Based on our experience with RPA software during our RPA benchmark as well as external market presence metrics like number of reviews and employees, we selected the leading and emerging RPA providers. Follow the links to see our rationale behind each selection:
| Vendor | Free trial | Number of Employees | Ratings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fortra Automate | ✅ | 1,721 | 4.6 based on 114 reviews |
| Argos Labs | ✅ (60-days) | 28 | Not enough reviews for a rating. |
| Automation Anywhere | Community edition | 2,368 | 4.4 based on 5,648 reviews |
| IBM Robotic Process Automation | ✅ (30-days) | 4.6 based on 296 reviews | |
| Microsoft Power Automate | ✅ (90-days) | 244,900 | 4.5 based on 524 reviews |
| UiPath RPA | Community edition | 4,932 | 4.6 based on 6,947 reviews |
| Blue Prism | ✅ (30-days) | 1,051 | 4.2 based on 364 reviews |
| Workfusion Intelligent Automation Cloud | Community edition | 272 | 4.2 based on 34 reviews |
| VisualCron | ✅ (30-days) | 1 | 4.7 based on 18 reviews |
| AssistEdge | Community edition | 317,793 | 4.0 based on 12 reviews |
| BotCity | ✅ (30-days) | 30 | Not enough reviews for a rating. |
Increasing number of RPA solutions and the different types of RPA solutions (e.g. low-code, no-code, Python RPA tools & Python RPA library, RPA-as-a-service) poses a challenge to businesses trying to choose the best RPA solution for process automation.
For a more comprehensive overview of RPA vendors, check out data-driven list of RPA solutions with an easy-to-use UI to sort and filter the results and learn more about the products.
See top RPA tools, their features, and limitations below as well as a guide on how you can choose the right robotic process automation tool for your business:
Top RPA vendors
Fortra Automate
Fortra’s Automate is a robotic process automation (RPA) platform designed to streamline business processes.
The platform can automate a wide range of tasks, including file transfers, report generation, and data extraction, across various applications.
Argos Labs
Argos Labs is a low-code python automation platform. It is less well-known compared to some other major players, but gaining traction in specific sectors.
For example, Argos Labs automated the manual validation and input of sales data from GEOPAL to the CRM system for a utilities provider in Northern Ireland. This eliminated manual entry errors and significantly speeds up the sales-to-CRM process.
Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere offers a cloud-native platform. It includes:
- IQ Bot for cognitive automation
- Bot Insight for built-in analytics
IBM Robotic Process Automation
IBM robotic process automation is often chosen by companies already using other IBM solutions. It leverages IBM’s Watson AI capabilities for intelligent automation.
Microsoft Power Automate
Microsoft Power Automate is a RPA with both cloud-based and desktop automation options. It is:
- High integration capabilities with Microsoft 365 ecosystem
- Includes AI Builder for intelligent document processing and form processing
- Provides low-code/no-code automation capabilities
- Often more cost-effective than other leading RPA providers for existing Microsoft customers
UiPath Business Automation Platform
UiPath offers a comprehensive platform with Studio (for developers), Orchestrator (for deployment and management), and Robots (for execution). UiPath provides:
- Strong AI and machine learning capabilities
- Extensive library of pre-built components and activities
- Supports both attended and unattended automation
- Robust community and marketplace for shared components
- Easy-to-use interface.
What are the key features of RPA tools?
The right RPA tool for a specific process in a specific industry depends on the capabilities of the tool. Robotic process automation bots from all robotic process automation companies can be categorized by the functionality they provide in these 3 dimensions:
- Programming options: RPA bots need to be programmed, and there are 2 ways to program them: Code-based, low-code / no-code (i.e. supported by a UI).
- Cognitive / AI capabilities: RPA tools vary in the range of their cognitive capabilities, which determine their actions based on the inputs they gather from other systems.
- See intelligent automation tools to learn more.
- Usage: Robotic process automation bots serve specific functions. Some tools are more optimized for attended, unattended, or hybrid automation, all of which dictate the extent of a human’s involvement in maintaining the functionality of the bot.
