Orchestration market includes sub-categories. See leading software in each category:
- Workload automation tools for all types of orchestration :
- ActiveBatch for API integrations
- RunMyJobs for SAP orchestration
- For container orchestration: DigitalOcean & Kubernetes
- For infrastructure orchestration: AWS CloudFormation
- For LLM orchestration: Langchain & LlamaIndex
- For other orchestration types:
- Cloud orchestration: AWS Step Functions
- Data orchestration: Google Dataflow
- Process orchestration: Pipefy
Browse the complete list below, arranged alphabetically, except for sponsored tools which appear at the top:
| Tool | Category | Free trial | Rating | The number of employees |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ActiveBatch | All | ✅ | 4.4 based on 251 reviews | 533 |
| RunMyJobs by Redwood | All | ✅ | 4.8 based on 140 reviews | 533 |
| Stonebranch | All | ✅ | 4.8 based on 79 reviews | 152 |
| Fortra's JAMS | All | ✅ | 4.7 based on 142 reviews | 1,721 |
| Ansible | All | ✅ | 4.4 based on 183 reviews | 5 |
| Google Dataflow | Data orchestration | ✅ | 4.3 based on 61 reviews | 300,114 |
| Prefect | Data orchestration | ✅ | - based on - reviews | 93 |
| Pipefy | Process orchestration | ✅ | 4.5 based on 539 reviews | 484 |
| Process Street | Process orchestration | ✅ | 4.5 based on 985 reviews | 56 |
| Kubernetes | Container orchestration | Open source | 4.5 based on 237 reviews | 116 |
| Red Hat Openshift | Container orchestration | ✅ | 4.2 based on 60 reviews | 5 |
| DigitalOcean | Container orchestration | ❌ | 4.5 based on 593 reviews | 1,746 |
| Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Container orchestration | ✅ | 4.5 based on 209 reviews | 300,114 |
| AWS Step Functions | Cloud orchestration | ✅ | 4.1 based on 42 reviews | 130,371 |
| Azure Logic Apps | Cloud orchestration | ❌ | 4.4 based on 137 reviews | 244,900 |
| AWS CloudFormation | Infrastructure orchestration | ❌ | 4.5 based on 214 reviews | 130,371 |
| Terraform | Infrastructure orchestration | ✅ | 4.6 based on 141 reviews | 2,393 |
| Puppet | Infrastructure orchestration | ✅ | 4.3 based on 67 reviews | 243 |
| Azure Resource Manager (ARM) | Infrastructure orchestration | ✅ | 4.5 based on 52 reviews | 244,900 |
*The table above lists the products in alphabetical order, with the exception of the sponsors.
* *The review and score data on the table is extracted from the leading review platforms.
Discover top orchestration tools, their categories and features:
IT orchestration
Service orchestration, also known as IT orchestration, includes tools for workflow, infrastructure, and container orchestration. These tools integrate systems, applications, and data to automate workflows and processes across an organization’s IT infrastructure, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
Leading enterprise workload automation and job scheduling tools deliver service orchestration capabilities. Here are some of them:
ActiveBatch
ActiveBatch is a workload automation tool that enables organizations to integrate, automate, orchestrate and monitor their entire technology stack centrally. ActiveBatch enables IT teams to unify automation across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments, supporting real-time infrastructure, business workflows, and data center tasks.
Features
Some of the unique capabilities of ActiveBatch include:
- Flow Control Job Steps, such as ForEachRow and If-Branch to manage jobs within workflows based on conditions and dependencies.
- Job step library with production-ready job steps to orchestrate processes using prebuilt, platform-neutral functions.
- DevOps integrations to streamline scheduling and orchestration for all types of applications.
- REST API creator for building custom connectors for any internal system.
Discover ActiveBatch‘s all major capabilities in-detail. Also, compare its strengths and weaknesses ActiveBatch alternatives in our deep-dive vendor analysis.
Here is a video showing the ActiveBatch Web Console interface and features:
RunMyJobs
RunMyJobs is a service orchestration and automation platform delivered as a SaaS solution, managed by the Redwood team. This allows users to centralize and optimize IT or business processes without any maintenance effort.
Features
RunMyJobs users can leverage:
- Native connectors for integrating with cloud providers like Azure and AWS, Databricks, ServiceNow, Oracle Fusion and more.
