RPA (robotic process automation) and generative AI are two popular tools in the digital transformation landscape:
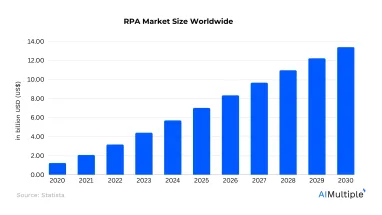
- RPA’s global market is expected to grow to more than $13B by 2030.1
- Generative AI is expected to add $2.6T annually to 63 use cases that McKinsey analyzed.2
These two tools are widely used because of their wide-ranging capabilities. RPA’s handling of repetitive tasks & generative AI’s automation through the creation of original content creates an opportunity for businesses to reshape their companies’ operational efficiency.
We will focus on:
- The characteristics of RPA and generative AI
- Their differences
- Top 15 joint use cases
Top 15 use cases for RPA and generative AI across various industries:
| Industry / Field | Generative AI Use Cases | RPA Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Financial services | Generate potential financial scenarios, improve fraud detection, provide personalized financial advice | Data entry, compliance reporting, due diligence, loan processing |
| Customer service | Create personalized responses to customer queries | Collecting customer information, updating databases, scheduling follow-ups |
| Marketing & advertising | Create personalized content (custom-tailored ads, personalized product recommendations), create tags or headlines | Collecting customer data, scheduling marketing campaigns |
| Product development & designs | Create new product designs or features based on existing data | Collection of customer data and managing their feedback, updating project management tools |
| Data analytics & management | Generate synthetic data, fill in missing values, create data for testing purposes | Gather and pre-process data |
| Healthcare | Create synthetic patient data for research, generate possible patient outcomes | Scheduling appointments, maintaining patient records, processing insurance claims |
| Human resources | Creating personalized training material, predicting employee performance, simulating responses to various HR policies | Granting PTOs, scheduling interviews, gathering employee data, administrating the onboarding process |
| Retail & e-commerce | Personalized product recommendations, virtual shopping experiences, dynamic pricing models | Inventory management, order processing, CRM management |
| Supply chain management | Create predictive models for demand forecasting, optimize routes for logistics, provide insights about disruptions by simulating scenarios | Track shipments, update inventory data, monitor freight conditions, generate invoices |
| Real estate | Create virtual property tours, predict property values, create architectural designs | Property data collection, updating listings, handling lease agreements |
| Cybersecurity | Simulate attack scenarios, generate synthetic datasets for training security models, predict future security leaks | Monitoring network traffic, identifying suspicious activities, updating security patches |
| Education | Create practice questions, develop personalized learning materials, give real-time feedback | Student registration, financial aid calculation, class scheduling, grade reporting |
| Legal services | Create legal briefs, simulate legal scenarios and mock trials, provide legal advice | Document review, contract analysis, legal billing |
| Agriculture | Create predictive models for crop yield, optimize farm layout, simulate the effects of dry seasons or different farming techniques | Data collection from crops, irrigation, manure addition |
| Manufacturing | Design product prototypes, optimize production processes, create stress testing scenarios | Inventory tracking, quality control, order processing |
How can generative AI speed up RPA developers?
Generative AI can speed up RPA bots’ programming by helping them overcome the “blank canvas” problem. Similar to writers facing a “writer’s block,” citizen developers can suffer from the “blank canvas” problem– not knowing where to start designing a program from scratch, especially one dealing with complex logic or handling error requirements.
With generative AI, the user can provide a high-level description of what they want to do, and the AI model translating the demands into functional codes. Python, specifically, can be essential for delivering AI and automation because of its being open-sourced and widely available.
Also, agentic process automation is a new way to integrate generative AI in RPA. AI agents can use complex data, such as unstructured textual data, and automate mundane tasks that regular RPA is not capable of. You can read agentic process automation to have more information.
How can generative AI be used in RPA bots?
1. Financial services
RPA in banking and finance can automate data entry, compliance reporting, due diligence, or loan processing.
Generative AI, meanwhile, can generate potential financial scenarios for asset management and risk modeling, improve fraud detection, or provide personalized financial advice to customers.
The automation of the accounts payable process is an example where both technologies are used. The accounts payable has a complex content that may require both the automation of repetitive tasks in areas such as document management and the use of AI in areas such as invoice and line item capture.
There are examples where customers who purchased ERP for the automation of these processes have improved automation with plug-ins that include RPA generative AI solutions:
- Dynamics 365 in Accounts Payable Automation
- Blackbaud Accounts Payable (AP) Automation
- Sage Accounts Payable (AP) Automation
- NetSuite AP Automation
Another example is Deutsche Bank’s use of AI and RPA to automate its Adverse Media Screening, lowering the number of false positives and improving compliance.3
Explore 10+ use cases of generative AI in finance.
2. Customer service
RPA bots can create automated workflows in customer service for:
- Collecting customer information
- Updating databases
- Scheduling follow-ups
Simultaneously, customer service centers can use Generative AI models in their workflows to create personalized responses to customer queries, based on each customer’s history and situational context.
The combination will allow a highly personalized, efficient, and scalable customer service operation.
3. Marketing & advertising
RPA can automate some of the marketing operations, like collecting customer data or scheduling marketing campaigns.
Generative artificial intelligence tools can create personalized content, like custom-tailored ads or personalized product recommendations based on the collected data. And copywriters can use generative writing tools, like ChatGPT, to create tags or headlines.
In Brazil, for instance, Burger King and McDonald’s ran advertising campaigns, where ChatGPT wrote the slogans.
