Conversational AI consists of software that enables human interaction, including chatbots powered by LLMs, voicebots, and interactive agents. These tools help users ask questions, get support, or complete tasks remotely.
To simplify selecting the right conversational AI, we’ve categorized conversational AI to help executives find the best fit:
| Types of Conversational AI | Best for | |
|---|---|---|
1. | E-commerce, customer support, healthcare (basic tasks) | |
2. | Automotive, banking, smart homes | |
3. | Legal services, retail, complex customer service | |
Comparison of 3 types of conversational AI
Advancements in AI integration technology have made it increasingly difficult to classify different types of conversational AI systems, as many solutions share similar capabilities, such as creating natural conversation flows and adapting to various business needs. To help distinguish them, the table below highlights each solution’s key features.
| Type | Highlight Feature* | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| AI Chatbots | Easily adaptable | Doesn’t have voice activation features |
| Voice Bots/Assistants | Convenient for multitasking | Depends heavily on accurate speech recognition |
| Interactive Voice Assistants (IVAs) | Integrations to contact center systems | Highest development cost |
*Other models can also have this feature, but we recommend this solution if this is your top priority.
1. AI chatbots
Large Language Model (LLM) -based chatbots
Modern AI chatbots use Natural Language Processing (NLP), generative AI, and large language models (LLMs) to conduct human-like conversations. NLP technology forms the foundation for these systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Unlike their rule-based predecessors, these advanced systems don’t simply follow a programmed path; they generate original responses by processing and understanding user intent and context.
Key benefits of AI chatbots:
- Complex query resolution with advanced reasoning: Sophisticated NLP algorithms allow LLMs to understand intent, sentiment, and context in user queries, enabling them to handle complex inquiries.
- Digital workforce support: AI chatbots can be fine-tuned with specialized knowledge to assist employees and customers with complex tasks, functioning as AI copilots rather than simple assistants.
- Personalized interactions: GenAI chatbots create personalized interactions by adjusting their tone, vocabulary, and response complexity based on user language patterns analyzed by NLP.
- Multilingual capabilities: Modern NLP and LLM technologies demonstrate near-native fluency across hundreds of languages, accurately processing linguistic nuances in each.
Examples
Recent advancements in conversational AI have introduced some notable models:1
- Zoho SalesIQ’s Zobot: Zobot is an AI chatbot platform designed to automate customer interactions across multiple channels. Using Zoho, you can create chatbots without coding through a codeless drag-and-drop builder provided by the platform. It enables you to develop chatbots that can converse in up to 30 languages and automatically detect the visitor’s language. It can implement multi-channel deployment across various platforms.
- GPT-4.5: OpenAI released a new model of ChatGPT in February 2025. The new model is multimodal, meaning that it can process and generate text, images, and audio.
- Claude 3.7 Sonnet: Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet can be used for coding, multistep workflows, and image text extraction. It also has the artifacts feature, which allows collaborative document generation.
- Custom GPTs: You don’t have to use Conversational AI just as it is presented to you. Projects like CustomGPT can enable you to develop this technology according to your purposes.
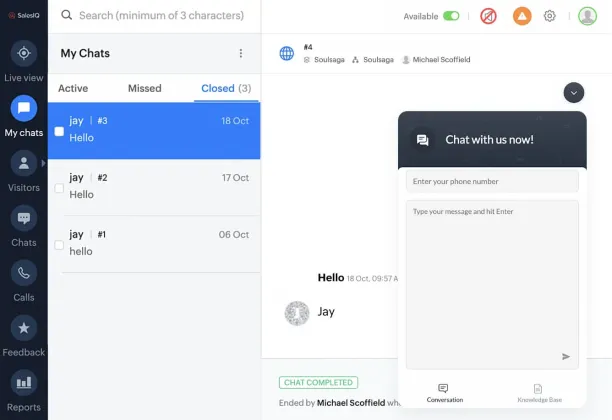
Figure 1. The live chat widget feature of Zoho SalesIQ2
Customizing LLM-based chatbots (Adding rules)
AI chatbots can be customized to meet various company demands by integrating business-specific rules during their training process. Typically, the customization process consists of multiple steps:
- Supervised fine-tuning: All models learn general language patterns by processing large volumes of text in pre-training. Then, developers improve the chatbot’s behavior by providing it with carefully chosen examples that demonstrate the appropriate answers and conversational tone.
- Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF): Human trainers improve the model, evaluate the chatbot’s responses, and assign a score based on how well they match the company’s regulations. This recurrent feedback loop guarantees that the chatbot keeps improving in providing accurate responses that satisfy business needs.
- Targeted prompt engineering: Structuring inputs to guide the chatbot toward desired answers without changing its fundamental model. This method is helpful for less retraining.
By combining fine-tuning, RLHF, and prompt engineering, enterprises can develop AI chatbots that are consistent with their brand language, follow company guidelines, and offer highly relevant responses suited to particular business requirements.
