The World Economic Forum (WEF) identifies climate change and environmental issues as the greatest threats to the global economy.1 My academic experience on sustainability practices points that embracing digital transformation and sustainability initiatives are strategic actions executives can take to move toward a more sustainable future.
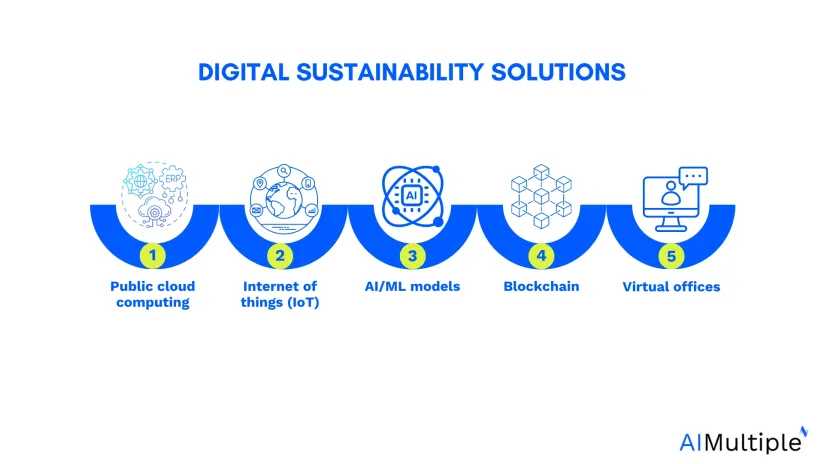
Explore the definition and importance of digital sustainability as well as 5 essential digital sustainability solutions that can help organizations to reduce its social and environmental impact while also improving its operating efficiency:
Top 5 digital technologies for sustainable digital transformation
1. Public cloud computing
Direct emission reduction
By using public cloud services, enterprises can cut their IT-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by over 6%, which is equivalent to the carbon emissions of more than 20 million cars.2
Organizations can outsource their IT requirements and can use cloud capabilities such as advanced analytics, AI models, data storage, and more by paying a subscription fee to the cloud service provider.
Organizations generally prefer cloud services because they reduce hardware expenditure for digital transformation. However, they are also environmentally friendly because distributing IT services to third-party sources saves energy use. If each corporation has its own data center, the amount of electricity used to run and cool each one is excessive.
On the other hand, centralization of data sources reduces energy consumption by 98%, so the GHG emissions.3
It is important to note that firms that use public cloud platforms for their daily operations may suffer non-optimal cloud costs, which also means non-optimal energy use. As a result, cloud cost optimization is a method of lowering a company’s carbon footprint as well as monthly expenses.
Indirect contribution of cloud systems to sustainability
Besides direct carbon emissions reduction, public cloud technologies can help businesses identify which activities are causing them to release too much GHG and visualize this information. Firms can calculate their carbon footprint and fill out their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reports more easily by utilizing public cloud computing and hence real-time data processing.
Figure 2. Data visualization example of a cloud carbon software
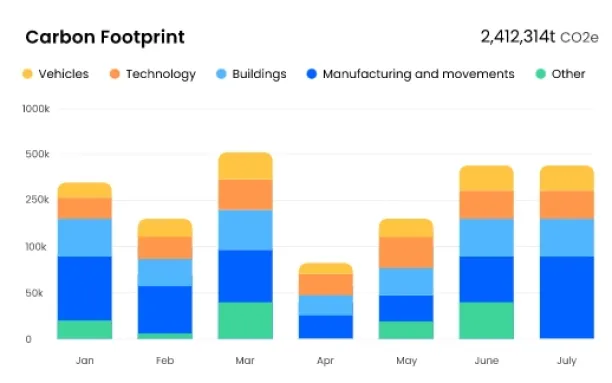
Source: Net04
Specialized cloud systems for calculating carbon footprints may easily import data of operation specific carbon emissions, which is required to calculate your company’s carbon footprint. Simulation capabilities in such solutions assist you in determining ways for minimizing your corporate carbon footprint and that of your products.
2. Internet of things (IoT)
Thanks to the sensors, smart devices such as smart factories/offices, smart vehicles, and smart tractors can collect data from the environment in which they are deployed. Their immediate interconnection aids companies in reducing transportation and heating/lighting energy consumption, as well as the amount of water, pesticides, and fertilizer used in agriculture, as follows:
Minimize office/factory energy consumption
Smart offices/factories can use sensors to optimize heating/cooling and lighting operations based on needs. For example, if no one is working in the office, lights/heating may be turned off automatically, or the cooling system of servers may be activated automatically in response to data center heat.
