Companies conduct online surveys to understand market trends and their target audience. However, finding the right survey participants can be both challenging and time-consuming. Survey participant recruitment tools help businesses to find appropriate participants.
Learn the metrics in choosing survey participant recruitment tools, and check the top vendors comparison list with their features and hands-on reviews from our experiences:
Top 6 online survey participant recruitment tools
Table 1. Market presence comparison
| Vendors | Reviews* | Employee size** | Free trial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clickworker | 5.0 out of 2 reviews | 995 | ✖️ |
| Qualtrics CoreXM | 4.6 out of 3,320 reviews | 26 | ✅ |
| User Interviews | 4.6 out of 822 reviews | 203 | ✅ |
| Pollfish | 4.5 out of 227 reviews | 62 | ✖️ |
| SurveyMonkey Audience | 4.6 out of 81 reviews | 1,421 | ✖️ |
| Amazon Mechanical Turk | 4.1 out of 29 reviews | 130,371 | ✖️ |
* Reviews are derived from B2B software review platforms
** Based on LinkedIn
Table 2. Features comparison
| Vendors | Survey respondent size | Languages offered | Multi-channel survey distribution | Customer support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clickworker | 6M+ | 45 | Web-based panel, Android or iOS | 24/7 phone support |
| Qualtrics CoreXM | N/A | 50 | Web-based panel | 24/7 live support |
| User Interviews | 2.4M | English only | Web-based panel, Android or iOS | N/A |
| Pollfish | 250M+ | 50 | Web-based panel, Android or iOS | 24/7 live support |
| SurveyMonkey Audience | 175M | 16 | Web-based panel | 24/7 phone support |
| Amazon Mechanical Turk | 500K | Not provided | Web-based panel | Through e-mail |
Disclaimer: N/A indicates that the information has not been publicly disclosed.
Ranking: With sponsored survey participant recruitment tools at the top, vendors are listed based on the number of total user reviews.
Check out our survey participant recruitment tools deep dive for top providers such as Pollfish, Qualtrics Core XM, Amazon Mechanical Turk Survey, and SurveyMonkey Audience.
Clickworker
Clickworker offers a platform for recruiting research participants, ideal for research across diverse markets and populations.
Key features include:
- Global reach: Access a diverse pool of research study participants across six continents, ranging in age from 18 to 80.
Figure 1. Survey participant selection based on participants’ country with Clickworker
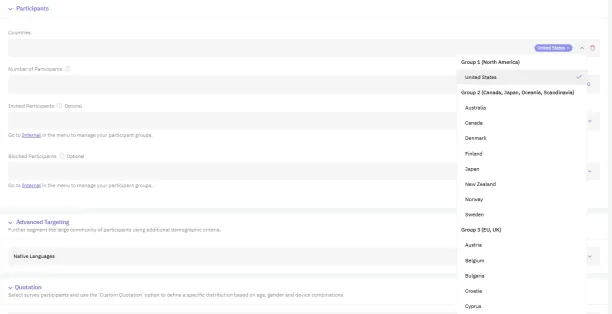
- Advanced segmentation: Recruit participants tailor to needs with detailed segmentation based on demographics, behaviors, or specific market.
Figure 2. Survey participant selection based on native language, gender, age, and devices with Clickworker
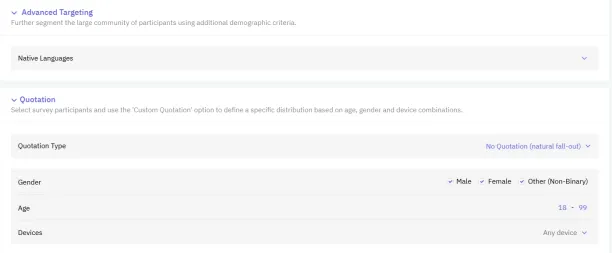
- Internal/external participant groups: Save participant teams from your own participants for streamlined future use.
