There are 2 main use cases for email servers. If you are looking for:
- A solution for sending outbound transactional emails (e.g. for marketing or customer service), which are automated and system-generated emails triggered by user actions, check out transactional email providers,
- Email server for businesses and organizations to manage high volume email communications while offering more control, security, and customization, then check out email software.
Top 5 transactional email providers
| Vendor | Number of reviews | Average rating | Starting price |
|---|---|---|---|
| SMTP.com | 44 | 3.9 | $25/month |
| Netcore Email API | 648 | 4.4 | $349/month |
| SMTP2GO | 479 | 4.8 | $10/month |
| Twilio SendGrid | 351 | 4.0 | $15/month |
| Amazon Simple Email Service | 177 | 4.3 | $0.10 per 1,000 email + additional chargers |
Sorting: The list ranks providers, with sponsored entries shown first along with their respective links. All non-sponsored providers are ordered according to the total number of B2B user reviews collected from G2 and Capterra. Pricing details and feature information were obtained directly from each vendor’s official website.
Sponsors are listed at the top with their links. The rest are sorted based on the number of B2B user reviews from G2 and Capterra. Pricing information and features are gathered from the vendor websites.
For a detailed comparison of the pricing options offered by transactional email services, refer to transactional email pricing.
To compare pricing plans of transactional email services, check out transactional email pricing.
Dive in for more information on best practices, advantages & challenges of transactional emails.
Vendor selection criteria: Only vendors with a minimum of 20 verified B2B reviews on platforms like Capterra and G2 were considered for this list.
Compare transactional email providers: Features
| Vendor | Differentiating features |
|---|---|
| SMTP.com | SMTP reputation defender by analyzing Big Data query to prevent blacklisting. API mapping and migration templates. |
| Netcore Email API | Inbox management with send time optimization. |
| SMTP2GO | Real time reporting for bounced emails and unsubscriptions, advanced email testing for deliverability. |
| Twilio SendGrid | Supports SMS, voice, and video communication. |
| Amazon Simple Email Service | Integration with Amazon Web Services tools. Pay-as-you-go pricing model. |
Top 5 email software
| Vendor* | Number of reviews | Average rating | Starting price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Workspace Gmail | 12,187 | 4.8 | $6/user/month |
| Zoho Mail | 1,399 | 4.5 | $1/user/month |
| MDaemon Email Server | 169 | 4.7 | $25/month for 5 user for cloud-based - $413/year for on premises |
| Zimbra Collaboration | 134 | 3.6 | Not publicly available |
| Microsoft Exchange Server & Microsoft 365** | 133 | 4.3 | $6/user/month for businesses - $10/month for 2-6 people for family plan |
*These providers focus on email hosting and collaboration rather than directly offering transactional email services. For transactional emails, integrations with additional platforms or services are necessary.
** The data shows the total average rating and number of reviews of Microsoft 365.
Sorting in the above table: The table is organized primarily by the number of B2B reviews gathered from review sites such as G2 and Capterra. Information on pricing, deployment, and product features has been sourced directly from the vendors’ official sites.
Vendor Selection Criteria
We refined our shortlist using specific criteria:
- Number of reviews: Vendors were prioritized if they had at least 100 public and verified B2B reviews, as a higher volume of such reviews signals a strong foothold in the transactional email server market.
- Server protocols: We included software supporting a hybrid server protocol with both outgoing and incoming server capabilities.
Compare email software: Deployment, focus & features
| Vendor | Deployment type | Focus | Differentiating features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Workspace Gmail | Cloud | Cloud-native businesses | AI-powered Smart Compose and Smart Reply features. |
| Zoho Mail | Cloud | Enterprises & mid-market | Zoho Streams for commenting on emails. |
| MDaemon Email Server | Cloud & on-premises | Mid-market | Passwordless authentication to minimize security issues. |
| Zimbra Collaboration | Cloud & on-premises | Enterprises | Online editor for text documents, spreadsheets, and presentations. |
| Microsoft Exchange Server & Microsoft 365 | Cloud & on-premises | Enterprises | Microsoft Outlook integration. |
What is an email server?
