Data is critical for business and internet is a large data source including insights about vendors, products, services, or customers. Businesses still have difficulty automatically collecting data from numerous sources, especially the internet. Web scraping enables businesses to automatically extract public data from websites using web scraping tools.
In this article, we will dive into each critical aspect of web scraping, including what it is, how it works, its use cases and best practices.
What is web scraping?
Web scraping, sometimes called web crawling, is the process of extracting data from websites. The table below presents a comparison of leading web scraping tools. For an in-depth analysis, refer to our comprehensive guide.
| Vendors | Pricing/mo | Trial | PAYG | JavaScript rendering | Built-in Proxy | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Data | $500 | 7-day | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | No-code & API |
| Smartproxy | $29 | 3K free requests | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
| Oxylabs | $49 | 7-day | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
| Apify | $49 | Unlimited | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | No-code & API |
| Nimble | $150 | 7-day | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
| SOAX | $59 | 7-day | ❌ | N/A | ✅ | API |
| Zyte | $100 | $5 free for a month | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
| Diffbot | $299 | 14-day | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
| Octoparse | $89 | 14-day | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | No-code |
| Nanonets | $499 | N/A | ✅ | N/A | ❌ | OCR API |
| Scraper API | $149 | 7-day | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | API |
How does web scraper tools / bots work?
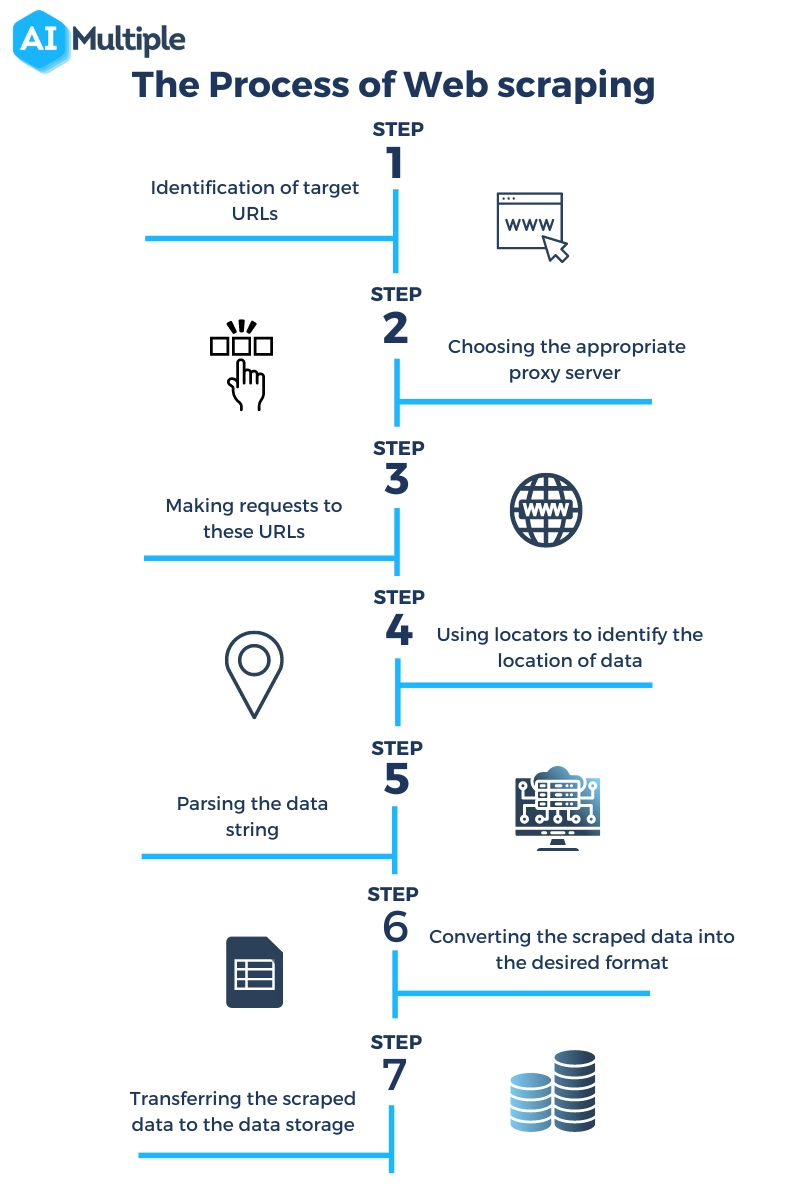
The process of scraping a page involves making requests to the page and extracting machine-readable information from it. As seen in figure 2 general web scraping process consists of the following 7 steps :
- Identification of target URLs
- If the website to be crawled uses anti-scraping technologies such as CAPTCHAs, the scraper may need to choose the appropriate proxy server solution to get a new IP address to send its requests from.
