Latest process mining trends and stats show that 93% of business leaders aim to leverage a process intelligence software like process mining since these tools enabled process improvement by 23%, digital transformation by 25% and automation by 25%.Process mining offers a variety of use cases beyond these broad application.
Explore the most common 44 use cases within their respective 12 categories:
- Process mining use cases by general processes:
- Process mining applications by industry: Finance, automotive, banking, education, healthcare, insurance, logistics, production
- Process mining use cases by business function: Sales, IT service management & customer service
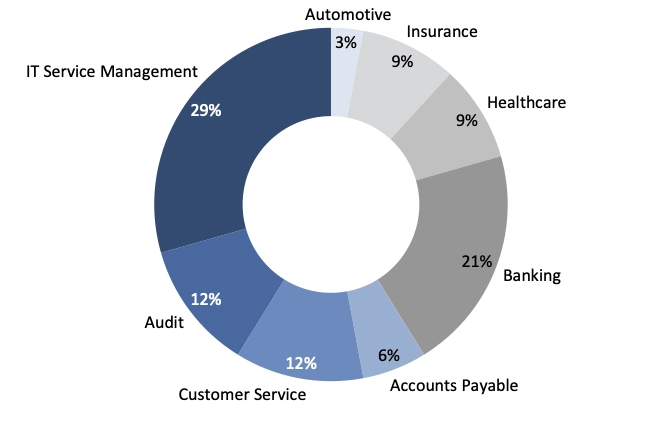
The image above displays share of process mining case studies for these 12 categories. You can see both use cases and real-life case studies:
Process Mining Software use cases with real-life examples
Process optimization
Analyzing event logs to identify inefficiencies and improve speed and accuracy. This involves refining workflows, minimizing resource waste, and leveraging technology to achieve peak operational performance.
Real Life Examples

Lyric Robot, a precision automation and industrial robot system integration company, faced challenges in optimizing processes and lacked a single source of truth. By implementing SAP Signavio Process Intelligence, they were able to map and model their manufacturing processes, resulting in a 60% decrease in time and resources needed for process improvement. The transparency provided by Signavio also helped in quickly diagnosing and responding to issues. Overall, Signavio's solution supported Lyric Robot's growth and provided benefits such as improved compliance, increased visibility, and cost savings.

Stadtwerke Essen AG (SWE), a German utilities company, digitized its accounting processes using Celonis. By leveraging Celonis' process mining solution, SWE was able to automate manual processes, improve data quality, and optimize their accounts payable process. They achieved significant efficiency gains, reduced unnecessary costs, and increased process automation. SWE plans to continue using Celonis to improve other processes and scale for future automations.

Eissmann Automotive, a leading car interior manufacturer, uses Celonis' process mining technology to monitor and optimize various processes. By digitizing their process chain and utilizing Celonis, the company achieves 100% transparency and improves efficiency in areas such as Purchase-to-Pay, master data management, production, and purchasing. The software helps identify bottlenecks, reduce throughput times, and improve overall process performance. Celonis also aids in supplier management, purchasing transparency, and data accuracy. Eissmann Automotive plans to expand its use of Celonis for future projects and optimizations.
Process discovery
Analyzing business processes to optimize automation and improve performance using event logs. This technique uncovers hidden patterns and inefficiencies, paving the way for enhanced process mapping and resource allocation.
Real Life Examples

Lyric Robot, a precision automation and industrial robot system integration company, faced challenges in optimizing processes and lacked a single source of truth. By implementing SAP Signavio Process Intelligence, they were able to map and model their manufacturing processes, resulting in a 60% decrease in time and resources needed for process improvement. The transparency provided by Signavio also helped in quickly diagnosing and responding to issues. Overall, Signavio's solution supported Lyric Robot's growth and provided benefits such as improved compliance, increased visibility, and cost savings.

Stadtwerke Essen AG (SWE), a German utilities company, digitized its accounting processes using Celonis. By leveraging Celonis' process mining solution, SWE was able to automate manual processes, improve data quality, and optimize their accounts payable process. They achieved significant efficiency gains, reduced unnecessary costs, and increased process automation. SWE plans to continue using Celonis to improve other processes and scale for future automations.

