This article, will analyze the top use cases of ChatGPT in audit, such as
- Automating audit responses
- Identifying anomalies
- Training and helping auditors
In addition, we will also explore the challenges of implementing ChatGPT in auditing practices and present a framework for establishing an effective collaboration between the human auditor and ChatGPT.
5 Use Cases of ChatGPT in Audit
Reporting automation
Manual processes, such as reporting, could be time consuming and error-prone. ChatGPT can help auditors automate repetitive tasks, such as paperwork and reports. Specifically, it can:
- Produce standardized reports (Figure 1) that offer consistency in how findings are presented
Figure 1. Introduction of ChatGPT generated sample audit report

Source: OpenAI
Data analysis
Audit programs involve the frequent analysis of large swaths of financial and operational data.
ChatGPT can automate some of these data analysis duties, such as in:
- Performing computations
- Aggregations
- Dataset comparisons
Data sharing is an issue for auditors. Still, they can engage with ChatGPT for sample calculations and questions, and the model can then analyze the data to produce insights, trends, and patterns (Figure 2). This can save the time and effort required for manual data analysis, freeing up auditors to concentrate on analyzing the findings and coming to insightful conclusions.
Figure 2. The Introduction of a sample ChatGPT conducting data analysis in an audit report.
Source: OpenAI
Real-time risk monitoring
ChatGPT can also be helpful in real-time risk monitoring. Auditors can interact with the model to discuss the organization’s activities, control systems, and business environment. ChatGPT can assist auditors assess risk levels (Figure 3), identify priority areas for more investigation, and get insights into potential hazards.
The accuracy and depth of risk assessment can be improved by auditors by utilizing the model’s knowledge and skills. Figure 3 displays 4 possible uses of ChatGPT in real-time risk monitoring:
Figure 3. Four uses of ChatGPT in real-time risk monitoring according to model itself

Source: OpenAI
Pattern recognition and anomaly detection:
Large datasets may reveal trends, patterns, or outliers indicating dangers or abnormalities.
ChatGPT can help auditors to spot and flag these abnormalities for further examination. When incorporated with human evaluation correctly, ChatGPT can be useful in identifying potential fraud and enhancing internal audit functions.1
Auditors can use the model’s natural language processing capabilities to reveal potential risks that might be difficult to identify manually by feeding it relevant data and asking it to look for odd or unexpected patterns.
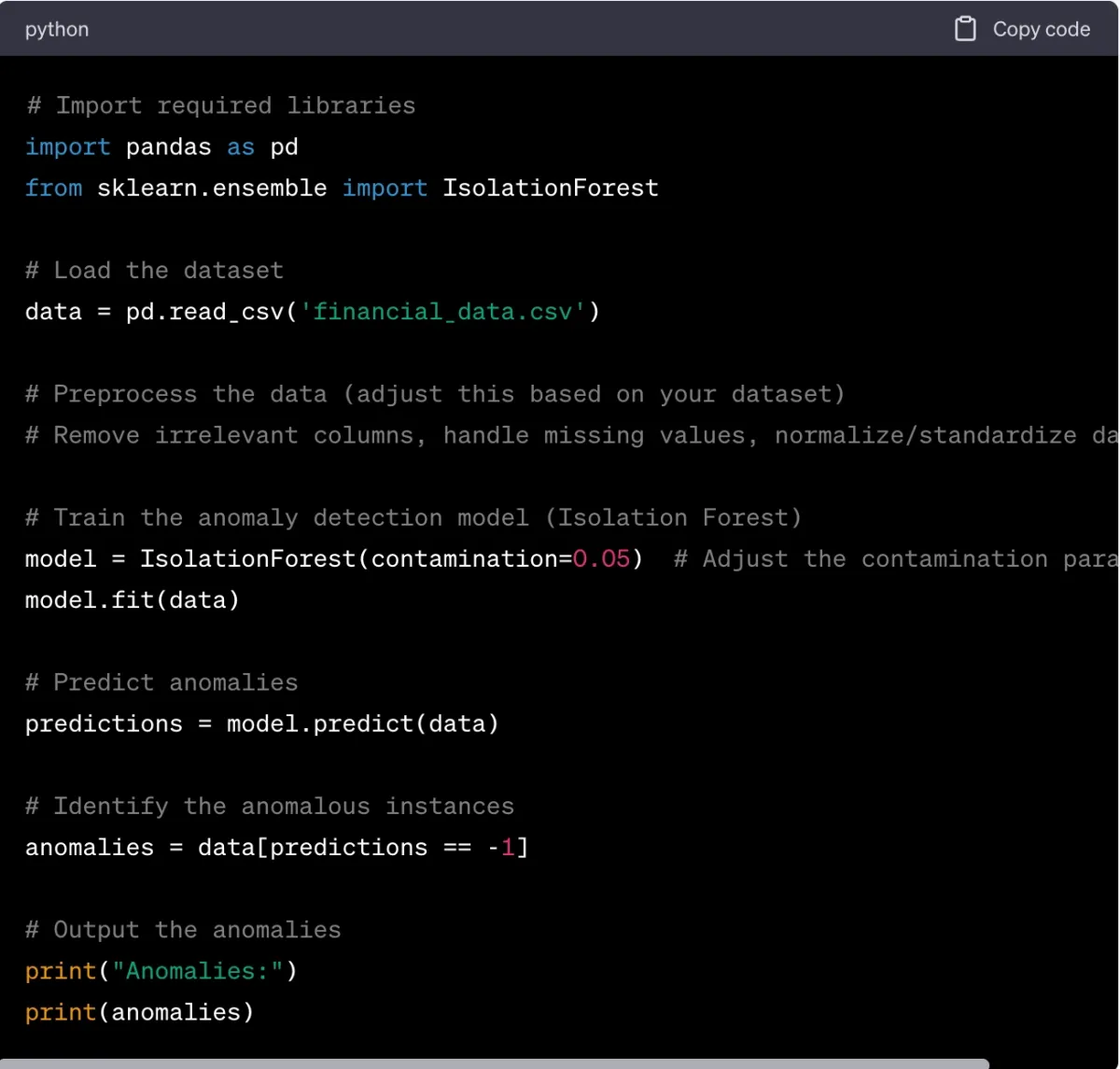