- Making requests to these URLs to get HTML code
- Using locators to identify the location of data in HTML code
- Parsing the data string that contains information
- Converting the scraped data into the desired format
- Transferring the scraped data to the data storage of choice
Figure 2: 7 steps of an web scraping process
Sponsored
Bright Data offers its web scraper as a managed cloud service. Users can rely on coding or no-code interfaces to build scrapers that run on the infrastructure provided by their SaaS solution.

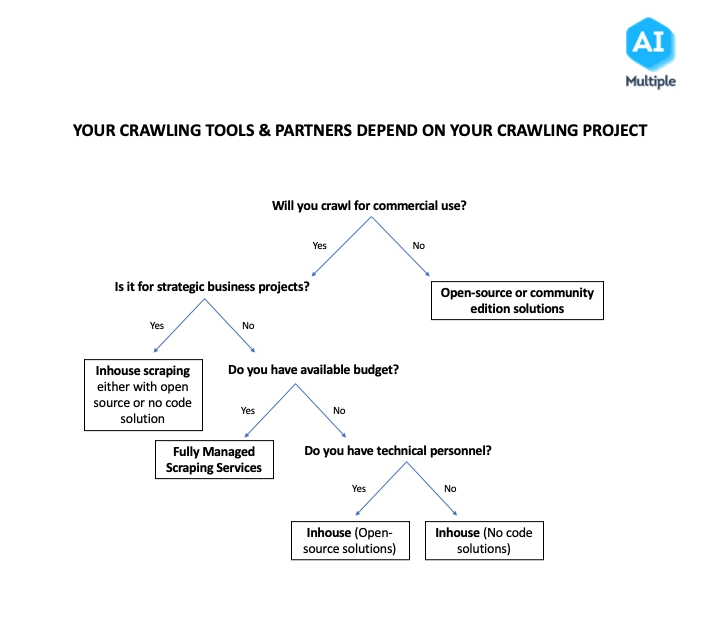
Which web crawler should you use?
The right web crawler tool or service depends on various factors, including the type of project, budget, and technical personnel availability. The right-thinking process when choosing a web crawler should be like the below:
We developed a data-driven web scraping vendor evaluation to help you selecting the right web scraper.
Figure 3: Roadmap for choosing the right web scraping tool
Top 10 web scraping applications/use cases
Data Analytics & Data Science
1. Training predictive models: Predictive models require a large volume of data to improve the accuracy of outputs. However, collecting a large volume of data is not easy for businesses with manual processes. Web crawlers help data scientists extract required data instead of doing it manually.
2. Optimizing NLP models: NLP is one of the conversational AI applications. A massive amount of data, especially data collected from the web, is necessary for optimizing NLP models. Web crawlers provide high-quality and current data for NLP model training.
Real Estate
3. Web scraping in real estate: Web scraping in real estate enables companies to extract property and consumer data. Scraped data helps real estate companies:
- analyze the property market.
- optimize their prices according to current market values and customers’ expectations.
- set targeted advertisement.
- analyze market cycles and predict the forecast sales.
Sponsored
Oxylabs’ real estate scraper API allows users to access and gather various types of real estate data, including price history, property listings, and rental rates, bypassing anti-bot measures.

Marketing & sales
4. Price scraping: Companies can leverage crawled data to improve their revenues. Web scrapers automatically extract competitors’ price data from websites. Price scraping enables businesses to:
- understand customers’ purchase behavior.
- set their prices to stay competitive by tracking competitors’ product prices online
- attract their competitors’ customers.
5. Scraping/Monitoring competitors’ product data: Web scrapers help companies extract and monitor products’ reviews, features, and stock availability from suppliers’ product pages. It enables companies to analyze their competitors, generate leads, and monitor their customers.
6. Lead generation: Lead generation helps companies improve their lead generation performances, time and resources. More prospects data is available online for B2B and B2C companies. Web scraping helps companies to collect the most up-to-date contact information of new customers to reach out to, such as social media accounts and emails.
Check out how to generate leads using Instagram search queries such as hashtags and keywords.
7. SEO monitoring: Web scraping helps content creators check primary SEO metrics, such as keywords ranking, dead links, rank on the google search engine, etc. Web crawlers collect publicly available competitor data from targeted websites, including keywords, URLs, customer reviews, etc. Web crawlers enable companies to optimize their content to attract more views.
8. Market sentiment analysis: Using web scrapers in marketing enables companies:
- analyze and track their competitors’ performance on social media
- optimize their influencer marketing activities
- track the actual performance of their ads
Human Resources
9. Improving recruitment processes: Web scrapers help recruiters automatically extract candidates’ data from recruiting websites such as LinkedIn. Recruiters can leverage the extracted data to:
- analyze and compare candidates’ qualifications.