- SOAP, REST APIs, JDBC, and other protocols to connect external systems.
- SAP Cloud Connector to facilitate communication between on-premises systems and SAP’s cloud services, including SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC), SAP BTP, SAP Cloud Platform, and various cloud applications.
Explore more on RunMyJob‘s SAP cloud connector and native connectors to see how it enables integration to SAP cloud services, DevOps tools and other cloud providers.
Some of the key RunMyJobs capabilities include:
- Lightweight and auto-updating agents to facilitate updates. Updates can be triggered with a single click and completed within minutes.
- Continuous integration and delivery tools for DevOps
- Load balancing and process prioritization
- Monitor dashboards for job status and resource allocation
RunMyJobs is a SAP Pinnacle award winner,1 thanks to its significant growth on the SAP store. Read our deep-dive vendor analysis on RunMyJobs or Redwood-SAP partnership.
For more on RunMyJobs architecture:
Stonebranch
Stonebranch UAC helps unify automation across hybrid environments by supporting collaboration between developers and IT operations
Features
Stonebranch UAC offerings include:
- Infrastructure-as-code to automate cloud resource deployments on AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Jobs-as-code for developers to create and publish jobs directly from their IDEs in JSON or XML format.
- Drag-and-drop workflow creation to enable low-code/no-code visual workflow design.
- DevOps lifecycle integration to orchestrate CI/CD tools and automate end-to-end DevOps workflows.
Explore more details on Stonebranch UAC and compare it against top Stonebranch alternatives.
Fortra’s JAMS
Fortra’s JAMS automates enterprise workloads by coordinating cross-platform jobs and workflows in both cloud and on-premises setups.
Features
Some of the main capabilities include:
- Cross-platform scheduling to control jobs on all business systems
- Job monitoring of jobs across the environment with dashboards and reports
- Integrations with native connections to leading business applications
Compare Fortra’s Jams alternatives based on capabilities, pros and cons.
Ansible
Ansible is a service orchestration tool that automates configuration management, application deployment, and infrastructure provisioning.
Features
It uses YAML-based playbooks for defining automated tasks.
Some of its main capabilities are listed as:
- Built-in orchestration capabilities to automate diverse tools and platforms.
- Automation controller with RESTful API, RBAC, workflows, and CI/CD integrations.
- Task ordering to ensure proper execution of automation efforts.
Compare all service orchestration and automation platforms via our comprehensive and constantly updated list.
Container orchestration tools
These tools handle the lifecycle of containerized apps, from deployment and scaling to operations across environments. They automate tasks like scheduling containers, managing container lifecycles, and ensuring high availability. Best container orchestration tools include:
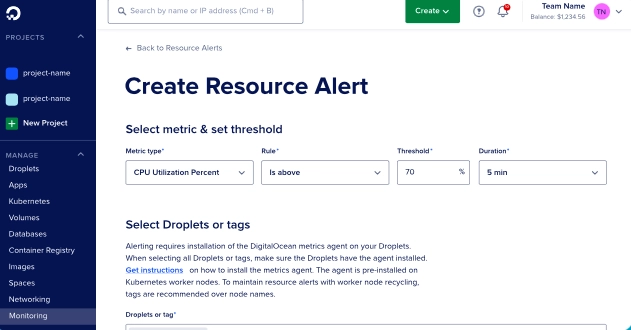
DigitalOcean
DigitalOcean is mainly a cloud infrastructure provider that offers scalable compute resources, storage, and networking solutions. It offers a container orchestration capability, DigitalOcean Kubernetes (DOKS) which can simplify the deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications.
Features
Some of its major features include:
- Automated Kubernetes cluster provisioning and management for streamlined deployment workflows.
- Built-in monitoring and logging features for real-time visibility into cluster performance.
- RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) enables fine-grained management of user permissions based on roles within an organization.
- Continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines integration for automated application delivery.
