Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a promising solution, capable of not only streamlining operations but also innovating personalized services, despite its potential implementation challenges.
The insurance value chain, from product development to claims management, is a complicated process. The complex nature of tasks such as risk assessment and claims processing presents significant challenges for an insurance company.
Explore 10 potential use cases of generative AI in insurance and its challenges that can be problematic in the insurance sector.
10 Use Cases of Generative AI in Insurance
1- Data augmentation
Generative AI can analyze existing customer data and create synthetic data from it, which can be particularly useful when there is a lack of certain types of data for modeling. This can be used to improve the performance of predictive models.
Also, these generated synthetic datasets can mimic the properties of the original data without containing any personally identifiable information, thereby helping to maintain customer privacy.
2- Content creation
Generative AI in insurance tools like ChatGPT can be utilized in the insurance industry for content creation in a variety of ways:
- Marketing materials: AI can be utilized to create customized marketing materials, including brochures, blog posts, social media content, and email campaigns. It can generate content related to various insurance products, tailored to different user segments.
- Customer communications: The AI can help draft emails, notifications, and messages to customers.
- Product descriptions: AI can create detailed, comprehensible descriptions for various insurance products offered by a company. These can be used on the company’s website, in brochures, or in other marketing materials.
3- Risk assessment and premium calculation
Generative AI can be used to simulate various risk scenarios based on historical data and calculate premiums accordingly. For example, by learning from previous customer data, generative models can produce simulations of potential future customer data and their potential risks. These simulations can be used to train predictive models to better estimate risk and set insurance premiums.
Real-life Example: Zest AI
Zest AI offers underwriting tools for the insurance industry, utilizing machine learning to enhance risk assessments. The platform analyzes historical data and predicts risks, making underwriting more accurate and efficient for insurers such as auto and life insurance companies.
Fore more on risk assessment, check out our article on the technologies to enhance risk assessment in the insurance industry.
4- Fraud detection
Generative AI in insurance can generate examples of fraudulent and non-fraudulent claims which can be used to train machine learning models to detect fraud. These models can predict if a new claim has a high chance of being fraudulent, thereby saving the company money.
For more, check out our article on the 5 technologies improving fraud detection in insurance.
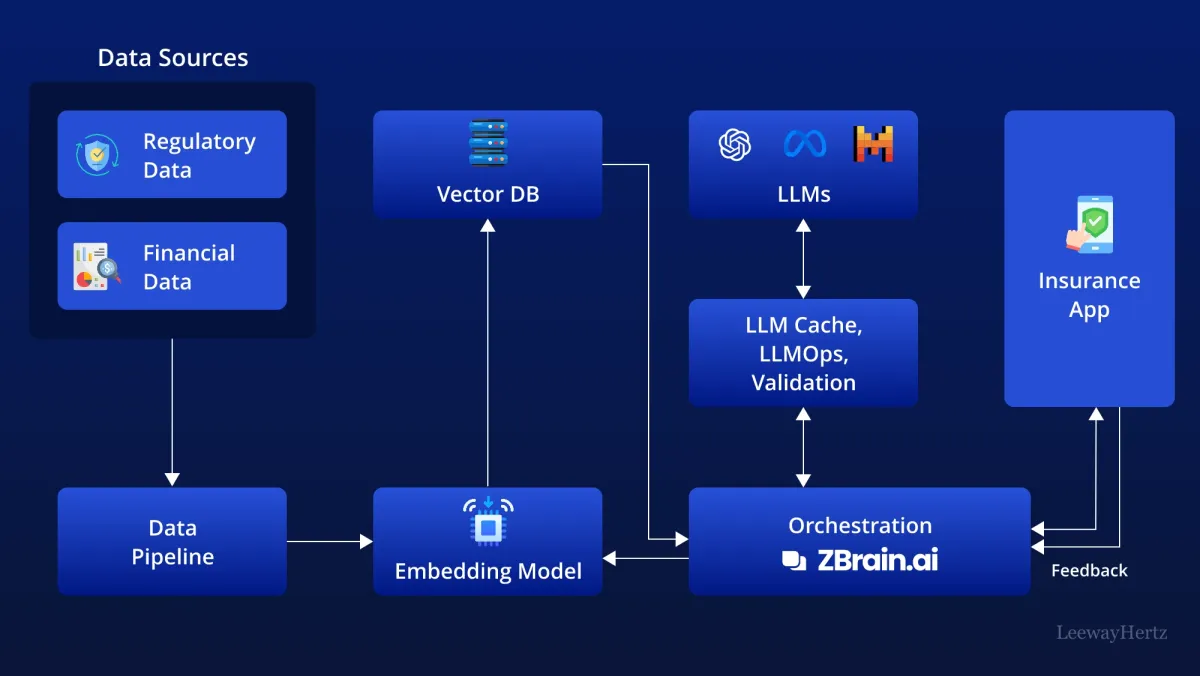
Source: Generative AI in Insurance
5- Customer profiling
Generative AI can be used to generate synthetic customer profiles that help in developing and testing models for customer segmentation, behavior prediction, and personalized marketing without breaching privacy norms.
6- Claims processing
Generative AI in insurance models can be employed to streamline the often complex process of claims management in an insurance business. They can generate automated responses for basic claim inquiries, accelerating the overall claim settlement process and shortening the time to process insurance claims.
