The industrial manufacturing industry is the top adopter of artificial intelligence, with 93 percent of leaders stating their organizations are at least moderately using AI.
Manufacturers are frequently facing different challenges such as unexpected machinery failure or defective product delivery. Leveraging AI and machine learning, manufacturers can improve operational efficiency, launch new products, customize product designs, and plan future financial actions to progress on their digital transformation.
Explore Manufacturing AI’s
- Top use cases and real-life examples to learn how to implement Manufacturing AI in your business
- Importance and benefits
- The current adoption level and market overview
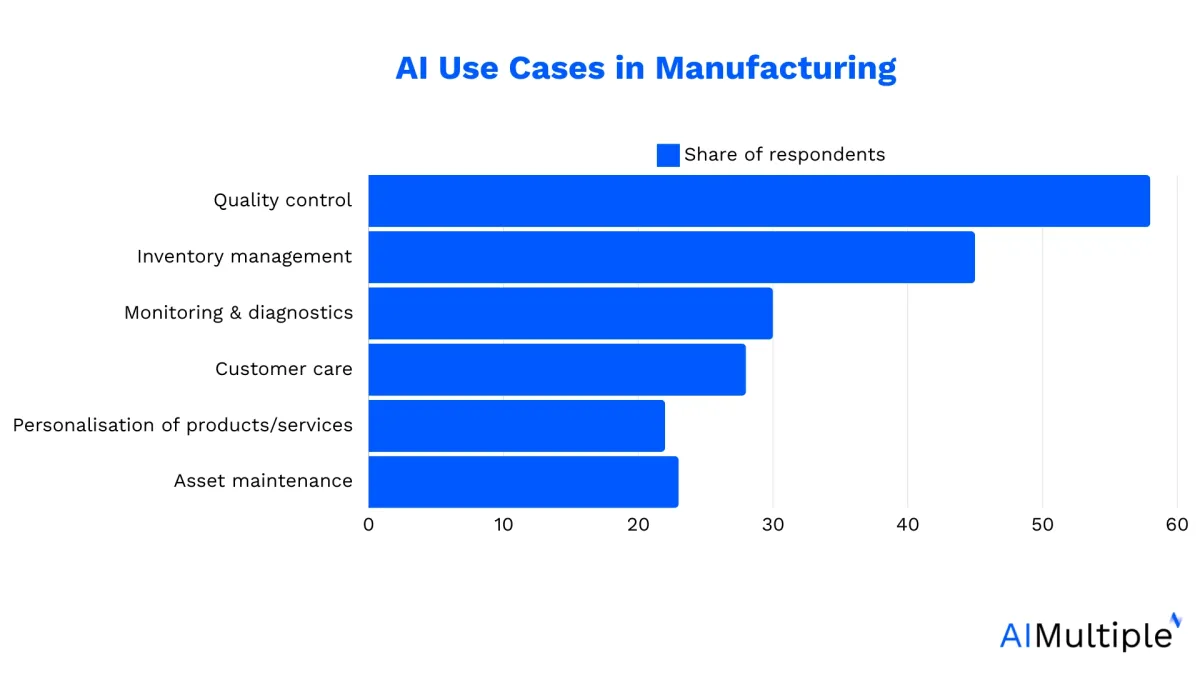
What are the common AI use cases in manufacturing?
1. Predictive maintenance
Manufacturers leverage AI technology to identify potential downtime and accidents by analyzing sensor data. AI systems help manufacturers forecast when or if functional equipment will fail so its maintenance and repair can be scheduled before the failure occurs. Thanks to AI-powered predictive maintenance, manufacturers can improve efficiency while reducing the cost of machine failure.
Real-life example
For example, PepsiCo’s Frito-Lay plants used AI-driven predictive maintenance to save costs and improve equipment performance. The firm could minimize unplanned downtime and increase production capacity by 4,000 hours. 1
2. Generative design
Generative design leverages machine learning algorithms to replicate an engineer’s design process. Designers input parameters like materials, size, weight, strength, manufacturing methods, and cost into the software, which generates all possible outcomes based on those criteria. This allows manufacturers to quickly produce thousands of design options for a single product.
Real-life example
Airbus implemented AI to cut aircraft aerodynamics prediction times from 1 hour to 30 milliseconds, allowing engineers to test 10,000 more design iterations in the same amount of time, significantly improving innovation capacity.2
3. Price forecasting of raw material
The extreme price volatility of raw materials has always been a challenge for manufacturers. Businesses have to adapt to the unstable price of raw materials to remain competitive in the market. AI-powered software like can predict materials prices more accurately than humans and it learns from its mistakes.