An email server is a computer system that sends, receives, and stores emails for its users. It acts as a central hub in the email delivery process while enabling communication over the internet or within a private network.
Some of the key features of an email server include:
Mailbox management: It stores and manages email accounts and their associated mailboxes to ensure that emails are correctly sorted and available to the users.
Protocol support: An email server supports 3 email protocols: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) for sending emails, and Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) or Post Office Protocol (POP) for receiving emails. SMTP handles the sending and forwarding of emails, while IMAP and POP manage the retrieval of emails by the end users.
Security measures: Email servers implement various security features to protect against unauthorized access, spam, phishing attacks, and malware.
This includes TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer) encryption for secure email transmission and authentication mechanisms like SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail), and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) for authenticity verification of email messages.
Spam filtering: Email servers enable advanced spam filtering techniques which are used to identify and block unwanted emails while helping to keep users’ inboxes free of potentially harmful content.
Data backup and recovery: Email servers regularly backup data to prevent loss due to hardware failures, software issues, or other disasters. They also provide recovery options to restore lost or accidentally deleted emails. Cloud based mail servers store user data in their cloud system.
Address resolution and routing: Email servers resolve recipient email addresses to their corresponding mail servers using DNS (Domain Name System) lookups and route emails to their destinations efficiently.
User authentication and access control: They ensure that email accounts are protected from unauthorized use by authenticating users before allowing access to send or retrieve emails.
Scalability: Email servers are designed to handle small volumes of email traffic in a private organization to large-scale operations for email service providers. These services also support eCommerce, tech start-ups, publishers, media, travel and financial services.
Integration with other services: Many email servers integrate with other services like calendars, contact lists, and task management to provide a unified communication platform.
Customizability and configuration: These solutions offer diverse configuration options to meet specific needs, such as setting up mail forwarding, auto-responders, and filters for organizing incoming emails.
Typically bundled products include video meetings and instant messaging.
Email server deployment: cloud vs on-premises
When choosing the right solution, it is vital to understand whether cloud-based or on-premises services suit your needs and expectations better.
Cloud-based email servers provide a hosted solution that minimizes the need for internal IT management and infrastructure, offering:
- scalability,
- ease of access,
- a subscription-based cost model that is suitable for businesses seeking flexibility and minimal upfront investment.
On the other hand, on-premises email servers offer organizations:
- full control over their email infrastructure,
- data security and compliance,
- a higher initial investment in hardware,
- ongoing management responsibilities than cloud-based services.
In short, cloud-based solutions have the advantage in accessibility and ease of scaling, but on-premises setups provide more control and customization.
Shared or dedicated email server?
In some cases, businesses opt to use private email servers and mail server software to manage their email operations, giving them exclusive control over both incoming and outgoing emails. These servers offer:
- more control over email server hardware, email server software, and server space
- customization of security measures, spam filtering, and authentication protocols.
Businesses that utilize their own servers can ensure that their email data and email communications are more secure and efficient, with advanced features such as spam protection and enhanced security.
In contrast, shared email servers are commonly managed by third-party providers, where multiple users share the same email infrastructure.
While shared servers offer lower costs, they come with limited control, and users rely on the third-party provider for security measures and spam filters.
This means that email deliverability and email data security can be more vulnerable to spam and malicious emails, potentially affecting email communications across multiple devices.
A dedicated mail server typically involves more technical expertise and higher costs to set up and maintain but allows for complete control over SMTP server configurations, mail transfer agent (MTA) settings, and other elements of email server infrastructure. This level of control ensures that businesses:
- can manage incoming and outgoing traffic,
- configure DNS settings
- integrate advanced security measures to protect sensitive data and email messages.
How to decide?
For businesses that prioritize sensitive information and the security of their email operations, having dedicated email servers is highly recommended to ensure smooth email delivery and to meet the demands of government agencies or organizations dealing with sensitive data.
On the contrary, shared email servers with limited control may be more suitable for personal use or smaller businesses with less need for advanced security and more control over their email communications.