For instance, after an accident, a customer may upload the details and pictures of the damaged vehicle. A generative model trained on similar data can evaluate the damage, estimate the repair costs, and hence help in determining the claim amount. The models can also generate appropriate responses to customer queries about the status or details of their claim, making communication more straightforward and efficient.
Real-life Example: Tractable AI
Tractable is an AI-powered tool that helps insurance companies process claims faster by generating damage assessments from photos of car accidents or property damage. Insurers like Geico and Admiral use Tractable to automate claims processes, reducing the time required for claims settlements from weeks to mere hours.
For more on claims processing in insurance, check out our articles:
- Top 7 Technologies that Improve Insurance Claims Processing
- Claims Processing Transformation: Trends & Strategy
- Top 3 Ways AI Improves Insurance Claims Processing
7- Policy generation
AI models can generate personalized insurance policies based on the specific needs and circumstances of each customer. Based on data about the customer, such as age, health history, location, and other relevant factors, the AI system can generate a policy tailored to those individual attributes, rather than providing a one-size-fits-all policy. This personalization can lead to more adequate coverage for the insured and better customer satisfaction.
Real-life Example: Lemonade AI
Lemonade, a digital insurance company, uses AI to offer personalized policy recommendations. By analyzing customer data through their AI-driven platform, they create personalized policies that cater to individual needs, taking into account factors such as lifestyle, risk tolerance, and coverage preferences.
8- Predictive analysis & scenario modeling
Generative AI in insurance models can generate thousands of potential scenarios from historical trends and data. The insurance companies can use these scenarios to understand potential future outcomes and make better decisions.
- For instance, in health or property insurance, these models can simulate how health conditions or natural disasters might evolve, respectively, helping insurers understand future risks and set accurate premiums.
- In life insurance or retirement planning, AI can create scenarios considering factors like inflation, market conditions, and life expectancy, to predict potential future payouts. These insights enable insurance companies to make informed decisions and better prepare for diverse potential future events. However, the quality of predictions depends heavily on the data quality and modeling assumptions, hence requiring careful consideration.
9- Chatbots and customer service
Generative AI can be used to create chatbots that generate human-like text, thereby improving customer interaction and answering queries in real-time. Implementing generative AI in insurance for customer service operations can increase customer satisfaction due to fast and 24/7 support, together with cost savings.
Real-life Example Tool: Spixii
Spixii is an AI chatbot designed specifically for the insurance sector. It handles customer queries, assists with claims, and offers advice on policy changes. Companies like Allianz use Spixii to improve customer service by offering round-the-clock support for customer inquiries.