To learn about the different types of RPA in more detail, click here.
What are the types of RPA tools?
With more than 50 players in the market, it is hard to identify the best RPA solution. The best solution for your company depends on your specific requirements.
RPA bots are software robots that complete specific automatable activities. There are 4 types of robotic process automation tools on the market.
- Even before RPA software, enterprises were using automation tools. Employees were automating simple processes with excel automation, macros and simple hacks. These solutions were not scalable or sustainable but they increased productivity of individual employees.
- First generation RPA tools were programmable bots that required specific inputs.
- Cognitive or intelligent automation bots augment programmable bots with advanced functionality like Natural Language Processing, image recognition or machine learning. These bots have augmented capabilities in interacting with unstructured data and can be effective in decision making. To achieve this functionality, solution providers generally bring together services from several companies such as NLP API providers and RPA providers.
- Self-learning tools are sometimes being marketed by vendors. These tools are supposed to watch employees in action, understand processes, take over processes when they reach confidence and ask for human input if they get completely new input. However, they are mostly confined to research projects and are not a commonplace automation technology. With enterprise agentic AI, bots may adopt some self-learning features.
How to choose the best RPA technology for your company?
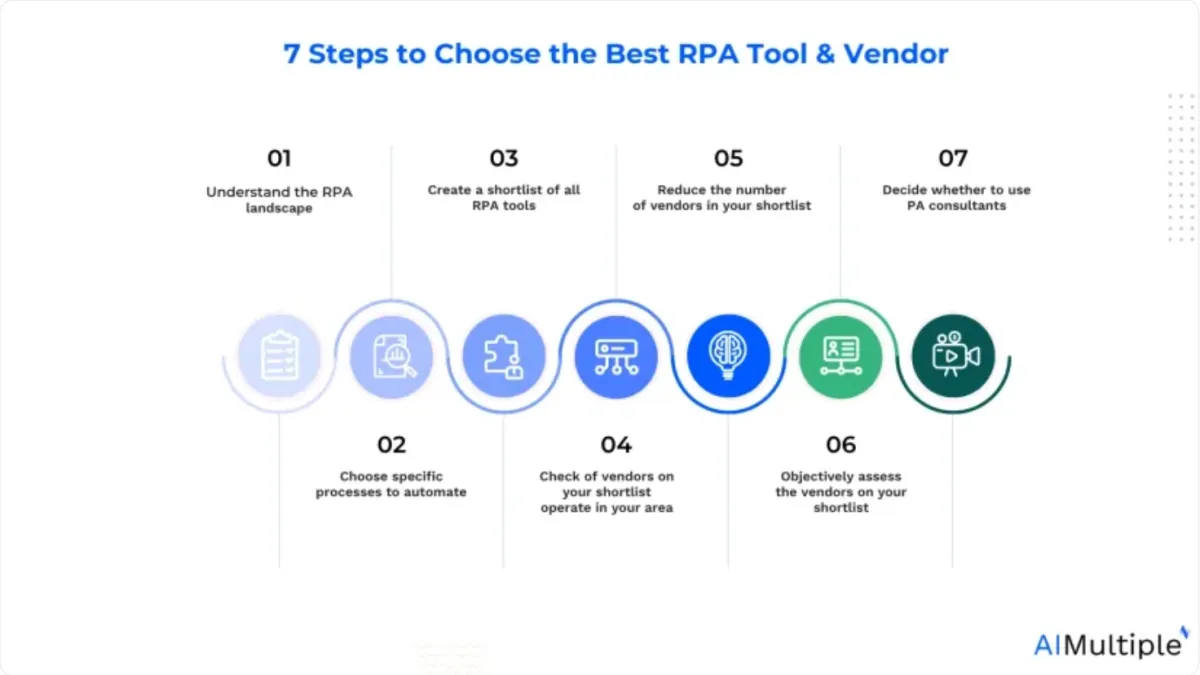
Global RPA market size is expected to reach $64 billion by 2032 thanks to more businesses selecting and leveraging RPA software. See the key steps for RPA adoption:
1. Understand robotic process automation vendor landscape
No RPA tool is the best one for every industry or process. This view was also shared by RPA consultants during our interviews.