Figure 3. Survey participant selection by creating a participant group with Clickworker
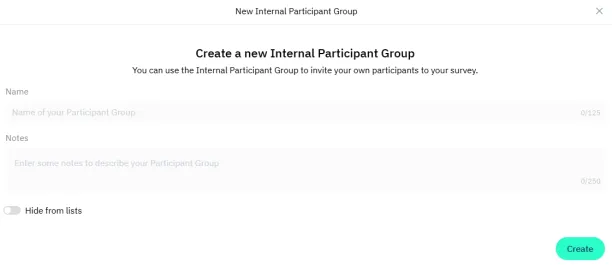
- Quota management: Set distribution quotas to maintain balanced participant representation.
Figure 4. Quota management for survey participants in Clickworker
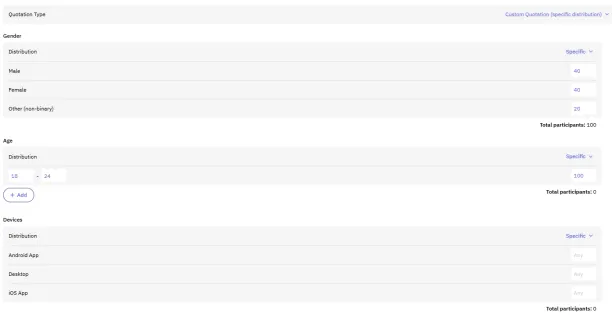
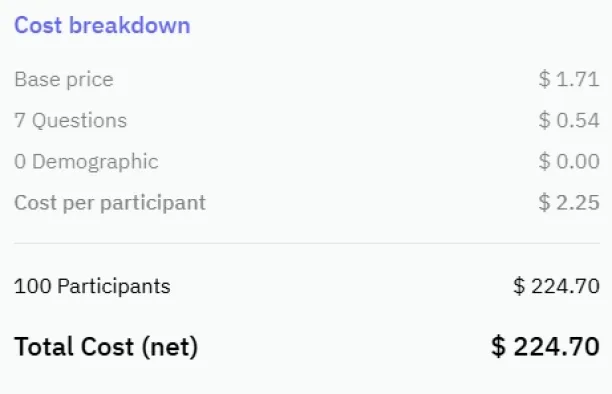
For enhanced visibility, Clickworker offers paid options to promote surveys via email or increase payouts for recruiting participants. The pricing of the Clickworker survey service is based on the number and types of questions included in the survey, as well as the number of participants recruited.
Figure 5. Pricing of Clickworker survey participant recruitment feature
The platform supports desktop and mobile (iOS/Android) access and provides 24/7 customer support.
Choose Clickworker for global reach, advanced segmentation, and data reliability.
Qualtrics CoreXM
Qualtrics CoreXM offers a suite of survey participant recruitment tools designed to enhance digital experiences and streamline survey participant recruitment. The platform allows for responsive, branded intercepts across multiple touchpoints, all without requiring coding expertise.
Key features include:
- Responsive intercepts: Easily design and deploy intercepts that engage right participants across different platforms, improving the ability to gather feedback.
- Abandonment insights: Understand why potential participants or customers exit funnels, enabling you to address pain points and improve conversion rates.
- Reputation management: Encourage participants to provide authentic reviews on social platforms like Google and Yelp, ensuring ongoing feedback.
- Lead generation: Strategically capture contact information from site visitors at optimal moments to ensure leads are not missed.
- Usability testing: Conduct usability tests with random or conditional targeting, gathering feedback to improve digital experiences.
- Mobile/in-app research: Engage mobile user research participants with targeted intercepts, ensuring consistency with the overall brand experience and gathering feedback on mobile engagement.
- Post-transaction research: Intercept users after they complete key processes to understand their satisfaction and experience with the transaction.
Qualtrics CoreXM supports surveys in 50 languages and offers 24/7 live support, making it ideal for global and diverse participant recruitment efforts. Its multi-channel distribution capabilities across web-based platforms, Android, and iOS ensure broad reach and engagement across all touchpoints.
User Interviews
User Interviews provides a platform for recruiting participants, enabling market researchers to quickly access quality respondents and complete the research process in a matter of days.