4. Robotics
Industrial robots, also referred to as manufacturing robots, automate repetitive tasks, prevent or reduce human error to a negligible rate, and shift human workers’ focus to more productive areas of the operation. Applications of robots in plants vary. Applications include assembly, welding, painting, product inspection, picking and placing, die casting, drilling, glass making, and grinding.
Industrial robots have been in manufacturing plants since the late 1970s. With the addition of artificial intelligence, an industrial robot can monitor its own accuracy and performance, and train itself to get better. Some manufacturing robots are equipped with machine vision that helps the robot achieve precise mobility in complex and random environments.
Cobots are another robotics application that uses machine vision to work safely alongside human workers to complete a task that cannot be fully automated. Feel free to learn more about cobots with our comprehensive guide.
Real-life example
At BMW’s Spartanburg plant, AI-managed robots managed to save the company $1 million yearly by optimizing manufacturing processes and reallocating workers to more critical tasks.4
Ford utilized six cobots to sand an entire car body in just 35 seconds, automating tasks like welding and gluing, which improves precision and speed in production.5
5. Edge analytics
Edge analytics provides fast and decentralized insights from data sets collected from sensors on machines. Manufacturers collect and analyze data on edge to reduce time to insight. Edge analytics has three use cases in manufacturing:
- Improving production quality and yield
- Detecting early signs of deteriorating performance and risk of failure
- Tracking worker health and safety by using wearables
To learn more about analytics in manufacturing, feel free to read our in-depth article about the top 10 manufacturing analytics use cases.
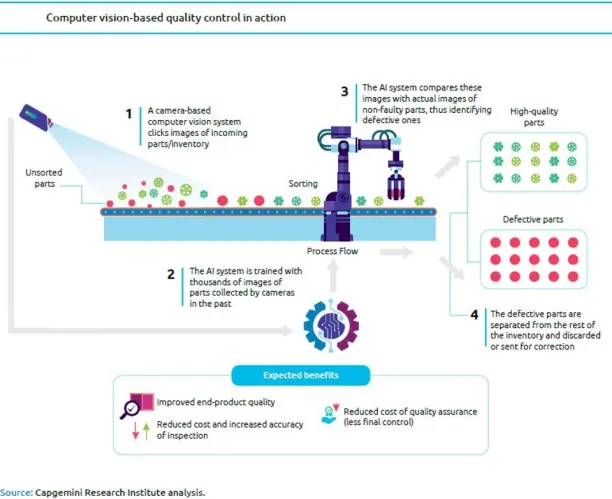
6. Quality assurance
Quality assurance is the maintenance of a desired level of quality in a service or product. Assembly lines are data-driven, interconnected, and autonomous networks. These assembly lines work based on a set of parameters and algorithms that provide guidelines to produce the best possible end-products.
AI systems can detect the differences from the usual outputs by using machine vision technology since most defects are visible. When an end-product is of lower quality than expected, AI systems trigger an alert to users so that they can react to make adjustments.
You can also check the lists of data annotation and AI/ML tools and services to find the option that best suits your project needs:
- AI/ML Development Services
- AI Consultant
- Data Science / ML / AI Platform
- Video annotation tools
- Data annotation services
- Medical Image Annotation Tool
Real-life example
Samsung uses automated vehicles, robots, and mechanical arms for tasks like assembly and quality checks, ensuring consistent inspection of 30,000 to 50,000 components.6
7. Inventory management
Machine learning solutions enhance inventory planning by improving demand forecasting and supply planning. AI-powered demand forecasting tools outperform traditional methods like ARIMA and exponential smoothing, commonly used in manufacturing. These tools help businesses optimize inventory levels, reducing the chances of cash-in-stock and out-of-stock situations.
8. Process optimization
AI-powered software can help organizations optimize processes to achieve sustainable production levels. Manufacturers can prefer AI-powered process mining tools to identify and eliminate bottlenecks in the organization’s processes.
For instance, timely and accurate delivery to a customer is the ultimate goal in the manufacturing industry. However, if the company has several factories in different regions, building a consistent delivery system is difficult.
Process mining tools allow manufacturers to break down and compare workflows across regions, pinpointing inefficiencies in cost, time, and labor. These insights help streamline processes and identify bottlenecks so that manufacturers can take action.
- Explore more on process mining in manufacturing and logistics.
- Check out for other process mining use cases and their real life examples which are process mining case studies.
