Companies use process improvement techniques to identify bottlenecks and improve them in a process flow based on their process scope and objectives. Yet, these techniques have been losing popularity with the emergence of process intelligence tools.
Explore the most common process improvement methodologies and tools with their popularity trends to choose the best fit for your firm:
| Process Improvement Methodology | Type | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| Agile | Methodology | Complex projects with frequent changes, especially in software development. |
| Kaizen | Methodology | Encouraging small, continuous improvements involving all employees. |
| Lean Manufacturing | Methodology | Enhancing efficiency by reducing waste and streamlining business processes. |
| Six Sigma | Methodology | Improving product and process quality by reducing defects and variability. |
| Total Quality Management (TQM) | Methodology | Embedding quality across processes and products with organization-wide involvement. |
| Theory of Constraints | Methodology | Identifying and addressing process bottlenecks to enhance profitability and efficiency. |
| 5S Method | Methodology | Organizing physical workspaces for enhanced efficiency, safety, and quality. |
| Kanban | Visualization technique | Improving flow, reducing cycle time, and ensuring continuous delivery with visual management. |
| Process Mapping | Visualization technique | Visualizing workflows to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. |
| SIPOC Analysis | Visualization technique | Mapping relationships between process components in complex or cross-functional projects. |
| Value Stream Mapping (VSM) | Visualization technique | Streamlining processes and reducing waste to improve customer value in various industries. |
| PDCA | Framework | Systematically implementing continuous improvements in processes and products. |
| People, Process, Technology (PPT) | Framework | Aligning workforce, optimizing processes, and leveraging technology in transformations. |
| Just-in-Time (JIT) | Strategy | Reducing inventory costs and waste by producing goods on-demand. |
* We categorize process visualization tools, techniques, and improvement strategies separately under relevant methods and technologies. Note that some blogs and vendors mistakenly classify tools and strategies as process improvement methodologies.
Agile
Agile is a software development methodology designed for processes requiring collaboration. It follows an iterative and incremental approach, where employees from different teams work together. The method includes incremental steps called “sprints” and “scrum” meetings, allowing teammates to give feedback. These sprints ensure flexibility, focusing on small improvements and allowing for continuous process enhancement with each iteration.
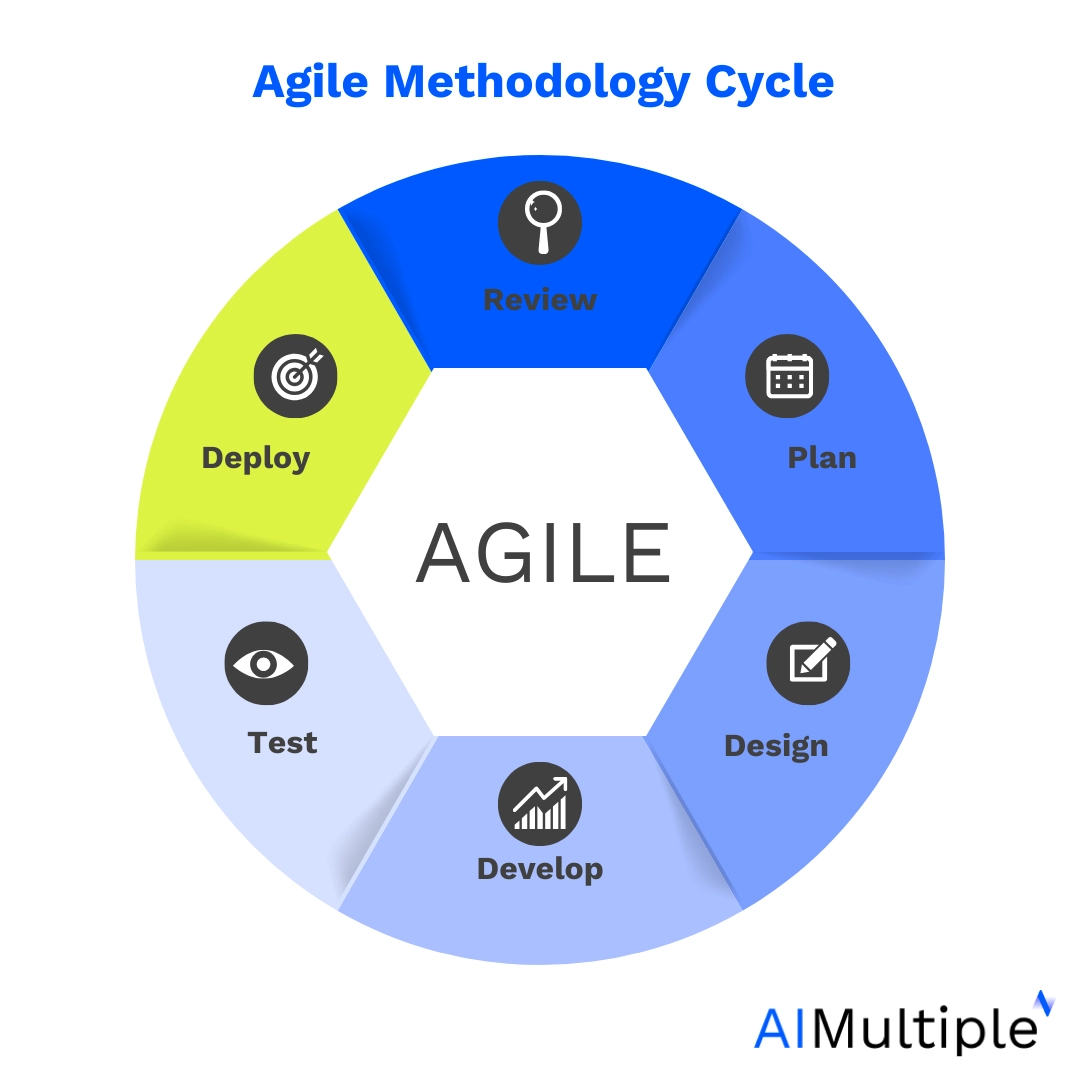
Similar agile approaches, including iterative changes and collaboration, are also becoming more popular in other areas such as manufacturing and construction. Rather than taking fundamental steps for updating processes, this methodology responds to the changes while taking incremental steps.
Kaizen
Kaizen is a philosophy which means “change for the better” or “continuous improvement” in Japanese. It refers to continuously improving business processes by including all the CEO and assembly line workers.