These are the main types of RPA vendors:
Established technology providers
Companies like Pegasystems or Kofax were launched in 1980s and 1990s to provide solutions that support various digitization needs of companies.
For example, Kofax established itself as a digital transformation vendor offering services like document digitization, e-signatures. Using their relationships with companies, process knowledge and understanding of change management in companies, they launched RPA products.
1st wave RPA focused vendors
Founded in 2000s, these vendors are focused on providing RPA solutions and already reached significant scale. Initially they provided and later perfected programmable bot solutions. Currently, they are focused on improving advanced capabilities of their bots, offering cognitive automation capabilities and a marketplace to extend the capabilities of their solutions. Some examples in this group are:
- Blue Prism already went public and works with numerous Fortune 500 customers
- UiPath, founded in 2005, works for 6 of Fortune 10, 8 of world’s top 20 financial services organizations
2nd wave RPA focused vendors
Founded in 2010s, these vendors are focused on providing latest generation RPA solutions like cognitive or intelligent automation. To achieve higher levels of automation, they focused on specific industries. For example, Workfusion, founded in 2010 is focused on the financial services industry.
Upcoming RPA vendors specialized in innovative RPA solutions
Recently, scope of RPA has grown significantly as we covered in our section on different types of RPA. As a result, specialized RPA companies are on the rise. As we covered in our future of RPA article, we see these as the areas of focus for new RPA companies:
- No code RPA: Companies develop RPA solutions that do not require coding. This facilitates and speeds up RPA development. However, the distinction between no code and low code RPA tools is not a clear one, most RPA solutions allow developers to embed code. For more, read our article on no code RPA.
- RPA for MSPs: RPA focused on Managed Service Providers (MSPs) needs. MSPs are called System Integrators (SIs), technology service providers or consultants. These tools provide pricing that is in-line with these companies’ needs. They offer affordable prices at scale or at individual bot level so these service providers can provide a cost-effective RPA-as-a-Service offering to their customers.
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) providers

Source: gdmanagement.com
Companies like Infosys from India already run numerous processes for large companies. It is only logical that these companies are striving to automate the processes they took over from other companies. As a result, they have accumulated significant expertise in RPA.
Most of these companies do not have their own RPA solutions however, they formed partnerships with RPA solution providers and offer turn-key solutions to companies. This model allows companies to focus on business while BPO provider automates the process so it is an interesting alternative for companies that have issues managing day-to-day business with their current headcount.
BPOs can leverage RPA solutions in-house to provide cost-effective outsourcing for automatable processes. They manage the automation while also addressing any edge cases that might disrupt bot operations. This model allows companies to avoid the complexities of automation, making it a hassle-free solution for business process outsourcing.
Now that you know the industry landscape, it is time to prepare your short list of vendors.
2. Pick a process to automate that will clarify your needs.
To identify the important RPA selection criteria for your business, it would be good to understand what are good candidate processes for RPA automation at your company. There are advantages offered to users in different areas such as the use of RPA in utilities and RPA in finance.
We have a comprehensive guide on popular processes for RPA automation and an RPA guide that includes steps to determine which processes in your company are good candidates for RPA automation.
Process mining is an emerging technology that can help businesses identify the best processes to automate. By using real-time data like event logs, process mining reflects the business processes’ actual performance and detects bottlenecks.
For example, in a process mining case study, Caverion, a building and industrial systems company, leveraged process mining to enhance their processes and accelerated their invoicing processes by 50%.
If you do not have the bandwith to pick the right processes, there are numerous companies including system integrators and Big 4 offering RPA consulting services. You can read more about this in our RPA consulting guide.
Now that you know the processes to be automated, you can understand which attributes of RPA vendors are more relevant for your business. For example, you should consider automating part of you candidate processes with RPA to see how easy-to-use the RPA tool is.
