Based on our analysis of 30+ case studies and 10 benchmarks, where we tested and compared over 40 products, we identified 125 generative AI use cases across the following categories:
- General genAI applications
- Industry-specific genAI applications
- Business-function-specific genAI applications
For other applications of AI for requests where there is a single correct answer (e.g., prediction or classification), check out AI applications.
You can also see generative AI applications, use cases, and real-life examples in a list that you can filter based on various criteria such as business function or industry.
General genAI applications
> Video applications
1. Video generation
AI-powered video production tools, including AI video generators, content creation platforms, and editing solutions, enable businesses to produce high-quality videos, personalize content, and optimize performance. These tools help reduce costs, manage production, and allow for dynamic, abstract visuals in just minutes.
We assessed leading AI video generation tools to determine their effectiveness in creating high-quality product demonstration videos for eCommerce.
Each AI tool was tested using stock images and scored out of 10 based on Prompt Compliance (accuracy in following instructions), Physical Accuracy (realistic physics and interactions), and Product Integrity (consistency in appearance and details). Here are some of our observations:
- Common issues: Many AI tools struggled with accurately conveying product details, maintaining brand-specific features, and ensuring prompt compatibility.
- Key findings: AI-generated videos are not yet fully reliable for eCommerce product visualization without further refinement. Enhancing prompts and fine-tuning AI models may improve results.
Real-life example: Netflix used generative AI for the first time in a TV show, adding AI-generated footage to the Argentinian sci-fi series “El Eternauta”. Co-CEO Ted Sarandos said AI helped VFX teams create complex scenes, such as a collapsing building, much faster and at lower cost than traditional methods, making the production financially possible.
Although the move has raised concerns about job losses in the entertainment industry, Sarandos said AI is meant to support human creators rather than replace them.1
Check out AI job loss to learn more about recent predictions on how AI will affect the job market.
2. Video prediction
A GAN-based video prediction system:
- Comprehends both temporal and spatial elements of a video
- Generates the next sequence based on that knowledge (See the figure below)
- Distinguishes between probable and non-probable sequences
GAN-based video predictions can help detect anomalies that are crucial in a wide range of sectors, including security and surveillance.
Real-life example: Lucid Dream Network enhanced its video production by utilizing Pictory’s script-to-video tool, which offered pre-built templates and smooth integration of music and visuals.
This innovation helped the company boost its productivity by 350% and amplified its social media reach and engagement by 500%.2
3. AI video editing and animation
Beyond generation, generative AI can help with editing, storyboarding, and animation. These tools automate camera motion, lip-syncing, and scene transitions.
Applications include:
- Automated corporate training videos
- Social media video summarization
- Style-transfer for animated storytelling
Real-life example: Runway Gen-3 enables text-driven video editing with scene consistency and motion control, reducing post-production time by over 70% for marketing teams.3
> Image applications
4. Image generation
With generative AI, users can transform text into images and generate realistic images based on a specified setting, subject, style, or location. Therefore, it is possible to generate the needed visual material quickly and simply.
It is also possible to use these visual materials for commercial purposes, making AI-generated image creation a valuable element in media, design, advertising, marketing, education, and other fields. For example, an image generator can help a graphic designer create whatever image they need (See the figure below).
Figure 1: This AI-generated image was produced based on the text description of “Teddy bears shopping for groceries in ukiyo-e style”.4
Real-life example: Coca-Cola, working with OpenAI and Bain & Company, launched the “Create Real Magic” platform.
By utilizing OpenAI’s GPT-4 and DALL-E models for creative generation, this project allowed users to create custom artwork using iconic Coca-Cola imagery, such as the contour bottle and Santa Claus.5
5. Semantic image-to-photo translation
Based on a semantic image or sketch, it is possible to produce a realistic version of an image. Due to its facilitative role in making diagnoses, this application is useful for the healthcare sector.
Figure 3: Generating Synthetic Space Allocation Probability Layouts Based on Trained Conditional-GANs.6
6. Image-to-image conversion
It involves transforming the external elements of an image, such as its color, medium, or form, while preserving its constitutive elements.
One example of such a conversion would be turning a daylight image into a nighttime image. This type of conversion can also be used for manipulating the fundamental attributes of an image, colorizing it, or changing its style.
7. Image resolution increase (super-resolution)
Generative AI employs various methods to generate new content based on existing content. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are one of these methods. A GAN consists of a generator and a discriminator that creates new data and ensures that it is realistic.
GAN-based method allows you to create a high-resolution version of an image through Super-Resolution GANs. This method is useful for producing high-quality versions of archival material and/or medical materials that are uneconomical to save in high-resolution format. Another use case is for surveillance purposes.
8. AI design co-pilots
Creative generative AI design tools can automate layout, color matching, and template creation while maintaining brand consistency.
Applications include:
- Text-to-template for presentations and social media
- Brand identity generation
- Dynamic campaign A/B design
Real-life example: Figma AI generates auto-layouts and typography pairings based on text prompts, cutting design time for marketing teams.7
9. 3D shape generation
In this area, research is ongoing to create high-quality 3D versions of objects. Using GAN-based shape generation, better shapes can be achieved in terms of their resemblance to the source. In addition, detailed shapes can be generated and manipulated to create the desired shape.
Applications include:
- Real estate visualization
- Product design and digital twin manufacturing
- Virtual tourism and simulation training
Real-life example: Luma AI uses Gaussian Splatting to reconstruct photorealistic 3D spaces for digital marketing and gaming environments.8
Figure 4: SP-GAN: Sphere-Guided 3D Shape Generation and Manipulation.9
> Audio applications
10. Text-to-speech generator
GANs allow the production of realistic speech audio. To achieve realistic outcomes, the discriminators serve as a trainer who accentuates, tones, and/or modulates the voice.
The TTS generation has multiple business applications, such as education, marketing, podcasting, and advertising. For example, an educator can convert their lecture notes into audio materials to make them more attractive, and the same method can also be helpful to create educational materials for visually impaired people. Aside from removing the expense of voice artists and equipment, TTS also provides companies with many options in terms of language and vocal repertoire.
Using this technology, thousands of books have been converted to audiobooks.10
Learn more about the capabilities of large language models in text generation.
Real-life example: Twilio enhanced its voice synthesis capabilities through collaboration with Amazon Polly, a cloud-based text-to-speech service.
This partnership introduced more than 50 voices across 25 languages to Twilio’s platform and provided developers with new APIs for more advanced speech synthesis control in their voice applications.11
11. Speech-to-speech conversion
An audio-related application of generative AI involves generating voices from existing audio sources. With STS conversion, voiceovers can be easily and quickly created, which is advantageous for industries such as gaming and film.
With these tools, it is possible to generate voiceovers for a documentary, a commercial, or a game without hiring a voice artist.
12. Music generation
Generative AI is also purposeful in music production. Music-generation tools can be used to generate novel musical materials for advertisements or other creative purposes.
In this context, however, an important obstacle remains to be overcome, namely, copyright infringement resulting from the inclusion of copyrighted artwork in training data. Learn more about AI ethics.
> Text-based applications
13. Idea generation
LLM output may not be suitable for publication due to issues with hallucination, copyrights, etc. However, idea generation is possibly the most common use case for text generation. Working with machines in ideation allows users to quickly scan the solution space.
It is surprising to get a machine’s help in becoming more creative as a human. This is possible because generative AI’s capabilities are quite different (e.g., more flexible, less reliable) than how we typically think about machines’ capabilities.12
14. Text generation
Researchers appealed to GANs to offer alternatives to the deficiencies of the state-of-the-art ML algorithms. GANs are also being trained for text generation, in addition to their initial use for visual purposes.