These solutions provide both comfort and a reduction in GHG emissions. Big hotel chains, for example, use IoT for their HVAC systems to improve efficiency and sustainability.5
Optimize transportation route
IoT has the potential to cut GHG emissions in two ways: Firstly, organizations may use track-and-trace systems to monitor the movement of raw materials, intermediate items, and final goods instantaneously, allowing them to improve their operations and reduce waste.
Second, IoT may be used to nudge drivers to drive trucks in a more ecologically friendly manner (e.g. driving with low rpm). Also, smart truck sensors can allow fleet firms to detect even modest degradation, and maintain them before leading to increased GHG emissions. Michelin launched such an initiative in 2013, which lowered oil use by 2.5 liters per 100 kilometers.6
Optimize warehouse temperature and humidity
Protecting the quality of some commodities requires storing them in specific circumstances, such as a specific temperature and humidity. Constantly changing the volume of commodities within the warehouse makes maintaining a steady temperature and humidity difficult.
Warehouse dynamism allows businesses to maintain the same conditions while spending less electricity. A median warehouse, on the other hand, can lower its GHG emissions by roughly 30% by employing led lights, smart sensor based lighting, and smart HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems.7
Produce enough energy
Energy companies can assess electricity consumption in real time using data from smart devices. As a result, supply will always be close to demand. Since storing energy is still challenging for energy companies, they can improve operational efficiency and minimize GHG emissions this way.
Digital twin technology is a sustainable innovation. General Electric’s (GE) optimized digital wind farms using sensors and digital twin technology. Each wind farm can create up to 10% more green energy as a result of the digital wind farm initiative, which helps to enhance our worldwide renewable energy mix.8
Reduce pesticide, fertilizer, and water consumption
Sustainability entails not just lowering GHG emissions but also removing pollutants from the land and water. The EU has decided to cut pesticide and fertilizer consumption by 50% and 20%, respectively, by 2030.9 Smart sensors can be used to analyze soil and guide farmers to use the necessary amounts of pesticide and fertilizer. Irrigation sensors can also detect soil dryness and optimize water consumption.
You can also read our 7 Ways to Improve Your Supply Chain Sustainability article.
3. AI/ML models
AI/ML models can improve global GDP by 4.4 percent while reducing GHG emissions by more than 4% until 2030.10
Figure 3: Global impact on AI on GHG emissions and GDP
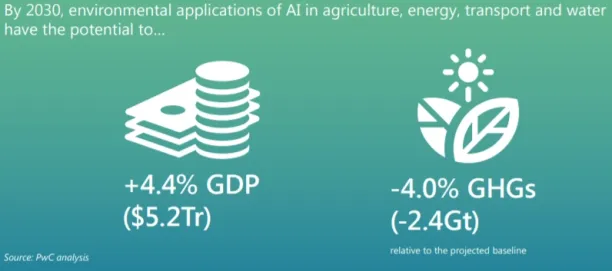
Source: PwC11
Effective prediction capabilities of AI/ML models can optimize commodities transportation-supply, and agriculture efficiency. By doing so, they can reduce resource consumption for optimizing energy usage for future generations.
Because of the growing importance of artificial intelligence/machine learning models and sustainable development, AI/ML specialists and sustainability specialists are expected to grow most quickly from 2023 to 2027 as a fraction of present employment. Similarly, digital transformation specialists are expected to be included in the top 10 fastest growing jobs.12
Figure 4: Top 10 fastest growing jobs
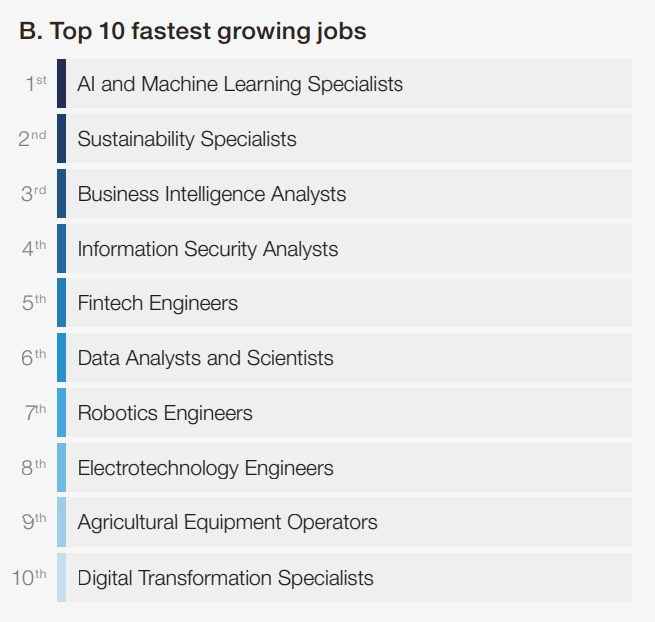
Source: World Economic Forum13
This figure shows that there are 3 jobs related to digital transformation and sustainability included in the top 10 fastest growing jobs according to expectations of correspondents of WEF survey.
