Top 7 Process Mining Audit Use Cases & Case Studies in '24
The internal and external audit ensures reliability of financial reporting, compliance with the laws and regulations and effective and efficient execution of operations. Yet, it is challenging and costly to achieve constant auditing of organizations. Process mining helps auditors and audit departments inspect their operations, automate their reporting, and manage risks by assessing process deviations and compliance levels.
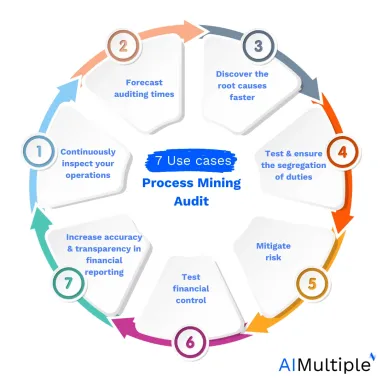
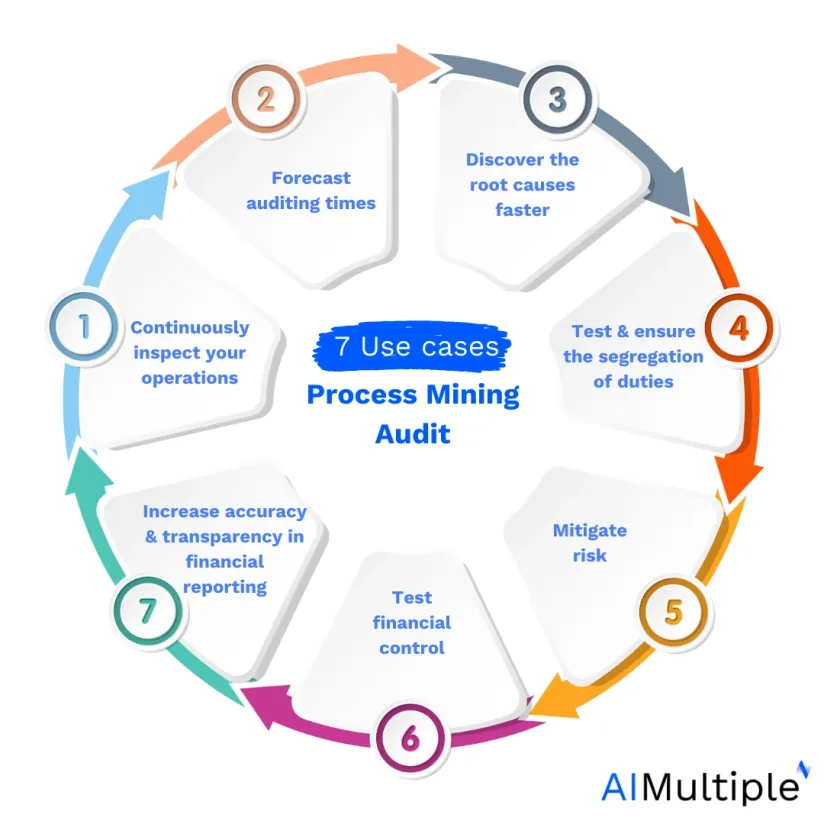
In this article, we explain seven process mining applications in auditing.
1. Continuously inspect your operations.
Process mining enables businesses to achieve internal audits by visualizing and monitoring their real-life operations. Businesses can upload a reference model, rule or assumption on expected operations to process mining conformance checks to compare the level of compliance between the uploaded model and these actual processes. As a result, firms assess their compliance and discover their outcome reliability, lead times and effectiveness.
In a process mining case study, ING (Netherlands) implemented process mining to achieve internal auditing. The organization achieved 100% transparency for all cases. The organization identified the most complicated and exceptional cases. ING verified the performance of internal controls such as authorization, compared designed processes with the entire operations and detected policy violations and unusual transactions.
2. Forecast auditing times
External auditing companies apply process mining to automate their reporting services. By mapping the workflow in an auditing process, process mining indicates the tasks that require prioritization or the steps that do not need long time allocations. Thus, external auditors can leverage insights they gain via process mining to change their plans or strategies in executing a process.
For example, Deutsche Post DHL Group in Germany integrated process mining into their audit process to discover areas to shorten the time spent on auditing. As a result, DHL found out that process mining reduced their auditing time by 25%. Thus, process mining enabled the company to detect unknown risks in processes.
3. Discover the root causes faster
Process mining facilitates the identification of anomalies and unexpected events in a process via the root-cause analysis feature. Process mining software often includes root-cause analysis tools and algorithms to help users detect the underlying reasons for deviations and errors.