Creating dialogues, headlines, or ads through generative AI is a common practice in the marketing, gaming, and communication industries.
A clear example of generative AI in action is using AI email assistants to generate email text. AI email assistants help users save time by generating complete, polished emails from brief prompts, ensuring consistent tone and quality.
They also offer context-aware reply suggestions for incoming emails, allowing quick, efficient responses to routine messages.
For example, a 2025 study investigated whether people can differentiate between therapy responses written by expert therapists and those generated by ChatGPT, how these responses align with key therapeutic principles, and their linguistic differences.
In a large sample, the results showed that participants could rarely distinguish between AI-generated responses and those of therapists, and ChatGPT’s responses were rated higher in terms of therapeutic quality. Linguistic analysis suggests that AI’s superior contextualization may contribute to its effectiveness.
While these findings highlight the potential for generative AI to enhance psychotherapy, ethical concerns such as technophobia and the balance between creativity and evidence-based practice must be carefully addressed as AI’s role in mental health continues to evolve.13
Real-life example: Meta AI’s Brain2Qwerty decodes sentences from brain activity during typing, using non-invasive electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) signals.
Unlike previous methods that required users to imagine movements or focus on external stimuli, Brain2Qwerty interprets natural typing motions, making brainwave decoding more intuitive. The model is composed of three key modules:
- Convolution Module: Extracts spatial and temporal features from EEG and MEG signals.
- Transformer Module: Processes input sequences to enhance understanding and expression.
- Language Model Module: Uses a pre-trained character-level language model to refine and improve text accuracy.
In evaluations, Brain2Qwerty achieved a character error rate (CER) of 67% using EEG and 32% with MEG, while the best-performing participant reached a 19% CER under optimal conditions.
While promising, the approach faces challenges, including the need for real-time decoding, the limited portability and availability of MEG equipment, and further testing for individuals with motor or speech impairments.14
Explore more large language model examples and applications, like text generation.
15. Personalized content creation
It can be used to generate personalized content for individuals based on their personal preferences, interests, or memories. This content could be in the form of text, images, music, or other media, and could be used for:
- Social media posts
- Blog articles
- Product recommendations
Personal content creation with generative AI has the potential to provide highly customized and relevant content.
16. Sentiment analysis/text classification
Sentiment analysis, also known as opinion mining, uses natural language processing and text mining to decipher the emotional context of written materials.
Generative AI can be used in sentiment analysis by generating synthetic text data that is labeled with various sentiments (e.g., positive, negative, neutral). This synthetic data can then be used to train deep learning models to perform sentiment analysis on real-world text data.
It can also be used to generate text specifically designed to convey a particular sentiment. For example, a generative AI system could be used to create social media posts that are intentionally positive or negative, aiming to influence public opinion or shape the sentiment of a particular conversation.
These can be useful for mitigating the data imbalance issue for the sentiment analysis of users’ opinions (as in the figure below) in many contexts, such as education and customer services.
Figure 5: The Impact of Synthetic Text Generation for Sentiment Analysis Using GAN-based Models.
17. Smart search
Smart Search leverages natural language processing and machine learning to deliver precise and context-aware results. Unlike traditional keyword searches, it understands user intent, processes natural language queries, and provides results based on meaning rather than exact word matches.
Features like autocomplete, real-time suggestions, and faceted filtering allow users to refine searches. Additionally, it can support voice and visual inputs.
Smart search is widely applied across industries. In eCommerce, Smart Search can help customers locate products efficiently, while in enterprise environments, it enables easy retrieval of documents and resources.
Real-life example: Booking.com introduced Smart Filters, a tool that allows users to articulate their preferences in natural language directly within a search box.
For example, a traveler planning a weekend trip to Amsterdam might search for “hotels with a great gym and canal views from the room.” Smart Filters then analyze the input, identify the user’s intent, and apply the most relevant filters from Booking.com’s inventory.15
> Code-based applications
18. Code generation
Ancileo, a software provider for insurance companies, utilized Amazon Q to improve the efficiency of its developers. Amazon Q helped developers resolve code issues faster, reducing troubleshooting time by 30%.
Additionally, Ancileo integrated ticketing and documentation to enhance onboarding processes and streamline internal communication.
Generative AI enhances software development by automatically generating code, therefore reducing the need for manual programming.
Figure 6: Generating an HTML form and JavaScript submit code with OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Real-life example: Amazon has introduced Amazon Q, an AI-powered tool that significantly reduces the time and effort required to update foundational software like Java.
This tool automates code transformations, reducing the upgrade time from 50 developer days to just a few hours and saving an estimated 4,500 developer years of work.
In six months, Amazon modernized over half of its Java systems, enhancing security and cutting infrastructure costs, resulting in $260 million in annual efficiency gains. This highlights how AI can drive major productivity improvements in software maintenance for large enterprises.16
19. Code completion
One of the most straightforward uses of generative AI for coding is to suggest code completions as developers type. This can save time and reduce errors, especially for repetitive or tedious tasks.
20. Code review
Generative AI can also be used to make quality checks of the existing code and optimize it either by suggesting improvements or by generating alternative implementations that are more efficient or easier to read.
21. Bug fixing
It can help identify and fix bugs in the generated code by analyzing code patterns, identifying potential problems, and suggesting fixes.
22. Code refactoring
Generative AI can be used to automate the process of refactoring code, making it easier to maintain and update over time.
23. Code style checking
Generative AI can analyze code for adherence to coding style guidelines, ensuring consistency and readability across a codebase.
24. Generating test cases
Generative tools like ChatGPT can help generate test cases based on user requirements or user stories, provide a clear description of the application’s functionality, and come up with multiple scenarios and test cases to cover various aspects of the application.
Real-life example: Anthropic teams apply Claude Code across a wide range of functions, including engineering, product design, marketing, legal, and data science, to increase efficiency, reduce manual workload, and support independent task execution.
Technical teams use it for rapid prototyping, debugging, test generation, infrastructure automation, and navigating complex codebases, often accelerating development cycles and improving code quality.
Non-technical teams such as legal and marketing utilize it to build internal tools, automate repetitive processes, and conduct experiments without requiring software engineering expertise.17
25. Generating test code
Tools like ChatGPT can convert natural language descriptions into test automation scripts. Understanding the requirements described in plain language can translate them into specific commands or code snippets in the desired programming language or test automation framework.
Figure 7: NLP to test scripts via ChatGPT-4.
26. Test script maintenance
ChatGPT can help manage test scripts by spotting obsolete or duplicate code, offering enhancements, and updating them automatically based on new requirements.
27. Test documentation
Generative AI models can generate realistic test data based on the input parameters, such as creating valid email addresses, names, locations, and other test data that conform to specific patterns or requirements.
28. Test result analysis
ChatGPT and other similar tools can analyze test results and provide a summary, including the number of passed/failed tests, test coverage, and potential issues.
> Other applications
29. Conversational AI
Another use case of generative AI involves generating responses to user input in the form of natural language. This type is commonly used in chatbots and virtual assistants, which are designed to provide information, answer questions, or perform tasks for users through conversational interfaces such as chat windows or voice assistants.
ChatGPT is a popular example of conversational AI. It offers a highly informative and integrated conversation to users, like philosophical discussions. For example, you can check a chat with ChatGPT below.
Figure 8: A conversation with ChatGPT.
Real-life example: O2, British telecommunications services provider, and VCCP’s AI creative agency Faith launched an innovative campaign to combat phone scammers using Daisy, a lifelike Conversational AI. Daisy is designed to engage scammers in lengthy conversations, thereby protecting the public from fraud.