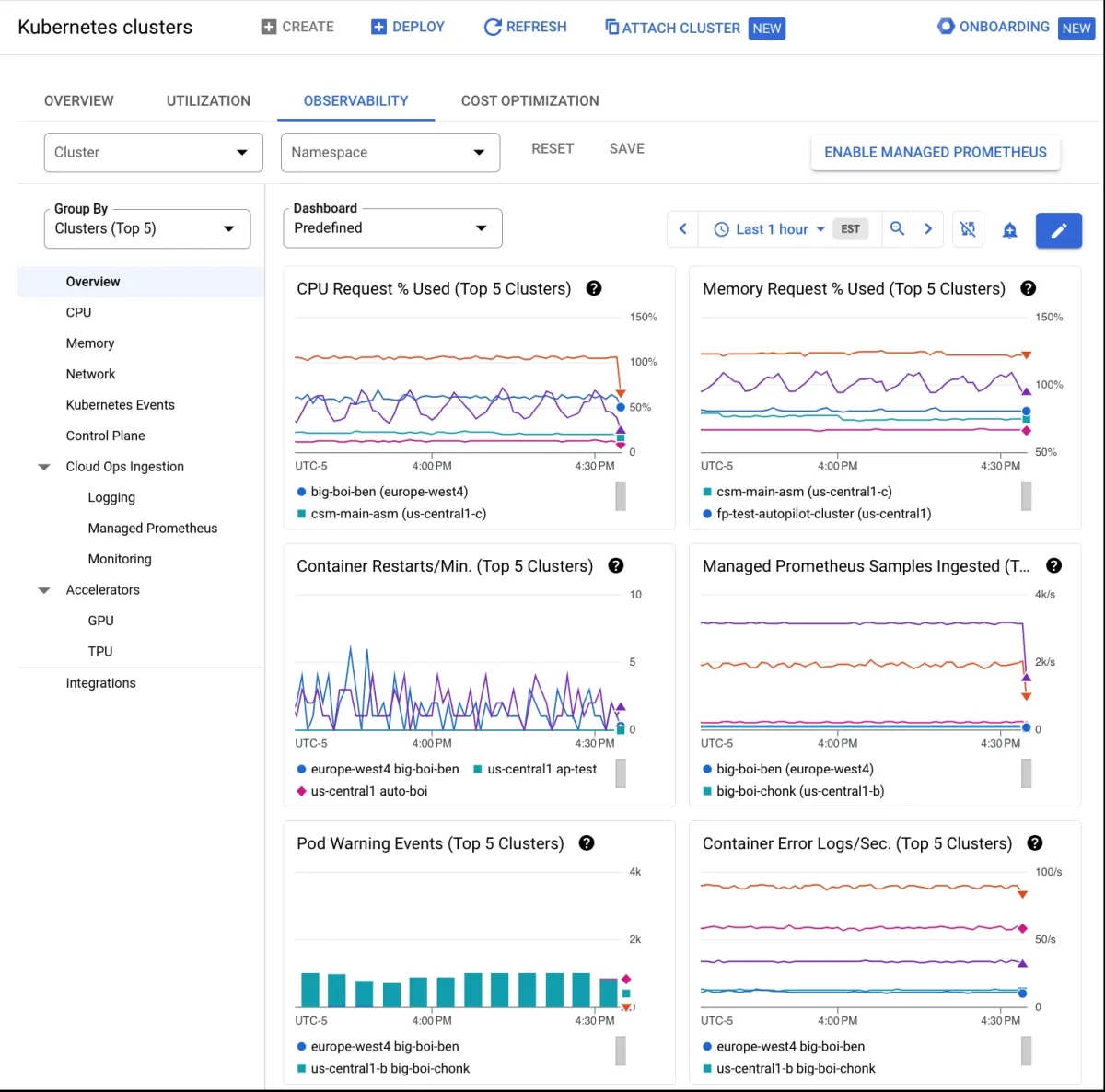
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
GKE is Google Cloud’s managed Kubernetes solution, emphasizing ease of use and operational flexibility.
Features
It provides features for scheduling and managing containerized applications, as well as support for mixed workloads including Docker, VMs, and standalone binaries.
- KE Autopilot to automatically handle cluster compute management
- Prebuilt applications to enterprise-ready containerized solutions
- GPU and TPU support for running specialized workloads benefiting from hardware accelerators
Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Features
It provides features such as container scheduling, service discovery, and horizontal scaling.
- Horizontal and vertical pod autoscaling to automatically adjusts the number of pod replicas based on resource utilization.
- Self-healing to automatically restarts containers that fail or become unresponsive.
- Service discovery and load balancing to automatically discover and route requests to containers.
- Resource quotas and limitations to control the amount of CPU, memory, and other resources each container can use.
