Process mining can be applied in multiple business areas in the financial services industry, such as Purchase-To-Pay, audit, and accounts payable to increase business efficiency and gain a comprehensive overview of business processes to implement and monitor digital transformation strategies. Targeting key bottlenecks in these processes through mining helps deliver strong improvements in performance.
This article provides a list of process mining applications and recommendations for financial institutions and businesses that want to leverage process mining. This list is informed by recent research on how process improvement tools can target high-impact areas.
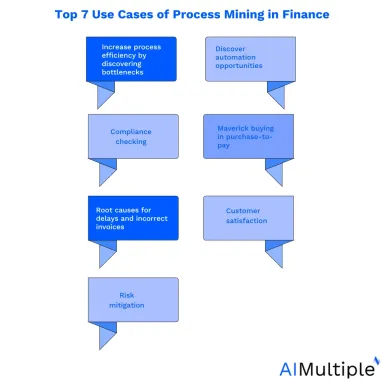
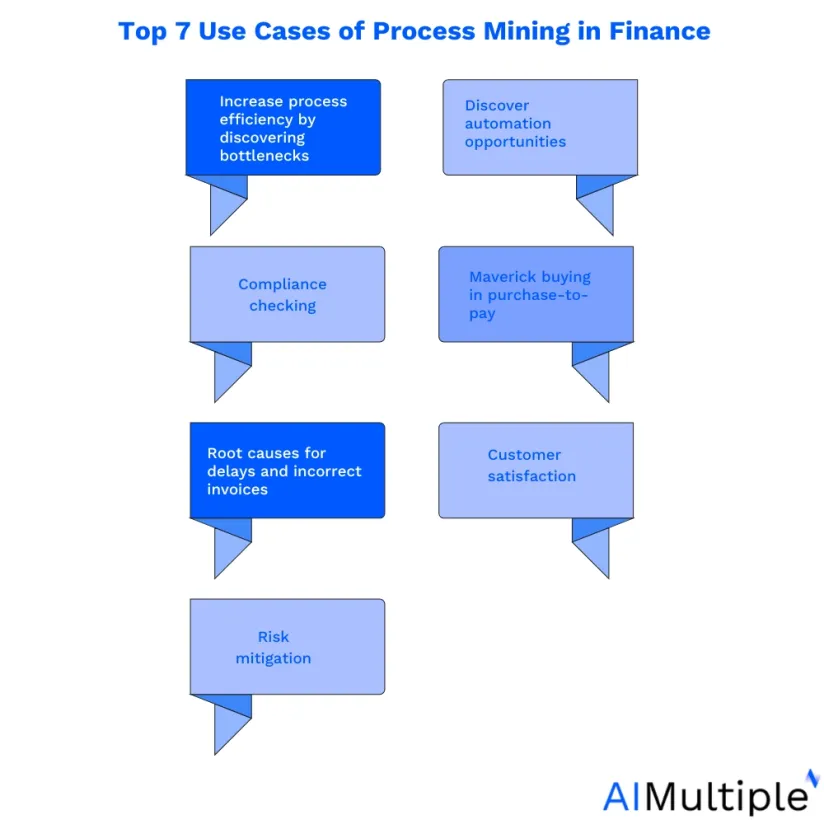
Some general and specific use cases of process mining include:
1. Increase process efficiency by discovering bottlenecks
Process mining can be applied to different financial processes that generate event logs such as account payables (AP), receivables (AR), and procurement to visualize process execution and identify bottlenecks. Research-driven insights can help target inefficiencies with strong evidence.
Process Mining can provide strategies and recommendations to eliminate process inefficiencies. For example, in claims settlement, mining can identify root causes by measuring the average amount of time to settle a claim. This type of process insights enables financial institutions to make strong operational improvements.
2. Discover automation opportunities
Leveraging process mining provides insights about processes that can benefit from automation. For example, process mining allows financial organizations to discover the possibility of automation in transactions such as:
- purchase-to-pay processes that take longer due to mistakes and manual interventions can be enhanced by implementing automation solutions such as RPA.
- Invoice processes where automation can enable quicker and less costly invoicing by automating repetitive tasks such as data extraction from PDFs.
Explore RPA use cases in finance to understand how to implement it right away. Research shows that identifying the right automation targets is easier when supported by process mining data.
3. Compliance checking
Process mining enables financial institutions to monitor and log process improvement overtime to ensure that their processes are audit-ready. Process mining also provides conformance check and root cause analysis, allowing financial institutions to compare their processes against rules and regulations and analyze the reasons behind the deviations. Such applications target risk-prone areas with strong accuracy.
To learn more on specific applications of process mining in compliance and audit:
4. Maverick buying in purchase-to-pay
Banks can leverage process mining in purchase-to-pay, which refers to a company’s entire purchasing process. For example, Process mining can help reduce maverick buying (i.e. purchases of employees without informing the procurement department). Process mining enables the user to check the necessary steps in a P2P process, including:
- Generating a receipt after a purchase order (PO)
- Matching the PO to a contract: There should not be a PO without a contract (especially if the amount of orders is large in quantity and regular)
5. Root causes for delays and incorrect invoices
Process mining enables users to discover the root causes of delays within the departments. Banks can uncover the reasons for the late fees (e.g. credit card debt payment, loan payments) and minimize late costs, for example, by introducing incentives to customers who pay their debts on time. Also, process mining allows banks to identify the root causes for mistakes and duplicate payments that generate extra workload.
Such detailed process insights allow financial teams to target inefficiencies early. Recent research shows that tackling root causes leads to a strong reduction in operational risk.
6. Customer satisfaction
Some process mining techniques (e.g. process discovery) can constantly monitor processes in real-time. Such monitoring enables companies to optimize their processes which increase customer satisfaction.
Process mining helps financial service providers understand customer behavior by uncovering insights like call length and issue patterns. Banks that grasp customer perspectives can improve operations to enhance experiences. For instance, process mining enabled retail banks to identify challenges in the bank account confirmation process, leading to faster account opening and improved customer satisfaction.
7. Risk mitigation
Process mining helps financial service providers to avoid potential risks when they innovate or modify processes in their systems by constantly monitoring processes and providing data-driven insights and optimization opportunities.
Banks that use process mining to target weaknesses are better prepared to prevent system-wide issues. Researchindicates that data-backed process evaluation is key to strong risk mitigation strategies.
Recommendations
The best practices to apply process mining in finance include:
- Understand the purpose and possible outcomes: Before applying process mining, providers must sort out the main purposes of the process mining application. For example, banks can update their website and FAQ section to prevent unnecessary customer calls.
- Ensure data quality and availability: To implement process mining, banks and financial institutions must identify, collect, and clean the data.
- Assure data security: Financial data is sensitive because it includes privileged customer information (e.g. spending records, credit score). To better protect customer data, financial organizations must leverage privacy-enhancing technologies, such as homomorphic encryption and zero-knowledge-proof to enable process mining users to process confidential data without exposing it to unauthorized individuals.
Further reading
To discover process mining use cases in banking and insurance, and their benefits, feel free to read:
If you believe your business can benefit from process mining tools, you can check our data-driven list of process mining software and other automation solutions.
Go through other alternative solutions before deciding over process mining, such as:
- Process intelligence software, including
- Process analysis tools.
- Process improvement techniques like
And you can let us find you the right vendor:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.