Kaizen emphasizes small, consistent changes to enhance productivity and adaptability. These changes do not mean that improvements are made slowly; but minor changes may significantly impact the future.
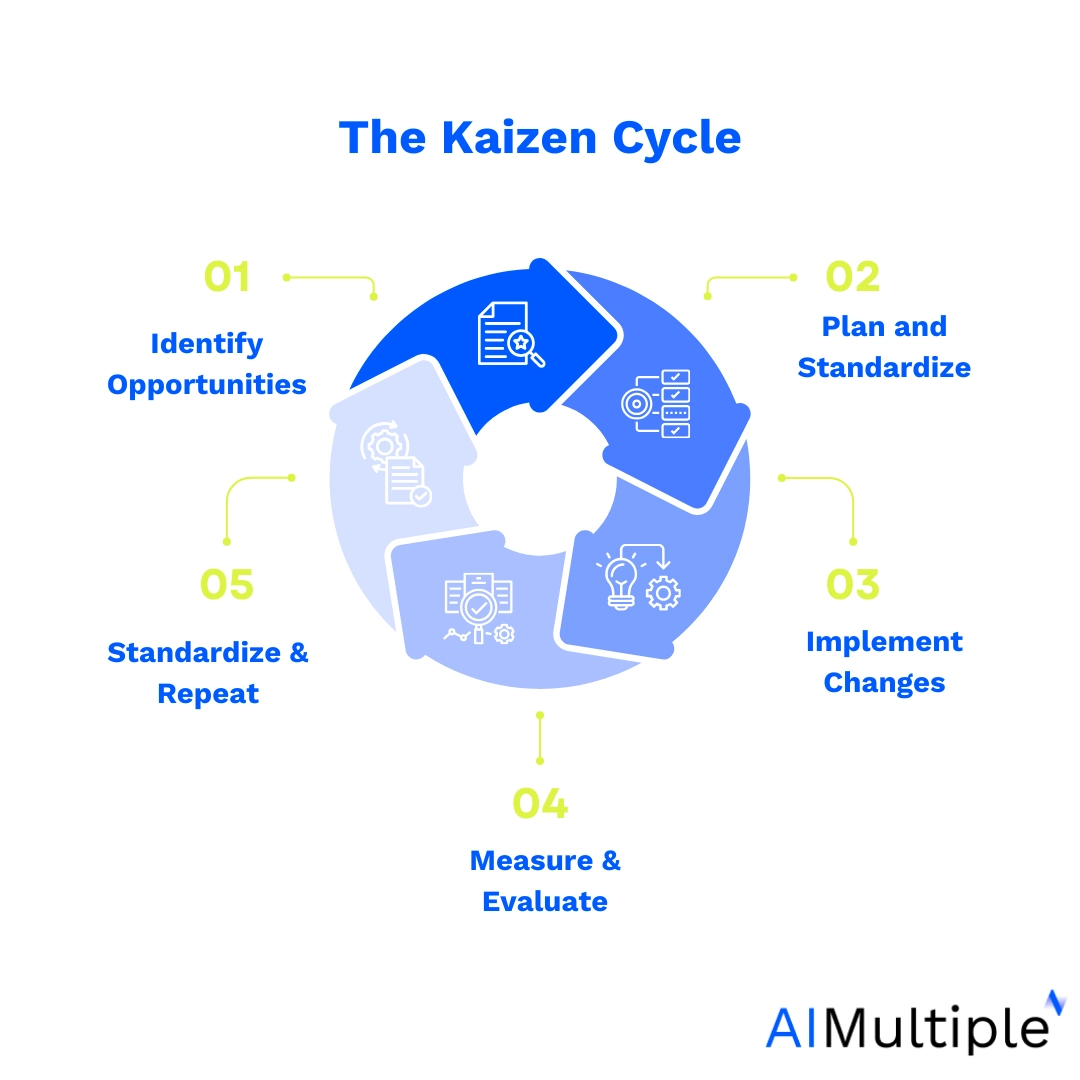
The method helps users identify and avoid three types of waste:
- Muda (wastefulness): Non-value-adding activities.
- Mura (unevenness): Inefficiencies due to overproduction or imbalanced workloads.
- Muri (overburden): Excessive strain on resources, leading to wear or burnout.
By applying this philosophy, businesses can achieve a more efficient work environment and create a team atmosphere. As a result, employee satisfaction improves as jobs become more fulfilling and less tiring.
Lean
Lean methodology, also known as Lean production or just-in-time production, reduces wasted resources that do not add any customer value while improving processes. The main goal of this approach is to create more customer value with fewer resources. Businesses need to identify customer value first and then eliminate waste until they reach “perfect” processes to implement this strategy.
The Five Principles of Lean
Lean is based on principles from Toyota’s manufacturing system, which are listed as:
- Identify value: Define what the customer perceives as valuable.
- Value stream mapping: Analyze the steps involved in delivering value.
- Create flow: Ensure smooth transitions between process steps.
- Establish pull: Produce only what is needed when it is needed.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly refine processes to maintain efficiency and adaptability.