Eissmann Automotive, a leading car interior manufacturer, uses Celonis' process mining technology to monitor and optimize various processes. By digitizing their process chain and utilizing Celonis, the company achieves 100% transparency and improves efficiency in areas such as Purchase-to-Pay, master data management, production, and purchasing. The software helps identify bottlenecks, reduce throughput times, and improve overall process performance. Celonis also aids in supplier management, purchasing transparency, and data accuracy. Eissmann Automotive plans to expand its use of Celonis for future projects and optimizations.
Conformance validation
Checking if processes adhere to specified standards and identifying deviations for improvement. This helps organizations ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and maintain high-quality performance across operations.
Real Life Examples

Stadtwerke Essen AG (SWE), a German utilities company, digitized its accounting processes using Celonis. By leveraging Celonis' process mining solution, SWE was able to automate manual processes, improve data quality, and optimize their accounts payable process. They achieved significant efficiency gains, reduced unnecessary costs, and increased process automation. SWE plans to continue using Celonis to improve other processes and scale for future automations.

Eissmann Automotive, a leading car interior manufacturer, uses Celonis' process mining technology to monitor and optimize various processes. By digitizing their process chain and utilizing Celonis, the company achieves 100% transparency and improves efficiency in areas such as Purchase-to-Pay, master data management, production, and purchasing. The software helps identify bottlenecks, reduce throughput times, and improve overall process performance. Celonis also aids in supplier management, purchasing transparency, and data accuracy. Eissmann Automotive plans to expand its use of Celonis for future projects and optimizations.

Siemens partnered with Celonis to improve its business processes and increase transparency. Using Celonis' process mining technology, Siemens was able to map and analyze its various business processes, identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and systematically improve them. This resulted in cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved customer satisfaction. Siemens continues to collaborate with Celonis and is piloting the use of Celonis Pi for advanced process analysis and forecasting. The partnership has allowed Siemens to achieve end-to-end transparency throughout its global supply chain.
Process harmonization
Aligning distinct processes to improve synergies, efficiency, and overall customer experience. This often involves standardizing workflows and eliminating redundancies to ensure consistent service delivery across departments.
Real Life Examples

Lyric Robot, a precision automation and industrial robot system integration company, faced challenges in optimizing processes and lacked a single source of truth. By implementing SAP Signavio Process Intelligence, they were able to map and model their manufacturing processes, resulting in a 60% decrease in time and resources needed for process improvement. The transparency provided by Signavio also helped in quickly diagnosing and responding to issues. Overall, Signavio's solution supported Lyric Robot's growth and provided benefits such as improved compliance, increased visibility, and cost savings.

Becker Buttner Held Consulting AG (BBHC), a consulting firm for energy and infrastructure companies, implemented the Signavio Process Editor to optimize their business processes. The tool provided a collaborative workspace and easy integration of customers in process design. BBHC achieved transparent and understandable business processes, successfully designing processes from different locations and connecting content-related processes. The intuitive process design of the tool was advantageous for all employees. The implementation resulted in improved process optimization, collaboration, and customer satisfaction.

AOK, a health insurance company, uses SAP Signavio Process Intelligence to improve process management and organizational development. The solution allows for the efficient exchange of process knowledge across company borders, supporting organizational change processes. AOK's subsidiaries share process models, enabling them to learn from and help each other. The tool also facilitates HR demand planning based on process models and generates Excel reports for benchmarking and identifying improvement potential. With features like commenting and integrated web-publishing, Signavio enhances collaboration and accessibility of process models.
Process simulation
Using predictive analytics to simulate processes and forecast future outcomes or scenarios. This enables organizations to test various strategies in a risk-free environment and choose the best course of action to achieve desired objectives.
Real Life Examples

Ocean Network Express (ONE) Pte. Ltd, a global container shipping company, used SAP Signavio Process Intelligence to synchronize and transform the business processes of three merged companies. The implementation resulted in streamlined integration, process improvements, time and cost savings, and the establishment of a Center of Excellence. The platform enabled collaboration, increased efficiencies, and provided a single source of truth for business processes. ONE successfully used business process management as a strategic driver for rapid growth and change.
Organizational mining
Analyzing process logs to uncover organizational relationships, performance gaps, and best practices. This process provides insights into team dynamics and collaboration patterns, enabling businesses to realign resources and streamline operations effectively.
Real Life Examples

