Though data privacy legislation such as GDPR in the EU and CCPA in California are meant to prevent privacy breaches, consumer’s privacy is frequently invaded by hackers, companies and governments.
Data leakages increase as businesses share consumers’ data with third-party companies in order to increase network visibility. Privacy enhancing technologies (PETs) allow businesses to leverage the increasing amount of data while ensuring personal or sensitive information stays private. Thus, improve corporate reputation and compliance.
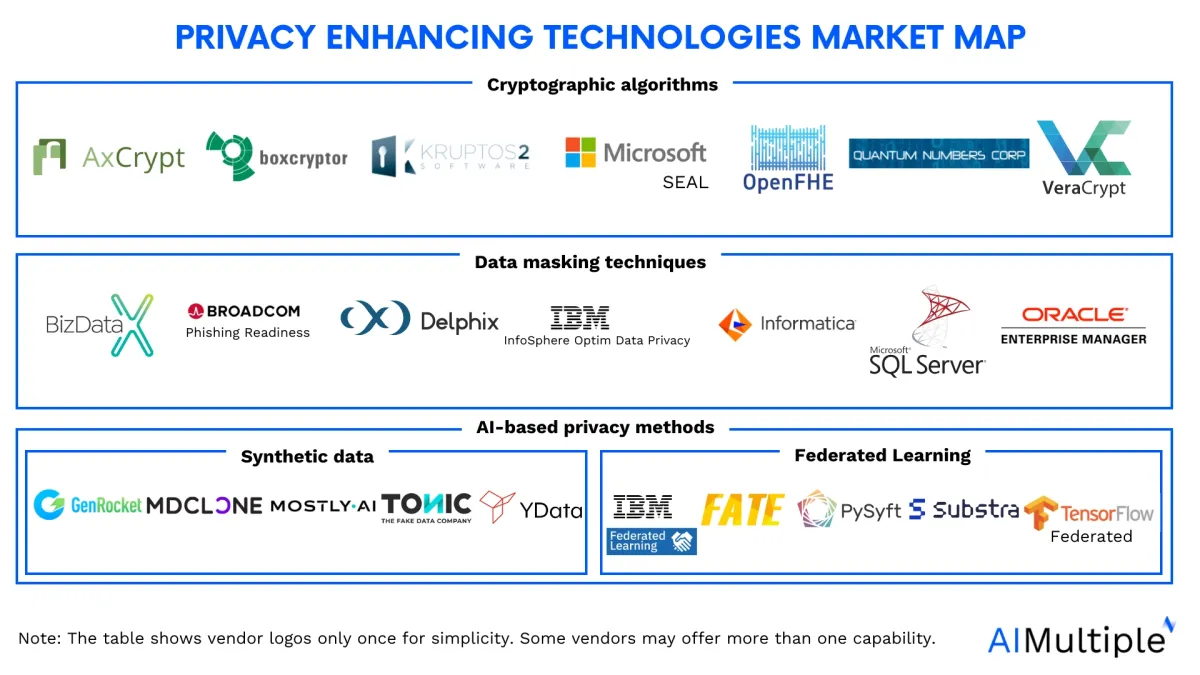
Explore top 10 PETs and their use cases to learn how to implement PETs to enhance your businesses:
| PETs | Data protected | Data use | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Homomorphic encryption | ✓ In storage ✓ During computation ✗ On release | Secure outsourcing | - Zero info loss - Supports operations - No trusted third party |
| Secure multi-party computation | ✗ In storage ✓ During computation ✗ On release | Joint analysis | - No trusted third party - Sensitive data hidden |
| Differential privacy | ✓ In storage (at point of data collection) ✓ During computation (with limitations) ✓ On release (with limitations) | Prevents disclosure | - Formal privacy guarantee - Privacy quantifiable - Limits information sharing |
| Trusted execution environment | ✓ In storage ✓ During computation ✗ On release | Secure outsourcing | - Commercially available - Zero info loss - Efficient computation |
| Data masking | ✓ In storage (through obfuscation and pseudonymization) ✗ During computation ✓ On release | Business protection | - Data obfuscation - Pseudonymization - Anonymization techniques |
| Synthetic data | ✗ In storage ✓ During computation (with limitations) ✓ On release (with limitations) | Prevents disclosure | - Privacy quantifiable - Differential privacy enabled |
| Federated learning | ✓ In storage ✗ During computation ✗ On release | Decentralized training | - Minimal info loss - Local computation - Data not centralized |
To leverage an automated tool, here is a list of the top data loss prevention software.