Key features include:
- Fast recruitment: Launch studies in minutes, source participants in hours, and complete studies in days, allowing for rapid turnaround times.
- Advanced targeting: Easily finding participants based on various criteria, such as professional roles, skills, and product usage, ensuring relevant feedback.
- Automated processes: Streamline participant recruitment by automating screening, scheduling, and incentives, reducing manual work for user researchers.
- Comprehensive Compliance: The platform is SOC2, SSO, 2FA, and GDPR compliant, ensuring high levels of security and privacy for both researchers and participants.
User Interviews supports a web-based panel accessible on Android and iOS, with a focus on the English language.
Pollfish
Pollfish is a market research platform that connects researchers with over 250 million respondents across 160+ countries. It offers a mobile-first approach and a wide distribution network through 140,000+ app and website partners.
Key features include:
- AI-driven survey creation: Users can input their research goals, and Pollfish’s AI generates targeted survey questions, streamlining the survey design process.
- Various research methods: The platform supports multiple research techniques, including A/B testing, advanced questionnaire logic, and survey templates.
- Real-time survey data collection: Surveys typically complete in a few hours to a few days, with real-time results available through the user panel for immediate analysis.
- Quality assurance: Pollfish implements extensive quality checks to eliminate survey fraud and irrelevant survey responses, ensuring that collected data aligns with specified targeting criteria.
- Global reach and language support: The platform facilitates surveys in multiple languages, translating open-ended responses into US English for consistent analysis.
- Dynamic sampling and random device engagement (RDE): The platform uses RDE to organically reach respondents at optimal times, reducing potential bias associated with traditional survey panels.
SurveyMonkey Audience
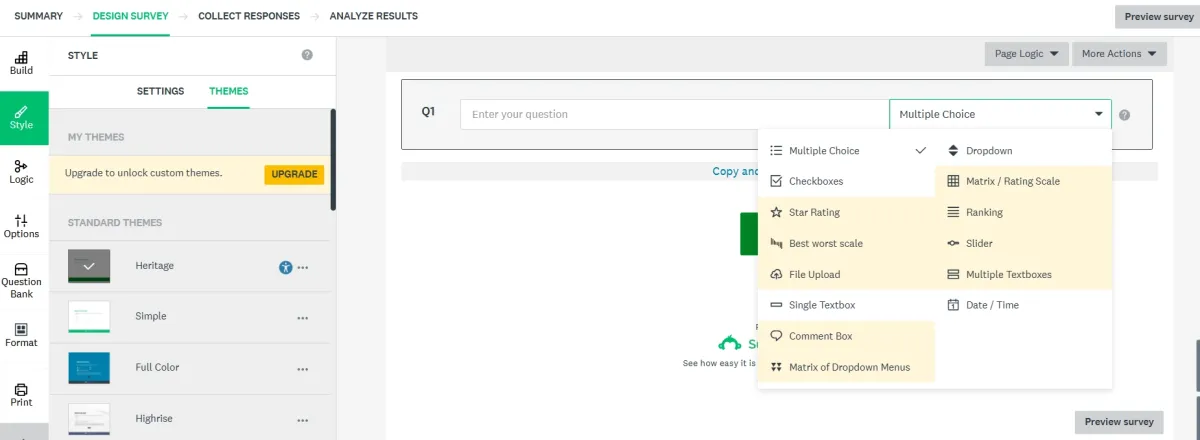
The platform provides survey participant recruitment tools for creating surveys and forms with ease, offering AI-powered guidance to help users ask relevant questions.
SurveyMonkey features 12 question types and a user-friendly interface, making it suitable for collecting contextual feedback in multiple languages.
Figure 6. Creation of survey in SurveyMonkey
The platform includes analytics tools for analyzing responses and deriving insights. It is commonly used for product research, market research, customer satisfaction surveys, and understanding audience preferences and customer experience.