Honda R&D Americas used the Worksoft Process Intelligence solution to automate business process testing and accelerate its SAP HANA migration. By implementing Worksoft Certify, HRA was able to automate 5,463 test steps and achieve 70% coverage in just five weeks with one person. The automation not only saved time and resources but also provided peace of mind and confidence in system functionality. HRA is now exploring a move to SAP S/4HANA, thanks to the success of the automation project.
Root cause identification
Analyzing process deviations to pinpoint the underlying causes and improve efficiency. By identifying specific points of failure or inefficiencies, organizations can implement targeted corrective actions to prevent recurrence and optimize workflows.
Real Life Examples

EDEKA Minden-Hannover, a regional company in the German EDEKA group, implemented Celonis Process Mining to analyze and optimize its IT service management processes. With over 15,000 tickets generated each month, the company needed a solution to quickly identify errors and improve efficiency. Celonis Process Mining provided real-time analysis, allowing for quick identification of main sources of error and deviations. The implementation resulted in increased analysis efficiency, reduced solution times, and improved process quality, ultimately benefiting the company and its customers.

Schukat Electronic, a distributor of electronic components, implemented Celonis Process Mining to optimize their processes and achieve same-day delivery. By analyzing and identifying vulnerabilities in their processes, they were able to improve efficiency, transparency, and customer satisfaction. The solution provided insights into areas for improvement in purchasing, warehouse management, and sales. With Celonis, Schukat gained visibility, reduced costs, and saved time, ultimately enhancing their competitive advantage in the market.