2. Voice bots/assistants
Voice assistants use natural language processing to transform human speech into actionable commands. They recognize user intent and execute programmed tasks while enhancing user engagement through intuitive, conversational interfaces.
Key benefits include:
- Hands-free interaction: Voice assistants enable effortless, hands-free operations, allowing users to perform tasks without manual input. This convenience is particularly beneficial in multitasking scenarios, improving accessibility and user experience.
- Integrations: After recognizing user intent, these conversational AI systems connect with various services (search engines, IoT applications like smart thermostats, etc.) to execute commands. This capability is particularly valuable for users navigating a voice-only interface who need context-aware responses and access to multiple systems through conversational artificial intelligence.
- Real-time language processing: Advanced voice assistants offer real-time, on-device processing, delivering swift and precise responses to complex queries. Instant language translation and multilingual support have become standard features that improve personalization and communication.
Example
Eno (Capital One) is a prime example of a voicebot designed for financial services.3 Eno helps customers manage their accounts by responding to voice commands to check balances, review transactions, and make payments via conversational interactions.
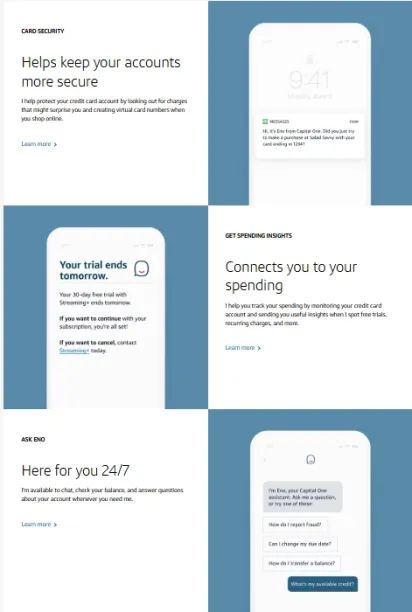
Figure 3. CapitalOne Eno’s features.4
3. Interactive voice response (IVR)/Interactive voice assistants (IVA)
AI-powered Interactive Voice Assistants (IVAs) are automated phone systems that can comprehend and react to voice commands or keypad inputs by utilizing machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and generative artificial intelligence. IVR (Interactive Voice Response) is the system that powers IVA technology, enabling callers to navigate a computerized system efficiently without human intervention.
IVAs are increasingly deployed across industries like banking, retail, utilities, travel, and healthcare, where they offer significant benefits, including:
- Efficient call routing: IVAs can direct calls to the correct department, enhancing communication and reducing wait times by utilizing natural language understanding (NLU).
- Support for rush hours: IVAs allow businesses to handle high call volumes more effectively by automating responses to common inquiries. IVA offers companies the ability for their callers to self-serve and leave messages. This self-service capability empowers customers to resolve mundane issues like tracking orders, checking status updates, or answering FAQs.
- Humanlike conversations: With generative AI, IVAs can deliver relevant responses and maintain conversation context, making user interactions feel more intuitive and personalized. Examples like Alexa and Google Assistant illustrate how these AI-powered virtual assistants extend beyond customer service to smart devices and home automation, enabling seamless engagement.
Example
Alexa (Amazon) exemplifies how IVAs can deliver humanlike conversational experiences. Through natural language understanding and machine learning, Alexa can handle tasks like setting routines, providing proactive responses, and integrating with a wide range of smart home devices.5 For example, Alexa can adjust thermostats, control lighting, and manage home security systems, all through voice commands.
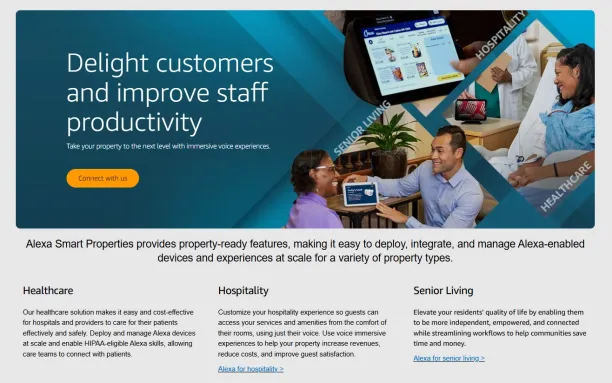
Figure 4. Amazon Alexa’s properties.6
Legacy conversational AI systems
Prior to LLMs being used in chatbots, two kinds of primitive chatbots might still be helpful in some situations. Although these approaches typically have fewer features, they are generally more budget-friendly.
Rule-based chatbots
Rule-based chatbots operate like conversation flowcharts with predefined rules. While they are predictable and easy to implement, they lack flexibility and offer minimal personalization. These chatbots are best for simple Q&A scenarios with no room for misunderstanding, such as basic banking FAQs or order tracking. Beyond these limited use cases, they primarily serve as a legacy foundation for modern AI chatbots.