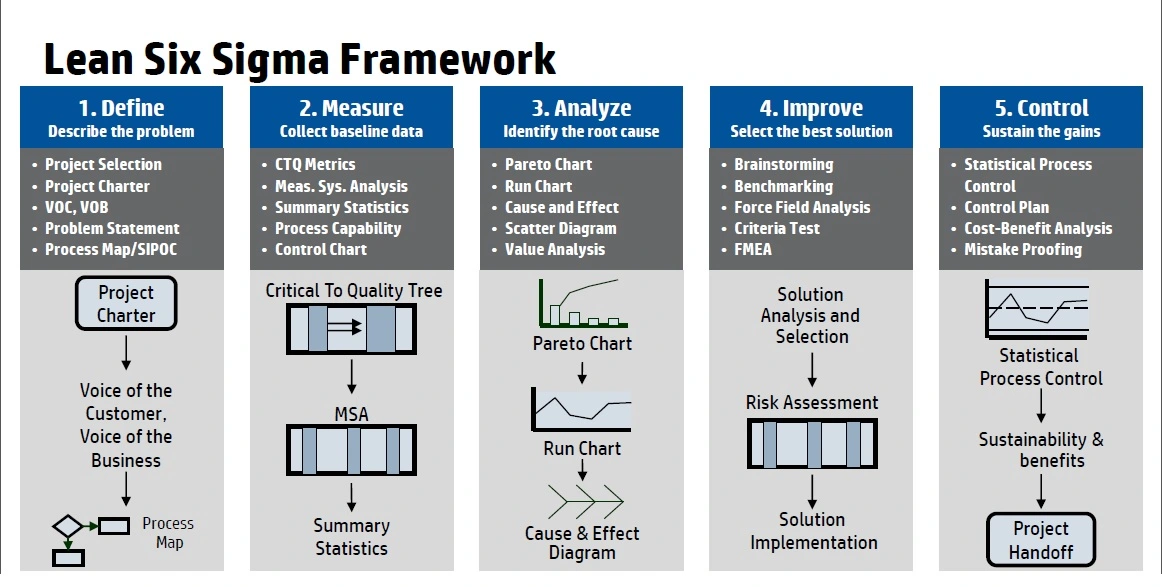
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a statistical methodology for process improvement, focused on reducing variations and defects in products. Developed in 1986 by Motorola engineer Bill Smith, it uses data-driven benchmarks to evaluate and optimize processes. This approach aims to keep the acceptable lower-upper limits in the six-sigma level so that the probability of having errors in a process will be 3.4 per million opportunities.
Primarily applied in manufacturing, Six Sigma enhances consistency and reduces defects, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction. The methodology employs two primary frameworks:
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) for refining existing processes.
- DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) for designing new processes.
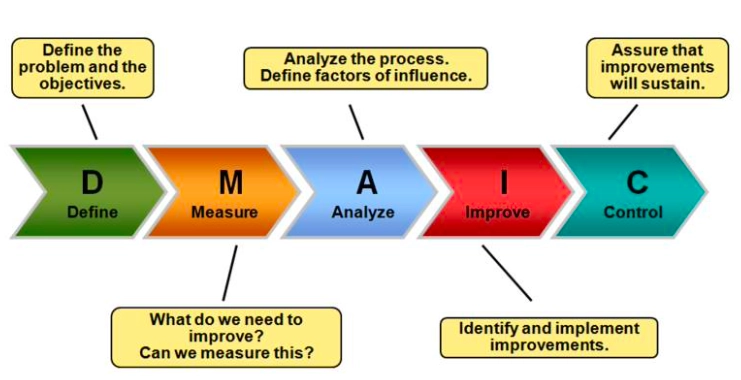
DMAIC Process
DMAIC focuses on improving existing processes through the following stages:
- Define opportunities for improvement.
- Measure current performance.
- Analyze root causes of defects.
- Improve processes by addressing identified causes.
- Control the improved processes and monitor future performance.
Current status
Successful businesses have used six Sigma like General Electric since the mid-1980s. Though it is less popular due to the popularity of new emerging approaches and companies’ focus on innovation, it is still a powerful method for process standardization today.
To learn more, feel free to read our in-depth Six Sigma guide.
Lean Six Sigma
Businesses adopted the lean approach to remove waste in processes to use their resources efficiently. Then, Six Sigma was created to reduce process variation. Lean and Six sigma work together successfully in a dynamic business environment.
Lean Six Sigma combines the Lean approach and Six Sigma methodology for businesses. This technique aims to eliminate defects in the Lean and reduce deviations as in Six Sigma for process improvement. It allows establishing efficient systems with high quality and efficiency while it increases bottom-line earnings and helps to achieve company goals.
Total Quality Management
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a customer- centric process improvement approach that continuously detects and eliminates production errors. It is widely used in facilitating supply chain processes and improving customer experience, and ensuring that employees are trained well enough.