Key features include:
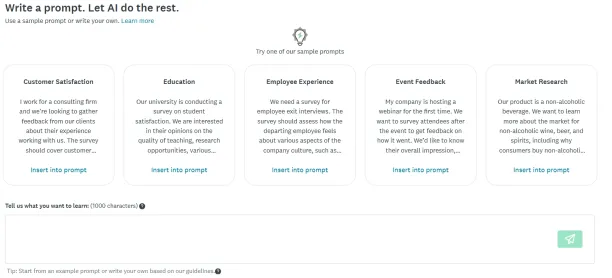
- AI usage: SurveyMonkey allows users to leverage AI tools for the creation of online surveys by generating questions based on research project prompts, suggesting answers for participants to choose from, predicting appropriate question types, estimating completion rates, and more.
Figure 7. AI usage in survey creation with SurveyMonkey
- Response collection: The platform offers access to a global panel of over 335 million respondents, facilitating valuable market insight collection.
- Workflow automation: Integrations with services like MailChimp, HubSpot, Zoom, Google Drive, Microsoft Teams, and Constant Contact allow for automated workflows.
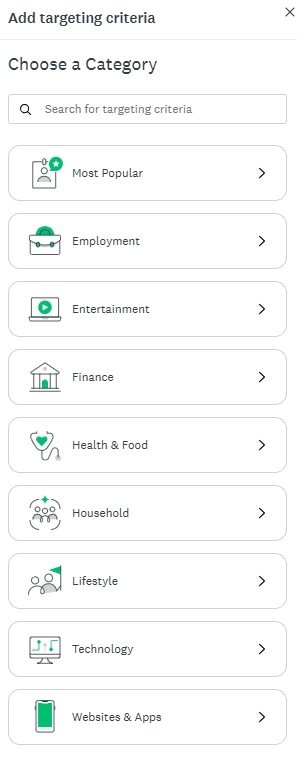
- Target audience access: Researchers can send surveys to specific target audiences using over 200 targeting options, ensuring relevant feedback is gathered for actionable insights. The platform provides lots of options for survey participant criteria, including employment, financial choices, and lifestyle preferences. Pricing of the survey response collection is affected by the respondent characteristics.
Figure 8. Survey participants criteria of SurveyMonkey platform
- Data analysis: The platform includes built-in reporting tools and customizable dashboards for analyzing responses to have a deeper understanding.
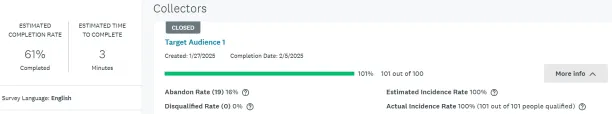
Figure 9. Summary of survey results on the SurveyMonkey platform
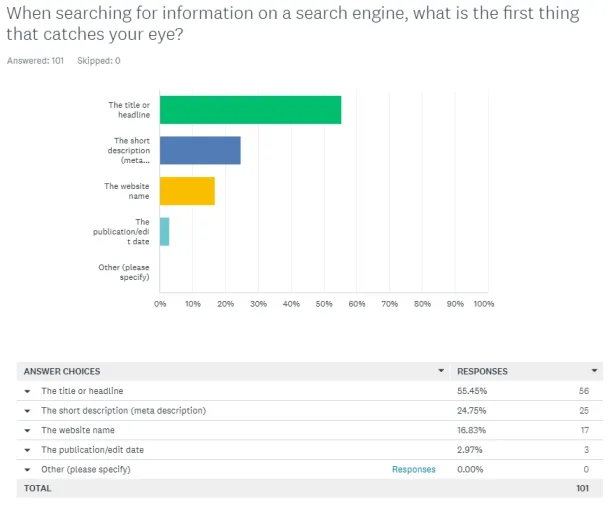
- Virtualization of survey results: SurveyMonkey Audience provides virtual graphics for each of the questions’ responses.
