During my academic research on corporate sustainability efforts, I realize that environmental and social practices have a significant impact on the long-term success of businesses. Some businesses outperform others in this area, giving them a competitive advantage.
See 13 sustainability case studies to incorporate sustainability strategies into corporate actions and 2026 sustainability trends:
1. UPS ORION: Improve transportation efficiency
Problem
Transportation activities accounted for almost 30% of US greenhouse gas emissions (GHG).1 For a company like UPS, which distributes goods across regions, transportation activities make up the bulk of GHG emissions. As a result, enhancing transportation efficiency is crucial for organizations like UPS to remain sustainable.
Solution
UPS adopted an AI system called ORION which is a route optimizer that aims to minimize the number of turns during the delivery.2
Result
Initiation began in 2012, and ORION saves UPS 10 million gallons of fuel per year, which means that in addition to the financial benefits, it decreases UPS’s carbon footprint by 100,000 metric tons per year, or the equivalent of removing more than 20,000 cars from the roads.(An average car emits 4.6 metric tons of GHG per year.3 )
In addition to private solutions like ORION, there are public cloud route optimizer systems that businesses can deploy without building hardware. These tools help firms to use their software as a service by paying a subscription cost.
To learn more about ensuring supply chain sustainability with technology you can read Technologies Improving Supply Chain Sustainability.
Figure 2: US GHG emission distribution
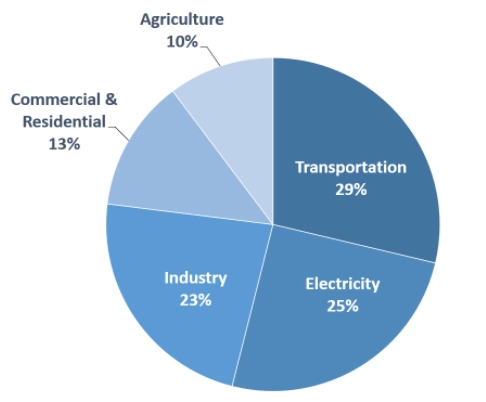
Source: U.S Environmental Protection Agency4
2. IKEA IWAY: Make business with ESG-oriented corporations
Problem
Supplier codes of conduct are established guidelines that require other businesses to demonstrate their operations’ social and environmental impacts. The objective is to reward companies that meet strong ESG standards. It is also one of the positive governance indications for organizations.
Solution
IKEA’s supplier code of conduct, IWAY, has been in place for over 20 years.5 IWAY six is the most recent version of IKEA’s supplier code of conduct, which evaluates:
- Core worker rights.
- Safety of the working place.
- Life-work balance of employees.
- Water and waste management of potential suppliers.
- Prevention of child labor.
Result
IWAY ensures that IKEA’s suppliers meet strict environmental and humanitarian standards, helping to promote responsible and sustainable practices in their supply chain.
3. General Electric digital wind farm: Produce green energy efficiently
Figure 3: How digital twins can optimize wind turbine productivity
Source: DNV6
Problem
Wind turbine productivity varies greatly depending on the design, weather conditions, and geography of the location it is deployed. Furthermore, the performance of wind turbines declines with time and may require maintenance; employing sensors and digital twins can assist in determining the appropriate time for repair.
Solution
Using IoT and digital twins to collect data on each wind turbine and simulate possible modifications, such as adjusting the direction of the wind turbine, can assist corporations in locating their wind turbines in a wind farm more effectively. General Electric’s (GE) digital wind farms are based on these two elements. GE optimized turbines using sensors and digital twin real-time monitoring technologies.
Result
Each wind farm can create up to 10% more green energy as a result of the digital wind farm initiative, which helps to enhance our worldwide green energy mix.7
4. Swire Properties green building: Minimize GHG emissions
Problem
Swire Properties is a construction company that operates in China and especially in the Hong Kong area. In 2018, the company built One Taikoo Place which is a green building that aims to reduce GHG emissions of Swire Properties in order to align with sustainability goals of the company’s stakeholders.
Solution
Swire properties use 3D modeling techniques to optimize the building’s energy efficiency. Reduce electricity consumption by using smart lighting systems with sunshine and motion sensors.8 A biodiesel generation system has been installed in the building, which converts waste food oil into biodiesel. Swire Properties additionally uses low-carbon embedded materials and a lot of recycled materials in their construction.9
Result
Swire Properties was able to cut GHG emissions intensity throughout their portfolio by nearly 20% because of the usage of digital technologies and low carbon integrated materials.10
5. H&M let’s close the gap: Deposit scheme for gathering raw material
Problem
We consume 1.8 times more resources than Earth generates annually because our economic outlook is based on production, use, and disposal.11 Such an economy is not sustainable, and that is the reason why the concept of circular economy (CE) is trending nowadays.