TQM emphasizes data-driven decision-making and collaboration across all organizational levels. All departments and production (like sales, marketing, finance) are accountable for improving processes. Management in TQM emphasizes that executives are obligated to actively manage quality through funding, training, staffing, and goal setting.
Key features of TQM include:
- Customer focus: Every improvement aims to enhance customer experience.
- Team involvement: TQM engages all teams, including non-production departments like sales and marketing, to achieve better outcomes for the customer.
- Continuous improvement: Iterative, incremental changes help adapt to evolving business conditions.
- Data-driven decisions: Performance metrics guide efforts to identify inefficiencies and prioritize improvement initiatives.
- Process-oriented approach: While Six Sigma focuses on defect reduction, TQM targets inefficiencies to optimize overall processes.
Current status
TQM was a popular approach between the late 1980s and early 1990s, while Lean and Six Sigma approaches are more popular today. TQM is similar to Six Sigma; TQM focuses on improving internal guidelines and process standards to reduce errors, while Six Sigma concentrates on reducing defects.
Theory of Constraints
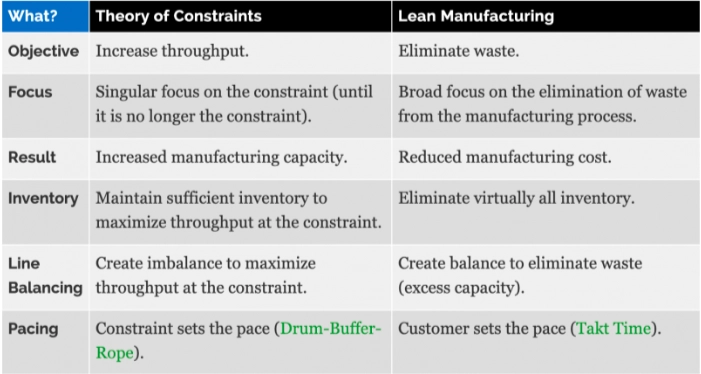
The Theory of Constraints states that there is always at least one constraint, and these constraints always prevent businesses from achieving more of their goals. Thus, this approach focuses on identifying and reducing the obstacles to improving processes.
The Theory of Constraints is another approach that aims to improve process efficiency. However, while the Theory of Constraints provides increased manufacturing capacity by detecting and eliminating bottlenecks, the Lean approach mostly reduces costs by targeting to eliminate defects in processes.
In the below table, you can also see the main differences between these two approaches:
5S method
The 5S method is a systematic approach to workplace organization and standardization, developed by the Toyota Motor Corporation to enhance productivity, safety, and quality. This method, originally tailored for manufacturing, is versatile and can enhance productivity and organization in diverse environments, including offices and warehouses.
The five principles of 5S
It is based on five Japanese principles:
- Sort (Seiri): Remove unnecessary items from the workspace to focus only on what is essential.
- Set in Order (Seiton): Arrange tools, equipment, and materials in a logical, accessible manner to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
- Shine (Seiso): Keep the workplace clean and inspect regularly to ensure everything is in working condition.
- Standardize (Seiketsu): Develop standardized practices to maintain organization and cleanliness.
- Sustain (Shitsuke): Foster discipline to follow the 5S practices consistently and encourage continuous improvement.

What are the most popular process improvement approaches now?
