Top 8 Use Cases & Benefits of RPA in Manufacturing in 2024
Introduction
The global automation market size was expected to generate ±$214B by the end of 2021, of which ±$29B (14%) would have come from manufacturing and factory automation.
This is because numerous processes in manufacturing are repetitive, rule-based, and automatable by RPA bots. For instance, bill of materials (BOM), data migration and analytics, invoices, and inventory reporting are highly repetitive and time consuming tasks if done manually.
These are all processes that can be automated with RPA.
In this article, we are exploring the benefits of RPA and its top 8 use cases in manufacturing.
Business benefits of RPA in manufacturing
A typical rule-based process can be up to 70%-80% automated. RPA bots handle rule-based repetitive tasks and minimize the need for human interference.
In manufacturing, RPA bots can:
- Decrease the labor time spent on routine tasks
- Decrease the time-to-market (TTM)
- Increase data quality and minimize process errors by minimizing human interference
- Maintain an audit trail
Additionally, data collected by RPA bots can be used as input to manufacturing analytics tools and digital twin of an organization software to analyze the overall progress, identify gaps, and find improvement opportunities.
For more, see a comprehensive list of RPA benefits.
Analysis of RPA use cases in manufacturing
The following processes are highly automatable by RPA:
Supply chain management
Invoice processing
RPA bots can automate invoice processing by:
- Extracting specific data from invoices using OCR
- Converting the extracted data into a structured format
- Compare invoices against purchase orders
- Cross-check for duplicates
- Updating invoice records in the ERP system
Learn more about invoice processing automation.
Supply chain optimization
Global supply chains are complex since they involve:
- Suppliers from variety of countries
- Suppliers with different levels of technical sophistication
Smaller suppliers rely more on manual processes. Their customers, as a result, need to use paper or PDF-based documents to track their order shipments. RPA can automate repetitive aspects of such processes, helping humans focus on more complex tasks.
For instance, instead of the user manually copying and pasting a tracking number on the website to know the shipment’s latest location, RPA bots can be programmed to send him/her a push notification, or an email, any time there is a change in the shipping status.
Learn more about supply chain automation.
Production: Bill of materials (BOM)
A bill of materials (BOM), also called product structure, is one of the most vital documents in manufacturing.
A BOM contains the list of raw materials, sub-assemblies, intermediate assemblies, sub-components, parts, and the quantities of each component required to manufacture an end product. RPA bots can be combined with OCR and be programmed to extract specific product or element data, and replicate human steps required to generate a bill of materials.
Stock optimization
Inventory management
Inventory management is the process of auditing and tracking the flow of assets and stock from the factory up until the point of sale. RPA bots can automate:
- monitoring inventory levels
- placing orders
- generating receipts
- tracking deliveries
- replying to quotations and queries emails
Inventory reporting
RPA bots track and replicate GUI steps, therefore they can automate inventory reports by:
- collecting and updating inventory data
- generating inventory reports
- sending reports to designated employees or personnel
For instance, a German, physical robot manufacturing company had to allocate labor to exchange data between its spare-parts inventory software and the ERP application. After leveraging RPA, they were able to have a real-time insight into their inventory of spare parts, thus automating 95% of reoders from different vendors. Moreover, manual errors from manual exchange of data — such as under/overestimating of inventory levels and wrongful reorders — were eliminated to increase reordering efficiency1.
Learn more about inventory management.
Data management
Statistics suggests that 37% of engineers’ time in the manufacturing is spent on collecting and analyzing data manually. On the other hand, manufacturing data requires continuous update and analysis. RPA bots can automate:
- Cleansing inventory and financial data
- Migrating data from older systems to newer systems
- Processing unstructured data (e.g. invoices) via OCR
- Scheduling data imports and conversions (i.e. converting data from one format to another)
- Updating structured data in ERP systems
- Managing data warehouses
Order fullfilment
Order fulfillment includes all the processes after receiving an order from a client, up until delivery. Bots can automate the end-to-end process of order fulfillment by:
- Identifying order emails and notifications
- Downloading order requirement files
- Extracting relevant data
- Updating the order fields and creating an order in the ERP system
- Replying to clients with information about product availability and shipping options.
Proof of delivery
Proof of delivery (POD) documents are a type of receipt that proves that products or goods have been delivered to the client. RPA bots can be integrated with logistics ERP modules to track deliveries. If delivery data is detected, the bot will extract the data, update delivery fields in the ERP module, and generate a proof of delivery receipt.
Recommendations to business leaders
Manufacturing can benefit from different emerging technologies to enhance performance, improve products, mitigate risks, and avoid human errors. Businesses should:
- Use intelligent automation: Intelligent automation is the next generation of RPA tools with AI capabilities that can automate complex processes.
- Leverage AI and Big data analytics: Manufacturing firms produce large amounts of operations and events data. Applying analytics to this data can uncover insights about production processes, analyze productivity, and identify recurring errors. In addition, analyzing manufacturing data will provide information about market trends and customer requirements in different periods, and enable predicting future customer needs.
- For more on smart manufacturing, read:
- Embrace virtual and augmented reality: Manufacturing businesses can rely on virtual and augmented reality to design and create product prototypes, maintenance, repair, and training new employees on machines or software.
- For example, some automobile manufacturers rely on virtual reality to ensure that vehicles are tested at early phases development, in order to optimize the design, tolerance and safety features.
However, there are some challenges that executives face in manufacturing digital transformation. A report in 2020 indicates that the following are the top barriers to the adoption of new tech:
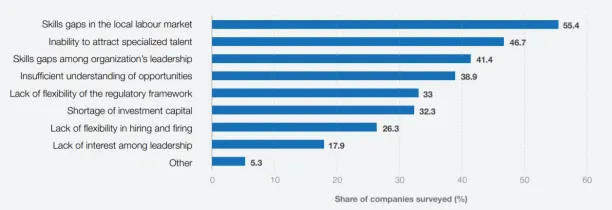
Nonetheless, statistics shows that ±93% of businesses agree that novel technologies are necessary to reach their digital transformation goals, and 70% of companies either have an on-going digital transformation strategy or are planning one.
For more on RPA
To explore RPA applications in different industries, to check out these articles:
- RPA Use Cases & Examples in Finance
- RPA Applications & Use Cases in Real Estate Industry
- RPA in Healthcare: Benefits, Use Cases & Case Studies
If you still have any questions about RPA, feel free to download our in-depth whitepaper on the topic:
And if you think your business will benefit from an RPA solution, don’t hesitate to check out our data-driven list of RPA platforms and vendors.
And we can guide you through the process as well:
This article was drafted by former AIMultiple industry analyst Alamira Jouman Hajjar.
Sources
- Physical robot manufacturing case study.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.