Inspired by a real-life grandmother and modeled after scammers’ stereotypes of elderly victims, Daisy interacts with scammers in real time, sharing fabricated stories, fake bank details, and hobbies like knitting. By deceiving scammers into believing they’ve targeted a real person, Daisy disrupts their operations and highlights common tactics to educate the public on scam prevention.
Daisy’s creation involved advanced AI technology, including a large language model for her personality, a diffusion model for photorealistic visuals, and voice modeling based on a VCCP employee’s grandmother.18
Explore types of conversational AI.
30. Data synthesis
Generative AI can produce synthetic data that mimics real-world statistics without relying on actual data points, making it useful for model training, data privacy, and NLP tasks.
31. Data visualization
Some generative models like ChatGPT can perform data visualization, which is useful for many areas. It can be used to load datasets, perform transformations, and analyze data using Python libraries like pandas, numpy, and matplotlib.
You can ask ChatGPT Code Interpreter to perform certain analysis tasks, and it will write and execute the appropriate Python code. Also, you can ask the model to visualize your data in a preferred format.
Figure 9: Data analysis with ChatGPT code interpreter.
Discover what ChatGPT Code Interpreter is and its various use cases.
32. File conversion
ChatGPT code interpreter can convert files between different formats, provided that the necessary libraries are available and the operation can be performed using Python code.
33. Solving mathematical problems
Generally, large language models are capable of understanding mathematical questions and solving them. This includes basic problems but also complex ones, depending on the model. Below is an example of ChatGPT’s capabilities in this.
Figure 10: Solving mathematical problems with OpenAI’s ChatGPT plugins.19
34. Multimodal AI assistants
Recent advancements, such as OpenAI’s GPT-4o, Google Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Anthropic Claude 3.5, have unified text, image, and audio comprehension into a single model. These multimodal assistants process and generate multiple formats simultaneously.
Applications include:
- Real-time voice and video chat with contextual reasoning
- Visual question answering and chart interpretation
- “See, hear, respond” customer service systems
Real-life example: OpenAI’s GPT-4o integrates speech recognition, vision, and text generation, allowing users to hold natural spoken conversations with real-time visual analysis of objects or documents.20
Industry-specific genAI applications
> Healthcare applications
35. Drug discovery and development
Leveraging the power of generative AI algorithms to find potential drug candidates and testing their efficacy with computer simulations could vastly expedite the process of discovering new drugs, from preclinical trials on animals to clinical tests on humans.
Real-life example: LeewayHertz21 develops custom AI agents and copilots to streamline drug discovery and help companies save time and resources across various stages:
- Target identification: Analyzes biological data to identify and prioritize promising drug targets.
- Lead optimization: Screens chemical libraries, generates new molecules, and optimizes molecular properties.
- Preclinical evaluation: Predicts drug behavior and potential interactions, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
- Drug repurposing: Finds new applications for existing drugs by analyzing databases and disease pathways.
- Clinical trial design: Analyzes patient data for targeted trial designs, improving efficiency and success rates.
Generative AI software also helps design novel biomolecules, proteins, and therapeutic agents by integrating biological knowledge and structured biomedical data (e.g., knowledge graph-augmented generative models for targeted drug discovery).22
Applications include:
- Tailored molecule generation with enhanced biological relevance.
- Design of multi-target therapeutics.
- Customized enzyme and biomaterial generation.
36. Personalized medicine
Another application of generative AI in personalized medicine is to create models that can serve as medical chatbots to understand patients’ symptoms and produce diagnoses with increasing accuracy based on patient declarations and test results.23 Then, these models can craft individualized treatment plans tailored specifically for a patient’s medical history, symptoms, and more.
Real-life example: AI4BetterHearts is a global initiative led by the Novartis Foundation, Microsoft AI for Health, and partners to improve cardiovascular health by uniting and analyzing heart health data.
The collaboration aims to break down data silos and leverage machine learning to transform health systems from reactive to preventive care. Partnering with Harvard’s Health Systems Innovation Lab, the initiative examines health system performance across 80 countries, with insights complementing the AI4HealthyCities Health Equity Network.24
37. Improved medical imaging
By combining the power of machine learning with medical imaging technologies, such as CT and MRI scans, generative AI algorithms can enhance precision in medical imaging, yielding improved results.
38. Population health management
Using generative AI in healthcare can also lead to better population-level health management by allowing policymakers to:
- Access more detailed demographic information
- Design targeted public health initiatives that benefit underserved communities.
Real-life example: BCG and Zeiss developed a generative AI application to help healthcare professionals provide accurate and timely responses to patient inquiries.
This AI tool generates responses based on pre-approved materials and ensures that accurate information is delivered to patients. Based on early feedback, 79% of AI-generated responses are found to be ready to send without edits.
The application aims to improve patient engagement and allow doctors to focus more on patient care, while potentially boosting demand for treatments.25
39. AI chatbots for symptom checking
Symptom assessment chatbots are designed to help individuals understand and manage their health by asking questions, providing recommendations, and, when necessary, connecting users with healthcare professionals.
These chatbots offer immediate medical guidance and preliminary information for patients to take a proactive approach to their health. By analyzing symptoms, they can also help identify potential health issues early and provide tailored advice.
However, the use of these tools comes with notable limitations:
- Limited diagnostic accuracy: Symptom checkers may lack the expertise of medical professionals, making their diagnostic accuracy unreliable for serious conditions. Users should use them cautiously and not as a replacement for professional advice.
- Lack of empathy: These tools cannot provide the emotional support, reassurance, or personalized guidance that healthcare professionals offer, limiting their ability to meet patients’ emotional needs.
- Over-reliance on chatbots: Dependence on chatbots for medical advice may lead to anxiety from generic or inaccurate information and discourage seeking proper medical care when necessary.
- Legal and privacy concerns: Missteps in advice or handling of personal data could result in legal issues, especially in regions with strict privacy laws like HIPAA. Proper design must prioritize compliance and data security.
40. AI agents in healthcare
AI agents in healthcare can schedule appointments, document patient information, support diagnosis through medical imaging, personalize treatment plans, assist in drug discovery, and automate processes like billing, claims handling, and prior authorizations.
These agents also enhance patient engagement through conversational support, provide real-time health monitoring, offer mental health assistance, detect billing anomalies, and integrate with systems such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to support care coordination and improve decision-making.
41. Regulatory documentation automation
Regulatory documentation automation refers to using AI-driven tools to create, review, and manage compliance-related documents in regulated industries such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals.
With this automation, organizations can reduce manual effort, ensure consistency with approved content, and accelerate the drafting of clinical study reports, regulatory submissions, and compliance documents.
Real-life example: Novo Nordisk has adopted Anthropic’s Claude to assist in drafting clinical study reports, reducing the process from weeks to minutes.
By reducing the number of writers from over 50 to just three, the company has achieved a 94% reduction in headcount and 92% in cost savings, while maintaining accuracy through human oversight.
They leverage retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to mitigate AI hallucinations, ensuring previously approved content is reused consistently. This approach helped enhance efficiency in regulatory documentation, demonstrating how AI and human collaboration can drive faster and more cost-effective compliance processes.26
42. Synthetic data generation in healthcare
Rather than producing generic synthetic data, AI now generates multi-modality synthetic datasets for medical research, training, and validation of clinical AI systems, effectively addressing privacy constraints while maintaining clinical realism.
Use cases include:
- AI-augmented development of synthetic disease simulations.
- Synthetic imaging, time-series EHR, and signal data.
> Education applications
43. Personalized lessons
By leveraging generative AI for education, personalized lesson plans can provide students with the most effective and tailored education possible.
These plans are crafted by analyzing student data such as their past performance, skill set, and any feedback they may have given regarding curriculum content. This helps ensure that each student, especially those with disabilities, is receiving an individualized experience designed to maximize success.