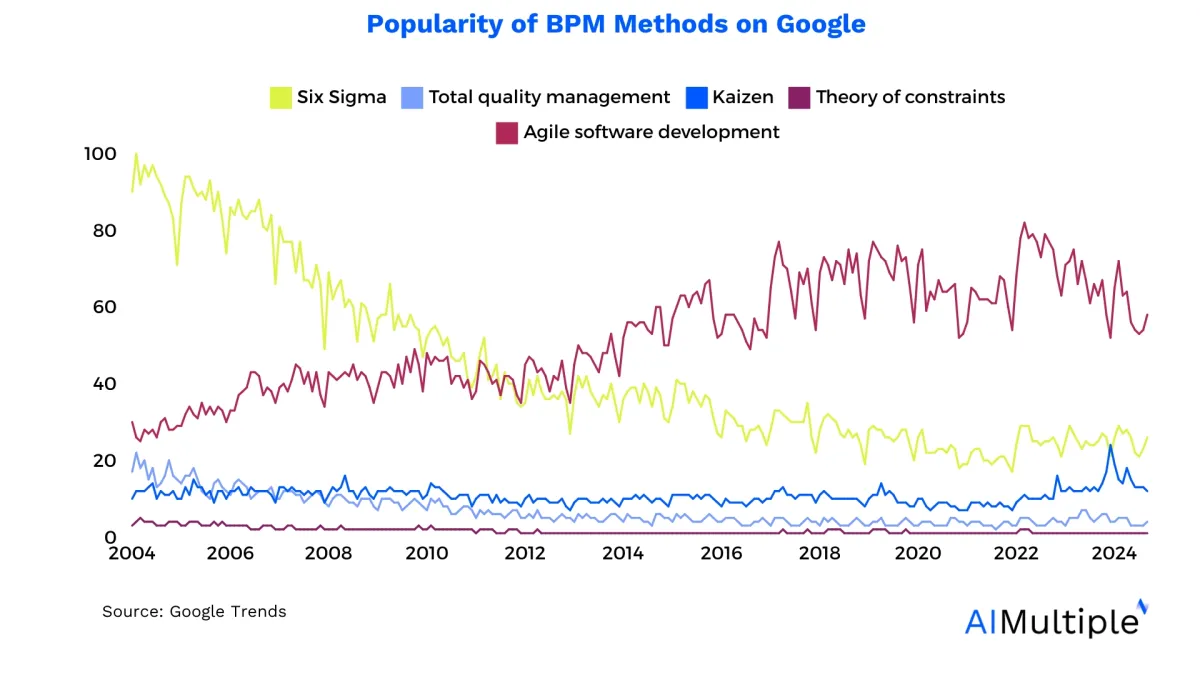
Most process improvement techniques have had a decreasing trend since the 2000s. We observe that Six Sigma has been a much more popular approach than other types of process improvement technique until the 2010s. Although it is a common process improvement strategy today, we see a significant fall in its trend.
On the other hand, agile development is an exception to the decreasing trend of other process improvement methodologies. This process improvement strategy has been increasing in popularity since the 2000s, and its popularity will seemingly continue to rise for the next few years.
Today, agile methodology stands out as the most popular process improvement method, and Six Sigma comes second, despite its decreasing trend. We observe that other methods have a slightly decreasing trend with similar popularity levels. We haven’t included the lean approach in this figure, as lean’s different popular meanings affect its trend-line.
These findings match with the latest BPM statistics:
- BPM projects with these techniques decreased from 21% to 12% over the last ten years, While automated process analysis and design increased to 28% and automation to 33% for the same year.
- 62% of businesses utilize one or two process management software to manage their tasks, and 70% have one software to model their processes.
Other process improvement frameworks and tools
Process visualisation tools and techniques SIPOC Analysis
Process visualization helps businesses visualise their workflows and processes to understand them better, identify inefficiencies and implement improvement strategies or methodologies including automation. Some well-known process visualisation tools and techniques include:
SIPOC
SIPOC is a high-level tool to visualize and improve processes by focusing on five components: Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. It can be used during the initial stages of process improvement to identify inefficiencies and streamline workflows.
Its purposes include:
- Providing a comprehensive understanding of workflows.
- Aligning stakeholders by identifying inputs, outputs, and connections.
- Explaining for cross-functional or complex processes in various industries.
Process Mapping
Process mapping is a visualization technique that can document and analyze workflows. It depicts business processes through flowcharts and models. It focuses on roles, goals, and workflows for productivity gains.
Process mapping can help:
- Collaboration across departments and stakeholders
- Understand end-to-end workflows
- Identify inefficiencies for improvement
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
It refers to a lean-management technique to visualize the steps in delivering a product or service, focusing on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. It maps the flow of materials and information in processes.
VSM helps
- Enhance customer value by highlighting waste and inefficiencies
- Aligns stakeholders by providing a visual representation of delivery processes.
Kanban
It is a visual workflow tool that manages and improves process flow, inspired by Lean principles. It focuses on enhancing process visualization, improving flow, and reducing delays.