What are privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs)?
Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) are a broad range of technologies (hardware or software solutions) to ensure privacy and data protection while allowing organizations to extract value from data and unleash its full commercial, scientific and social potential. These technologies use various methods, including cryptography, anonymization, and obfuscation, to secure data during data processing.
By implementing PETs, organizations can help companies by
- Maximizing data security by reducing the risk of data breaches or leaks
- Preventing bad actors by rendering the data useless for malicious purposes
- Facilitating safe data collaboration across departments and even organizations.
This way, PETs play a critical role in data governance and protected data utility.
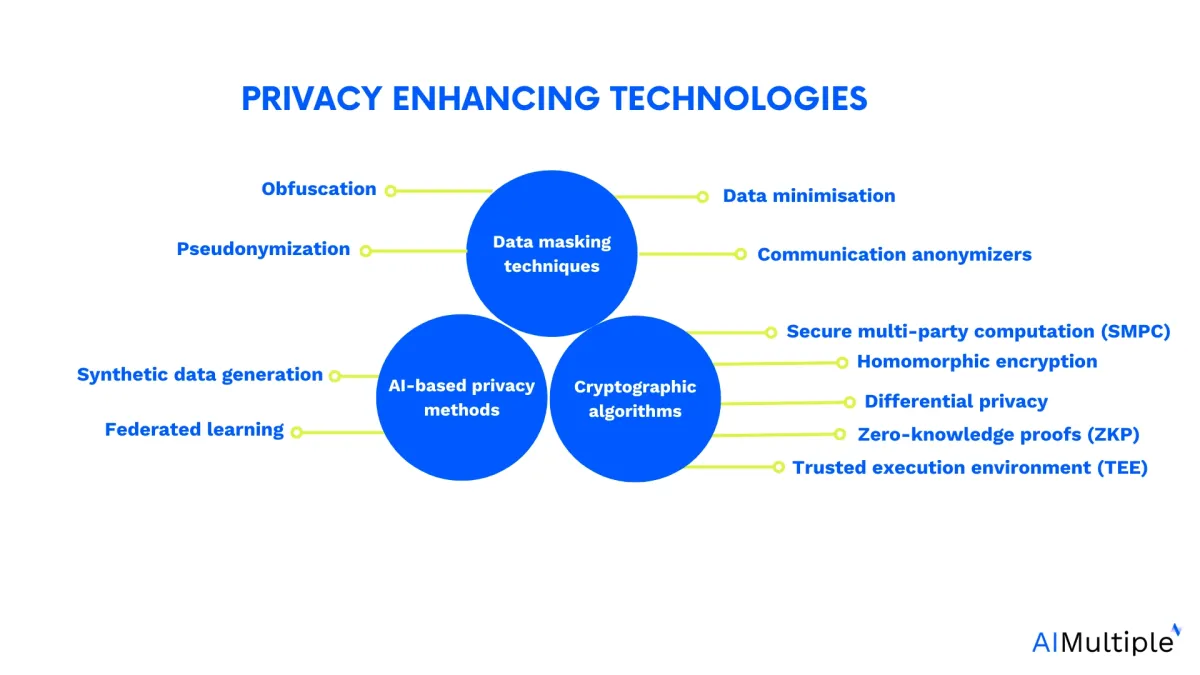
Why are privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) important now?
Like any other data privacy solution, privacy-enhancing technologies are important due to three reasons for businesses:
- Regulatory compliance: Data protection laws such as GDPR, CCPA and the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) are forcing organizations to preserve consumer data. Businesses can pay serious fines because of data breaches. These fees are already being levied, according to a GDPR Data Breach Survey 2022, GDPR fines are over US$1.2 billion from January 2021 to January 2022.1 PETs can provide a reliable way to comply with these regulations, avoiding legal and financial penalties.