Hybrid chatbots
Hybrid chatbots can analyze user behavior, integrate with messaging platforms and conversational interfaces, and employ machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) to improve dialogue management. They are the stepping stones between rule-based chatbots and AI chatbots.
Example
Bank of America’s Erica recognizes various ways customers might refer to their accounts:
- “My checking” (Common conversational reference)
- “Bank of America account” (Full formal name)
- “BoA account” (Abbreviated reference)
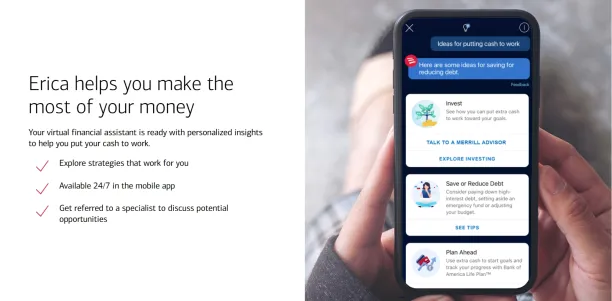
Figure 2. Bank of America Erica’s content page.7
Use cases across industries
1. AI chatbots/conversational AI systems
- Healthcare: Used for patient triage and scheduling. They can analyze symptoms provided by patients, offer preliminary diagnoses, and schedule appointments with specialists.
- Finance: Assist customers with tasks such as loan eligibility checks, providing investment advice, and detecting fraud by analyzing large datasets.
- E-commerce: Personalizes the shopping experience by offering product recommendations, handling returns, and answering product-related inquiries.
- Customer service (retail): Handle FAQs such as store hours, refund policies, and basic order tracking, ensuring consistent and reliable responses.
- Education: Automate administrative queries, including course schedules, enrollment requirements, and other basic inquiries, providing students with quick access to necessary information.
- Hospitality: Manage simple tasks such as checking room availability and reservation confirmations, enhancing the guest experience with faster response times.
- Travel: Combine rule-based functions (such as booking confirmations) with intelligent support for personalized travel recommendations, streamlining the booking process and creating a seamless customer experience.
- Insurance: Help policyholders process claims smoothly while escalating complex issues to human agents when necessary.
2. Voice bots/assistants
- Automotive: Voice assistants integrated into vehicles help with hands-free navigation, weather updates, and music control, enhancing driver safety and convenience.
- Banking: Allows users to perform tasks such as checking balances and transferring money via voice commands, increasing accessibility and convenience.
- Smart homes: Enable control of smart appliances, such as adjusting thermostats, lighting, and security systems, with simple voice commands.
3. Interactive voice assistants (IVAs)
IVAs take voice interaction further by incorporating context awareness, memory retention, and humanlike conversation flows, making them ideal for more complex and personalized customer interactions.
- Retail: Provides customer engagement with conversational shopping experiences, guiding customers through their purchase journey with personalized suggestions and assistance.
- Legal Services: Provide initial legal consultations, use memory retention to ask follow-up questions based on prior inputs, and streamline legal intake.
FAQ
What are the different types of conversational AI technologies available today?
The conversational AI landscape includes AI chatbots, virtual assistants, voice-activated systems, conversational IVR, and rule-based chatbots. Conversational AI applications span a spectrum, from simple platforms that adhere to predefined rules to more advanced systems that leverage natural language processing (NLP) to interpret human language and deliver responses that closely resemble human interaction through messaging platforms and voice commands.
How do conversational AI solutions process and respond to user queries?
Conversational AI technology leverages natural language understanding and machine learning to interpret user input and identify user intent. Through dialogue management and natural language generation, these systems maintain context-aware interactions and provide personalized responses. Advanced conversational AI platforms continuously learn from past interactions to improve user interactions, providing more accurate and relevant answers to customer inquiries across technical support and customer service scenarios.
What business benefits do conversational AI tools offer?
Implementing AI-powered chatbots and conversational interfaces significantly enhances customer interactions while reducing operational costs. These conversational AI solutions provide comprehensive support through multilingual support and 24/7 availability. Conversational AI gathers valuable customer data that businesses can use to further optimize their conversational AI applications.
How should businesses select the right conversational AI platform for their needs?
When evaluating existing conversational AI platforms, organizations should consider integration capabilities with current systems, understanding human language across various user queries, and support for interactive conversations. The ideal conversational AI solution should demonstrate the benefits of conversational AI through improved customer service, virtual shopping assistants, and the capacity to deliver humanlike conversations. Examples of conversational AI success include generative AI applications that provide natural language conversations while maintaining consistent user experiences across multiple channels.
Further Reading
External Links
- 1. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2501.11067
- 2. What is Live Chat Software? All You Need to Know - Zoho SalesIQ.
- 3. Eno, your Capital One assistant | Capital One.
- 4. Eno, your Capital One assistant | Capital One.
- 5. Alexa Smart Properties Homepage.
- 6. Alexa Smart Properties Homepage.
- 7. Erica® - Virtual Financial Assistant from Bank of America.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.