~54.7 billion people around the world have been recorded to use the internet, creating 1.7MB of data every second. Crawling this exponentially growing volume of data could provide many opportunities for breakthroughs in data science. Data scientists can leverage crawled data to perform many tasks like real-time analytics, training predictive machine learning models, and improving natural language processing capabilities.
In this article, we highlighted each aspect of web scraping for machine learning, including how it works, why it matters, its use cases and best practices.
How do data scientists collect data?
Data scientists have several ways to collect their data:
- Find an existing dataset:
- Use public datasets: There are many datasets used to benchmark accuracy of common computer science problems like image recognition.
- Buy datasets: There are numerous marketplaces and platforms where data scientists can buy datasets. These datasets can range from consumer data, environmental data, to even political data.
- Use your company’s datasets: Companies have access to their own private data
- Create a new dataset:
- Generate data with human labor: Data scientists can create surveys and collect their results, use old surveys conducted and shared by others or use services like AmazonTurk that help them pay humans for tasks like data labeling and classification.
- Transform existing data into a dataset: Another way to collect public data is to crawl websites and download their data. Web crawling can be done manually, via RPA web scraping, or by using dedicated data collecting software called web crawlers or web scrapers.
Sponsored:
Bright Data’s Data Collector is a no code web scraping solution that extracts real-time public data from online platforms and delivers it to businesses on autopilot in different formats. It is especially useful when collecting data from websites that protect themselves against scraping. Using proxies and other techniques, Bright Data can bypass web scraping protection mechanisms.
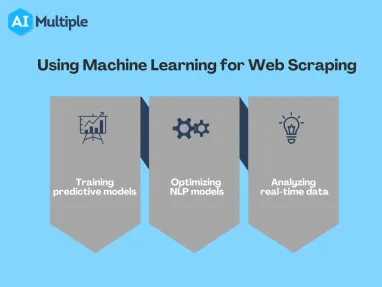
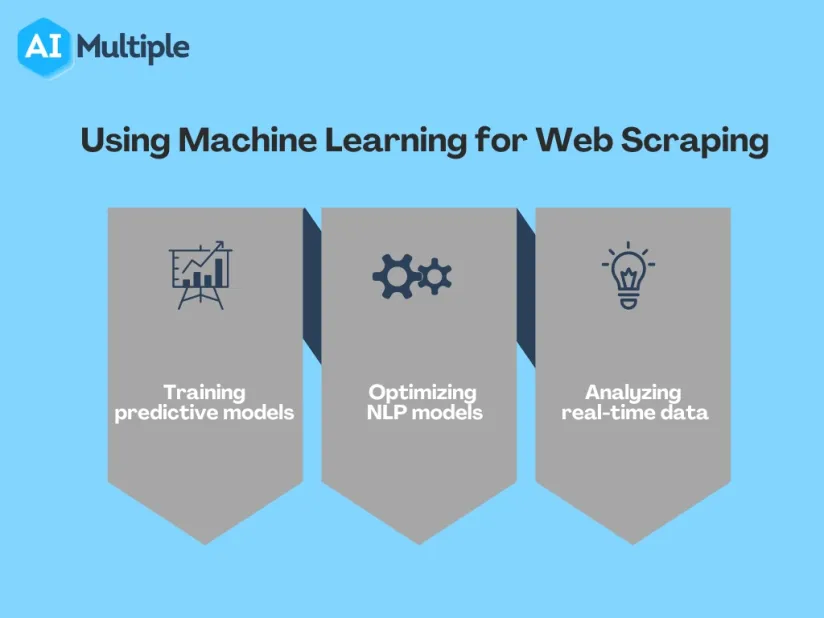
Top 3 use cases of web scraping in data science
Websites and online platforms have become important resources for raw, real-time data. Web scraping tools automate the process of extracting data from websites, therefore they can be useful for data science projects for:
1. Training predictive models
Predictive modeling, also known as predictive analytics, focuses on creating an AI model that can recognize patterns in historical data, and classify events based on their frequency and relationships, in order to predict the possibility and probability of an event happening in the future. Predictive models can require massive data in order to have accurate results, therefore data scientists typically prefer using web crawlers to extract online data instead of doing it manually.
2. Optimizing NLP models
Natural language processing (NLP) is the heart of conversational AI applications today. However, NLP faces many challenges due to the complexity of human speech demonstrated in abbreviations, sarcasm, or ambiguity.
Optimizing NLP models depends heavily on large data, especially data collected from the web. Internet data represents a continuously growing resource of human speech data which contains numerous human languages, syntaxes, and sentiments.
Crawling this data provides a growing pool of up-to-date training data for NLP and conversational AI models.
3. Analyzing real-time data
Web crawlers can be programmed to crawl data from websites at specific time intervals, such as every hour/day/week/month, etc. According to the project, data scientists can choose to acquire the data in an almost real-time manner in order to make better decisions. For example, data about natural disasters, such as hurricanes or volcanos, can be crawled from social media (e.g. tweets), news websites, government online updates, etc. Crawling this data enables data scientists and government workers to analyze the situation and act accordingly.
Sponsored:
Oxylabs’ web scraper API is designed for real-time data extraction. You can gather data from static and dynamic websites without triggering anti-bot measures. The web scraper API includes a proxy rotator and JavaScript rendering to circumvent anti-scraping systems by adhering to the terms of service of the scraped websites.

Top 3 examples of data science projects based on web scraping
There are numerous data science projects and applications based on web data, and some of the most famous projects are:
1. GPT-3
GPT-3 is the third Generative Pre-trained Transformer language model built by OpenAI. It was trained on web data crawled from Wikipedia and Common Crawl‘s web archive, and is used for multiple applications today such as building code for machine learning and deep learning frameworks, generating website layouts according to user specifications, and autocompleting human speech.
2. LaMDA
LaMDA is Google’s language model which can have open-ended conversations with anyone. Unlike other language models, LaMDA was trained on “dialogue” training sets crawled from internet resources in order to have free-flowing conversations instead of producing fixed responses.
3. Similar Web
Similar Web is an online platform that provides information about websites such as traffic, engagement, and world ranking. They collect public data from Wikipedia, Census, Google analytics, browser plug-ins, etc. and they claim to create 10k+ traffic reports per day. Business use Similar Web data for competition analysis and marketing strategy optimization.
What are the challenges of web scraping?
Many public data owners have legal and technical issues with web scrapers because they don’t know where and how their data will be used, so they adopt anti-crawler strategies to minimize non-human access to their data. Nonetheless, web crawlers are also leveraging different strategies such as using proxies to bypass the barriers set by data owners.
Check out top 7 web scraping best practices to learn how to circumvent anti-crawler strategies.
For more on web scraping
To get a better grasp on web scraping, feel free to read our in-depth guide on web scraping and how it works. And to explore other use cases of web scraping, feel free to read our articles about web scraping in finance, and dynamic pricing.
If you think your business will benefit from using web scraping tools, make sure to check out our data-driven list of web crawlers.
And we can guide you through the process

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.