- Secure data sharing: Data may need to be tested by third-party organizations due to the lack of your business’ self-sufficiency in analytics and application testing. PETs enable privacy protection while data sharing.
- Preventing Data Breaches: Privacy breaches can harm your business’ reputation, businesses or customers (depending on your business model) may want to stop interacting with your brand. PETs help safeguard sensitive information, reducing the risk of breaches that expose personal data, such as credit card details.
- A real-life example is the share price loss of Facebook after Cambridge Analytica scandal.2
Top 10 privacy-enhancing technology examples?
Cryptographic algorithms
1. Homomorphic encryption
Homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data, producing encrypted results that match the outcome of operations on unencrypted data (i.e. plaintext). This lets companies share sensitive data with third parties for analysis while keeping it secure. The data can be analyzed and returned to the owner, who can decrypt it to view the results. It’s also valuable for storing encrypted data in cloud applications.
Some common types of homomorphic encryption are:
- Partial homomorphic encryption:can perform one type of operation on encrypted data, such as only additions or only multiplications but not both.
- Somewhat homomorphic encryption: can perform more than one type of operation (e.g. addition, multiplication) but enables a limited number of operations.
- Fully homomorphic encryption: can perform more than one type of operation and there is no restriction on the number of operations performed.
2. Secure multi-party computation (SMPC)
Secure multi-party computation is a subfield of homomorphic encryption with one difference: users are able to compute values from multiple encrypted data sources. Therefore, machine learning models can be applied to encrypted data since SMPC is used for a larger volume of data.
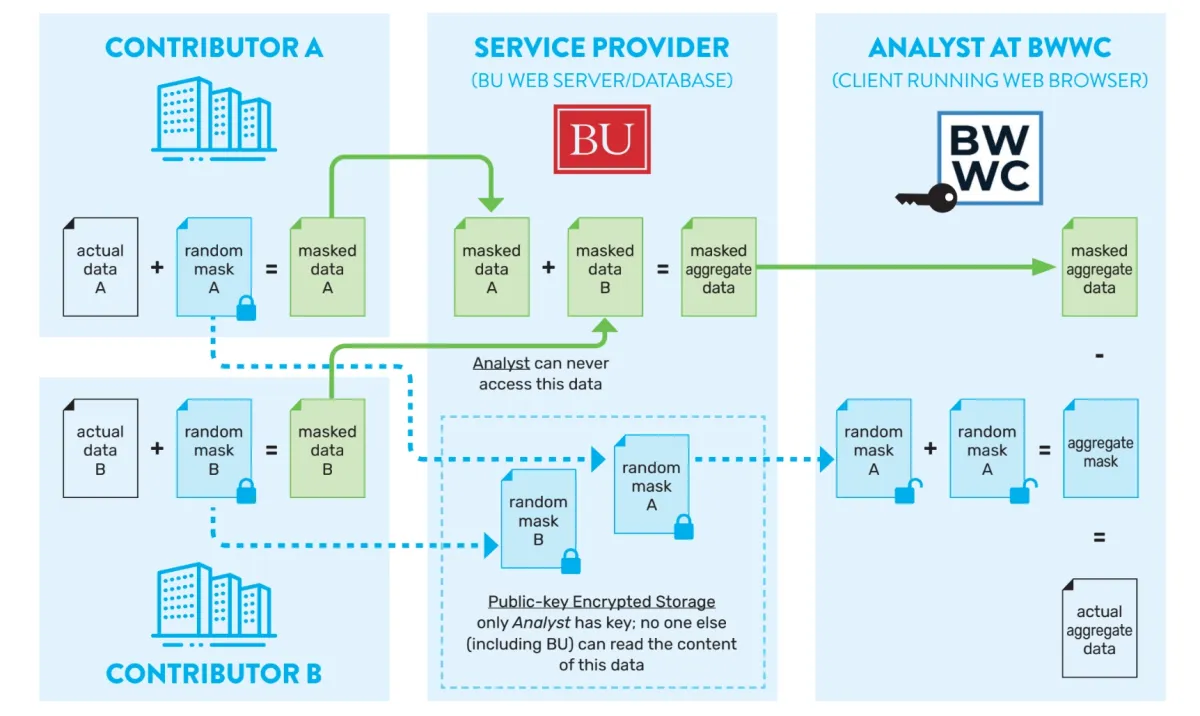
Case study
The Boston Women’s Workforce Council (BWWC) seeks to eliminate gender and racial wage gaps in Boston through a public-private partnership, with over 250 employers pledging to address these disparities by signing the “100% Talent Compact.”