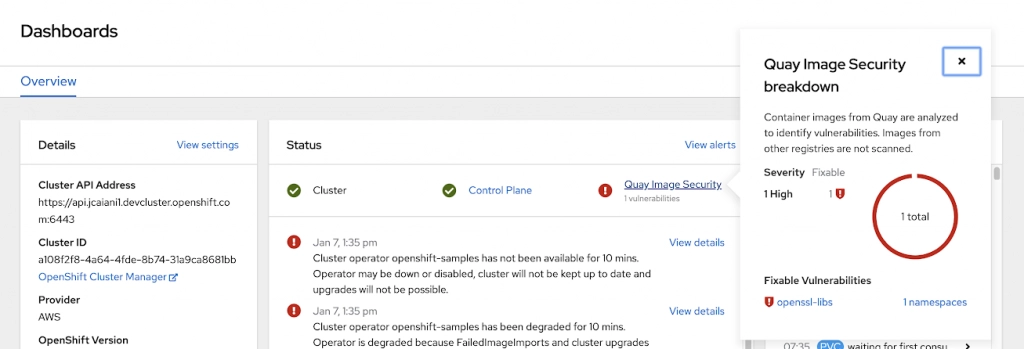
OpenShift
Red Hat OpenShift extends Kubernetes with enterprise features for managing containerized applications at scale.
Features
The platform also adds additional features for application development, deployment, and management, including developer tools and integrated CI/CD pipelines, such as:
- Operator framework to automate application deployment, scaling, and management through custom operators
- Containerized infrastructure to run containerized applications on-premises or in the cloud
- Built-in security features such as role-based access control (RBAC) and network policy enforcement.
Infrastructure orchestration tools
Infrastructure orchestration tools automate the setup and management of IT resources like VMs, networks, and cloud storage to ensure consistent deployments.
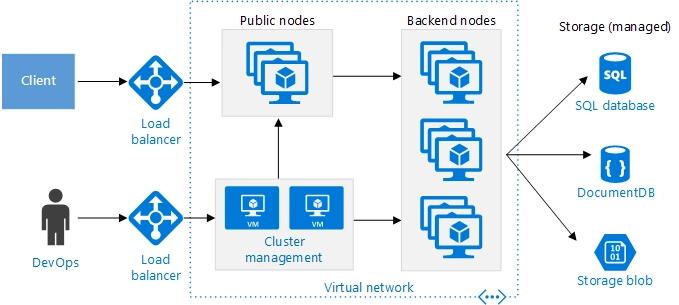
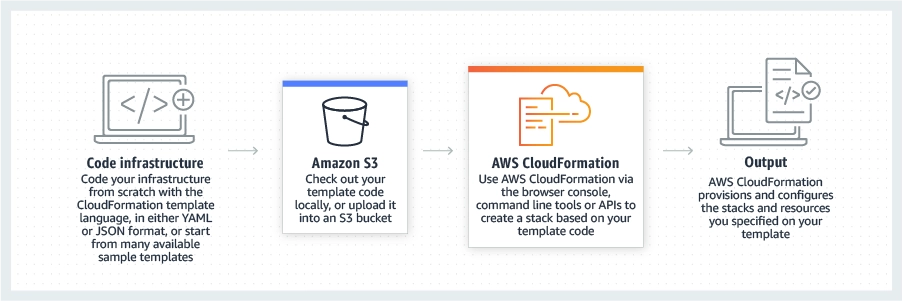
AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation automates AWS resource management through infrastructure-as-code templates for consistent deployments.
Features
It allows users to:
- Define infrastructure as code to automate the deployment process, enabling efficient scaling and management of AWS infrastructure
- Automate provisioning, updating, and deleting stacks as a single unit
- Express functions, APIs, databases, and event source mappings using shorthand syntax in YAML, which is transformed into CloudFormation syntax during deployment
- Resource Management to orchestrate the deployment and management of AWS resources, ensuring consistency and reliability.
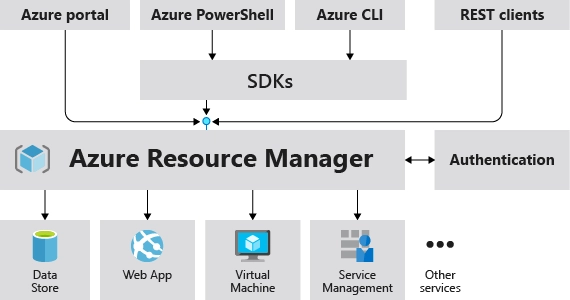
Azure ARM
Azure ARM (Azure Resource Manager) is a service for managing and orchestrating Azure resources.