44. Course design
From designing syllabi and assessments to personalizing course material based on students’ individual needs, generative AI can help make teaching more efficient and effective.
When combined with different types of virtual reality, it can also create realistic simulations that will further engage learners in the process.
45. Content creation for courses
Generative AI allows the rapid creation of diverse teaching materials, including quizzes and concept reviews. This would help educators quickly generate unique content.
Also, AI can generate scripts for video lectures or podcasts, streamlining multimedia content creation for online courses (see the figure below).
Figure 11: An example of AI-generated course content from NOLEJ.
46. Tutoring
AI-generated tutoring can allow students to interact with a virtual tutor and receive real-time feedback in the comfort of their homes. This makes it an ideal solution for those children who may not have access to traditional face-to-face education.
Real-life example: Khan Academy leverages GPT-4 in its AI assistant, Khanmigo, and it serves as a virtual tutor for students and a support for teachers by addressing different educational needs.
Khanmigo facilitates deeper learning by asking individualized questions and contextualizing content relevance. Early results show promise in improving student engagement and learning outcomes. Khanmigo also helps teachers create instructional materials and tailor learning experiences (See Figure below).
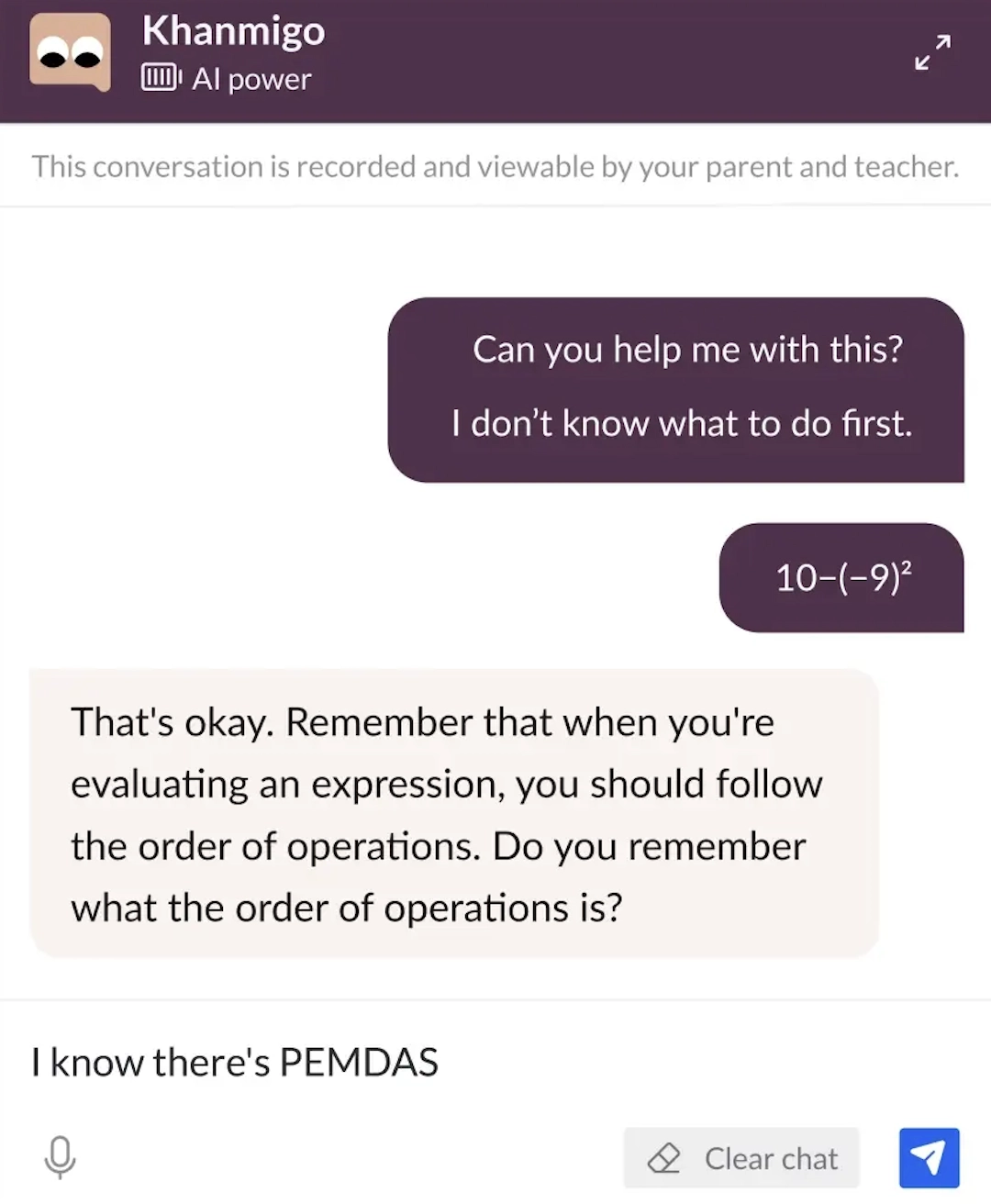
Figure 12: Khan Academy’s Khanmigo personalized question generation for deeper learning.27
Real-life example: A study conducted in Nigeria evaluated the impact of generative AI on student learning outcomes in secondary education. The intervention involved using Microsoft Copilot, powered by GPT-4, as a virtual tutor for English language instruction in a six-week after-school program. The study employed a randomized controlled trial across nine public schools.
The results indicate that students who participated in the program experienced statistically significant improvements in English proficiency, digital literacy, and knowledge of artificial intelligence.
The approach combined AI-driven tutoring with teacher oversight and curriculum alignment. The study also found the program to be cost-effective in comparison to traditional interventions.
These findings suggest that generative AI, when integrated into structured educational programs, may offer a viable method to support learning in contexts with limited educational resources.28
47. Data privacy protection for analytical models
One advantage of using generative AI to create training data sets is that it can help protect student privacy. A data breach or hacking incident can reveal real-world data containing personal information about school-age children.
AI-generated synthetic data, derived from learning real-world patterns, helps ensure anonymity and safeguard student privacy. Synthetic data sets produced by generative models are effective and useful for training other algorithms while being secure and safe to use.
48. Restoring old learning materials
Generative AI can improve the quality of outdated or low-quality learning materials, such as historical documents, photographs, and films.
By using AI to enhance the resolution of these materials, they can be brought up to modern standards and be more engaging for students who are used to high-quality media.
> Fashion applications
49. Creative designing for fashion designers
From creating innovative styles to refining and optimizing existing looks, the technology enables designers to stay current with the latest trends while preserving their creativity in the process. This can be done by a variety of techniques, such as unique generative design or style transfer from other sources.
Real-life example: ClothingGAN is an AI tool designed to generate creative garment designs. The platform utilizes GitHub’s resources and allows designers to create innovative and unique designs efficiently (See Figure below).
Figure 13: Garments generated by ClothingGAN.
50. Turning sketches into color images
Utilizing Generative AI, the fashion industry can save both precious time and resources by quickly transforming sketches into vibrant pictures.
51. Generating representative fashion models
By leveraging generative AI to create a variety of fashion models, fashion companies can better serve their diverse customer base and accurately display their products in a more authentic manner. They can use such models for virtual try-on options for customers or 3D rendering of a garment.
Real-life example: Miami-based photographer Dahlia Dreszer incorporates generative AI into her artistic practice, treating it as an additional medium alongside photography. For her exhibition “Bringing the Outside In,” she trained AI models on her visual style, produced one AI-generated piece, and created an AI clone to guide visitors and answer questions.
She views AI as a tool that can accelerate idea generation, broaden creative possibilities, and support experimentation, while acknowledging its limitations, such as unpredictable outputs and reduced artistic control.