To measure the city-wide wage gap, the BWWC used secure multiparty computation (sMPC) from 2015 to 2023, analyzing salary data from one-sixth of local employees without revealing individual salaries. Employers shared payroll data with BWWC and Boston University researchers, who only accessed aggregated statistics. A user-friendly web application was developed for easy data entry by participating organizations.
Based on these applications, the BWWC found that:
- Collaboration with usability experts is essential, as the privacy features of sMPC can complicate data entry processes and recovery from errors.
- sMPC is a quicker and safer alternative to establishing trust relationships with sensitive data.3
3. Differential privacy
Differential privacy protects from sharing any information about individuals. This cryptographic algorithm adds a “statistical noise” layer to the dataset which enables to describe patterns of groups within the dataset while maintaining the privacy of individuals.
4. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP)
Zero-knowledge proofs uses a set of cryptographic algorithms that allow information to be validated without revealing data that proves it.
5. Trusted execution environment (TEE)
A TEE is a secure area within a main processor that ensures the integrity and confidentiality of code and data loaded inside. The TEE operates in isolation from the rest of the system, meaning that even if the main operating system is compromised, the TEE remains secure.
The way it operates:
- The TEE provides a protected execution environment where sensitive data and operations, such as cryptographic processes or secure authentication, can be performed without interference from the main system or potential attackers.
- It keeps sensitive data isolated and computes operations in a secure environment, protecting against threats like malware or unauthorized access.
- TEEs are widely used in mobile devices, IoT systems, and cloud environments for performing tasks like encryption, digital rights management (DRM), and securing payment systems.
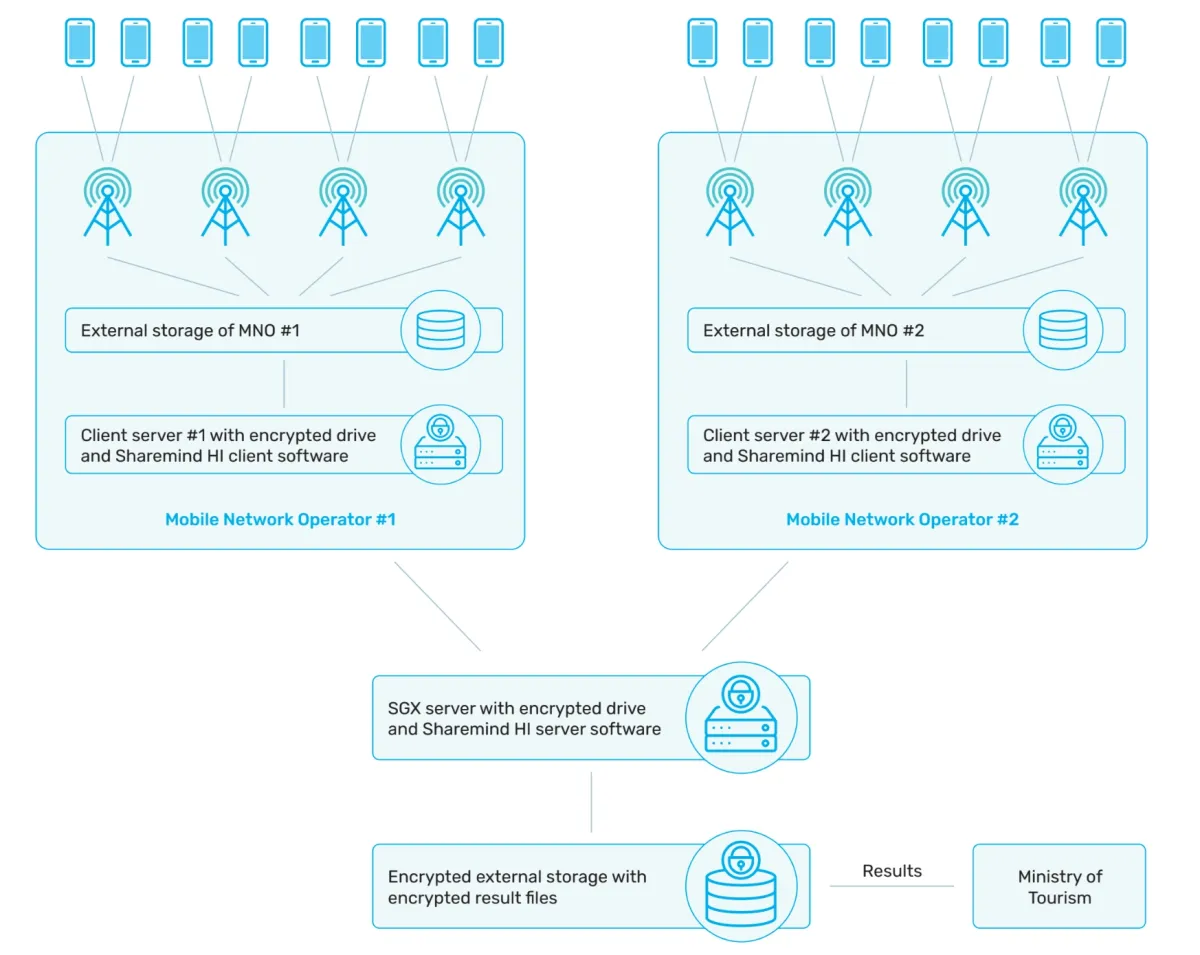
Case study
Indonesia’s Ministry of Tourism aimed to generate accurate tourism statistics from mobile roaming data while addressing privacy concerns when sharing datasets from two mobile network operators (MNOs). The technology used was a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), specifically Intel SGX, to securely process uniformly hashed IMSIs through the Sharemind HI platform.
As a result, the ministry:
- Enabled accurate calculation of roaming market share.
- Provided monthly tourism statistics based on mobile phone data.
- Established a framework for confidential data sharing among stakeholders.
- Remains the only known solution for analyzing cross-roaming subscriber overlap.
- Performance is efficient even on commercial hardware.4
Data masking techniques
Some privacy enhancing technologies are also data masking techniques that are used by businesses to protect sensitive information in their data sets.
5. Obfuscation
This one is a general term for data masking that contains multiple methods to replace sensitive information by adding distracting or misleading data to a log or profile.
6. Pseudonymization
Identifier fields (fields that contain information specific to an individual) are replaced with fictitious data such as characters or other data. Pseudonymization is frequently used by businesses to comply with GDPR.
7. Data minimisation
Collecting minimum amount of personal data that enables the business to provide the elements of a service.
8. Communication anonymizers
Anonymizers replace online identity (IP address, email address) with disposal/one-time untraceable identity.
AI-based privacy methods
9. Synthetic data generation
Synthetic data is an artificially created data by using different algorithms including ML algorithms. If you are interested in privacy-enhancing technologies because you need to transform your data into a testing environment where third-party users have access, generating synthetic data that has the same statistical characteristics is a better option.
10. Federated learning
This is a machine learning technique that trains an algorithm across multiple decentralized edge devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them. With the decentralization of servers, users can also achieve data minimization by reducing the amount of data that must be retained on a centralized server or in cloud storage.
Case Study
The CARRIER project uses secondary processing of medical, lifestyle, and personal data to estimate risks and enable early detection and intervention for coronary artery disease. However, it must ensure compliance with legal standards and protect against re-identification risks when linking datasets from different organizations, adhering to national laws and the European GDPR.
To overcome this challenge, the project employed federated learning that controls the execution of approved Docker images, allowing secure data processing without direct data sharing.
