Technology as a service delivers tech benefits to businesses without on-premise tools or long-term investments. BaaS providers let businesses use chatbots or RPA bots on a pay-as-you-go basis, avoiding licensing and extensive training.
Bot-as-a-Service (BaaS) has been gaining popularity, and businesses that adapt will have increasing advantages over those that don’t. We have gathered essential information about what BaaS solutions are, including the types and platforms.
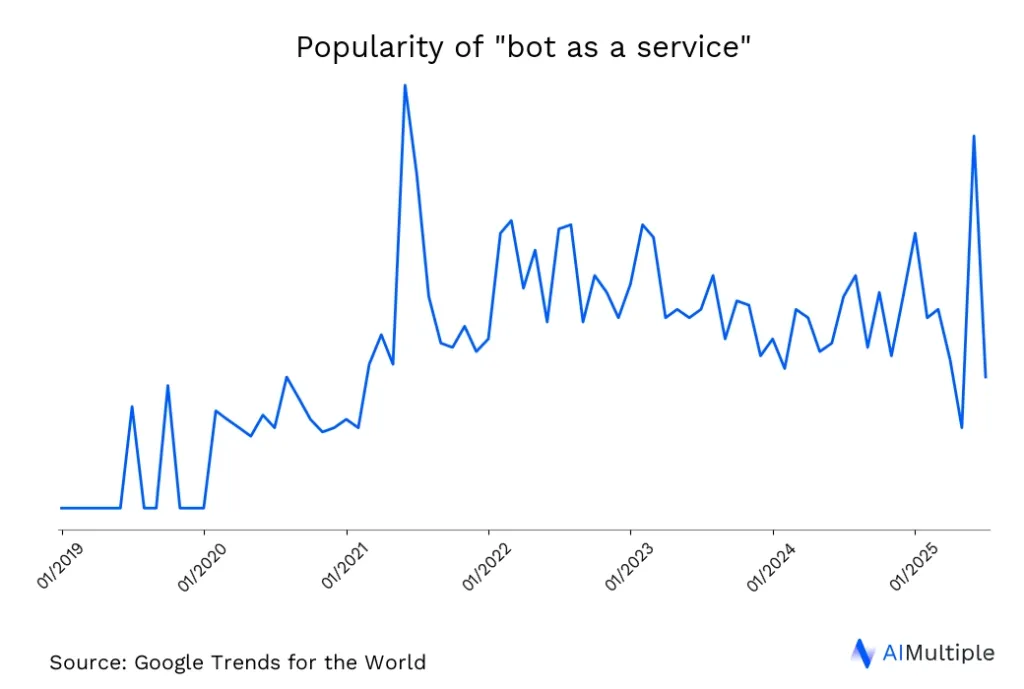
Figure 1. Change in the keyword “bot as a service” since 2019 (worldwide)
Which bots can be provided as a service?
Growth in BaaS is driven by businesses optimizing their digital transformation strategies by increasing their exposure to emerging technologies with minimal complexity. Types of technology-as-a-service can be defined as:
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Subscription software offered online, with the vendor hosting and maintaining the program so users can access it immediately without the need to install or manage it themselves.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Cloud-based, on-demand access to virtualized computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, allowing businesses to extend their infrastructure without purchasing physical hardware.
- AI as a Service (AIaaS):AI as a Service (AIaaS) is a cloud platform offering AI capabilities to organizations without needing dedicated infrastructure or data scientists. It enables integration through APIs, web, and chat interfaces, simplifying AI adoption and scaling machine learning and generative AI solutions.
- Bot as a Service (BaaS) (Robot as a Service (RaaS)): Robotic or conversational bot solutions deployed on a pay-as-you-go basis, enabling clients to add automation quickly without upfront capital expenditures or technical maintenance, as the provider supplies, maintains, and upgrades the hardware or AI agents.
There are many types of bots today, such as:
- Web crawling and scraping bots
- Social media bots
- Virtual assistants, and others.
However, the most common bots offered as a service are RPA bots and chatbots. These can be provided as cloud services instead of being maintained by in-house teams. They automate repetitive tasks and enable communication with customers without human intervention.
Web scraper as a service
Web data is valuable; however, websites often change their layout, making it hard to extract structured data. Web scraping companies identify the data their clients need and create autonomous web scrapers that they maintain to ensure access to fresh data. This is a type of data-as-a-service offering that, for example, helps hedge funds stay ahead of public markets.
Chatbot as a service
Chatbots are a type of software that allows people to obtain information from machines in a natural, conversational manner using text and voice. Chatbots depend on natural language processing to understand the user’s intent during a conversation and to produce responses based on training data or AI capabilities.
Chatbots have numerous applications in:
- Finance:
- Onboarding clients/employees
- Improving customer service
- Transactions
- Providing financial advice
- Cross-selling
- Preventing fraud
- Healthcare:
- Provide medical information
- Schedule medical appointments
- Collect patient data
- Handle insurance inquiries
- Real estate:
- Generate leads from digital users
- Build customer profiles
- Answer questions about properties
- Answer questions about properties
- Travel:
- Search for booking opportunities
- Manage inquiries
- Complete reservations
- Cross-sell
Chatbot as a service, also known as Chatbot SaaS, allows businesses to utilize chatbot features through low-code/no-code cloud platforms with ready-made templates for various customer-facing roles such as call center agents or shopping assistants, as well as back-office functions like employee support.
