind them of their check-in and check-out times, so misunderstandings about this matter are minimized.
79. Automated room pricing
RPA bots can scrape competitors’ websites for the prices they charge for similar rooms. The data can be put into spreadsheets and sent to the hotel manager for analysis.
The bot can also automatically adjust the hotel’s room prices, based on predetermined rules, to match those of competitors with minimal human intervention.
Learn more about RPA’s use cases in the hospitality industry.
Healthcare:
80. Patient Appointment Scheduling
RPA can schedule a patient’s appointments based on diagnosis, doctor availability, location, and other variables, including financial statements and insurance information.
Real-life example: AccentCare, with a small administrative staff, needed a solution to manage the growing amount of patient information and back-office tasks efficiently. Intelligent automation helped AccentCare automate several processes, including medical record management, patient transitions, and patient eligibility verification. By automating patient record migrations for 10,000 patients, AccentCare saved $100,000.29
81. Enhancing patient care by supporting analytics
RPA bots can collect various medical data. For example, RPA bots can transfer patient data to third-party healthcare analytics services to deliver accurate diagnoses and improved patient care without restricting any confidentiality regulations.
Manufacturing:
82. Bill of Material (BOM) processing
A bill of materials is a document that contains each raw material, component, and the instructions required to manufacture or repair a product. Errors in the BOM can affect the production cycle.
RPA can automate Bill of Material processing with OCR and data extraction technologies based on deep learning.
Real-life example: British American Tobacco (BAT) used a robot to transfer data to the Bill of Materials (BOM), improving the accuracy of transferring the recipe and the cost of materials in the SAP system. This automation ensured that changes in recipes and materials were accurately reflected in production.30
83. Inventory control
Real-life example: A global automotive manufacturer automated its inventory control process using RPA. Previously, demand planners manually updated safety stock levels, leading to errors and stockouts. Now, an RPA bot automatically extracts data from structured emails, updates safety stock levels in the ERP system, and notifies relevant stakeholders, eliminating manual effort and ensuring accurate inventory management.31
RPA eliminated 100% of manual work in updating safety stock levels, saving 40 hours weekly and significantly reducing stockouts.
84. Proof of Delivery (POD)
PODs are important for three-way matching and manufacturing planning.
The document is highly labor-intensive and contains a high risk of human errors. RPA bots can track logistics systems, and once the delivery occurs, link the shipping data into the warehouse management system.
This frees time for customer service employees, along with improving response time.
85. Identifying production malfunction
RPA-IoT integration can notify whether the production equipment is functioning correctly by transferring its real-time status data, such as pistons’ RPM, heat data, vibration level, etc.
Restaurants:
86. Floor management
RPA bots in restaurant POS systems can automatically:
- Split a table’s tab amongst diners
- Allow the simultaneous monitoring of multiple tables’ orders and tabs
- Send waiters notifications whenever a table’s food is ready to serve
- Keep records of the number of diners throughout the day, on each table, and the highest/lowest ordered food
87. Meal price updates
RPA bots can be configured to track small changes in ingredient pricing and automatically adjust the meal cost accordingly.
The benefit is that, especially in times of inflation, restaurants can adjust their meal prices to reflect ingredient costs.
Retail:
Retail includes constant operational and analytics activities, such as launching new products or promotions.
Though RPA companies rely on API connections for such operations, there are still many legacy systems without API interfaces where RPA can be used for integration to complete the following processes:
88. Product categorization
Global retail companies need to harmonize SKU (stock keeping unit) data from multiple markets to be able to look beyond numbers to insights such as, “What is our toothpaste market share in Eastern Europe?”.
Traditionally, these tasks required employees to manually match SKUs to categories in complex spreadsheets. Since this is a task that does not directly impact customers, fault tolerance is not very high, and RPA bots can be used to automate the process, saving thousands of hours of work and reducing manual errors.
89. Automated returns
Automating returns can improve customer satisfaction and reduce manual labor.
RPA bots can be used to automate the steps of the return process, which include:
- Checking customer purchase records from the system
- Checking the reason for the return
- Asking more questions, such as “Has the item been worn?”
- Assessing the return’s eligibility
90. Trade promotions
Shop floor trade promotions require back-end admin work. RPA bots can automate relevant tasks such as:
- Creating and allocating funds for promotions
- Generating reports that give visibility into promotion performance
Automation makes it easier and faster for retailers to launch trade promotions.
91. Inventory and supply chain management
Some retailers rely on legacy systems for stockkeeping. RPA bots can perform constant checks on these systems, providing data on key metrics like items with low stock levels or rapidly changing stock levels.
Telecommunications:
92. Credit checks
KYC automation can be done for post-paid accounts.
Real-life example: A major telecommunications company implemented 102 automation over two years, resulting in a 108x increase in collections efficiency and monthly savings of $635,000. Notably, the automation of overdue invoice notifications escalated from sending 200 letters per month to 17,722 emails and 3,811 postal letters. Additionally, the company automated credit checks and service restriction processes, significantly reducing manual effort and increasing operational efficiency.32
93. SIM swapping
Assigning a new SIM to a user. RPA can help SIM swapping by automating the process of customer authentication, indemnification, and authorization.
94. Customer dispute resolution
Automatically classifying disputes, resolving simple ones, and assigning complex ones to related parties is a relatively simple yet effective back-office automation example through RPA.
95. Porting customer numbers
Utility companies can automate number porting when customers switch operators.
96. Telecom billing automation
RPA bots can automatically fill out the billing information on each user’s bill and send it to them.
Utilities:
97. Meter readings
RPA can extract each meter’s usage amount from the meter’s cloud database, put it on the bill, and automatically calculate its cost/watt.