As a result, the project could:
- Develop a robust legal data governance framework to support federated learning procedures.
- Ensured privacy and data security during the development of the prognostic model, facilitating continuous research.
- Identified the need for ongoing governance to maintain ethical and legal compliance during project phases..5
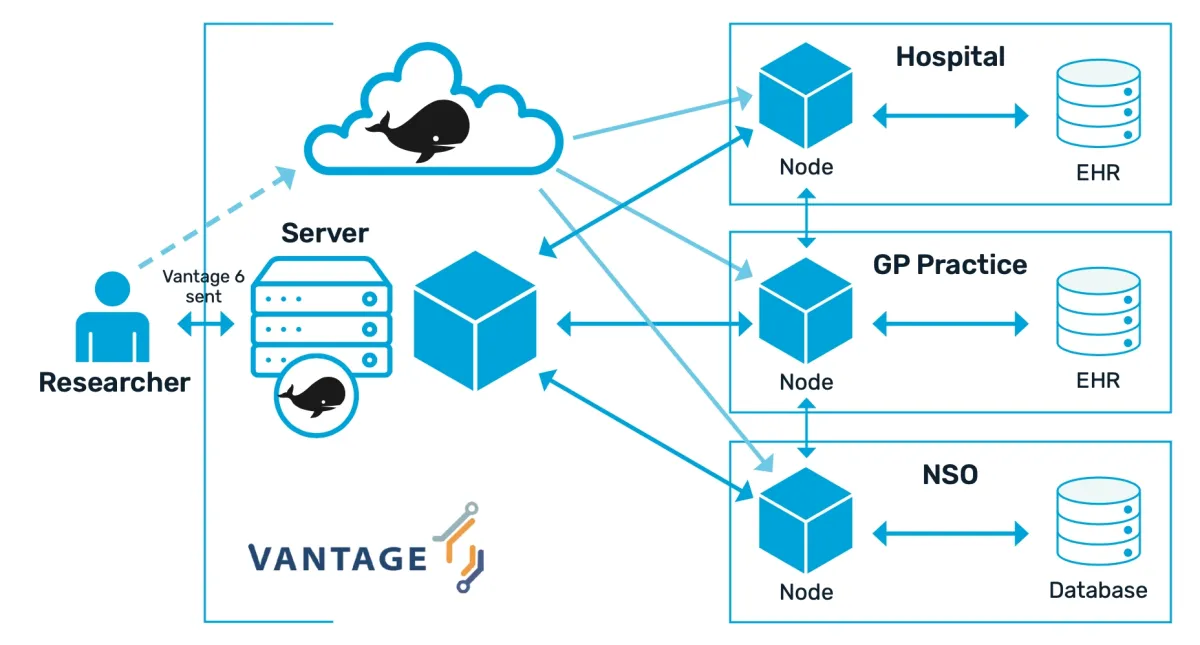
PETs market overview
The PETs market encompasses a diverse array of tools, models, and libraries designed to safeguard data privacy. For instance, each category, such as synthetic data generators or data masking tools, boasts over 20 distinct tools.
These tools are challenging to shortlist individually due to their vast diversity. To enhance clarity, we’ve grouped them, providing a comprehensive overview on the cover image above.
What are the top use cases of PETs?