Email server processes
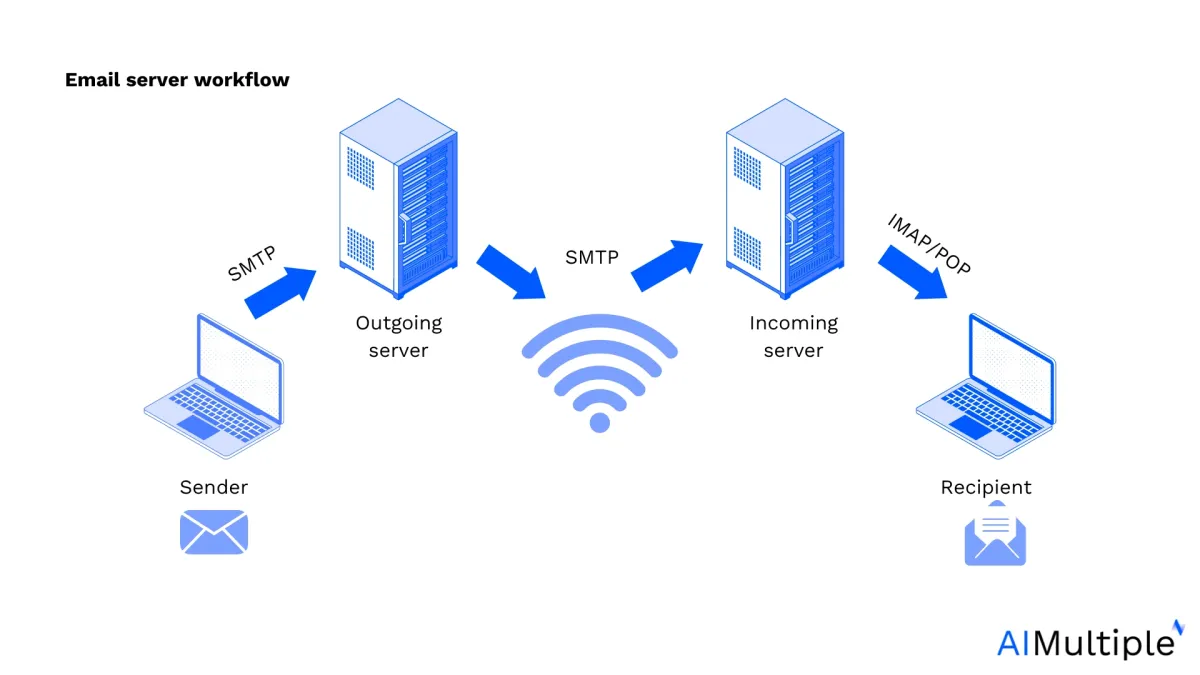
The email servers work by managing the sending, receiving, and storing processes of email messages over the internet. These processes involve multiple steps and components, such as Mail Transfer Agents (MTAs), Mail Delivery Agents (MDAs), and Mail User Agents (MUAs).
Creating and sending emails
- Composing an email: The process begins with a user creating an email using the email client (MUA), such as Microsoft Outlook, Yahoo Mail, Apple Mail, or a web-based service like Gmail.
- Client connecting to SMTP Server: The email client connects to the outgoing mail server using the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) which is responsible for sending emails.
Email routing
- Email processing with SMTP Server: The SMTP server checks the email’s recipient address to determine where the email needs to be sent.
- DNS query for recipient’s server: The SMTP server queries a DNS server to find the Mail Exchange (MX) records for the recipient’s domain. The process enables the SMTP server to identify which incoming mail server that the email will be sent to.
- Sending to recipient’s SMTP server: The sender’s SMTP server connects to the recipient’s SMTP server and transmits the email. If the recipient’s server is unavailable, the sender’s server will queue the email and try again later.
Receiving emails
- Recipient’s SMTP server receives email: Once the email reaches the recipient’s SMTP server, it’s handed off to a Mail Delivery Agent (MDA). The MDA is responsible for depositing the email into the appropriate mailbox on the server.
- Email storage: The email remains stored on the recipient’s email server until the recipient’s email client requests it.