An electric utility company, E.ON, implemented process mining to audit their purchase to pay processes. This case study enabled the firm to automatically discover actual processes and generate figures and risk indicators to compare with their real-life processes. Based on the comparison, the firm detected deviations and the root causes.
4. Test and ensure the segregation of duties
Process mining facilitates testing IT controls by comparing the actual processes with designed control mechanisms and assessing their effectiveness. Process mining also helps businesses ensure segregation of duties by providing information about breaches and people involved in activities in a workflow. By doing so, any internal audit team can detect unauthorized access attempts.
As a real-life example, Heineken, a retailer and e-commerce company in the Netherlands, used process mining to ensure segregation of duties. The company discovered 100% violation of the controls across their global operations with process mining.
5. Mitigate risk
Businesses can employ process mining to get insights about their risk assessment processes and identify higher risk areas. Some process mining tools include predictive tools and digital twin of an organization (DTOs) to allow users to run what-if simulations and make predictions based on historical process data. By estimating possible risk scenarios, business analysts can develop strategies and take precautions to mitigate the risk.
Becton Dickinson (BD), a healthcare facility, service and equipment firm in the USA, benefited from process mining to audit the procure to pay and vendor master business processes. They identified all the transactions concerning risk assessment and their root causes. In turn, BD targeted lost cash discounts and detected the vendors leading to lost discounts to improve how they use their capital.
6. Test financial control
Auditing financial departments require checking the control framework. Process mining ensures that the control framework corresponds to the reality by testing this control framework with a conformance check.
For instance, Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) in the US leveraged process mining to detect transaction fraud. The firm analyzed the procurement processes by running process diagnostics in their SAP system. Leveraging process mining, the auditing firm compared the process with internal controls and business policies. As a result, the firm could detect fraud and other flaws at the earlier stages.
7. Increase accuracy and transparency in financial reporting
Auditors can implement process mining to map the money flow, similar to workflow visuals. Doing so helps auditors easily track transactions and detect highly frequent and valued transactions. Then, auditors can compare the maps with the financial reports to assess accuracy and transparency.
PGGM, a Dutch pension fund service provider, utilized process mining to audit several processes of different clients at once. Then, the insurance firm compared the results with assurance standard reports prepared for each customer specifically. In this case study, process mining helped create more efficient and better quality auditing than the traditional assurance standard reporting of the organization.
While the benefits are evident, implementing process mining in auditing poses challenges:
Benefits of process mining audit
Process mining technology empowers auditors by enabling them to analyze entire event log records, providing audit evidence related to the company’s core business processes.
1. Cost-effective and swift auditing: Employing process mining technology streamlines audit procedures, facilitating quick and efficient analysis of process instances and event logs.
2. Enhanced efficiency and accuracy: Auditors utilize process mining analysis to visualize the core business processes, assessing process efficiency and identifying potential internal control ineffectiveness.
3. Improved compliance: Internal audit teams leverage process mining to identify unauthorized employee actions, ensuring process compliance and strengthening the entity’s internal controls.
4. Data-Driven decision making: Process mining aids internal audit departments in performing analytical procedures, using relevant management assertions to assess control risk and provide additional audit evidence.
Challenges and solutions in implementing process mining for auditing
While the benefits are evident, implementing process mining in auditing poses challenges:
1. Data quality issues: Poor data quality may impact audit effectiveness; hence, auditors need to perform analytical procedures using process mining to gather reliable audit evidence.
2. Process complexity: Training and education are essential for auditors to effectively interpret process statistics and flows, particularly in analyzing frequent and infrequent paths.
3. Privacy concerns: Proper data protection measures are crucial, especially when applying process mining to identify key controls and assess operational processes.
4. Slow implementation: Although studies apply process mining for audit in only a few instances, applying process mining to identify processes can significantly enhance the audit approach, providing business intelligence beyond manual audit procedures.
What is process mining?
Process mining enables auditors to identify and study operational processes by applying process mining technology to entire process flows. This approach not only ensures audit data analytics states are met but also strengthens the audit approach by incorporating additional audit evidence through the analysis of business transactions and other audit procedures.
Further Reading
To learn how process mining is used in compliance and other business sectors:
- Intelligent Automation in Audit: Benefits & 3 Steps to Implement
- 6 Ways Process Mining Enhances Compliance
- 33 Use Cases and Applications of Process Mining
To choose a vendor and leverage process mining, you can check out our data-driven list of software.
Check out our comprehensive and constantly updated process mining case studies list to learn more process mining audit real-life examples.
Also, feel free to contact us if you need more help to find the right vendor.

![51 Process mining case studies & project results [2024 update]](https://research.aimultiple.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/process-mining-case-studies-190x107.png.webp)
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.