3. Get the list of all RPA tools to prepare your short list within minutes
Prioritize vendors your company already works with, especially if you’re in a Fortune 500. Established relationships with technology or BPO providers for RPA services can expedite purchases. Buying multiple services from a vendor also gives procurement more leverage to negotiate better prices.
If you are feeling lazy, just query the the list below against your procurement database. You could also use the list of vendors below but that list is not may not be as up-to-date as the one on our platform. Now you have the beginning of a short list of vendors.
You can finalize your shortlist after adding leading vendors with whom your company has no relationship yet. Our list above and database allows you to make those additions. Instead of trying to compare vendors by looking at a marketing employee’s fancy adjectives, we offer you the real and up-to-date data.
You can compare established companies and startups on objective metrics using this list. By ranking the most suitable vendors based on your own insights, you will never be fooled with subjective rankings and choose what is best for your company.
We get the question “What’s the best rpa software?” from companies after they go through the list. It is unfortunately impossible to say that without understanding your company’s automation need in detail and this guide helps you do that. However, if you insist, you can check out our attempt to rank different RPA software with objective and transparent metrics.
4. Check if vendors in your shortlist are operating in your area
RPA vendors are expanding their geographic coverage rapidly. It’s easy to find testimonials from Japan to Africa on leading vendors’ websites. And even if they do not have an office in your country, they are probably serving it from a regional office or serving it via their partners like Big 4.
However, if you are considering a large RPA roll-out, it is still good to check if the vendors you selected are offering their services in your country. Having access to their experts can reduce implementation time and improve the success of your RPA project.
5. Reduce the number of vendors in your shortlist
Now that you have your short list of vendors and your partially filled list of criteria, it is time to start communicating with vendors. Before talking to vendors, we recommend going to their profile on our website to understand a bit more about who they work with and how they describe their services.
After meeting with vendors and evaluating them across these criteria, you will be ready to choose your vendor. After choosing your vendor, you can use our guide on RPA application areas to explore processes ripe for automation.
6. Use a checklist to help you fairly and clearly assess RPA vendors.
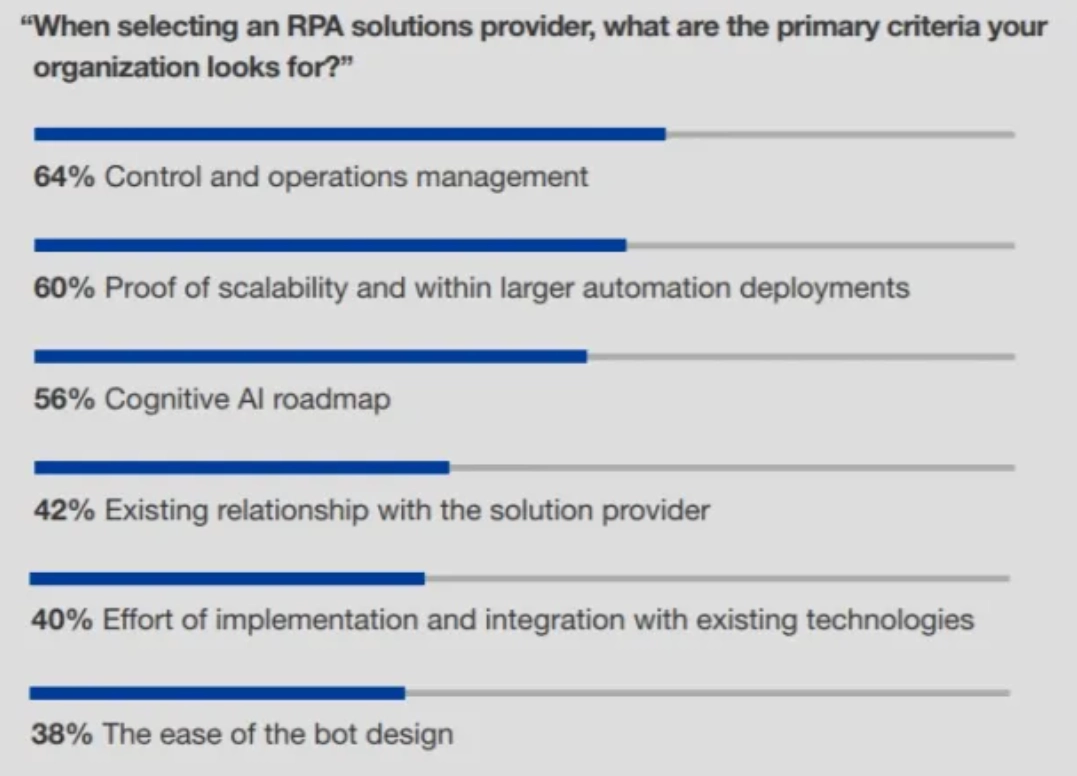
There are plenty of sources on criteria for choosing RPA providers. For example, the list above from Forrester which is based on 105 answers by managers listing their primary criteria for selecting an RPA solutions provider. We created the full list of criteria and categorized them to make the list more manageable.