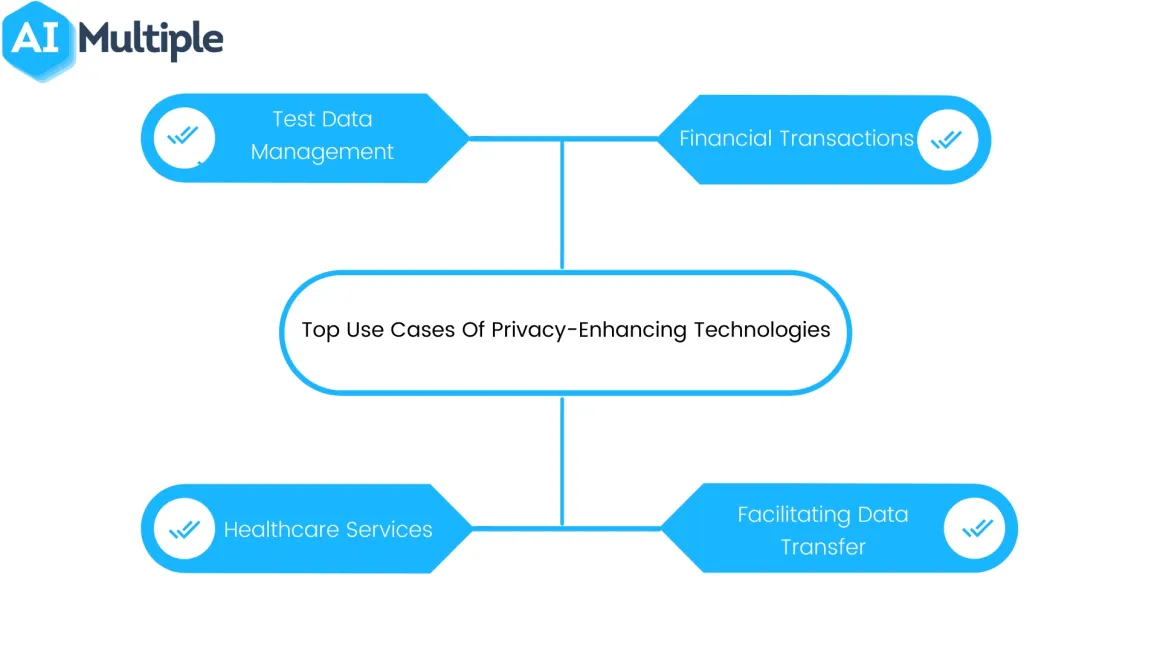
- Test data management: Application testing and data analysis are sometimes handled by third-party providers. Even when they are handled in-house, companies should minimize internal access to customer data. Using a suitable PET that doesn’t significantly affect test results is important for organizations.
- Financial transactions: Financial institutions are responsible for protecting the privacy of the customers due to citizens’ freedom to conduct private deals and transactions with other parties.
- Healthcare services: Healthcare industry collects and shares (when needed) electronic health records (EHR) of patients. For example, clinical data can be used for searching for adverse effects of various drug combinations. Healthcare companies ensure the privacy of patients’ data in such cases by using PETs.
- Facilitating data transfer between multiple parties including intermediaries: For businesses that work as a middle man between two parties, the usage of PETs is crucial since these businesses are responsible for protecting the privacy of both parties’ information.
FAQ
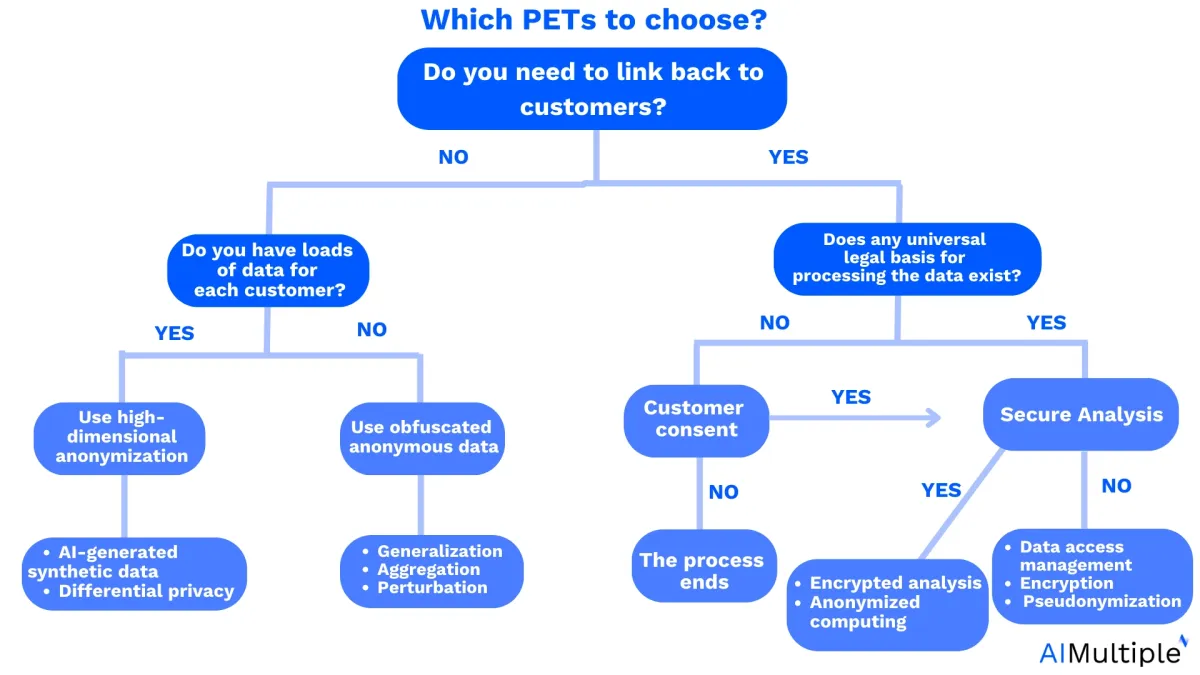
Choosing the right privacy-enhancing tool for your business
Navigating the array of privacy-enhancing tools (PETs) in the market requires a strategic approach tailored to your unique business needs. To ensure optimal integration and alignment with your software stack and IT infrastructure, consider the following steps:
1. Identify your needs and goals
You must identify issues you aim to solve by deploying a PET. To do this you may:
a.) Assess your data landscape: Identify the volume and nature of the data your business manages. Determine if it is predominantly structured or unstructured, as this influences the choice of PETs that best suit your requirements.
b.) Map third-party data sharing: Understand the intricacies of third-party data sharing. If your data traverses external channels, prioritize solutions like homomorphic encryption to maintain security and confidentiality during transit.
c.) Define data access needs:
Clearly distinguish the level of access required to the dataset—assessing whether full access is essential or if accessing only the result/output suffices. Additionally, consider the ability to obfuscate personally identifiable information for enhanced privacy.