Solution
The most basic principle of CE is to use trash as a raw material for production through innovation, recycling, or repairing and reusing existing products.
H&M’s “Let’s Close the Gap” project began in 2013 as a CE best practice that collects and categorizes discarded clothing from customers.12 If the garment is in decent condition, they will restore it and find a new owner for it. If a garment reaches the end of its useful life, H&M will recycle it and reuse the material in new goods.
Result
Customers who bring in their old clothes are rewarded with tokens that can be used to get a discount at H&M shops. Incentivizing customers creates a complete CE loop. In 2019, 57% of H&M’s raw materials were sustainable. By 2030, the company plans to improve it by 100 percent.13
6. Gusto: Hiring female engineers to close gender inequality gap
Problem
Gender inequality remains a major social issue despite all the improvements.14 There are two common types of gender disparity in the workplace. The first is gender pay disparity, which occurs when companies pay male employees more and provide better working conditions than female employees in the same position.
The second is occupational segregation, in which women are hired for non-technical jobs while men hold the majority of leadership roles. This was the situation at the software firm Gusto, where female engineers made up slightly more than 5% of the engineering team at the beginning of 2015.15 Julia Lee, one of Gusto’s first female engineers, claimed that other engineers did not accept her ideas because she was a “female engineer.”
Solution
Gusto initiated an HR drive to reduce gender inequality by prioritizing the recruitment of female engineers, prohibiting female workers from scrolling, and deleting masculine job ads like “ninja rock star coder.”
Result
Gusto was able to improve its female engineer ratio to roughly 20% by the end of 2015 thanks to the campaign.16 The average ratio among software businesses’ engineering teams was 12% in 2013. Therefore, this was a significant improvement in a short period of time.
7. HSBC: ESG concerned green finance
Problem
Finance companies can play a key role in promoting sustainable business practices, but many still need to increase their support for responsible initiatives.
Solution
Finance companies can help speed up the transition to sustainable business practices by supporting initiatives run by responsible businesses. HSBC has committed to investing $100 billion in sustainability projects by the end of 2025.17
Result
In 2021, HSBC’s ESG practices were rewarded with an AA rating by MSCI.18 HSBC is also working toward a goal of using 100% renewable energy as their source of electricity by 2030. The company reduces its consumption of paper and single-use plastic packaging for coffee and beverages.19
8. Signify light-as-a-service: Enhance production stewardship
Problem
Traditional business models often lead to resource waste and a lack of product stewardship, contributing to the circularity gap.
Solution
The product-service system (PSS) is a business model in which producers acquire a product over its lifetime and rent or lease it to the users. PSS ensures product stewardship since the product always becomes the asset of the company. It encourages producers to provide high-quality, repairable items in order to extend the product’s useful life. As a result, it helps to close the circularity gap by ensuring better use of natural resources.
Signify, a luminaire producer, adopts such a business strategy where it demands a subscription fee according to the usage period of their lighting systems.
Result
Signify claims that PSS allows them to produce 0 luminaire waste and drops maintenance costs.20
9. Airbus: Manufacture lighter planes with 3D printing
Problem
Traditional airplane manufacturing is slow, expensive, and produces heavier parts that increase fuel consumption.
Solution
Additive manufacturing is a process where a computer-aided design (CAD) file is converted into a stereolithography (STL) file, which is then sliced into layers to guide the 3D printing of an object.21 AIMultiple expects that additive manufacturing will disrupt airplane manufacturing since:
- It speeds up the manufacturing of parts compared to traditional molding techniques.
- It is cheaper due to effective use of raw materials and time reduction of production.
- It enables the manufacturing of lighter parts by up to 45%, resulting in lighter planes that burn less fuel.22
To effectively use 3D printers, Airbus partnered with Materialise, a Belgium-based technology company that specialize in additive manufacturing.23
Result
According to Airbus, additive manufacturing technology can reduce an A320 plane’s annual GHG emissions by around 465,000 metric tons, which is roughly the same as eliminating 100,000 automobiles from the road for a year.24
For more information regarding improving corporate sustainability by digital transformation you can read Digital Technologies that Improve Corporate Sustainability.
10. Tata Power: Solar plants on the roofs
Problem
Rooftops are often unused, missing an opportunity to generate green energy.
Solution
Tata Power in India utilizes rooftop space to install solar panels, generating clean electricity.