Dreszer argues that AI requires significant work and should be understood as part of a long creative process rather than a shortcut. She sees the current moment as an early stage in the broader integration of AI into artistic workflows, with artists determining how to adapt to rapidly evolving tools.29
52. Marketing & trend analysis for fashion brands
Generative AI can help trend analysis in fashion by:
- Bringing together a variety of techniques, such as machine learning and probabilistic programming. These techniques allow for powerful generative models that consider the customer’s desires in the fashion business.
- Generating deeply personalized options for specific consumer desires that go beyond what traditional analytics and customer demand algorithms can do.
It also improves fashion marketing capabilities by:
- Utilizing data analysis, natural language processing, and machine learning to create a highly tailored and personalized product range for the target audience
- Designing emails, website pages, captions, and ads that are tailored to a specific person’s interests and preferences in order to engage them
- Plotting creative and authentic marketing and ad content that is likely to storm search results
53. Cosmetics with generative AI
Many companies in the cosmetics industry are leveraging generative AI, with one company altering perfume development by automating formulation, reducing production time, and changing how scents are designed and evaluated.
Real-life example: Companies like Osmo utilize machine learning to analyze odor molecules and generate custom fragrances in under 48 hours, thereby bypassing the traditional months-long process that involves aging raw materials and manual compounding.
Major industry players, including Givaudan, DSM-Firmenich, IFF, and Symrise, integrate AI into regulatory checks, ingredient selection, and scent optimization.30
> Banking applications
54. Fraud detection
Generative AI offers banks a powerful tool to detect suspicious or fraudulent transactions, thereby enhancing their ability to combat financial crime. Training GANs for the purpose of fraud detection by utilizing them with a training set of fraudulent transactions helps identify underrepresented transactions.
Real-life example: Stripe integrated OpenAI’s GPT-4 to improve its ability to detect malicious activities and understand user needs by analyzing vast amounts of data, resulting in more tailored and accurate responses to customer inquiries.
By analyzing the syntax of Discord posts, GPT-4 flags suspicious accounts for Stripe’s fraud team to investigate. GPT-4 also scans inbound communications to identify coordinated malicious activity to support Stripe’s ability to manage fraud.
The integration of GPT-4 has improved Stripe’s operational efficiency with more personalized customer support and advanced fraud detection capabilities to maintain a secure platform.31
55. Risk management
By leveraging GANs, it is possible to compute value-at-risk estimations that display the potential amount of loss in certain periods or build economic scenarios for forecasting financial markets.
GANs also aid in understanding volatility by generating new and assumption-free situations founded on historical data trends.
56. Generating user-friendly explanations for loan denial
Decision makers and loan applicants need to understand the explanations of AI-based decisions, including why the loan applications were denied. A conditional GAN is a useful tool to create applicant-friendly denial explanations as in the figure below.
Figure 14: Generating User-Friendly Explanations for Loan Denials Using Generative Adversarial Networks.32
57. Data privacy protection
Synthetic AI-generated data can help banks navigate data privacy challenges by creating shareable and privacy-compliant datasets ideal for training models in credit assessment.
For more, you can check out:
> Gaming applications
58. Procedural content generation
Generative AI can generate game content, such as levels, maps, and quests, based on predefined rules and criteria. This can help game developers to create more varied and interesting game experiences.
Real-life example: Ubisoft leveraged generative AI to create the non-playable characters (NPCs) in Watch Dogs: Legion.
Each character in the game was uniquely designed with distinct appearances, behaviors, and backgrounds. This process increased the realism and immersion of the game while making the player experience more dynamic and engaging.
59. Player behavior analysis
It can be used to analyze player data, such as gameplay patterns and preferences, to provide personalized game experiences. This can help game developers to increase player engagement and retention.
60. Non-player character (NPC) behavior
Generative AI can create realistic and dynamic NPC behavior, such as enemy AI and NPC interactions. This can help game developers to create more immersive and challenging game worlds.
61. User interface design
Generative AI can design user interfaces that are intuitive and user-friendly. This can help game developers to improve the player experience and increase player engagement.
62. Game testing
Generative programming tools can be used to automate game testing, such as identifying bugs and glitches and providing feedback on gameplay balance. This can help game developers to reduce testing time and costs and improve the overall quality of their games.
> Travel applications
63. Identity verification
Generative AI in face identification and verification systems at airports can aid in passenger identification and authentication. This is accomplished by generating a comprehensive image of a passenger’s face utilizing photographs captured from various angles, streamlining the process of identifying and confirming the identity of travelers.
Real-life example: Allpass.ai developed a mobile tool that transforms smartphones into contactless ID scanners to make check-ins faster and travel processes more convenient.
This solution also integrates biometric verification and fraud detection, improving security by leveraging a global database of identity documents.
64. Personalized travel and destination recommendations
Generative AI can analyze customer data, such as past bookings and preferences, to provide personalized recommendations for travel destinations, accommodations, and activities.
> Retail applications
65. Product recommendations
Using generative models, retail tools can suggest new or alternative products to customers that they might be interested in, based on their buying history and preferences. It further predicts future customer needs and preferences, enhancing the overall shopping journey.
Real-life example: Adoric offers a tool that helps websites show product recommendations at various points in the customer journey, such as on the homepage or during checkout.
The tool uses advanced features such as Audience Targeting and Campaign Triggers to optimize customer engagement based on factors such as location and traffic source.
66. Product and display design
Generative AI can create new product designs based on the analysis of current market trends, consumer preferences, and historical sales data.
For instance, creating designs for clothing, furniture, or electronics can be an option. Personalizing the display options according to customer choice is another option.
67. Automated retail content generation
Retailers can use AI to create product descriptions, social media promotional content, blog posts, and other content that improves SEO and drives customer engagement.
68. Inventory management & supply chain optimization
Generative AI can help forecast demand for products, generating predictions based on historical sales data, trends, seasonality, and other factors. This enhances inventory control by minimizing both excess stock and shortages.
69. Virtual shopping assistants
Generative AI can power conversational virtual assistants that help customers in their shopping journey, generating responses to their queries and guiding them through the purchasing process.
> Insurance applications
70. Policy documentation
Generative AI in insurance tools can help generate policy documents based on user-specific details. It can automatically fill in the information where necessary, speeding up the process of creating these documents.
Real-life example: Lemonade Insurance implemented AI and chatbot technology, known as Maya, to manage its insurance offerings.
Lemonade’s Maya interacts with customers in real-time, collects information, and generates policy documents instantly to manage the process for renters’ and homeowners’ insurance applications.
71. Risk assessment and premium calculation
Generative AI can be used to simulate different risk scenarios based on historical data and calculate the premium accordingly.
Generative models can study historical customer data to simulate future scenarios and associated risks. Such simulations support the training of predictive models aimed at improving risk estimation and determining appropriate insurance premiums.
72. Fraud detection
Generative AI can generate examples of fraudulent and non-fraudulent claims, which can be used to train machine learning models to detect fraud. These systems help identify potentially fraudulent claims early, contributing to cost savings for insurers.
73. Customer profiling
Generative AI can be used to generate synthetic customer profiles, which can help in developing and testing models for customer segmentation, behavior prediction, and personalized marketing without breaching privacy norms.
74. Claims processing
Generative AI models can be employed to streamline the often complex process of claims management. They can generate automated responses for basic claim inquiries, accelerating the overall claim settlement process and shortening the time of processing insurance claims.
75. Policy generation
Generative AI models can generate personalized insurance policies based on the specific needs and circumstances of each customer.
Based on data about the customer, such as age, health history, location, and more, the AI system can generate a policy that fits those individual attributes, rather than providing a one-size-fits-all policy.