Vodafone implemented Celonis' process mining technology on SAP HANA to gain transparency and actionable insights into their processes. The technology visualized the as-is process, identified bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and analyzed root causes for process weaknesses. This led to improvements in business critical areas and increased efficiency. The implementation allowed Vodafone to save time, increase productivity, and enhance overall compliance.
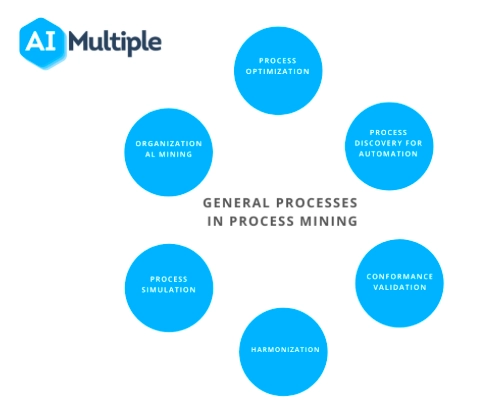
General Processes
1- Process discovery for automation: Automation provides faster and lower-cost solutions. However, companies need to examine their business processes to use automation tools, such as robotic process automation (RPA) efficiently. Process mining vendors claim that their technology can reduce automation implementation time by 50%.
2- Process optimization except automation: Companies can use process mining for faster, more accurate process analysis. Event logs infer performance metrics and models to identify bottlenecks and costly steps for optimization. For instance, we evaluated every benefit of process mining in 51 case studies, revealing a 43% reduction in bottlenecks and a 4% elimination of unnecessary steps
3- Conformance validation: Companies can check if their as is process conform to the given specifications with conformance checks. For example, purchasing decisions need different approvals based on the ticket size and nature of the item purchased.
Nonconforming cases, reasons for deviations and, conformance trends can be analyzed, too. Companies can take action to reduce these deviations and ensure standardized processes.
4- Harmonization: Companies can use process mining to harmonize distinct processes efficiently. Insights from process mining tools enable quick realization of planned synergies. Example: In a process mining case study, Nokia applies process mining to its purchase-to-pay and order-to-cash processes, achieving a smooth customer experience and gaining knowledge on how to conjugate these processes effectively.
5- Process Simulation: Process mining capabilities can include process simulation and predictive analytics. Firms can make future predictions by mining and simulating their processes with the data gained from event logs. Their predictive analysis can be used to inform stakeholders and customers. Real-life example: the customer can receive an accurate estimate of when her loan application will be processed.
6- Organizational Mining: Process logs can identify organizational relationships, performance gaps, and best practices. However, almost all processes have a human component. Process data can be used to understand and improve the human aspects of business processes.
Sales
Lead-To-Order
7- Reduced sales cycle time: Lead-to-order processes can take a long time. This causes the payback time of marketing investments to increase. Companies can uncover the reasons behind this issue and, take action to reduce sales cycle time.
8- Increased conversion rate: Converting marketing strategies into sales is critical for companies. With a process mining tool, companies can discover if they have proper strategies for increasing conversion rates.
Order-to-Cash
Order-to-cash (O2C) encompasses all steps from receiving an order to completing payment and delivery. Process mining can help identify all the little bottlenecks that might exist in the process that hamper a smooth operation.
Read more on how to optimize order-to-cash processes with process mining.
9- Increasing on-time delivery: For customer satisfaction, on-time deliveries are essential. Companies can use process mining to uncover the reasons behind late deliveries.
10- Identifying reasons that hurt monthly revenue: Companies may lose a portion of their earnings during this process due to long-running holds or order cancellations. Process mining tools may point out the root causes of those issues and, companies can minimize those losses accordingly.
11- Locating key regions: With process mining, the companies can detect their high-value customers and critical areas to focus on those areas.
12- Identifying root causes of order changes: Customers sometimes change their orders which causes processes to take a longer time. The unclarity of pre-order stages might cause these order changes. Companies prefer to decrease these order changes to stabilize their processes.
13- Benchmark the amount of returned goods: Companies can discover the value of returned goods by using process mining. According to this insight, they can focus on improving their order-to-cash processes.
Find more details on how to apply process mining to sales processes.
IT Service Management
14- Reduced risk in ERP related developments: In Lassila & Tikanoja’s process mining case study, the company has implemented a new ERP system by employing process mining. The company achieved their goal to reduce the risks by increasing visibility to the ERP system and operational processes.
15- Reduced costs in ERP maintenance, development and support: Process mining can pinpoint mistakes or gaps in the IT systems, such as SAP. The same process mining case study (Lassila & Tikanoja) showed that the company reduced their implementation costs along with the risks of ERP deployments even though it was not primary goal of the project.
16- Delivering higher first-time resolution: IT systems may not provide the correct solution at their first try. Process mining tools can produce data-driven insights to increase the first-time resolution rate.
17- Discovering root causes of delays: Long-running tickets is a common issue. Companies can mine their processes to understand why those tickets are open for long. From the results gained from process mining tools, companies may discover shortfalls in their IT systems.
18- Automating for faster resolution times: IT service management is another field that is open to automation. Companies can use process mining to find areas to automate and provide faster resolution times. Some case studies claim that process mining tools decrease resolution times by 65%.
Find out 10 reasons to leverage process mining for IT service management.
Finance
Here we cover applications of process mining in the finance function of companies (not financial services industry specific applications):
Purchase-To-Pay
19- Identifying manual steps to automate: Mistakes and manual interventions in purchase-to-pay processes increase lead time. By analyzing processes, process mining uncovers automation potential that boosts accuracy and cuts rework. In some process mining case studies, process mining tool can increase automation by 35% and decrease rework time by 52%.