Transportation optimization
Deploying AI for transportation optimization can cut world GHG emissions by 1% until 2030 and have a positive effect on environmental sustainability.14 They are energy efficient devices since
- Autonomous vehicles powered by AI can be programmed to travel in the most environmentally responsible way possible.
- AI powered autonomous vehicles have greater storage area since there is no need for a space for a driver. Thus, fewer trucks can distribute the same amount of goods.
- Supply chain managers can use traffic and route optimization algorithms to determine the most ecologically friendly routes to reduce GHG emissions.
Supply optimization
AI/ML models can reduce waste or energy usage for preserving inventories by forecasting demand. Therefore, AI/ML models will have the greatest impact on reducing GHG emissions in the energy sector, since energy storage is currently inefficient or unattainable in some circumstances.
Also, hyperlocal weather forecasting helps energy companies to better locate their solar panels or wind turbines. The contribution of AI/ML models to GHG emission reduction in the energy sector is estimated to be around 2% till 2030.15
Agriculture efficiency
AI/ML models can be used to estimate the appropriate split of forest and agricultural regions for land-use management. Farmers can plant their crops on land that requires minimum irrigation or fertilizer thanks to these models.
Additionally, AI/ML models’ hyper-local weather forecasting capabilities improve resource efficiency for farmers. The contribution of AI models to agriculture can reduce GHG emissions by roughly 0.3% until 2030.16
4. Blockchain
AIMultiple considers blockchain as a critical digital technology for environmental sustainability. Blockchain enables parties to share data securely and transparently. Thus, blockchain technology improves supply chain visibility, which is important because for many businesses, indirect activities related to the supply chain account for more than 80–90% of organizational carbon footprint.17
Figure 5. Indirect activities (gray) account for the bulk of GHG emissions for some sectors.
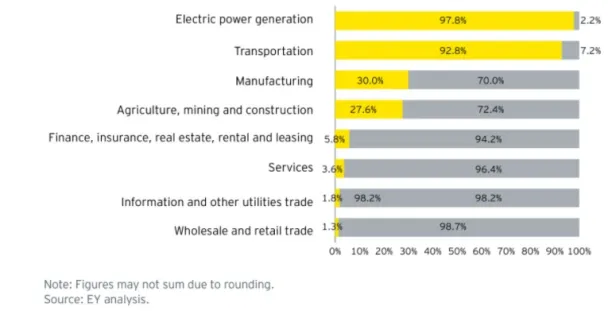
Source: EY18
Moreover, tracking supply chains closely assists companies in measuring their businesses’ circularity gap since companies can measure circular economy metrics such as:
- Percentage of non-virgin material used
- The exact recycling rate of the products
- Percentage of circular water consumption and so on.
For instance, Renault plans to invest more into Blockchain technology to enhance visibility regarding recycling operations. For more details read supply chain related blockchain case study.
Due to data validation use cases of blockchain, companies can:
- Execute supplier code of conduct accurately: Supplier code of conduct is an ESG metric where companies determine environmental and social sustainability criteria for supply chains. Businesses can assess whether or not their suppliers are sincere environmentalists by using automated and transparent data validation applications of blockchain.
- Increase product stewardship: Blockchain allows firms to monitor their products easily. So they can switch to a business model where customers rent the goods.
- Reduce the expense of non-compliance: International treaties and agreements like the Paris Climate Agreement force states to modify their laws. Organizations can lower the costs associated with non-compliance by exchanging data with officials in a transparent and automated manner with blockchain.
To learn more about product stewardship and circular economy best practices you can read Circular Economy Best Practices for Businesses.
5. Telecommuting technologies and virtual offices
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown that technological infrastructure can enable companies to move remote or hybrid business model. Because offices and daily commutes are significant sources of GHG emissions, digital technologies such as Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams, can significantly cut GHG emissions and electronic waste.
As one of the sustainable practices, supporting digital transformation in seminars and training programs can also help businesses to minimize their environmental footprint. Employment of digital tools such as virtual reality for education when an intern or student needs hands-on experience to grasp the subject helps to reduce energy consumption19
The Oxford Medical Simulation platform, for example, uses virtual reality glasses to assist interns in interacting with unconscious patients.20 They learn how to diagnose and treat such patients thanks to this digital platform.
What is digital sustainability?
Digital sustainability is a sub-branch of digital transformation where firms aim to reach their sustainable development goals by utilizing new technologies such as:
- Blockchain
- Artificial intelligence
- IoT and so on.
