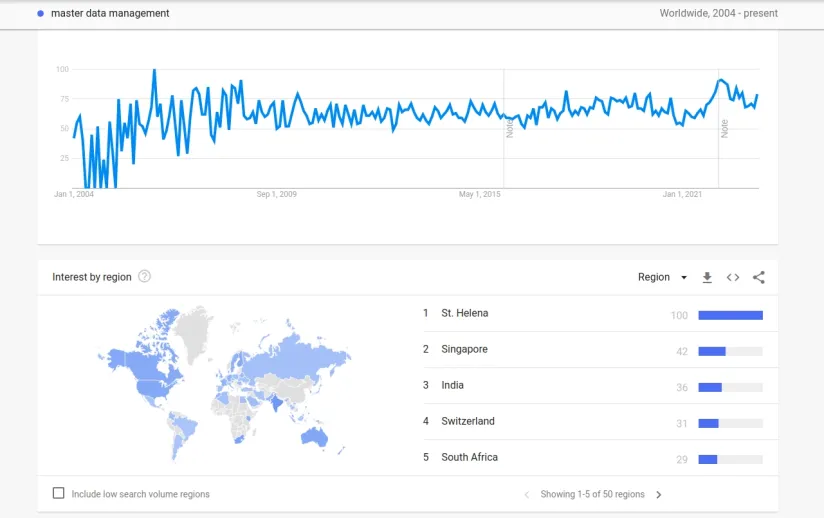
Figure 1. Worldwide interest in master data management since 2004.1
Master data management (MDM) is the process of collecting, storing, organizing, and maintaining a company’s critical data. This data can include information about customers, products, suppliers, financial data, and compliance data. Master data management, in particular, can be applied to data governance. Unfortunately, interest in master data management has remained consistent in comparison to data governance, which has been steadily increasing since 2016.
Master data management capabilities are essential for businesses that want to make informed decisions based on accurate and complete data. In this article, we explore the seven use cases for master data management and their benefits.
1. Data governance
Data governance is the process of managing data accuracy, availability, usability, integrity, and security. It can be an essential component of effective master data management because it can ensure that data is of high quality and properly secured.
Since 2004, interest in data governance has been increasing, with high search volume in almost every state in the U.S. Data governance is the ability to improve data quality, which is critical to effectively managing master data. With accurate, complete, and consistent master data records, organizations can create a single, trusted source of data systems. It can be used across the organization to support various business processes, such as:
- Sales: Accurate customer data can assist sales teams in identifying potential customers and tailoring their approach. MDM can provide a single, trusted master data record of customers that can be used to inform sales decisions.
- Marketing: Product data that is complete and accurate can assist marketing teams in developing targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience and drive engagement and sales. MDM can provide a centralized repository for product data to support marketing initiatives.
- Finance: Consistent financial data can assist finance teams in tracking revenue and expenses, developing budgets, and making sound financial decisions. MDM can provide a centralized, trusted source of financial data for use in making financial decisions.
Data security
Another benefit of master data management is that it can improve data security, reducing the risk of data breaches and protecting the organization’s reputation. By creating accurate master data, MDM can help reduce the risk of data breaches and protect the organization’s reputation.
2. Customer data management
In 2020, the global interest in master data management and customer data management peaked. Customer data management (CDM) is a subset of MDM that focuses on the management of customer-related data within a company. The process of collecting, organizing, and maintaining customer data is referred to as customer data management.
Effective customer data management enables businesses to keep accurate and complete customer information on hand, which can then be used to improve customer service and gain insights into customer behavior.
As a result, the CRM benefits include:
- Improved customer service through personalized interactions based on accurate and complete customer data.
- Gaining insights into customer behavior by analyzing their data, which can be used to develop new products and services and improve customer loyalty.
3. Financial data management
Financial data management is a critical component of master data management that focuses on managing financial-related data within an organization. Financial data management refers to the process of collecting, organizing, and maintaining financial data. Financial data can include information related to transactional data, revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and other financial metrics that are essential for decision-making and financial reporting.