- Total cost of ownership which includes initial setup cost of RPA system, ongoing vendor license fees and maintenance cost.
- Initial setup cost: Initial setup costs can also be negligible if in-house process experts can train bots. However, if in-house resources are better utilized elsewhere, business consulting companies like Accenture and Infosys can augment your workforce and speed up implementation.
- Ongoing vendor license fees: Vendors like Workfusion and UiPath offer free editions. However, these vendors only offer their rule-based bots for free. Cognitive bots that learn by watching employees are a premium product and can be priced per bot or per process. Since different vendors use different pricing models, you need to estimate the total vendor license fee you will pay.
- Maintenance cost: As inputs and systems change, your bots will require maintenance. When you roll-out bots, your teams will need to set up the alerts needed to identify bot issues. As those alerts arise, your teams will be fixing bot configurations to maintain bots. This is not a directly measurable financial cost however it will distract your employees. An easy-to-maintain solution will make your employees happier and more productive.
- Ease of programming and control:
- Ease of automation: A user friendly solution easy enough to be used by your team can help them implement RPA in new areas and increase both efficiency and employee satisfaction. Easier to use solutions will also require less training and allow your new hires get up to speed faster.
- In-person or virtual training options: Quality of available training is also an important factor here. Great text or video tutorials and availability of hands-on training can help employees become quickly proficient in RPA solutions. Some leading RPA solutions providers offer community versions of their products. To support RPA development by their community, they offer free courses, training material and community forums helps users support one another.
- Ease of control: Once your process is automated, you will need to make adjustments to how it is running. For example, you may need to stop bots during systems maintenance and add bots when process volume increases. Different providers offer different levels of automation and granularity of control. That’s why it is good to use the bot orchestrator before the purchase.
- Ease of use depends on bot development options, such as availability of Graphical User Interface (GUI) for drag&drop bot building and macro recording. Additionally, new vendors are pushing for completely code free RPA solutions that are simpler/easier to implement.
- You can’t know ease of use without using the product. Once you reduce your shortlist to 2 or 3 vendors, pick the simplest use case that you really need to automate, sit down with vendor personnel for an hour and automate that process on a demo environment. Automating a process will help you understand how easy to use each RPA solution is.
- Ease of use (from an end-user perspective): Attended RPA or RDA (Robotic Desktop Automation) bots are triggered by end-users such as call center agents. Therefore, ease of use of bots from an end user perspective is important for these bots. The most important feature we noticed in this case is concurrency which enables an end-user to work at the same time as a bot. Without this feature, bots that need to take long periods of processing time do not become feasible to use in attended RPA.