Importance of digital transformation
Organizations that improve their sustainability by using effective digital solutions are more likely to become industry leaders in the future.21
Figure 1. Odds of adoptation of sustainable transformation and technology for successful businesses
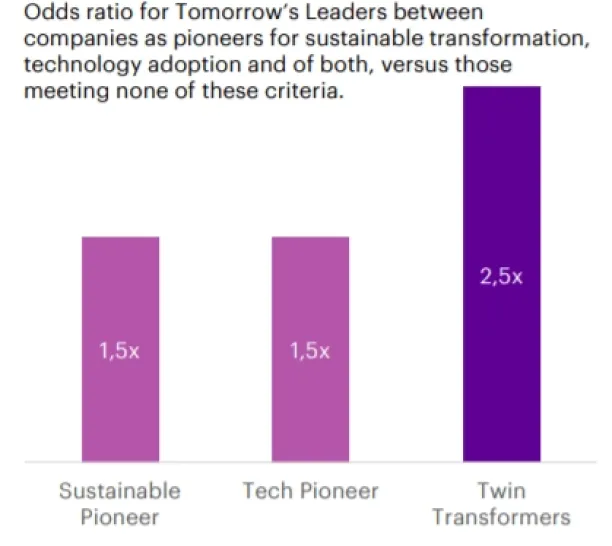
Source: Accenture22
The rationale behind digital sustainability is increasing corporate efficiency to promote sustainability. Consider a transportation company: by using route optimization software to reduce the number of right and left turns. The company can achieve the same economic value while
- consuming less energy, as vehicles use less fuel
- operating in a more environmentally-friendly manner by reducing carbon emissions.
Thus, thanks to digital sustainability firms can reduce:
- Per product carbon footprint
- Corporate greenhouse gas emissions
- Usage of virgin materials and natural resources
- Social inequalities which is one of the UN sustainable development goals of 202423
while enhancing operational efficiency.
It is crucial to remember that, if not implemented carefully, digital transformation can make the climate situation worse.24 For instance, businesses may be able to manipulate customers to increase their consumption by combining AI/ML models with big data. The UN released its action plan for sustainable digital transformation in response to this concern.25
To learn more about the importance of ESG reporting for scaling up your business you can read our article 4 Ways ESG Reporting Will Boost Your Business Performance. To find which metrics to include in the report you can read our 3 Types of Metrics CEOs Must Use in ESG Reporting article.
You can also check our list of digital transformation consultants.
External Links
- 1. The Global Risks Report 2024. World Economic Forum.
- 2. The green behind the cloud. Accenture.
- 3. The Carbon Benefits of Cloud Computing.
- 4. Net0 | Enterprise AI Platform for Corporate Sustainability.
- 5. Luxury hotel retrofit maximizes efficiency. Schneider Electric.
- 6. EFFIFUEL™ from MICHELIN® solutions Delivers Fuel Savings – Motorindia.
- 7. King, J., & Perry, C. (2017). Smart buildings: Using smart technology to save energy in existing buildings (pp. 1-46). Washington, DC, USA: Amercian Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy.
- 8. Digital Wind Operations Optimization from GE Renewable Energy. General Electrics.
- 9. Language selection | Agriculture and rural development.
- 10. How AI can enable a sustainable future. PwC.
- 11. How AI can enable a sustainable future. PwC.
- 12. The Global Risks Report 2024. World Economic Forum.
- 13. The Global Risks Report 2024. World Economic Forum.
- 14. How AI can enable a sustainable future. PwC.
- 15. How AI can enable a sustainable future. PwC.
- 16. How AI can enable a sustainable future. PwC.
- 17. Why calculating your company’s carbon footprint matters | EY - US. MIT OpenCourseWare
- 18. Why calculating your company’s carbon footprint matters | EY - US. MIT OpenCourseWare
- 19. Haleem, A., Javaid, M., Qadri, M. A., & Suman, R. (2022). Understanding the role of digital technologies in education: A review. Sustainable operations and computers, 3, 275-285.
- 20. Digital Technology and Sustainability in Europe | Accenture. Accenture
- 21. Digital Technology and Sustainability in Europe | Accenture. Accenture
- 22. Digital Technology and Sustainability in Europe | Accenture. Accenture
- 23. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2024. United Nations. Accessed: September/10/2024.
- 24. Wu, C. J., Raghavendra, R., Gupta, U., Acun, B., Ardalani, N., Maeng, K., … & Hazelwood, K. (2022). Sustainable ai: Environmental implications, challenges and opportunities. Proceedings of Machine Learning and Systems, 4, 795-813.
- 25. Action Plan for a Sustainable Planet in the Digital Age | UNEP - UN Environment Programme.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.