As Figure 4 displays, ChatGPT can generate python codes to detect anomalies. The code trains an anomaly detection model using the Isolation Forest algorithm from the Scikit-Learn library. Anomalies in the dataset are then predicted, and based on the model’s output, it determines which instances are considered as anomalies.
Figure 4. Python codes generated by ChatGPT to detect anomalies
Further case studies reveal that GPT was tested to depict issues such as reentrancy attacks. 2
Training auditors
ChatGPT is widely used in education to help students, teachers, and researchers.
In audit, it can train auditors by offering them expertise, explanations, and examples that are relevant to their jobs.
- Conceptual knowledge: Auditors can ask ChatGPT about auditing concepts, rules, and best practices. It can give inspectors explanations and examples to help them understand complicated topics and the basic ideas behind them.
- Case studies: With relevant data provided by the auditor, ChatGPT can model real-life situations and give inspectors case studies to look at. Using the provided information, ChatGPT then creates a hypothetical situation that includes pertinent financial data, documents, and any other elements that could be required. These scenarios can be examined and discussed by auditors to help them develop their auditing methods or techniques.
- Review and comments: Auditors can ask ChatGPT for comments on their audit work or strategies they want to try. They can talk about their results, methods, or ideas for answers and get advice or criticism from ChatGPT. Here are 2 ways (Figure 5) auditors can benefit ChatGPT in reviewing:
Figure 5. Two ways auditors can benefit ChatGPT

7 challenges to consider when using ChatGPT in an audit
When using ChatGPT’s features in the audit process, human oversight and teamwork are the most important factors.
Even though ChatGPT can be helpful and simplify some parts of auditing, it shouldn’t be seen as a replacement for human auditors. Instead, like any AI model, it should be seen as a tool that improves human judgment and enhances their knowledge.
Here’s why human supervision and employee-robot collaboration are important in auditing:
Understanding and interpretation of context:
ChatGPT, as an AI model, cannot completely comprehend (Figure 6) the subtleties, ramifications, and context of the audit tasks and objectives.
Human auditors bring their expert judgment, sector expertise, and comprehension of the particular conditions of the business to the table. They can give the essential context and, using their knowledge, interpret the results produced by ChatGPT. Human auditors can evaluate the usefulness, accuracy, and applicability of the data provided by ChatGPT and take appropriate action.
Figure 6. Comparison of ChatGPT and professional human auditor
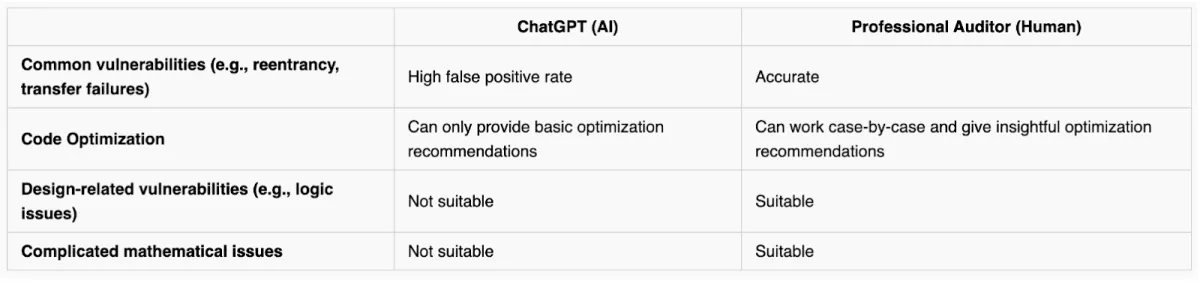
Source: Certik.3
Communication:
A key component of auditing is having effective communication, for instance, with stakeholders.