Result
In 2021, Tata Power was able to spread their program throughout 90 Indian cities, producing 421 million watts of electricity, which is equivalent to nearly 40 thousand homes’ yearly electricity use in the US.25 The average annual power usage for a residential utility customer in the US was 10,791 kWh in 2022.26
We expect that in the near future, the cooperation between energy and construction companies will enhance the use of idle places in buildings in a more effective way. Such an industrial symbiosis reduces both sectors’ ESG risk.
For more information on the top carbon footprint calculators, check Carbon Footprint Calculator Software/Tools for Businesses.
11. Impact Foundation: Put charitable capital to work
Problem
Over $1 trillion sits in donor-advised funds and foundations, yet only 10% is granted annually. Most of this capital is passively invested with no alignment to charitable goals, missing the opportunity to drive real-world impact.27
Solution
Impact Foundation, founded in 2015, offers Impact Accounts, donor advised funds built for impact investing. Donors can recommend investments in businesses and nonprofits that generate both social or spiritual change and financial returns. Returns are reinvested or granted, multiplying the long-term impact of each dollar.
Result
To date, over $650 million has been deployed for impact through these accounts. Families are using their investment expertise to support 70,000 job creation, fight poverty, and advance the Gospel, putting more charitable capital to work for lasting good.
12. Global Recycling Foundation: Highlight the benefit of recycling
Problem
The Earth’s natural resources, such as air, water, coal, oil, gas, and minerals, are being depleted at an unsustainable pace. Combined with rising temperatures and climate emergencies, our planet faces escalating threats like deforestation, pollution, and resource scarcity.
Solution
Founded in 2018, the Global Recycling Foundation created Global Recycling Day to promote recycling as the “Seventh Resource.” Recycling helps conserve raw materials, save energy, and reduce CO₂ emissions. The foundation urges people to see waste not as trash but as a valuable resource.
Result
Recycling already prevents over 700 million tons of CO₂ emissions each year and is projected to save 1 billion tons by 2030. Global Recycling Day has galvanized youth, governments, and communities, especially across Africa, to act. By recognizing #RecyclingHeroes and promoting circular economy practices, the foundation underscores the long-term benefit of recycling to the planet and future generations.28
13. O.N.E Amazon: Protecting the rainforest using technology
Problem
The Amazon rainforest is one of the planet’s most important ecosystems. It regulates global climate, produces oxygen, and supports millions of people and species. But deforestation and lack of sustainable funding threaten its future.
Solution
O.N.E Amazon created a digital asset security backed by a 30-year land contract. The goal is to attract sustainable investment without transferring land ownership. Proceeds go into the O.N.E Amazon Impact Fund (O.A.I.F.), which supports forest protection, local job creation, and reforestation.29
To monitor and protect the forest, they use Edge AI, IoT sensors, and data analytics to build the Internet of Forests (IoF), a digital network that monitors the health of every hectare in real time.
Result
The project began with a 10,000-hectare pilot and provides investors with both potential returns and real-world impact. Technologies like AI-powered sensors and early warning systems help detect threats like illegal logging and climate stress quickly. The project supports biodiversity, local communities, and long-term rainforest preservation, showing how technology and finance can work together to protect the planet.
Sustainability use Cases to watch in 2026
In 2026, sustainability is about balance. Companies must manage both short-term pressure and long-term risk simultaneously.
According to a report of S&P Global, key focus areas in 2026 will be: 30
- Climate adaptation: Extreme weather is now a business risk. Firms invest in resilience, not just emissions cuts.
- Energy transition: Fossil fuels remain, but renewables grow fast. Grids, storage, and flexibility matter more.
- AI and data centers: AI boosts productivity, but raises energy and water use. It is both a solution and a risk.
- Water and food: Water scarcity affects factories, farms, and cities. Water risk management becomes critical.
- Supply chains: Climate shocks, trade rules, and carbon fees reshape sourcing decisions.
- Nature and biodiversity: Nature loss affects costs and growth. New rules push firms to measure impact.
- Reporting and regulation: Rules fragment. Global standards still guide investors and companies.
- Sustainable finance: Capital shifts toward resilience, transition projects, and blended finance.
- Workforce aging: Fewer workers increase pressure on productivity, automation, and skills.
Further readings
- Top Circular Economy Metrics to Assess Businesses
- Sustainable Management Definition & Top 10 Best Practices

Comments 1
Share Your Thoughts
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
A wonderful collection of case studies on corporate sustainability. I enjoyed the read. I am convicted to delve into promoting sustainability in Africa.
Hello, James! Thank you for your feedback. Awesome! That's a great cause to pursue.