76. Predictive analysis & scenario modeling
Generative AI models can generate thousands of potential scenarios from historical trends and data. Insurance companies can use these scenarios to understand potential future outcomes and make better decisions.
> Manufacturing applications
77. Predictive maintenance
By using deep learning algorithms, manufacturers can predict equipment failures and maintain their equipment proactively. These models can be trained on data from the machines themselves, like temperature, vibration, sound, etc.
As these models learn this data management, they can generate predictions about potential failures, allowing for preventative maintenance and reducing downtime.
Real-life example: BlueScope collaborated with Siemens to leverage Senseye’s Predictive Maintenance platform to address operational downtime in its production lines.
Through IoT-based monitoring of machinery, BlueScope detected equipment failures earlier, which helped reduce resource waste and improve production efficiency.
78. Quality control
AI can help improve quality control processes in manufacturing. By learning from images of past products and identifying defective ones, generative AI tools can generate a model to predict whether a newly manufactured product is likely to be defective.
79. Production planning and inventory management
Generative AI models can simulate various production scenarios, predict demand, and help optimize inventory levels. It can use historical customer data to predict demand, thereby enabling more accurate production schedules and optimal inventory levels.
Business function-specific genAI Applications
> Customer service applications
80. Personalized customer responses
Conversational generative AI tools can be trained on customer data, such as past purchases, chat history, and customer feedback to create a personalized profile for each customer. When a customer sends a message, ChatGPT or other similar tools can use this profile to provide relevant responses tailored to the customer’s specific needs and preferences.
Real-life example: During the COVID-19 pandemic, Banc Sabadell partnered with Zendesk to implement an AI-powered chat system.
This virtual assistant helped manage the surge in customer inquiries by providing self-service options for common questions and routing more complex issues to human agents for resolution.
81. Multilingual customer support
The multilingual support offered by generative AI tools like ChatGPT for customer service involves using the system’s large language model capabilities to provide support to customers who speak different languages. Conversational AI tools can be trained in a variety of languages and can translate messages from one language to another in real-time.
Figure 15: An exemplary multilingual customer response generated by ChatGPT. Discover the diverse business applications of ChatGPT.
82. Quick responses to customer inquiries & complaints
Conversational tools can be trained to recognize and respond to common customer complaints, such as issues with product quality, shipping delays, or billing errors.
When a customer sends a message with a complaint, the tool can analyze the message and provide a response that addresses the customer’s concerns and offers potential solutions.
Real-life example: ServiceNow’s GenAI has increased employee self-service by 14% and customer self-service by 10%, by allowing users to intuitively find answers on their own with its self-service function. This shift reduces the load on help desks, enabling agents to focus more on engaging tasks and providing users with timely solutions.
The ServiceNow DT team has saved $5.5 million annually through this method, with 54% ITSM issue deflection rate and Now Support achieving nearly 20% case avoidance. This approach ensures quick resolutions and enhances satisfaction, as 56% of customers report positive experiences with AI-summarized solutions.33
83. Creating customer emails
Tools like ChatGPT can create personalized email templates for individual customers using the provided customer information. When composing customer emails, ChatGPT can leverage templates to create messages personalized to the recipient’s preferences and requirements.
Figure 16: ChatGPT provides an email template for a certain customer problem.
84. Replying to customer reviews
When a customer leaves a review or comment on online review platforms or your website, ChatGPT or other tools can generate a response that addresses the customer’s concerns and offers potential solutions or assistance.
85. Answering FAQs
For example, ChatGPT can be trained on a company’s FAQ page or knowledge base to recognize and respond to common customer questions.
> Finance applications
86. Personalized financial and investment advice
AI systems can tailor financial advice, risk profiles, and investment strategies using generative models that simulate financial outcomes personalized to a user’s goals and risk tolerance.
87. AP automation/invoice processing
Generative AI solutions go beyond extracting key-value pairs from documents and allow users to query documents in a flexible manner, helping unlock automation for more complex documents.
Figure 17: Invoice processing with generative AI.34
AP teams don’t need to switch their systems of record, like ERP, to take advantage of such technologies; their ERP can be enriched via plugins as outlined here: Blackbaud AP automation.
Real-life example: BBVA, Spain’s second-largest bank, collaborated with OpenAI to acquire 3,000 ChatGPT Enterprise licenses. ChatGPT Enterprise, a business-oriented version of ChatGPT, enables employees to create customized “GPTs” tailored to specific tasks or workflows.
BBVA staff across various departments, including legal, risk, marketing, talent, and finance, have developed over 2,900 GPTs. These tools perform various functions, such as interpreting risk-related terminology like “write-off” to drafting responses to inquiries from retail banking clients.
BBVA reported that early adopters have experienced an increase in productivity, with 80% of users stating that the tools save them more than two hours per week. However, concerns about measurable bottom-line impacts and the challenges of scaling the technology is still ongoing. The company highlighted the difficulties of integrating ChatGPT Enterprise with complex internal systems and databases.
The bank has since expanded to 3,300 licenses and plans further growth in 2025.
For more, see AI applications in accounts payable.
> Marketing applications
88. Content creation for marketing
Generative AI tools enable businesses to create personalized content such as product descriptions, social media posts, video ads, and email campaigns.
A recent study of over three years of research found that human-AI synergy is more likely in creative tasks than decision-based ones. In creative work like content creation, AI complements human creativity by handling repetitive tasks, while humans provide the insight and originality.35
For example, AI tools can generate headlines, structure articles, and suggest calls to action, while marketers refine messaging and ensure brand consistency. This collaboration increases efficiency without losing the creative touch that engages audiences.
As AI evolves, businesses should focus on strategically integrating AI into content workflows, rather than automating creative processes entirely.
Figure 18: AI-generated content for advertising a new electric car model by using ChatGPT.
89. Personalized customer experience
ChatGPT and other similar generative tools with their natural language processing can generate personalized content for your customers based on their preferences, past behavior, and demographics. This can help you create targeted content that resonates with your audience, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Check out conversational AI for sales to discover how it enhances customer interactions
90. Audience research
Generative AI can be used to analyze customer data such as:
- Search queries
- Social media interactions
- Past purchases to identify patterns and trends in customer behavior.
By analyzing this data, generative AI tools can help you identify your target audience’s preferences, interests, and pain points. This information can inform your marketing messaging, content, and product development.
91. Writing product descriptions
Product descriptions play a crucial role in marketing, as they provide potential customers with detailed information about a product’s features, benefits, and value. Generative tools like ChatGPT can help create compelling and informative product descriptions that resonate with your target audience.
92. Creating customer surveys
Marketers can use surveys as a valuable tool for collecting customer feedback and insights to enhance products, services, and promotional tactics. Here are some ways that generative AI can help with creating customer surveys:
- Question generation
- Organizing survey structure
- Making surveys multilingual with its translation ability
- Survey analysis
93. Generating video ads or product demos
Video generation applications in GenAI include:
- Video ads: With generative AI, businesses can create high-quality video ads that can be used on various platforms, including social media and video-sharing sites. This can help to increase brand awareness and drive conversions.
- Product demos: Video generation can also be used to create product demo videos. By using generative AI to create these videos, businesses can showcase their products in a visually appealing way, which can help to increase engagement and sales.
94. Email marketing campaigns
Leveraging generative AI for email marketing supports marketing processes by streamlining automation and increasing personalization and creativity with engaging content generation.
Generative AI tools can be utilized to generate personalized:
- Email text
- Subject lines
- Images within the email body
- Call-to-actions (CTAs).