Real-life example
For example, a manufacturer that employed a process mining tool in their procure-to-pay processes decreased deviations and maverick buying worth to $60,000. 7 The firm also identified process automation opportunities for invoicing tasks by 75%.
9. AI-Powered digital twin use cases
A digital twin is a digital replica of a physical asset, system, or process used for analysis and simulation. By combining AI techniques with digital twins, manufacturers can improve their understanding of the product and allow businesses to experiment in future actions that may enhance asset performance. There are typically 4 applications of digital twins in manufacturing:
- Predictive maintenance
- Shop floor performance improvement
- Self-driving car developments
- Design customization
Real-life example
Rolls-Royce leveraged digital twins combined with AI to enhance predictive maintenance, led to a 48% increase in time before the first engine removal, improving aircraft maintenance efficiency.8
10. Product development
Manufacturers can use digital twins before a product’s physical counterpart is manufactured. This application enables businesses to collect data from the virtual twin and improve the original product based on data.
Real-life example
Using AI, Pfizer designed the Covid-19 drug Paxlovid in just 4 months, cutting computational time by 80-90%, demonstrating the potential of AI in speeding up drug discovery.9
Explore other applications of AI in pharmaceutical industry.
11. Design customization
To meet rising personalization demands, manufacturers use digital twins to explore different product variants before production. This allows customers to purchase the product based on performance metrics rather than its design.
12. Shop floor performance improvement
Digital twins enable real-time monitoring of production to detect quality issues or underperforming components early on.
Real-life example
Nvidia uses AI to streamline the design of complex silicon chips, optimizing a layout with 2.7 million cells and 320 macros in just 3 hours, drastically speeding up the design process and enhancing control over cost and performance.10
13. Logistics optimization
Digital twins allow manufacturers to gain a clear view of the materials used and provide the opportunity to automate the replenishment process.
Learn how AI—especially generative AI—supports smarter, more adaptive supply chain strategies.
Why is AI important in the manufacturing industry?
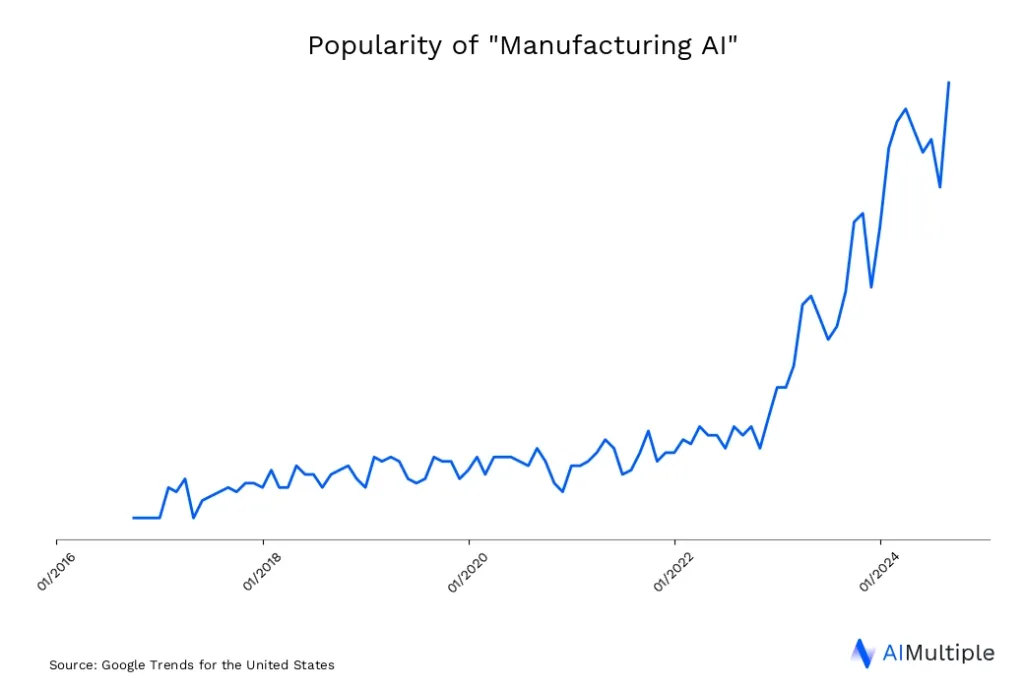
Manufacturers are increasingly integrating generative AI to streamline processes like inventory control and production scheduling.
Manufacturing AI market overview
The Manufacturing AI market forms a dynamic landscape, showcasing a variety of tools with distinct goals and functionalities. Some tools are specifically designed for predictive maintenance, ensuring the seamless operation of machinery, while others excel in quality control, enhancing product precision.