98. Predictive maintenance
Issues in cell towers and cellular wires can cause fires. RPA bots can automatically schedule maintenance by observing each tower’s last maintenance, age, server load, and geographical location.
RPA applications for personal use
99. Personal Tasks
Hobbyists use free editions of RPA solutions to build bots for personal use for applications like transferring business cards to Salesforce or pulling data from multiple websites to identify the best deals on auction websites.
100. Guest Greeter
Another app from a hackathon was built for P&G: An automated receptionist for welcoming visitors to enterprise campuses.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers a powerful solution for handling repetitive, rule-based tasks across various business areas, including the front office (such as customer service) and the back office (such as finance or human resources). To truly benefit from RPA and maximize the value of technology investments, it’s crucial to identify specific, high-value use cases where automation can make a tangible difference.
As demonstrated by the 100 examples provided, RPA can be applied across a wide variety of business functions and specific industries, including finance, manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. These real-life scenarios, along with potential personal applications, demonstrate the versatility of RPA in streamlining processes, reducing errors, and freeing up human workers for more complex tasks.
FAQ
Where is robotic process automation (RPA) used in real life?
Robotic process automation (RPA) software is widely used in real-life scenarios across various industries. Common applications include accounts payable, invoice processing, employee onboarding, customer data entry, financial data management, supply chain, and delivery tracking, where repetitive manual tasks are automated to improve operational efficiency. These robotic process automation use cases highlight RPA’s versatility across sectors.
Where is RPA mostly used?
Identifying RPA use cases involves evaluating tasks that are repetitive, routine tasks, and prone to human errors, such as data entry errors. Processes involving high volumes of data entry, report generation, employee data handling, processing of financial data, and tasks requiring integration between relevant systems are ideal candidates for automation. Such robotic process automation candidates can offer substantial improvements in efficiency.
How to identify RPA use cases?
Identifying RPA use cases involves evaluating tasks that are repetitive, routine, and prone to human errors, such as data entry errors. Processes involving high volumes of data entry, report generation, employee data handling, and tasks requiring integration between relevant systems are ideal candidates for automation.
How is RPA used in industry?
Implementing RPA contributes significantly to digital transformation efforts in many industries. RPA tools are deployed to streamline business process automation by automating tasks such as data entry, report generation, and task tracking. By offloading mundane tasks to robots, human workers can focus on other critical tasks that require creativity and problem-solving abilities.
How does RPA help reduce operational costs?
RPA reduces operational costs by automating routine and time-consuming tasks, offloading mundane tasks and minimizing manual labor. Automating these tasks helps organizations to allocate human resources towards more strategic business functions.
Can RPA enhance employee productivity?
Yes, RPA enhances employee productivity by automating tedious tasks, routine processes, and repetitive manual tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic, complex tasks that require creativity and decision-making.
How does intelligent automation differ from traditional RPA?
Intelligent automation expands traditional RPA by integrating advanced automation technology, enabling automation solutions to handle more complex tasks involving unstructured data, data processing, and more sophisticated decision-making capabilities across different industries such as the healthcare industry, banking sector, and telecommunications industry.
External Links
- 1. Finastra used UiPath Apps to Create a UX-friendly Interface for their Automations | UiPath.
- 2. Carglass Grows Sales and Employee Satisfaction with UiPath Apps | UiPath.
- 3. Automation at Protelindo: Faster Billing & Seamless SAP Migration | UiPath.
- 4. Encova Insurance Scales Automation | UiPath.
- 5. HUB International Transforms Insurance with AI and Automation | UiPath.
- 6. HBL's Digital Journey Fueled by Automation | UiPath.
- 7. Sopra Steria - Use Cases of RPA in Technology | UiPath.
- 8. Why Sales Reps Spend Less Than 36% Of Time Selling (And Less Than 18% In CRM).
- 9. FlySafair Introduced Automation as one of its Innovations | UiPath.
- 10. “HubSpot” Retrieved on December 21, 2022.
- 11. How Many Emails Are Sent per Day? - MacKeeper.
- 12. “Fake online reviews cost $152 billion a year. Here’s how e-commerce sites can stop them | World Economic Forum” Retrieved on December 21, 2022.
- 13. Task Mining and AI-powered Automation Drive Growth at Leaf Home | UiPath.
- 14. 400-Year-Old PostNord is Automating Testing | UiPath.
- 15. “trinet.” automationanywhere, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 16. How a firm enhanced efficiency using Automation Co-Pilot.. Automation Anywhere
- 17. Attended Automation in Action: Three Real World Scenarios. UiPath Inc.
- 18. The Loan Store/MOZAIQ | Automation Anywhere. Automation Anywhere
- 19. “Bank.” blueprism, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 20. “Bank.” blueprism, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 21. “Bank.” blueprism, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 22. The Loan Store/MOZAIQ | Automation Anywhere. Automation Anywhere
- 23. ManpowerGroup: A dramatic leap in candidate validation capacity | UiPath.
- 24. Attended Automation in Action: Three Real World Scenarios. UiPath Inc.
- 25. “Walgreens.” blueprism, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 26. “eletrobras.” automationanywhere, Retrieved on March 2, 2025
- 27. Insurance Claims - Improved Service | Automation Anywhere. Automation Anywhere
- 28. FlySafair Introduced Automation as one of its Innovations | UiPath.
- 29. AccentCare | Automation Anywhere. Automation Anywhere
- 30. BAT Uses UiPath’s Software Robots to Speed Up Production | UiPath.
- 31. RPA case for automation of inventory management | Birlasoft.
- 32. “telecom company.” automationanywhere, Retrieved on March 2, 2025



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.