Kanban operates by:
- Using a visual board with columns (e.g., “To-Do,” “In Progress,” “Completed”).
- Tracking progress and eliminates bottlenecks.
- Encouraging continuous improvement
- Shorting cycle times.
Process improvement frameworks
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)
The PDCA cycle, developed by Walter Shewhart and refined by W. Edwards Deming, is an iterative framework for problem-solving and process improvement. It uses the scientific method to implement and test changes in small, manageable steps.
The Four Steps of PDCA
- Plan: Identify a problem and create an actionable plan.
- Do: Implement the plan on a small scale.
- Check: Evaluate the results of the implementation.
- Act: Decide whether to expand, refine, or abandon the change based on outcomes.
The cycle is repeated until desired results are achieved, fostering continuous refinement.
5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys analysis is a technique for identifying the root cause of a problem by asking “Why?” repeatedly—typically five times. This approach targets systemic issues in processes rather than human error.
Example
- Problem: Increased customer complaints about damaged products.
- Why? Packaging was insufficient.
- Why? Packaging tests were limited.
- Why? Testing standards were outdated.
- Why? Standards were based on older product requirements.
- Why? New product testing protocols were not established.
The root cause, in this case, is the absence of stress-testing in the product launch template. Solutions involve addressing the systemic gap and updating procedures. By engaging stakeholders in this process, teams can co-develop practical solutions to enhance production outcomes.
Process improvement technologies
Recent technological developments affect the loss in popularity since more businesses adopt process improvement technologies, such as process mining and RPA to discover and improve their processes.
Process intelligence
Process intelligence automates process simulation, modeling, and analysis. These tools include:
- Process intelligence software
- Process mining
- Task mining
- Digital twin of an organisation (DTO)
- Process modelling tools
- Automated Process Discovery Tools
Process automation
Process automation includes technologies and solutions that can automate the processes, tasks and workflows to improve efficiency and reduce human errors.
- Business process automation software
- RPA Tools
- Workflow management software
- Business process management software
- Low-code/No-code development platform
- Onboarding software
Business process management vs Process improvement
Definition
- Business process management (BPM) is a holistic management approach that focuses on aligning an organization’s business processes with customer demands and achieving operational efficiency. It is a continuous practice aimed at optimizing all existing processes across the organization.
- Process improvement is a systematic approach aimed at improving specific processes by eliminating process inefficiencies and improving quality, often in targeted projects.
Scope
- BPM covers the entire organization’s business processes, ensuring continuous process improvement. It’s ongoing and aims for long-term optimization of complex processes.
- Process improvement is more project-based and focuses on specific process improvement project within current processes, such as manufacturing processes to streamline workflows, improve productivity and reduce inventory costs.
Methodologies
- BPM uses various tools, including process modeling, workflow automation, and value stream mapping to optimize complex processes and ensure ongoing enhancements.
- Process improvement applies methodologies like Six Sigma, Lean manufacturing, and Kaizen as well as process intelligence tools to implement process improvement strategies and tackle process inefficiencies through the specific process improvement initiative.
Tools and techniques
- BPM leverages software for performance monitoring, process mapping, and standardizing processes.
- Process improvement uses root cause analysis, the PDCA cycle, and the DMAIC process to identify and implement solutions for improvement opportunities in business processes.
FAQs
FAQ
What are the benefits of process improvement?
Business process improvement methodologies help organizations:
1. Identify problems in their existing processes and implement changes that boost efficiency.
2. By eliminating waste and optimizing workflows, companies can achieve quality improvement and reduce inventory costs.
3. Techniques like value stream mapping improve resource use and productivity.
4. Business process improvement encourages a continual improvement mindset, fostering better outcomes for the customer service team and increased customer satisfaction.
This leads to new processes, improved profitability, and greater success metrics. Ultimately, continuous data-driven approaches lead to sustained operational excellence.
Further Reading
If you want to discover more on process improvement case studies and how AI transforms process improvement, read our in-depth articles:
- 4 Technologies that Accelerate Process improvement
- 55 Process Improvement Case Studies & Project Results
If you have questions about how process improvement methodology can help your business, feel free to ask us:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.