Accessing emails
Lastly, the email client connects to the incoming mail server using:
- the Post Office Protocol (POP3) or
- the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP).
Then, the email client retrieves the email from the server thus allowing the recipient to read it.
Categories of email server solutions
Email servers can be categorized as outgoing (SMTP servers), incoming (IMAP/POP servers) or hybrid servers supporting all three protocols.
Email software
Email software utilizes hybrid servers with sending, receiving, and storing capabilities for managing large volumes of email communications. These solutions can be open source, cloud-based or on-premise. They provide a foundation for email delivery and management.
With its integration capacities for both web and mobile devices such as shared calendars, task management, contact management, and document sharing, email software can boost teamwork and support project management processes.
Most email software enables offline mode for users to read and respond to emails without an internet connection.
Transactional email providers
On the other hand, transactional email providers integrate SMTP servers to allow system-generated emails that are sent to individuals based on specific actions or events. These emails provide one-to-one communications that contain information relevant to the recipient’s action or transaction with a website, application, or service.
Key features include:
Trigger-based: Transactional email providers enable automated responses triggered by a user’s action. These automated emails include order confirmations; account notifications for delivery rates, clicks, bounces, and spam complaints, password resets, account activation links, and privacy updates; shipping confirmations and updates; payment invoices and purchase receipts; and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) codes.
Personalized emails with high open rates: Transactional emails are personalized for each customer and essential for providing timely and relevant information to users, while supporting customer experience, and increasing trust between the customer and the business. These emails are often expected by recipients, which makes them engaging with high open and click-through rates.
Integration: Transactional email services also enable RESTful API integration for supporting the automated email sending processes.
Analytics and reporting: These tools offer in-depth reporting by examining email metrics, allowing you to monitor performance indicators like open rates and click-through rates.
SMTP relay services: Transactional email providers enable SMTP relay services. SMTP relay is an essential process in email communication where emails are transferred from one server to another until they reach the recipient’s email server.
- This process begins when an email is sent and the sender’s SMTP server takes over, performing a DNS lookup to find the recipient’s server based on the domain in the email address.
- The email is then relayed across the internet, passing through multiple servers, and it arrives at the destination server and to the recipient’s inbox.
- SMTP relay services are important because they enable seamless delivery of emails across different email systems and networks while ensuring that messages can be sent and received between any email providers.
Dedicated IP addresses: Companies with large-scale email sending requirements can use dedicated IPs through these services to maintain high deliverability and sidestep the challenges associated with shared IPs.
IP warm-up: The aim of this service is to increase email sending reputation by boosting the volume of emails sent from a new IP address.
Transactional email best practices
Here are some best practices for effective transactional emails:
- Use clear and descriptive subject lines: Keep subject lines concise, ideally under 50 characters, and directly convey the email’s content. This clarity helps users quickly understand the purpose of the email, such as a shipping notification, even without opening it.
- Avoid “No-Reply” email addresses: Use email addresses that allow customer responses instead of “no-reply” addresses. This fosters customer engagement, enhances email deliverability, and demonstrates that user feedback is valued.
- Personalize content: Tailor transactional emails to users by utilizing personalization tools and recommendation systems. This increases relevance and engagement, making the content more appealing to recipients.
- Maintain brand consistency: Make sure your transactional emails reflect your brand’s personality by using consistent visuals like logos and colors, along with a unified tone.
- Optimize for mobile devices: Design emails to be responsive across all screen sizes. This ensures a seamless experience for users who access emails on mobile devices.
- Ensure secure email communication: Protect sensitive data in transactional emails by using secure links and avoiding the inclusion of information like full credit card numbers. Implement email authentication protocols (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) and consider BIMI for added security and brand visibility.
- Comply with legal requirements: Ensure transactional emails comply with regulations like GDPR or the CAN-SPAM Act by obtaining user permissions and providing clear sender information.
- Avoid overloading with promotional content: While subtle promotion is acceptable, focus transactional emails on their primary purpose. Overloading them with marketing content can detract from their effectiveness and confuse users.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.