20- Eliminate maverick buying: Companies can mine their purchase-to-pay processes to reduce maverick buying. If companies have a specific problem on maverick buying, they may find certain areas to improve the use of frame agreements with process mining. Process mining vendors claim that they can detect maverick buying by following the rules below:
- A receipt shouldn’t be generated before a purchase order is created
- All invoices should be created after a PO
- PO without a contract should not exist (especially if the order is large in quantity and happens regularly)
Uncover how to deploy process mining for P2P processes.
21- Uncovering root causes for delays: Process mining enables companies to pinpoint which suppliers, products or departments cause delays. By taking relevant actions, they can achieve more on-time deliveries internally.
Accounts Receivable
22- Discover actions to encourage on-time payments: Customers don’t always pay on time. Companies can’t collect their receivables on-time in the end, and this might affect other processes. Process mining can identify the causes of this problem and find appropriate solutions.
23- Quicker invoicing: Billing your customers is another process that can become expensive and complicated from time to time. Process mining discovers the bottlenecks in the invoicing process and may find ways to automate it. As a result, it is possible to diminish invoice costs and provide quicker invoicing.
Accounts Payable
24- Reducing late payments: Companies can mine their business processes to uncover the reasons for their late payments. By fixing these inefficiencies, companies can diminish late payments and improve cash discounts.
25- Identifying real reasons behind incorrect invoices: Mistakes on the invoices or duplicate payments are common issues that cause extra workload. Companies can identify the reasons for these cases with process mining. It is stated that process mining software can reduce customers’ duplicate payments by 67%.
Audit
26- Compare “before” and “after”: When a company makes a change in its process, verifying the improvement may be a challenge. For consultants, process mining enables consultants to relate “before” and “after” of the processes.
27- Improve response time: While traditional process discovery may take months, process mining is faster. As a result, consultants like EY can complete end-customer process analysis within days using process mining tools
28- Risk identification: Process mining assures data-based information to consultants. With insights, consultants can identify risks and advise companies accurately.
Discover top use cases of process mining in finance in-detail.
Automotive
29- After-sales services: After-sales services refers to the customer support services to vehicle owners to improve their experience with the company while obtaining feedback over the product and service. Automotive manufacturers can deploy process mining to drive insights from the after-sales tasks and operations. These insights can improve after-sales services.
Read more on process mining in automotive industry.
Banking
Banks also benefit from process optimizations as most banks’ processes still include legacy systems and paper-based documentation. Process mining tools can help identify bottlenecks and automation opportunities improving customer satisfaction and efficiency. Processes to optimize include:
30- Mortgage: Mortgage is the most complicated B2C loan process and there are opportunities to improve it in most cases. Using process mining, banks can visualize mortgage workflows to spot delays caused by repetitive actions. This helps reduce customer waiting time and improve collaboration across different units.
31. Other loans
32. Card operations
Process mining supports banks in analyzing card operations to identify inefficiencies and delays.
Customer Service
33- Cross-channel analysis to identify anomalies: Process mining software can help analyze process steps across different channels to identify compliance issues and inefficiencies
34- Map customer journey: Process mining tool can illustrate the customer journey in a given channel by extracting data from CRM and ticket systems). By doing so, process mining facilitates tracking customer experience, challenges that customers face, and interactions between responsible agents and customers.
Education
35- Online learning platforms: Process and task mining can reveal details on how users navigate on learning platforms to improve user experience for students. For example, process mining can show the potential root-causes behind students’ exit rates from the given platform, such as the length of videos or organization of materials.
Discover applications of process mining in educational settings.
Healthcare
36- Administrative processes: Process mining discovers event logs that contain information about healthcare processes including the personnel in-charge, steps, and cost of processes and identifies areas for improvement.
37- Clinical pathways: serve for standardizing healthcare practices and detect issues that might lead to wrong treatments or delays which are crucial for many patients (e.g. cancer). Process mining can be used to identify clinical pathways and track bottlenecks and anomalies.
Learn about the growing role of process mining in healthcare organizations.
Insurance
38- Risk assessment: Insurance firms calculate risk to set premiums. Overestimating risk can lose customers, while underestimating it can lead to losses. Process mining helps by analyzing actual or historical data to map underwriting steps and identify risk factors. This allows insurers to monitor and improve the underwriting process for better decision-making.
39- Quote-to-bind ratio: Insurance companies try to reduce their quote-to-bind ratio which measures the conversion rate of quotes to the binding policies. Process mining offers insights to streamline operations by addressing inefficiencies and automation opportunities.
Explore more use cases, benefits & best practices of process mining for insurance.
Logistics
40- Reducing warehousing costs: It is hard to identify which warehouses cause logistics problems. Making mistakes in inventories also causes extra warehousing costs. Process mining provides full transparency in warehouse management. Thus, companies can locate problematic warehouses, diminish warehousing costs and save up to 40% of their warehousing costs.