- Technical criteria needs to be evaluated by the company’s technology team. RPA software needs to comply with the technology guidelines of the company in terms of:
- Minimum system requirements in terms of software and hardware
- Security
- Integrations
- Screen scraping capabilities
- Cognitive or intelligent automation capabilities
- Compliance to company’s product roadmap
- Vendor experience: Ideally, it is best to work with a vendor that served a company similar to yours both in terms of size and industry. This may not be easy to find but it would be easier to work with a vendor that understands the needs and processes of your business. Such experience can drastically improve speed of implementation by reducing the work required to implement RPA software.
- Vendor support: While some companies will require quite some hand-holding, others have technically competent, eager-to-learn staff who can program RPA bots themselves. Based on the needs of your company you need to consider the level of support you will require from your RPA vendor. For a company that requires a lot of support, working with a BPO provider may be a good solution.
- Existing vendor relationship: It is faster to get started with a provider that is already familiar with your company
7. Deciding whether to turn to RPA consultants
RPA consultants assist companies in implementing RPA solutions. If your team lacks the expertise or time for deployment, consider partnering with RPA consultants. Discussions with RPA vendors suggest that experienced consultants can significantly speed up project rollouts, making them valuable even if your team is capable.
Read our RPA consulting article to learn more and to compare 150+ RPA consultants.
Tips to turn your next automation project into a success story
Always bear in mind that there are alternatives to RPA such as system upgrades. If RPA costs are approaching system upgrade costs, you could upgrade your underlying systems and automate the tasks rather than using RPA bots. With either an upgrade of your legacy systems or a flexible RPA solution you will end up with an optimized, automatized operation that can carry your business forward.
If you embark on an automation project, focus on the end-to-end process. Automation provides a chance to rethink the whole process from the customer to the service delivery. Unnecessary steps can be eliminated, and non-compliant or legacy activities can be improved.
For example, removing fields from forms filled out by customers can improve the user experience and reduce the work to be automated. And definitely check out RPA implementation guide before starting any RPA program.
RPA is just one of the areas where AI can add value to your business. You can check out AI applications in marketing, sales, customer service, IT, data or analytics.
And we are aware that though we are constantly improving our content, you probably still have unanswered questions. Please take the time to ask those questions as comments. We regularly talk to leaders of RPA companies. If you can be specific, we can get even your hardest questions answered and email you the answers after adding them here.
How to use RPA for natural language processing?
Robotic process automation has evolved beyond automating simple tasks and is now increasingly applied to unstructured data processing, including NLP. By leveraging intelligent automation combined with machine learning and cognitive technologies, RPA tools can interpret and automate processes involving human language, such as invoice processing, customer inquiries, or sentiment analysis.
These ai-powered automations can process large volumes of text-based data, seamlessly integrating with legacy systems and modern digital systems to enhance overall efficiency. AI tools can also support process mining to identify and automate hidden automation opportunities for business users.
Integrating specialized AI into automation systems has opened the door to more advanced capabilities. Unlike traditional automation, which focuses on predefined rules, AI-enhanced RPA can handle more complicated tasks, such as interpreting complex data or making decisions based on patterns.
This approach enables users to achieve higher levels of precision and scalability, transforming how businesses operate and adapt to changing demands. With artificial intelligence plugins avaliable in many RPA software, developers can easily apply AI to their business processes.
What are the use cases of RPA tools?
Robotic process automation tools are used across industries to automate tasks that are repetitive and manual, improving accuracy and speed. For example, RPA technology can be applied in human resources for onboarding, or in finance for invoice processing and document processing. Software robots can scrape data from web pages or integrate with web services to pull information from various systems.
RPA adoption is growing in healthcare, where software bots automate patient records management. AI-powered automation can further enhance use cases, such as image recognition for sensitive data processing, and optical character recognition for processing scanned documents. In each case, RPA solutions enable businesses to streamline manual processes while freeing up human employees for more complex tasks.
For more on RPA
- Top 100+ RPA Use Cases/Projects/Examples
- 11 Steps to Successful RPA Implementation
- Workload Automation vs RPA: 3 differences you need to know
Before you invest in an off-the-shelf RPA solution, scroll through our data-driven list of RPA tools and automation solutions hub to identify the best fit for your business.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.