Figure 10. Virtualization of survey results in SurveyMonkey platform
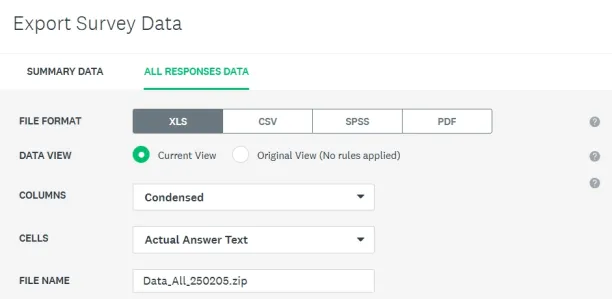
The SurveyMonkey Audience platform provided 101 responses in less than two days with the broadest participant targeting (ages 18-99, all genders, any devices, and no quotas in sample selection). Survey results can be downloaded in XLS, CSV, SPSS, and PDF formats for further analysis using tools like SPSS and STATA.
Figure 11. Exporting survey data in SurveyMonkey platform
Amazon Mechanical Turk
Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) is a crowdsourcing platform that facilitates the outsourcing of tasks to a distributed global workforce. This platform supports a wide range of tasks, including data validation, research, survey participation, and content moderation.
Key features include:
- Task outsourcing: MTurk allows businesses to break down complex projects into smaller, manageable tasks known as microtasks, which can be completed by workers online.
- Cost efficiency: MTurk operates on a pay-per-task model, reducing the overhead and labor costs typically associated with hiring temporary staff.
- Survey distribution: Surveys can be conducted through a web-based panel, with respondents completing tasks from various locations.
Vendor selection criteria
We narrowed our survey panel company list based on some criteria. We used the number of B2B reviews and employees of a company to estimate its market presence, as these criteria are public and verifiable.
As a result, we set certain parameters to focus our efforts on the top 6 companies in terms of market presence. We selected firms with more than 60 employees. We conduct user tests on Clickworker and SurveyMonkey to explore their features firsthand.
Top 6 metrics in choosing the best participant recruitment service
1- Diverse and large respondent pool
Ensure the service provides access to a broad and diverse group of respondents. This is especially important for B2B companies targeting decision-makers or B2C businesses focusing on affluent shoppers. A large respondent pool guarantees that the survey reaches a wide and representative audience, increasing the reliability of the results.
For those interested, here is our article on the best practices for conducting online surveys.
2- Multilingual respondents
Most recruitment participants‘ services rely on English while collecting feedback from their audience. However, customers of global companies come from diverse parts of the world and speak various languages. Thus, conducting user research in different languages and obtaining feedback from non-English speaking customers can help businesses get deeper and more inclusive insights.
3- Segmentation possibilities
To obtain reliable data, researching the right audience is as crucial as the sample’s representativeness. Vendors can divide their crowd into segments based on certain demographic characteristics (e.g., age, language, country, disposable income). As a result, only participants who match the target audience’s profile can complete the survey.
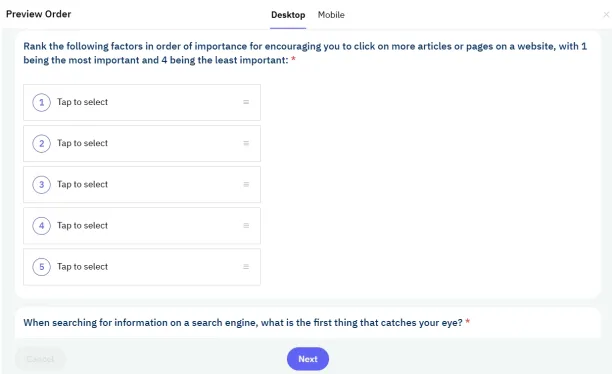
4- Prescreening participants
The recruitment service should have robust screening processes to ensure that participants are genuine and fit the criteria you’re looking for. This helps in filtering out unqualified or fraudulent respondents, maintaining the integrity of your user research.
Figure 12. Example of prescreening questions before the participants take the survey
5- Multi-channel survey distribution
Companies can deploy participants through a variety of methods. Most businesses offer web-based panels where customers can register and complete activities. However, some also offer desktop or mobile implementations (Android or iOS).
6- Free trial options
Companies can sometimes get stuck between two options and may want to try both before investing in one of the survey tools. While some services let you try them out for free with some basic tools, others require payment in advance.
Here is also our data-driven list of survey participant recruitment services and survey tools for those interested.
You can also check our data-driven list of market research tools.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.