10- Virtual Claims Assistants
Insurers are leveraging generative AI to deploy advanced virtual claims assistants that guide policyholders seamlessly through the entire claims process.
- Instant Claim Filing: Policyholders can easily initiate claims through virtual assistants, which collect necessary documents, ask for essential details, and upload photos or videos of damages, streamlining the initial filing process.
- Real-Time Status Updates: AI-powered assistants provide real-time tracking of claim status. Whether the claim is under review, approved, or awaiting additional documentation, policyholders are kept informed without needing to contact customer service representatives.
- Automated Document Processing: Generative AI automates document verification and processing, instantly validating policy terms, coverage limits, and supporting documents. This eliminates manual errors and speeds up the claims review process, leading to faster settlements.
For more on the use of generative AI solutions in the customer service, you can check our articles:
- 10 Use Cases of Conversational AI for Customer Service in 2024
- ChatGPT for Customer Service: 7 Use Cases & Benefits in 2024
- Top 9 Customer Service Chatbot Use Cases in 2024
5 Challenges of Leveraging Generative AI in the Insurance Industry
1- Data quality
Generative AI in insurance relies heavily on the quality of the training data. Poor quality or biased data can lead to inaccurate or misleading outputs. In addition, generated synthetic data might not perfectly represent the complexities and nuances of the real world.
2- Reliability and accuracy
Generative models can sometimes produce unrealistic or implausible outputs. Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the generated data or predictions is a significant challenge.
3- Explainability and transparency
Generative AI models, like most deep learning models, are often referred to as “black boxes” because their decision-making processes are not easily understandable by humans. This lack of transparency and explainability can be a significant issue, particularly in a heavily regulated industry like insurance.
4- Computational resources
Training and fine tuning generative models, particularly large ones, requires substantial computational resources. Smaller companies may struggle to implement generative AI in insurance tools due to the high costs involved.
5- Regulatory challenges
The regulatory environment for AI in insurance is evolving, and companies must navigate these changes carefully. Regulators may require companies to demonstrate the robustness, fairness, and transparency of their AI systems, and especially of the generative AI solutions due to their ethical concerns.
For more about the ethical problems of generative AI, check out our article.
FAQ
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to AI systems that can create new content based on the data they have been trained on.
What are the benefits of using Generative AI in insurance?
Generative AI offers numerous benefits to insurance companies:
Efficiency: Automates time-consuming tasks such as claims processing and policy generation.
Personalization: Provides tailored insurance solutions for individual customers.
Cost reduction: Reduces administrative overhead and human error.
Improved customer experience: Enhances customer engagement through AI-driven chatbots and personalized services.
What challenges come with implementing Generative AI in insurance?
While there are many benefits, companies face several challenges when using Generative AI in insurance:
Data privacy and security: AI relies on large amounts of sensitive customer data, which can raise privacy concerns.
Bias in AI models: AI can perpetuate biases if the training data used is not representative.
Lack of transparency: AI models can function as “black boxes,” making it difficult to explain decisions to customers.
Integration with legacy systems: Many insurers use outdated systems, which can make it difficult to integrate AI solutions.
Regulatory and legal challenges: The use of Generative AI in insurance and claims assessment brings new legal and compliance issues.
For more on generative AI across different sectors
- Enterprise Generative AI: 10+ Use cases & LLM Best Practices
- 10+ Generative AI Finance Use Cases
- Generative AI Legal Use Cases & Examples
- Generative AI Fashion Industry: 5 Use Cases with Case Studies
- Top 6 Use Cases of Generative AI in Education
- Top 4 Use Cases of Generative AI in Banking
- Generative AI Healthcare Industry: Benefits, Challenges, Potentials


![Generative AI in Manufacturing: Use Cases & Benefits ['25]](https://research.aimultiple.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Generative-AI-in-Manufacturing-Use-Cases-190x107.png.webp)
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.