41- Widening geographic range: Companies can widen their geographic reach by optimizing the locations of their warehouses. Process mining vendors claim that companies using their tools can increase their geographical reach by up to 20%.
42- Identifying the root causes of delays: Logistic delays may cause late deliveries and reduce the expected revenue. Process mining can discover the root causes of these delays. Companies can focus on these issues to avert possible revenue losses. Some companies claimed that they have increased their on-time delivery by 18%.
Learn the benefits of process mining for logistics/ supply chain.
Production
43- Reduced cycle time: To improve the output, reducing the production cycle time is a smart solution. Process mining can show the inefficiencies within the production processes. Companies can reduce their cycle time by fixing these inefficiencies. It is estimated that the throughput time can be shortened by 22% in the production processes.
44- Reduced rework in production: Companies can reduce their reworks by creating in-process alerts. As the manufacturing deviates from the standard, the process mining software can report to the relevant units in real-time. The benefit is that it provides companies with better quality products.
Read 6 use cases of process mining in manufacturing.
Software industry
45.Tracking the life cycle activities: The software development life cycle (SDLC) refers to the required stages while developing software (See Figure 2). Process mining can help track the entire software development life cycle by discovering and mapping the actual process model. This way, developers and project managers can identify if any steps are skipped.
46. Monitoring and managing software projects: Process mining can map the entire project flow, allowing every party in the software development team to monitor and manage the project while identifying issues and risky areas. Also, process mining illustrates process KPIs (e.g., cost and time), resources and parties involved in the given process.
Real-life example
For example, a BPM software provider company in Australia applied process mining to manage their customer project journey. With the help of process mining, the firm identified and solved compliance and performance problems.
47. Quality assurance: QAs control for software’s usability, accuracy, maintainability and portability. Process mining offers conformance checks and automated root cause analysis, which can help testers oversee their QA processes. This way, testers can ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of the QA process with process mining.
Real-life example
In a case study, researchers deployed process mining in a software development process dataset provided by a Brazilian software house with more than 2,000 cases (See Figure 3). In their conformance analysis, researchers pointed out that:
- 90% of the cases follow the order of execution defined in the formal process
- 25% of the processes skipped the planning stage
- 44% of projects were not documented.
48. Incident management: Incident management Incident management addresses unplanned activities that affect service quality. Process mining improves incident management by identifying automation and optimization opportunities. Predictive process mining and monitoring capabilities help developers, testers, and managers forecast potential incidents and intervene before they occur.
Real-life example
In a case study, researchers applied process mining to software development processes (See Figure 4) and identified that:
- 3 users in the support team were responsible for reworking items the most
- The analysis step in the model was skipped in real applications
- 50% of entities for which an analysis is not performed a required reworking.
FAQ
What is process mining?
Process mining is a method that extracts and analyzes event logs to reveal business process details. It enhances automation efforts, including RPA, and supports ongoing process improvement.
Process mining vs. data mining
Data mining leverages different algorithms or methodologies to explore a given dataset. Similarly, process mining analyzes event logs and process-related data to “mine” processes.
The full understanding of processes includes:
Identifying process trends, patterns, and deviations
Detailed visualization of actual processes
Defining automation opportunities
Discovering new ways to increase process efficiency
How does process mining work?
Process mining tools discover actual process models out of the raw event logs. By extracting event logs from each case, and combining them, these tools show companies how their processes perform in reality.
Understand how process mining works through the following steps:
1. These tools retrieve and analyze activity sequences from event logs to identify process variations.
2. These tools extract the activity sequence for each case from the event logs.In this step, variations between cases will become apparent. These variations occur because of manual changes or errors in the process.
3. After deriving the activity sequence of each case, process mining tools start to “merge” these sequences. As variations occur, the actual process will be more complicated than the planned one. This output also enables the company to understand where its process has deviated.
what is intelligent process mining?
Intelligent process mining is an AI-powered process mining software that leverages process mining algorithms and machine learning process mining applications to automate process discovery, process analysis, process modeling and process diagnostics via automated root cause analysis.
Process intelligence vs process mining
Some vendors refer to process-related tools, such as process management software or process mining, as process intelligence software. Process intelligence tools combine machine learning, process mining, task mining, and digital twin technologies for deeper insights.
Many process mining tools benefit from process mining algorithms and context awareness to automatically collect and discover data and identify the root causes behind inefficiencies and deviations. ML also enables building predictive capabilities, generating a DTO or process simulation and offering task mining.
What are the process mining challenges and tips to improve?
d
1.Expand the coverage of process mining
Challenge:
Currently, process mining is limited to processes that take place on systems with detailed and accessible log files like SAP.