Learn more: Generative AI for marketing
4. Product development & designs
RPA can create automated workflows to handle:
- The collection of customer data and managing their feedback
- Updating project management tools
Generative AI, on the other hand, could create new product designs or features based on existing data, enabling companies to prototype and innovate rapidly.
5. Data analytics & management
RPA can gather and pre-process data, while generative AI could generate synthetic data to augment existing datasets, fill in the missing values, or create data for testing purposes.
This conjunction can automate the entire process of data analytics and data management, leading to reliable data analytics outcomes.
6. Healthcare
RPA in healthcare can automate administrative tasks, like scheduling appointments, maintaining patient records, or processing insurance claims.
An intelligent automation technology like generative AI can create synthetic patient data for research without violating privacy laws, as well as generate possible patient outcomes based on their health data.
The health clinic Phoenix Children’s4 , for example, used RPA and generative AI for complex tasks like predicting patient malnutrition, reducing appointment no-shows, and projecting emergency room visits based on seasonal data.
Learn more about how generative AI is being used in healthcare systems.
7. Human resources
RPA can automate HR tasks like granting PTOs, scheduling interviews, gathering employee data, or administrating the onboarding process.
Generative AI can assist HR staff by:
- Creating personalized training material
- Predicting employee performance based on historical data
- Simulating responses to various HR policies
8. Retail & e-commerce
RPA can automate tasks related to inventory management, order processing, or CRM management.
In parallel, generative AI can be used to create:
- Personalized product recommendations
- Virtual shopping experiences
- Dynamic pricing models based on real-time market conditions
For example, Chinese researchers used5 a PPGAN (Personalized Pointer Generative Adversarial Network) model to create short product titles. Their model outperformed conventional models by a click-through rate of 5.18% compared to 3.53%.
9. Supply chain management
RPA can create an automation platform where users can track shipments, update inventory data, monitor freight conditions, and generate invoices.
Incorporating generative AI in the supply chain can help create predictive models for demand forecasting, optimize routes for logistics, or provide valuable insights about disruptions by simulating scenarios.
RPA and generative AI in supply chain management can minimize supply delays and optimize responses to unforeseen circumstances.
10. Real estate
RPA can be used in real estate to automate property data collection, update listings, or handle lease agreements.
Generative AI can create virtual property tours, predict property values, or even create architectural designs with respect to cost, environmental, and spatial criteria.
For example, users6 have been able to create different designs and furnishing layouts of bedrooms using Stable Diffusion.
11. Cybersecurity
Tasks like monitoring network traffic, identifying suspicious activities, or updating security patches can be automated with RPA.
Generative AI can, at the same time, simulate different attack scenarios, generate synthetic datasets for training security models, or predict future security leaks based on patterns.
12. Education
The use of RPA in education could entail student registration, financial aid calculation, class scheduling, or grade reporting.
Generative AI can, by extension, create practice questions, develop personalized learning materials, give real-time feedback, and more.
Explore how generative AI is transforming the education sector in more detail.
13. Legal services
Robotic process automation can automate document review, contract analysis, or legal billing.
Generative AI can create legal briefs, simulate different legal scenarios and mock trials for training, or even provide legal advice based on similar previous cases.
Learn more about how generative AI is being used in the legal field.
14. Agriculture
RPA in agriculture can automate tasks like data collection from crops, irrigation, or manure addition.
Generative AI can improve forecasting and productivity by creating predictive models for crop yield, optimizing farm layouts for efficient planting, or simulating the effects of dry seasons or different farming techniques on supply.
15. Manufacturing
RPA in manufacturing could include inventory tracking, quality control, or order processing. Generative AI, on the other hand, can design product prototypes, optimize production processes, or create stress-testing scenarios.
Explore the top use cases of AI in manufacturing.
FAQ
What is RPA (robotic process automation)?
RPA focuses on relieving workers from routine tasks and helps organizations streamline existing business processes and improve overall operational efficiency. RPA’s programming can be code-based, no-code, or hybrid, with each approach having its own characteristics.
It is also frequently integrated with intelligent process automation to extend its automation capabilities. RPA is flexible enough to automate more than 100 business tasks, including, but not limited to data extraction, transaction processing, application integration, and document processing tasks.
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is a part of artificial intelligence that creates new content. It uses algorithms like generative adversarial networks (GANs) and LLMs (large language models) to generate data that’s similar to the input data it’s been trained on. By effectively training machine learning models on large, diverse datasets, generative AI can produce novel outputs, such as realistic text, images, or even molecular structures.
Generative AI has been used in content creation to make images and music, while it’s recently made strides in areas like drug discovery and design engineering. Additionally, generative AI and RPA often converge under the umbrella of intelligent automation solutions, enabling businesses to automate complex workflows that require both creative outputs and structured processes.
Explore the use cases of generative AI in more detail.
Generative AI faces several challenges such as necessity to build an AI inventory, AI bias, and other generative AI risks. To mitigate these challenges and ensure AI compliance, we recommend businesses adopt ethical AI tools, such as:
-AI governance tools
-Responsible AI platforms
External Links
- 1. Robotic process automation (RPA) market 2030| Statista. Statista
- 2. The Economic Potential of AI
- 3. Robotic process automation in banking industry: a case study on Deutsche Bank | Journal of Banking and Financial Technology . Springer Singapore
- 4. AI Elevates Patient Care at Phoenix Children’s
- 5. Selling Products by Machine: a User-Sensitive Adversarial Training method for Short Title Generation in Mobile E-Commerce
- 6. Exploring the possibilities of Generative AI for Real Estate: use cases at Casavo. | by Alberto Bellini | Casavo | Medium. Casavo

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.