AI email marketing tools can also enable businesses to:
- Automate email responses
- Select the target audience
- Optimize email delivery times
SEO Applications
95. Generating topic ideas for content writing
Generative tools like ChatGPT can be used for generating topic ideas for SEO content writing by utilizing its language processing capabilities to:
- Produce relevant keywords and phrases
- Analyze competitors’ content to identify gaps in coverage
- Suggest topics based on current trends and user search queries
96. Conducting keyword research
The process of including related keywords in content is crucial for a successful SEO strategy as it helps determine the terms and phrases that potential customers use when searching for products or services related to the website’s offerings.
Generative tools like ChatGPT can perform functions in keyword search optimization, such as:
- Generating keywords: It can generate a list of relevant keywords for a topic or theme by analyzing the context and language used in the provided information.
- Identifying keyword trends: It can analyze search data to identify current keyword trends and suggest terms that are likely to be popular in the near future.
Figure 19: Generating keyword ideas for B2B marketing content with ChatGPT.
97. Finding the right titles
Generative tools like ChatGPT can generate SEO-friendly titles by ensuring that the titles are:
- Descriptive and clearly convey the topic of the content
- Capable of incorporating relevant keywords that are related to the topic
- Concise and to the point, typically falling within the 60-70 character limit for optimal display in search engine results pages.
- Eye-catching and likely to attract clicks, which can help improve click-through rate (CTR) and, ultimately, SEO
98. Grouping search intent
Understanding the search intent behind a query is crucial for creating content that accurately and effectively addresses customer needs, leading to higher engagement and conversions.
Tools like ChatGPT can assist in search intent grouping by analyzing search queries and categorizing them based on the user’s intended goal or purpose, thanks to Natural Language Processing (NLP) methods. This enables companies and marketers to understand the purpose of specific search queries and refine their content and strategies to more effectively meet their audience’s needs.
99. Creating content structure
Tools like ChatGPT can assist in creating a content structure by generating outlines and organization suggestions for a given topic. This can be useful for SEO maximization because well-structured and organized content not only provides a better user experience but also helps search engines understand the context and relevance of the content.
Figure 20: ChatGPT creates the structure of content.
100. Generating meta descriptions
A meta description is an HTML attribute that provides a brief summary of a web page’s content. The meta description serves as an advertisement for the page, encouraging users to click on the link and visit the page. Therefore, meta descriptions are an important element in SEO.
ChatGPT can be used to create effective meta descriptions by generating summaries of the content that accurately and concisely describe the main topic of a page.
101. Creating sitemap codes
A sitemap is a structured XML file that lists all of a website’s pages and content. It helps search engines understand the structure and organization of a website. The sitemap code provides information about each page, such as its URL, the date it was last modified, and its priority relative to other pages on the site.
ChatGPT can be used to generate sitemap codes, producing an XML file that lists all the pages and content on a website.
> HR applications
102. Job description generation
Generative AI can be used to create job descriptions that accurately reflect the required skills and qualifications for a particular position.
Real-life example: To process and retrieve relevant resumes based on natural language job descriptions, DataToBiz developed an AI-powered resume filter. Using semantic search and large language models (LLMs), resume filtering enabled the interpretation and matching of job descriptions with resumes. The system enhanced user queries, indexed resumes, and provided contextually accurate results.
The solution also improved user satisfaction, optimizing operational efficiency, and enabled strategic talent acquisition, which would result in quicker and more accurate candidate selection.36
103. Creating interview questions
HR departments often need to develop a set of questions to ask job candidates during the interview process, which can be time-consuming. AI can generate interview questions that are relevant to the job position and that assess the candidate’s qualifications, skills, and experience.
Figure 21: ChatGPT creates a set of interview questions for a job position.
104. Generating onboarding materials
AI can generate onboarding materials for new employees, such as training videos, handbooks, and other documentation.
105. Employee support with AI chatbots
Leveraging AI tools can enhance employee satisfaction by simplifying access to information and automating routine HR processes. These systems support HR agents to efficiently manage tasks such as:
- Addressing frequently asked questions,
- Processing time-off requests,
- Managing payroll, and
- Overseeing benefits like healthcare, retirement plans, and career development opportunities.
Real-life example: IBM HR agents leverage a comprehensive library of prebuilt conversational AI automation, referred to as “skill-flows.” These automations help manage complex HR tasks while ensuring compliance with regulations and company policies. It also provides employees with a self-service chat experience powered by natural language.37
106. Increase workplace productivity
Large enterprises face a persistent challenge in optimizing the time of knowledge workers, as significant effort is spent on routine tasks such as email and meeting preparation, rather than on core responsibilities.
A six-month field experiment using Microsoft 365 Copilot demonstrated that generative AI can reduce the time spent on emails by 25%, accelerate document completion, and increase focus time, all without disrupting team workflows or meeting structures.
The most notable improvements occurred in tasks that workers could adjust independently, highlighting early productivity gains but also underscoring the need for broader organizational changes to realize full AI-driven transformation.38
> Supply chain & procurement applications
107. Demand forecasting and supply chain management
Generative AI can help businesses predict demand for specific products and services to optimize their supply chain operations accordingly. This can help businesses reduce inventory costs, improve order fulfillment times, and reduce waste and overstocking.
Explore how generative AI transforms supply chain operations by predicting demand and optimizing processes.
Real-life example: FLO, a footwear retailer, partnered with Invent Analytics to improve its omnichannel inventory management.
Invent Analytics’ forecasting solutions helped FLO reduce lost sales by 12%, optimize stock levels, and increase net profit by 4.7%. This collaboration also provided more accurate inventory distribution across their network.
108. Inventory management with AI chatbots
AI chatbots can manage procurement processes by automating tasks such as monitoring inventory levels, reordering goods, and tracking orders in real time. They also improve decision-making through demand forecasting, product categorization, and providing real-time inventory updates. Here are the benefits of leveraging AI chatbots for inventory management:
- Automated procurement: AI chatbots can reorder items automatically based on stock thresholds.
- Inventory tracking: Provide real-time updates on stock levels and order statuses.
- Customer support: Handle inquiries about product availability and order details.
- Improved categorization: Use machine learning to better classify and suggest products.
109. Transportation and routing
Generative AI can greatly enhance transportation and routing in supply chain management. By processing large volumes of data from multiple sources, it can create optimized transport plans, saving time and boosting logistics efficiency.
Key benefits include:
- Cost-effective route planning and on-time deliveries.
- Smarter vehicle and fleet management with better resource use and reduced wear.
- Adaptive routing that responds to disruptions and delays.
> Legal applications
110. Contract generation
Generative AI can generate contracts based on pre-defined templates and criteria. This can save procurement departments time and effort and help ensure consistency and accuracy in contract language.
Real-life example: Orangetheory worked with Ironclad to automate its contract management processes and leverage AI Assist to manage over 1,000 contract templates across its franchise network.
This collaboration reduced project timelines from six months to three and improved the customer experience with digital contract solutions.
111. Contract compliance
Companies have thousands of contracts with various negotiated terms. LLMs or generative AI applications with language understanding capabilities can:
- Categorize contracts
- Identify common terms
- Highlight unique or rare terms
112. Legal chatbots
Generative AI enables chatbots to deliver basic legal guidance by interpreting user queries and providing clear, accurate answers. These chatbots can assist with common legal questions, such as tenant rights or contract basics, and help users prepare simple legal documents through guided prompts.
They can also direct users to the right resources, such as legal aid services or government portals, based on the issue at hand. By automating early legal support, AI-powered chatbots make legal assistance more accessible, particularly for individuals who may face cost or accessibility barriers.
113. AI governance and compliance automation
Organizations are deploying AI governance tools for regulatory reporting, model auditing, and explainability.