Financial data management strategy can be critical for ensuring that an organization’s financial data is accurate, complete, and consistent across all systems and applications. This is significant for several reasons. To begin, precise financial data is required for financial reporting, regulatory compliance, and tax reporting. Second, financial data is an important input for business decision-making processes like budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning.
One of the primary advantages of incorporating financial data management into an MDM strategy is that it allows organizations to gain a comprehensive view of their financial operations. Organizations can gain valuable insights into their financial performance and identify areas for improvement by integrating financial data with other master data domains. Organizations, for example, can use financial data to determine which products or services are the most profitable, which regions generate the most revenue, and which cost centers drive expenses.
4. Supplier data management
One of the lesser-known aspects of MDM is supplier data management. In the last five years, supplier data management has seen consistent interest from India, the United States, and Canada. The process of collecting, organizing, and maintaining supplier data is referred to as supplier data management. This information may include details about:
- Supplier contracts
- Performance
- Compliance
Reduced supplier risks
Effective supplier data management is critical for companies that want to ensure that their suppliers meet quality and compliance standards. Knowing what is happening in your supply chain can prevent snowball effects.
One of the benefits of supplier data management is the ability to reduce supplier risks. By maintaining accurate and complete supplier data, businesses can identify potential supplier risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them. This can help businesses reduce the risk of supply chain disruptions and improve the overall quality of their products and services.
Supplier performance
Another benefit of supplier data management is the ability to improve supplier performance. By analyzing supplier data, businesses can identify areas for improvement and work with their suppliers to improve performance. This can help businesses build stronger relationships with their suppliers and improve the overall quality of their products and services.
5. Compliance data management
Since the 2020s, there has been an increase in interest in compliance management. The process of collecting, organizing, and maintaining compliance data is referred to as compliance data management. This information may include regulatory requirements, internal policies and procedures, and audits.
Reducing compliance risks is one of the advantages of compliance data management. Businesses can recognize possible compliance issues and take preventative action to mitigate them by storing accurate and complete compliance data and reduce the risk of storing incorrect data. By doing this, businesses can lessen the chance of non-compliance fines and reputational harm.
The capacity to enhance compliance reporting is a further advantage of compliance data management. Businesses can produce more accurate compliance reports that can be utilized to make decisions by preserving accurate and full compliance data. By doing this, organizations can ensure that they are fulfilling their duties and enhance their compliance performance.
6. Product information management
Product data management (PDM) is an important component of master data management that focuses on managing product-related data within an organization. Product data management refers to the process of collecting, organizing, and maintaining product data. Product data can include information such as product descriptions, specifications, prices, inventory levels, and other relevant information that is essential for managing an organization’s product catalog and sales operations.
Good product data management ensures that an organization’s product information is accurate, complete, and consistent across all systems and applications. MDM includes product data as a master data domain, together with customer, financial, and supplier data. This means that product data is vital for precise and consistent operations management.
One benefit of product data management is that it can improve product quality. Product quality can be improved through product data management. By preserving precise and full product data, organizations can identify and correct product problems, improve product features, and increase product quality.
Another benefit of product data management is product development. Product development can be streamlined with product information management. Businesses can save product development time and expense by retaining accurate and complete product data. Businesses may launch new items faster and more efficiently with this.
7. Reference data management
The management of reference data within an organization is the focus of reference data management (RDM), a critical component of master data management. Data that is used to categorize, classify, or otherwise define other data elements within an organization’s systems and applications are referred to as reference data. Product codes, industry codes, geographic codes, and other standard or regulatory codes are examples of reference data. In the last five years, reference data management has been frequently searched on Google.
Reference data management benefits
Reference data management benefits include:
- Improved data quality: One of the benefits of reference data management is the ability to improve data quality. By maintaining accurate and complete reference data, businesses can ensure that data is properly classified and can be used effectively. This can help businesses make informed decisions based on high-quality data.
- Improved data integration: Another benefit of reference data management is the ability to improve data integration. By maintaining accurate and complete reference data, businesses can ensure that data can be integrated across different systems and platforms. This can help businesses streamline their processes and reduce the risk of data errors.
If you have more questions about master data management, please contact us at:
This article was drafted by former AIMultiple industry analyst Yılmaz Doğukan Özlü.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.