- collect candidates’ contact information such as email addresses, and phone numbers.
- collect salary ranges and adjust their salaries accordingly,
- analyze competitors’ offerings and optimize their job offerings.
Finance & Banking
10. Credit rating: The process of evaluating the credit risk of a borrower’s creditworthiness. Credit scores are calculated for an individual, business, company, or government. Web scrapers extract data about a business’s financial status from company public resources to calculate credit rating scores.
Check out top 18 web scraping applications & use cases to learn more about web scraping use cases.
Top 7 web scraping best practices
Here you can find top 7 web scraping best practices that help you to imply web scraping:
- Use proxy servers: Many large website operators use anti-bot tools that need to be bypassed to crawl a large number of HTML pages. Using proxy servers and making requests through different IP addresses can help overcome these obstacles. If you cannot decide which proxy server type is best for you, read our ultimate guide to proxy server types.
- Use dynamic IP: Changing your IP from static to dynamic can also be useful to avoid being detected as a crawler and getting blocked.
- Make the crawling slower: You should limit the frequency of requests to the same website due to two reasons:
- It is easier to detect crawlers if they make requests faster than humans.
- A website’s server may not respond if it gets too many requests simultaneously. Scheduling crawl times to start at the websites’ off-peak hours and programming the crawler to interact with the page can also help to avoid this issue.
- Comply with GDPR: It is legal and allowed to scrape publicly available data from websites. On the other hand, under GDPR, It is illegal to scrape the personally identifiable information (PII) of an EU resident unless you have their explicit consent to do so.
- Beware of Terms & Conditions: If you are going to scrape data from a website that requires login, you need to agree on terms & conditions to sign up. Some T&C involves companies’ web scraping policies that explicitly state that you aren’t allowed to scrape any data on the website.
- Leverage machine learning: Scraping is turning into a cat & mouse game between content owners and content scrapers with both parties spending billions to overcome measures developed by the other party. We expect both parties to use machine learning to build more advanced systems.
- Consider open source web scraping platforms: Open source is playing a larger role in software development, this area is no different. The popularity of Python is high. We expect open source web scraping libraries such as Selenium, Puppeteer, and Beautiful Soup that work on Python to shape the web crawling processes in the near future.
What are the challenges of web scraping?
- Complex website structures: Most web pages are based on HTML, and web page structures are widely divergent. Therefore when you need to scrape multiple websites, you need to build one scraper for each website.
- Scraper maintenance can be costly: Websites change the design of the page all the time. If the location of data that is intended to be scrapped changes, crawlers are required to be programmed again.
- Anti-scraping tools used by websites: Anti-scraping tools enable web developers to manipulate content shown to bots and humans and also restrict bots from scraping the website. Some anti-scraping methods are IP blocking, CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), and honeypot traps.
- Login requirement: Some information you want to extract from the web may require you to log in first. So when the website requires login, the scraper needs to make sure to save cookies that have been sent with the requests, so the website recognizes the crawler is the same person who logged in earlier.
- Slow/ unstable load speed: When websites load content slowly or fail to respond, refreshing the page may help, yet, the scraper may not know how to deal with such a situation.
To learn more about web scraping challenges, check out web scraping: challenges & best practices
Web scraping vs API
Web scraping tools extract all the content, such as text, images or videos from a publicly available web page and store it as a data file. It is similar to taking a picture of a website and analyzing different elements of the picture. The main actor in this case is the web scraper.
API builds an automated data pipeline between a website and the requester targeting a specific part of the website content. Data can be pulled on an automated schedule or manually on demand. It is similar to a subscription where you automatically get an updated content on regular basis. Both the website and the receiver take active role in APIs.
The main difference between APIs and web scraping is the availability of readily available tools. APIs will often require the data requester to build a custom application for the specific data query.
On the other hand, there are many external web scraping tools that require no coding. Some of them are free browser extensions that scrape the web page you are at or paid service providers that apply readily available templates to scrape data from your target websites. Let’s go into more detail.
1. Solution availability
- API technology should be provided by the website you want the data from. If they don’t support an API, then this is not an option in the first place. You can check out the specific website you are interested in or API repositories to learn about the availability of a specific website, whether it is free or paid after a certain limit. 1
- Web scraping does not need to be technically supported by the website. A common rule of thumb is, if you find a website through a search engine, it is possible to scrape that website. However, the website should allow their content to be scraped. This is done by the website specifying what can or can not be scraped on their robot.txt file where the data owner either gives or denies permission to data scraping.
2. Stability
- One strength of APIs is that, since it is an authorized access to data, the requester does not need to worry about being detected as a malicious actor and can expect support from the websites in case the API fails unexpectedly.