Certain tools specialize solely in optimizing manufacturing processes, while a comprehensive set addresses both manufacturing processes and supply chain optimization. Manufacturing AI solutions can be categorized into three segments, aligning with the diverse objectives they fulfill within the manufacturing ecosystem.
The market segments include:
1. Pure Play Startups: Within this category, nimble startups focus on developing specialized tools catering to specific aspects of the manufacturing process. These startups often introduce cutting-edge solutions for predictive maintenance, quality control, and streamlined manufacturing operations.
2. Scale-ups: Scale-ups, having successfully navigated initial stages, bring a mix of innovation and reliability. Their tools cover a spectrum of functionalities, from optimizing manufacturing processes to addressing supply chain challenges. This category offers scalable solutions to meet the evolving demands of the industry.
3. Big Tech Companies:Big tech companies leverage extensive resources and expertise to offer comprehensive toolsets that excel in predictive maintenance, quality control, and manufacturing processes. They also play a crucial role in optimizing supply chains and driving the standardization and widespread adoption of AI technologies across the manufacturing industry.
For more, explore and compare top manufacturing AI solutions.
What are the benefits of AI in manufacturing?
Safety
Manufacturing is one of the highest-risk industrial sectors to be working in with more than 3,000 major injuries and nine fatalities occurring each year. The involvement of robots in high-risk jobs can help manufacturers reduce unwanted accidents.
Cost Reduction
AI technologies can reduce the operation costs of manufacturers due to several applications:
- Leveraging AI technologies can enhance organizations’ analytics capability so that they can use their resources more efficiently, make better forecasts, and reduce inventory costs. Thanks to better analytics capabilities, companies can also switch to predictive maintenance leading to eliminating downtime costs and reducing maintenance costs.
- This one is obvious but manufacturers don’t need to pay monthly salaries to robots. However, robots require CAPEX which needs to be weighed against the recurring cost of labor.
Faster decision making
Thanks to IoT sensors, manufacturers can collect large volumes of data and switch to real-time analytics. This allows manufacturers to reach insights sooner so that they can make operational, real-time data-driven decisions.
24/7 production in dark factories
Factories without any human labor are called dark factories since light may not be necessary for robots to function. This is a relatively new concept with only a few experimental 100% dark factories currently operating.
However, dark factories will increase over time with the application of AI and other automation technologies since they have the potential to unleash significant savings, end workplace accidents and expand their production capacity. Read more on AI applications in different industries:
FAQ
What is Industry AI?
Industry AI refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies tailored specifically for various industrial sectors, such as manufacturing, energy, logistics, and construction.
Industry AI involves using AI to optimize processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enable smarter decision-making within industrial environments.
What kinds of AI technologies are included in Industry AI?
Industry AI can include:
– Machine learning for predictive maintenance and quality control
– Computer vision for defect detection and monitoring
– Robotics and automation powered by AI
– Natural language processing for smart documentation and voice control
– Data analytics for supply chain and production optimization.
Is Industry AI relevant for Manufacturing AI?
Yes, Manufacturing AI is a core part of Industry AI. Industry AI provides the broader framework and technologies that Manufacturing AI leverages.
Many Industry AI solutions are designed to address manufacturing-specific needs, making the two closely connected.
If you still have questions on how AI revolutionizing the manufacturing industry, don’t hesitate to contact us:
External sources
- 1. ‘Predictive-Maintenance’ Tech Is Taking Off as Manufacturers Seek More Efficiency - WSJ. The Wall Street Journal
- 2. AI in Aerospace Industry: Redefining Intelligent Engineering | Neural Concept. Neural Concept
- 3. Deplazes, R. (2019). “Autodesk and Airbus Demonstrate the Impact of Generative Design on Making and Building.” adsknews. Retrieved at December 19, 2024.
- 4. How BMW uses AI to make vehicle assembly more efficient. CNBC
- 5. Ford Choreographs Robots to Help People – and Each Other – on the Fiesta Assembly Line | Ford of Europe | Ford Media Center.
- 6. Inside the Factory Where Robots Are Building Your Next Samsung Phone - CNET. CNET
- 7. Global Manufacturing Company | IBM.
- 8. The IntelligentEngine - Aerospace Manufacturing and Design. Aerospace Manufacturing and Design
- 9. 11 Big Pharma companies are using AI for industry transformation.
- 10. Nvidia shows new research on using AI to improve chip designs | Reuters. Reuters
- 11. Deloitte Survey on AI Adoption in Manufacturing | Deloitte China | Consumer & Industrial Products.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.