Communication of audit findings, suggestions, and the assurance given to stakeholders is crucial and is best done by human auditors. They can adjust the message to the audience, respond to inquiries, and offer more insights outside of what ChatGPT can.
Human auditors are essential for building trust and maintaining open lines of communication with stakeholders.
Accountability:
ChatGPT can help auditors, but ultimately, the buck stops with the human worker.
The auditors are responsible for the:
- Choices they make
- Quality of the audit work
- Maintenance of professional standards
Human oversight ensures that inspectors are held accountable and do their jobs with the right amount of care.
Learning how to use ChatGPT effectively in internal auditing
Auditors can design the GPT in a format that allows them to focus only on audit questions. In this way, they can get unique answers from GPT to the auditing process. Internal Audit GPT is an example of this. Through this GPT you can access generic services such as:
- template executive summary report
- finding and sorting risks
- remedition plan request
- getting information about the compliance process
Figure 7. Example of designed GPT for specific audit purposes

Facilitate collaboration between human auditors & ChatGPT
ChatGPT as a language model is a remarkable development. We’ve covered +40 ChatGPT’s use cases before, including: ChatGPT as a language model is a remarkable development. We’ve covered +40 ChatGPT’s use cases before, including:
- Textual (i.e., content creation, translation)
- Coding
- Educational
- Marketing & SEO
- Customer service
- Human resource
However, the challenges we listed are still persistent. Regarding those, auditors must master how to interface with and analyze AI technologies like ChatGPT due to their rapid development. AI technology training is a must for auditors because of these reasons:
Awareness in AI fundamentals:
In order to interact with AI technologies like ChatGPT, auditors need a basic awareness of AI concepts, principles, and procedures. This includes understanding the many categories of AI models, their constraints, and their uses in the auditing industry.
Auditors can more accurately evaluate the capabilities, potential hazards, and acceptable use cases for AI in auditing by having a basic understanding of AI.
Evaluating AI systems:
Auditors should be capable of assessing AI systems, especially ChatGPT-like models.
This entails evaluating the fairness, precision, and dependability of AI algorithms as well as comprehending their advantages and disadvantages.
The design of the model, the training data used, and the procedures for continuing monitoring and validation of the AI system should all be able to be critically assessed by auditors. With the use of this knowledge, auditors may decide wisely whether to use AI in the auditing process.
Identifying potential biases in AI systems and evaluating data quality:
Auditors must be skilled at evaluating data quality and seeing potential biases in AI systems.
This entails being aware of the implicit and explicit biases present in training data, as well as their possible effects on audit results.
The representativeness and integrity of the data used to train AI models should be evaluated by auditors, and they should be able to put policies in place to lessen biases that can affect the objectivity and fairness of audit procedures.
FAQ
How can ChatGPT assist internal auditors?
ChatGPT can support internal auditors by helping them review documents, analyze data, and prepare internal audit reports. It can also assist in the automation of repetitive tasks during the internal auditing process.
Can ChatGPT help with both internal and external auditing?
ChatGPT can assist with both. Internal auditors can use it to generate reports and analyze risk management practices, while external auditors can employ it for reviewing financial statements and other external auditing task
How does ChatGPT contribute to the preparation of internal audit reports?
ChatGPT can summarize findings, suggest report structures, and analyze internal auditing data, making it easier for internal auditors to produce accurate and timely internal audit reports.
Can ChatGPT improve risk management practices during internal audits?
Yes, ChatGPT can analyze large datasets to identify potential risks and assist internal auditors in improving risk management practices.
What role does ChatGPT play in reviewing financial statements?
ChatGPT can help internal and external auditors by analyzing financial statements, identifying inconsistencies, and providing insights into financial data trends.
How can external auditors benefit from ChatGPT?
External auditors can use ChatGPT for tasks such as reviewing large volumes of data, summarizing reports, and generating insights based on financial statements and external auditing criteria.
Is ChatGPT capable of assisting internal auditors in regulatory compliance?
ChatGPT can review compliance-related documents and regulations, helping internal auditors ensure that their findings and reports align with regulatory standards.
How does ChatGPT support collaboration between internal and external auditors?
ChatGPT can facilitate the sharing of information, reports, and insights, enabling both internal and external auditors to collaborate more effectively on auditing tasks.
Can ChatGPT identify areas of improvement in internal auditing processes?
ChatGPT can analyze audit data, review internal audit reports, and suggest areas for improvement, helping internal auditors enhance their processes.
Is ChatGPT secure enough for use in internal and external auditing?
The security of ChatGPT depends on its deployment and integration. Both internal and external auditors should ensure that they use secure platforms and follow best practices for data confidentiality.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.