- Web scrapers can be blocked by the websites because they bring additional traffic to the website.
3. Access to data
- Even if an API is available, not all the data may be available to the API. The scope and the granularity of the data you can pull will be specified in the API documentation by the website. For example, LinkedIn provides a limited API for pulling only the basic information of people’s profiles and you need to justify your use case if you want to access the full profile information.
- Technically, all the content on a publicly available web page can be scraped. However, the scraper should respect the data limitations that the website specified in their terms and conditions.
4. Technical difficulty
- APIs will need you to build a custom code including your access keys and specifying the data you need. Websites will often provide an API guide but even this will require a basic understanding of a data query code, such as using a code notebook to run the query, understanding API response codes or specifying parameters to access the needed data.
- Building a web scraper from scratch also requires coding skills but compared to API, there are more readily available tools that you can scrape the data without any coding. This is often because websites often have similar foundational structures that web scrapers can recognize, because websites need to be scraped by search engines to get ranked in searches. This makes web scraping a reapplied practice for similar websites or the same website across multiple requesters.
5. Cost
- APIs can be free or paid depending on how the data the website offers can be used commercially. If it is the API for a service you already pay for, such as an analytics service, it is likely that the API will be free of charge. However, even free APIs may charge beyond a certain data limitation in order to control the volume of requests.
- Web scraping can be free if you built a solution in-house or leverage an open source solution, such as a browser extension. However, if you leverage an external no-code web scraper, you will have a variable cost or sign up for a subscription plan. Many web scraping solutions offer a free trial or dataset sample for businesses to assess the ROI of such an investment.
6. Data Cleaning
- API query outputs can be very complicated and you will often need to parse the data that you need. However, if the API supports more granularity, you may be able to target the specific data point you need and minimize further data processing.
- Web scraping provides the entire content on a web page. If you need only a specific part of the web page, such as the price of a product page, then you will need to apply a rigorous data parsing to filter the data you need. It is an exhaustive task to do in-house, but external web scrapers often provide the data processed and readily available for analysis.
7. Legal Implications
- APIs are provided by the website you need data from. Therefore, as long as you follow their API guideline and do not share your API access with any other party, pulling data via API is fully legal.
- Web scraping is legal as long as the scraper follows the website’s terms and conditions specified in their robot.txt file. If businesses leverage an in-house soltuion, they should make sure checking this step or leverage an external service provider to benefit from their experience. Check out our detailed post about the legal and ethical aspects of web scraping.
Recommendation on when to use which solution
Use APIs
- If you need data from a service that you work together with and they support API for the data you need, then you may be able to get technical support to build an API data pipeline.
- If you need to get data from a page that is not publicly available, such as your analytics data for a paid analytics solution that is available only to you, then API will often be the only solution.
Use web scrapers
- If you need data from a popular website such as Amazon or Twitter, which you may save time by using already available web scraper solutions instead of getting API access.
- If you are not sure about the business value of the data, you may get a sample via free web scraping tools or free trial with web scraping services and evaluate whether you should invest in API or web scraper in the long term.
Web Scraping vs screen scraping
Screen scraping and web scraping are terms often used interchangeably, but there are slight differences between them. Web scraping primarily involves extracting data directly from web pages using HTML and structured formats, while screen scraping focuses on capturing the content displayed on the screen.
Many modern web scraping tools are capable of processing visual data, which can blur the line between web scraping and screen scraping. Screen scraping involves capturing data as it appears to the user on the screen, rather than accessing the underlying code or data structures. Advanced web scraping tools can include taking page screenshots, interacting with user interface elements, and extracting visually displayed data.
Common methods used for automated screen scraping
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition) screen scraping: Extracts data from visual sources, desktop applications, and Citrix applications. OCR uses different OCR engines, such as Google OCR and Microsoft OCR, to retrieve the screen coordinates of each word from an image but may be more resource-demanding.
- FullText: Extracts hidden (underlying source code) or visible text data from a specified user interface (UI) element or scanned documents.
- Native screen scraping: Unlike FullText and OCR, this method can only extract data from an application’s user interface. Users can extract the screen coordinates of each word displayed on a screen.
Conclusion
Web scraping is the most common method for gathering data from web sources, enabling insights for market research and competitive analysis. However, the process must respect ethical standards and website terms.
For more on web scraping
- Web Scraping tools: Data-driven Benchmarking
- Top 7 Python Web Scraping Libraries & Tools
- The Ultimate Guide to Efficient Large-Scale Web Scraping
If you still have questions about the web scraping landscape, feel free to check out the sortable list of web scraping vendors.
You can also contact us:
This article was originally written by former AIMultiple industry analyst Izgi Arda Ozsubasi and reviewed by Cem Dilmegani

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.