Some of the companies providing chatbots as a service include:
- AtBot
- AI BaaS
- Fonetic
- IBM
- Microsoft Azure
RPA bot as a service
RPA is a type of software that utilizes GUI elements and screen scraping, along with other technologies, to create specialized agents that automate repetitive GUI tasks, such as reporting, test automation, or SAP processes.
RPA bot as a service, also known as RPA as a service (RPAaaS), is the process of outsourcing RPA tasks to a service provider that relies on automation, machine learning (ML), and computer vision in order to run repetitive rule-based tasks on the cloud.
Some of the companies providing RPAaaS include:
- Automation anywhere
- UiPath
- BluePrism
- Robocloud
- Digital Workforce
Vendor landscape in BaaS solutions
| Vendor | Chat | Voice/IVR | RPA | Gen-AI Engine | Security Certifications* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Azure Bot Services/ Copilot Studio | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | GPT-4o | HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO 27001 |
| IBM watsonx Assistant | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Granite 3.2 | ISO 27001 |
| Google Dialogflow CX | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Gemini 1.5 | SOC 2, ISO 27001 |
| AWS Lex V2 | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Titan | SOC 2, ISO 27001 |
| OpenAI Assistants API | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | GPT-4o Voice | SOC 2 (Type 1) |
| UiPath Automation Cloud | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | Autopilot | SOC 2, ISO 27001 |
| Automation Anywhere Cloud | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | GenAI Process Models | ISO 27001 (controls) |
| Blue Prism Cloud | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | OpenAI Plug-in | ISO 27001 |
| WorkFusion AI Workers | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Tara LLM | SOC 2, GDPR |
| Digital Workforce | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | OpenAI Plug-in | ISO 27001 |
| Fonetic | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Domain NLU | ISO 27001 |
| SoftBank Robotics | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | N/A | ISO 9001 |
| Amazon Alexa for Business | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | Alexa-LLM | ISO 27001 |
*Security certifications column highlights the most recognizable enterprise audit; many vendors also hold additional attestations such as PCI-DSS, FedRAMP, or regional certifications.
Case study
With over 30 million customers, VPBank’s manual loan approval, contact center, and onboarding processes caused backlogs, higher overtime costs, and lower customer satisfaction ratings. Leadership needed to automate complex, multi-step procedures without hiring thousands of RPA engineers or building new on-premises infrastructure.
VPBank chose the UiPath cloud platform, which it uses as a third-party service provider offering governance, orchestration, robots, and continuous improvements as a managed service. New automated bots can be deployed in hours and managed centrally from the UiPath tenant via an internal “Automation Centre of Excellence” that uses low-code tools and pre-built interfaces.1
Some of the outcomes are:
- Customer inquiries were previously handled manually, but in 2024, 1.8 million inquiries were automated.
- The average process build time decreased from 3 weeks to 2.7 days, resulting in a 10-fold increase in speed.
- The live automation count in 22024 increased from fewer than 20 to 102.
- Processing speed has increased by a factor of 10.
- Contact center load is now reduced by bots, resulting in higher CSAT.
What are the benefits of implementing BaaS?
Bot-as-a-Service providers enable businesses to leverage RPA or chatbot capabilities on the cloud, offering the following benefits:
- No installation or deployment time
- No licensing, hosting, or infrastructure costs
- No need to train technical staff to program the bots (BaaS are mostly no-code platforms)
- Customized permissions to assign bot skills based on the user
- Automated software updates with new versions
- Consumption-based or outcome-based pricing options
What are the challenges of BaaS?
Since bot as a service is a cloud-dependent solution, it encounters cloud-related challenges such as:
- Data security: When using cloud services, business data (e.g., security keys, customer data, partner data, employee data) is stored and processed by a third party, making it vulnerable to breaches, hacks, or credential issues. However, most BaaS providers ensure data privacy through data encryption and by following cybersecurity best practices. Some providers document these measures by obtaining certificates like ISO 27001 or SOC 2.
- Cloud adoption: Not all businesses have fully moved their systems and applications to the cloud; according to a survey, 8% of organizations still keep all their data and IT environment on-premises. It is important for businesses that want to leverage BaaS to have all relevant data and information already migrated and set up in the cloud.
Nonetheless, BaaS providers can address these challenges by integrating data privacy solutions and APIs that facilitate hybrid automation (e.g., on-premises and cloud).
FAQ
Why is Bot as a Service considered an attractive option for many businesses?
Bot as a Service (BaaS) eliminates on-prem overhead by letting third-party service providers host automated services in the cloud on a subscription basis, reducing both cap-ex and complexity. Because these cloud-based solutions bundle advanced AI out of the box, organisations realise business benefits faster without hiring niche talent or managing complex processes.
How do BaaS platforms protect against cybersecurity threats such as bot attacks or malware?
Leading service providers apply strong authentication methods, encrypted secure connections and regular audits that flag unusual activity or traffic from malicious IP addresses. These controls, plus real-time bot-attack monitoring, shut down sophisticated bots before they spread malware or disrupt affected systems.
Which day-to-day tasks can automated bots handle, and how does this help companies streamline operations?
Automated, conversational AI bots powered by natural language processing take over customer interactions and data entry across multiple channels, while web crawlers and social media bots analyze data in the background to surface insights. This mix of cloud computing and AI assistants streamlines operations, enabling businesses to offload complex tasks and focus on higher-value work.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.