However, a significant amount of employee activity takes place on the OS or the browser where personal and professional activities take place and logs may not be as detailed as an ERP.
Advice:
In these cases, enterprise AI agents can complete thousands of process runs to generate data which can be analyzed for bottlenecks. This is a novel use case which is not yet commercially offered but we expect AI agents to contribute significantly to process understanding within the next 3 years.
Improve data quality
Challenge:
PM tools may not inform you about data quality issues but the quality of their output relies on data quality. Most enterprise data can be incomplete, inaccurate, or have confusing timelines. Therefore, PM tools may analyze faulty data and provide inaccurate results.
It is important for data analysts, domain experts, data stewards and others involved in data quality initiatives to clean and prepare the data before implementing process mining.
Advice:
It is recommended that businesses have data quality assurance strategies and incorporation with AI and ML algorithms and data quality tools to constantly improve data quality.
Some of the ways the AI and ML can help with data quality is to
– Automate the process of data entry
– Identify and eliminate duplicate records
– Deploy random forest algorithm to classify data.
Accurate root cause analysis
Challenge:
Traditional process mining tools identify and portray process-related issues. Yet, they cannot provide granular answers on the root causes of these issues.
Advice:
However, this problem has been tackled by leveraging machine learning process mining algorithms in process mining. Combined with ML algorithms, diagnostic process mining identifies the root causes of the problems. There are 2 common approaches here:
– Some PM vendors offer software providing detailed process data for business intelligence (BI) tools and data mining/machine learning platforms or separate PM discovery tools identifying root causes
– Some other PM vendors integrate root cause analysis tools into the software to automatically run the analysis
Convert unstructured data into machine-readable formats
Challenge:
Business data can be both structured and unstructured, however, some traditional process mining tools can only process structured data, leaving unstructured data, such as invoices or receipts, out of the investigation process.
Advice:
This problem can be tackled by integrating OCR, NLP, and machine learning algorithms to convert unstructured data into machine-readable formats in order to include all data sources in the decision-making process.
However, converting unstructured data to machine readable data is an imperfect process and can introduce errors into process mining output. Therefore users need to pay attention in such cases.
Enable faster process mining output generation
Challenge:
Traditional process mining tools used to provide less clarity in analyzing complex processes because they lacked the sophistication to evaluate processes with a large number of variables. For instance, including numerous stakeholders or extensive data in the process used to generate complexity in PM outputs which were hard for humans to understand and take action on.
In addition to the number of tasks or variables added, in some cases, processes are heterogeneous and cross-sectional. For example, in healthcare processes, it becomes difficult to generalize and model processes that include heterogeneity and multi-disciplinary collaboration.
Advice:
New process mining tools that integrate AI and machine learning algorithms aim to overcome these complexity issues. For instance, leveraging AI and computer vision to capture and discover all process data, vendors can generate process mining output in a matter of days. A similar PM effort using traditional PM software could take months.
Predict future process performance
Challenge:
As the initial process mining tools focus on event data analysis, it monitors and analyzes past performances of processes rather than ongoing processes. As a result, it cannot alert users in cases of deviations or predict the process performance in the future.
Advice:
However, applications of AI and ML in process mining can help develop predictive and
prescriptive process mining models where PM predicts final results and future events in terms of key performance indicators and can notify users of possible shortcomings or areas for improvement.
Identify dependencies or bottlenecks within a process
Challenge:
Process mining does produce results in the shape of visualizations and tables, however, it requires the human analyst to interpret the outcomes and make suggestions to improve processes.
Advice:
Businesses can leverage AI and analytics tools to process results obtained from process mining tools in order to better identify dependencies or bottlenecks within a process.
The benefits of process mining
Reduced Costs
Process mining allows users to identify areas that require automation or any other change. Automating processes increases efficiency while reducing costs.
Improved Customer Experience
By identifying bottlenecks, discovering areas of improvement, and optimizing different processes, the total process time reduces. This situation enables faster delivery for customers and improves their experience with businesses. As a result, customer satisfaction increases, impacting revenues and customer loyalty.
Compliance Benefits
While auditing is a time-consuming process, fast analysis with process mining tools can shorten it. Besides, these tools can detect non-compliant processes and notify companies about such issues in real time. In a process mining case study, EY reduced its end-customer process analysis in less than a week by leveraging process mining.
Read and learn more on process mining benefits.
Process mining tools
The process mining market has various process mining tools with different capabilities.
– Some tools leverage AI and pattern recognition to improve their platforms. Discover more on these tools by exploring machine learning process mining applications.
– Some vendors offer process mining tools as open source or on free trials.
Further Reading
For more details on process mining, explore our articles covering use cases, software options, and case studies.
- How you can benefit from process mining
- A list of process mining case studies including project results
If you believe your business can benefit from process mining tools, you can check our data-driven list of process mining software and other automation solutions.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.