d.)Determine data utilization: Check you aim to use data for statistical analysis, market insights, machine learning model training, or similar purposes.
2. Evaluate different types of PETs:
Consider the three main categories of PETs—cryptographic tools, data masking techniques, and AI-based solutions like synthetic data generators. Identify which type aligns best with your privacy objectives and data protection needs.
3. Shortlist tools based on categories:
Once you’ve identified the PET categories relevant to your needs, shortlist specific tools within each category. Consider aspects such as functionality, scalability, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
4. Evaluate IT infrastructure:
Conduct a thorough evaluation of your IT infrastructure, taking into account network and computational capabilities. This assessment will guide you in selecting PETs that seamlessly integrate with your enterprise resources. Identify areas that may require upgrades for compatibility.
5. Consider budgetary allocations:
Be proactive in budget planning, recognizing that PETs can vary in cost. Allocate resources based on your specific privacy requirements and financial capacity. Consider factors such as scalability, maintenance, and potential additional costs associated with the chosen PET solution.
Don’t forget to check our article on data security best practices. If you still have questions about privacy-enhancing technologies, we would like to help:
External sources
- 1. DLA Piper GDPR fines and data breach survey: January 2022 | DLA Piper.
- 2. Facebook Loses $35B in Value After Cambridge Analytica Breach | Fortune. Fortune
- 3. 1. Boston Women’s Workforce Council: Measuring salary disparity using secure multi-party computation - UN GWG on Big Data - Privacy Preserving Techniques Wiki - UN Statistics Wiki.
- 4. 4. Indonesia Ministry of Tourism: Confidentially sharing datasets between two mobile network operators via a trusted execution environment - UN GWG on Big Data - Privacy Preserving Techniques Wiki - UN Statistics Wiki.
- 5. 12. Statistics Netherlands: Developing privacy-preserving cardiovascular risk prediction models from distributed clinical and socioeconomic data - UN GWG on Big Data - Privacy Preserving Techniques Wiki - UN Statistics Wiki.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.