Applications include:
- Policy and compliance document generation
- AI risk assessment and bias detection
- Audit trail and explainable decision summaries
Real-life example: Credo AI offers capabilities such as the AI Registry for system visibility, Governance Workspaces for compliance management, Policy Intelligence for standardized oversight, and Guardrails to ensure the responsible use of generative AI.
Available in public cloud, private cloud, and self-hosted configurations, the platform enables organizations to maintain transparency, regulatory compliance, and accountability across the AI lifecycle.39
> Sales applications
114. Sales video generation
Generative AI can be used to create personalized sales videos tailored specifically to the customer’s needs and expectations. These personalized sales videos enable sales reps to individually address sales goals, increase personal relationships with customers, and generate more leads.
Real-life example: Xerox partnered with Synthesia’s AI avatar video platform to cut down on video production costs by 50% and reduce the time needed to create training content by 30%.
The platform also allowed Xerox to localize training materials for its global workforce while improving engagement and knowledge retention for over 1,000 sales reps.
115. Sales coaching
Generative AI can be used to provide personalized sales coaching to individual sales reps, based on their performance data and learning style. This can help sales teams improve their skills and performance and increase sales productivity.
116. Sales forecasting and pipeline optimization
Generative AI can analyze historical sales data and generate forecasts for future sales. So, sales teams can optimize their sales pipeline and allocate resources more effectively.
117. Lead identification and qualification
AI can be used to identify potential sales leads based on customer data and behavior, and qualify leads based on their likelihood to convert. Also, it can generate customized sales tactics and campaigns for generating leads.
> Audit applications
118. Audit reporting automation
Manual processes, such as reporting, could be time-consuming and error-prone. Generative models like ChatGPT can help auditors automate repetitive tasks, such as paperwork and reports. Specifically, they can produce standardized reports (such as the figure below) that offer consistency in how findings are presented.
Figure 22: Generating audit reports with OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
Real-life example: KPMG collaborated with MindBridge to leverage AI for analyzing financial data and automating audit processes.
This partnership increased the accuracy and efficiency of audits by using AI to detect anomalies and flag risky transactions. It enabled KPMG to provide more reliable financial insights to its clients.
119. Data analysis of documents
Audit processes regularly analyze extensive financial and operational datasets.
ChatGPT can automate some of these data analysis duties, such as in:
- Performing computations
- Aggregations
- Dataset comparisons
120. Real-time risk monitoring
Generative AI tools can also be helpful in real-time risk monitoring. Auditors engage with the model to explore the organization’s operations, control measures, and business context.
ChatGPT, for example, can assist auditors in assessing risk levels, identifying priority areas for further investigation, and gaining insights into potential hazards.
121. Pattern recognition and anomaly detection
Generative AI can help auditors spot and flag audit abnormalities for further examination. When incorporated with human evaluation correctly, generative AI tools can be useful in identifying potential fraud and enhancing internal audit functions.
Auditors can use generative AI models’ natural language processing capabilities to reveal potential risks that might be difficult to identify manually by feeding it relevant data and asking it to look for odd or unexpected patterns.
122. Training auditors
In audit, ChatGPT can train auditors by offering them expertise, explanations, and examples that are relevant to their jobs. It can offer educational materials such as:
- Conceptual knowledge
- Case studies
> Research & Development (R&D) applications
123. Team collaboration for R&D teams
Generative AI can function as a collaborative teammate in high-level decision-making and problem-solving. By offering suggestions, evaluating trade-offs, and synthesizing knowledge across domains, AI tools can enhance interdisciplinary teamwork.
Real-life example: A study was conducted with 776 professionals at Procter & Gamble to assess the impact of AI, specifically GPT-4, on teamwork and individual performance in product development tasks.40 Key findings from the study include:
- Performance enhancement: Individuals assisted by AI performed on par with traditional two-person teams without AI, indicating that AI can replicate the benefits of human collaboration. Teams utilizing AI showed the highest performance levels, particularly in producing top-quality solutions.
- Expertise integration: AI assistance enabled both commercial and R&D professionals to develop balanced solutions that integrated technical and market perspectives, effectively bridging traditional expertise silos.
- Efficiency gains: Participants using AI completed tasks 12-16% faster than those without AI, while also generating more detailed and extensive solutions.
- Emotional impact: AI users reported increased positive emotions, such as excitement and enthusiasm, and decreased negative feelings, like anxiety and frustration, compared to their non-AI-using counterparts.
124. Generative AI in AI research
As the demand for generative capabilities increases, researchers are exploring new architectural innovations and training methods to improve efficiency, scalability, and performance.
This includes addressing challenges such as computational cost, memory limitations, and the ability to handle longer context windows while maintaining high-quality outputs.
Real-life example:
According to recent research, a new neural architecture called the Retentive Network (ReN) has been proposed as an alternative to Transformers for large language models.
ReN introduces a retention mechanism that replaces traditional attention, offering linear time and memory complexity for improved efficiency on long sequences. It combines the memory advantages of recurrent models with the parallel training capabilities of Transformers through a method known as linear recurrent decomposition.
Experimental results show that ReN matches or exceeds Transformer performance on key benchmarks while enabling faster inference and reduced resource consumption.41
> Productivity and automation Applications
125. AI workflow agents
AI agents can perform end-to-end tasks by chaining reasoning, memory, and actions across applications such as CRM, Slack, or Jira.
Applications include:
- Document generators and summarization assistants
- Presentation makers
- Web browser assistants
- Automated meeting follow-ups
- Workflow orchestration between enterprise tools
For example, we benchmarked AI-powered Excel tools to evaluate their accuracy, features, and pricing. Here are some of the outcomes:
- Claude Max: Offers the highest precision and most user-friendly experience.
- R2 Copilot: Performs well on basic tasks but struggles with more complex calculations.
- Quadratic: Stands out for its powerful visualization features and coding capabilities in Python and PHP.
- Tryshortcut: Provides thorough explanations and analytical functions, making it ideal for financial modeling.
- GPTExcel: Excels in supporting multiple languages, making it suitable for international teams.
Generative AI applications with use cases and examples summary
*An industry, business function, or other area of application
Conclusion
Generative AI is rapidly expanding across industries and business functions, enabling new levels of content creation, personalization, automation, and decision-making. From creating video ads and personalized lesson plans to managing workflows in legal, HR, and finance, its applications are diverse and increasingly practical.
However, adoption requires thoughtful implementation. Accuracy, ethics, privacy, and model limitations still present challenges. While generative AI holds clear promise, success will depend on pairing these tools with human oversight, domain knowledge, and strategic integration into existing systems.
FAQ
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence algorithms designed to create new content or data that is similar to human-generated examples. This can include text, images, music, and other types of media. These AI systems learn from a large set of existing data and then use that knowledge to generate new, original content that resembles the learned material.
GPT by OpenAI: This is an advanced language model series known for its ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text based on given prompts. It’s used in applications like chatbots, content creation, and language translation.
DALL-E by OpenAI: A specialized AI for generating images from textual descriptions, DALL-E is known for its creativity and ability to create complex and detailed images based on specific prompts.
DeepMind’s AlphaFold: This AI system is used for predicting protein structures with remarkable accuracy, which is a significant advancement in biological research and drug discovery.
Google BERT: Although primarily a language understanding model, BERT has significantly improved the way Google’s search engine understands and processes natural language queries.
ChatGPT is a specific type of generative AI. While generative AI broadly refers to AI systems that create new content, like text, images, or music, ChatGPT focuses specifically on generating human-like text based on the input it receives, often used for conversation, answering questions, and similar language-based tasks.
Reference Links
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.

Comments 6
Share Your Thoughts
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
thanks for these examples.
Thank you!
Real examples, thanks
The examples are real.
The examples were pretty realistic.
This is comprehensive and useful Cem, thanks for documenting this.
The examples were pretty realistic