Features
It allows users to:
- Define infrastructure templates using JSON and automate the deployment and management of Azure resources
- Manage and visualize application resources within resource groups
- Identify resource dependencies and categorize resources using tags for management and billing.
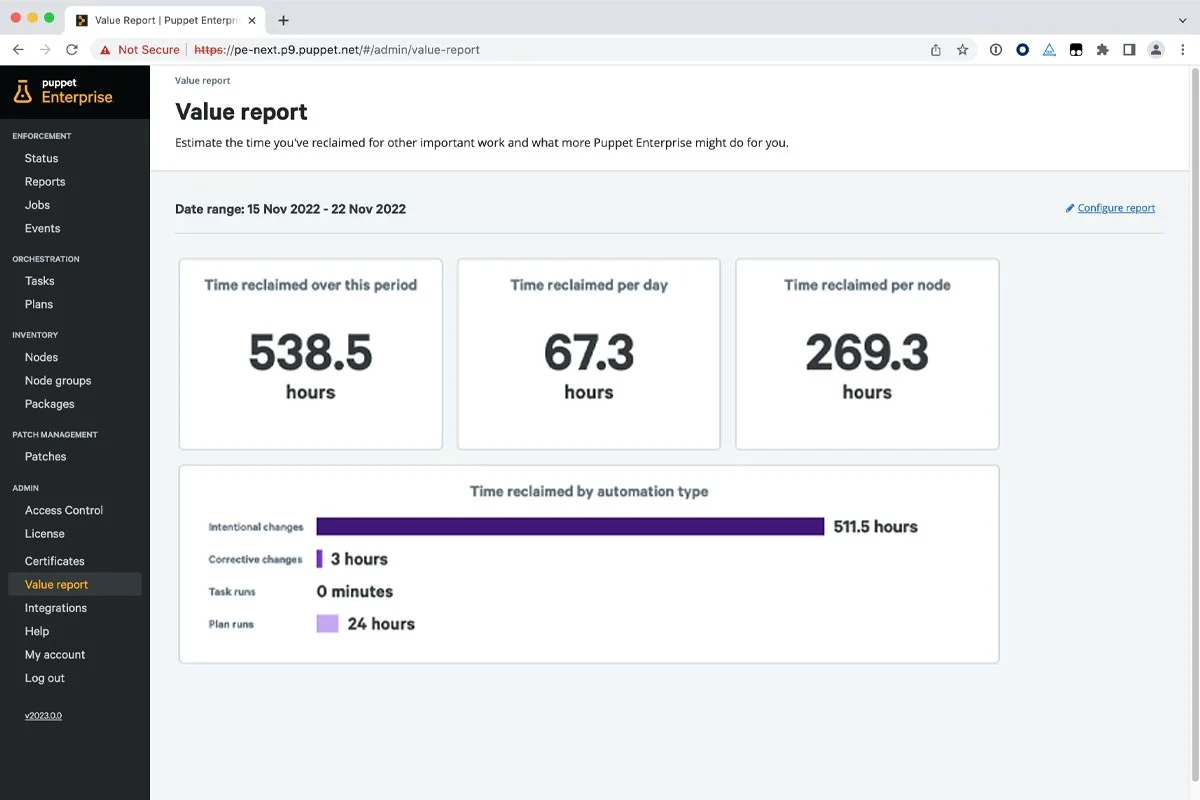
Puppet
Puppet is an infrastructure orchestration platform that automates the configuration and management of IT infrastructure.
Features
It provides features for defining infrastructure as code, enforcing desired state configurations, and managing infrastructure at scale, such as:
- Compliance automation to automatically run compliance checks and enforce regulatory standards across infrastructure.
- Configuration management to define and maintain desired system configurations consistently across environments.
- Code delivery to facilitate continuous delivery pipelines for deploying infrastructure changes as code.
- Vulnerability management to identify and remediate vulnerabilities in system configurations and software packages.
- Patching & upgrades to automatically manage patch processes and ensure systems are up-to-date and secure.
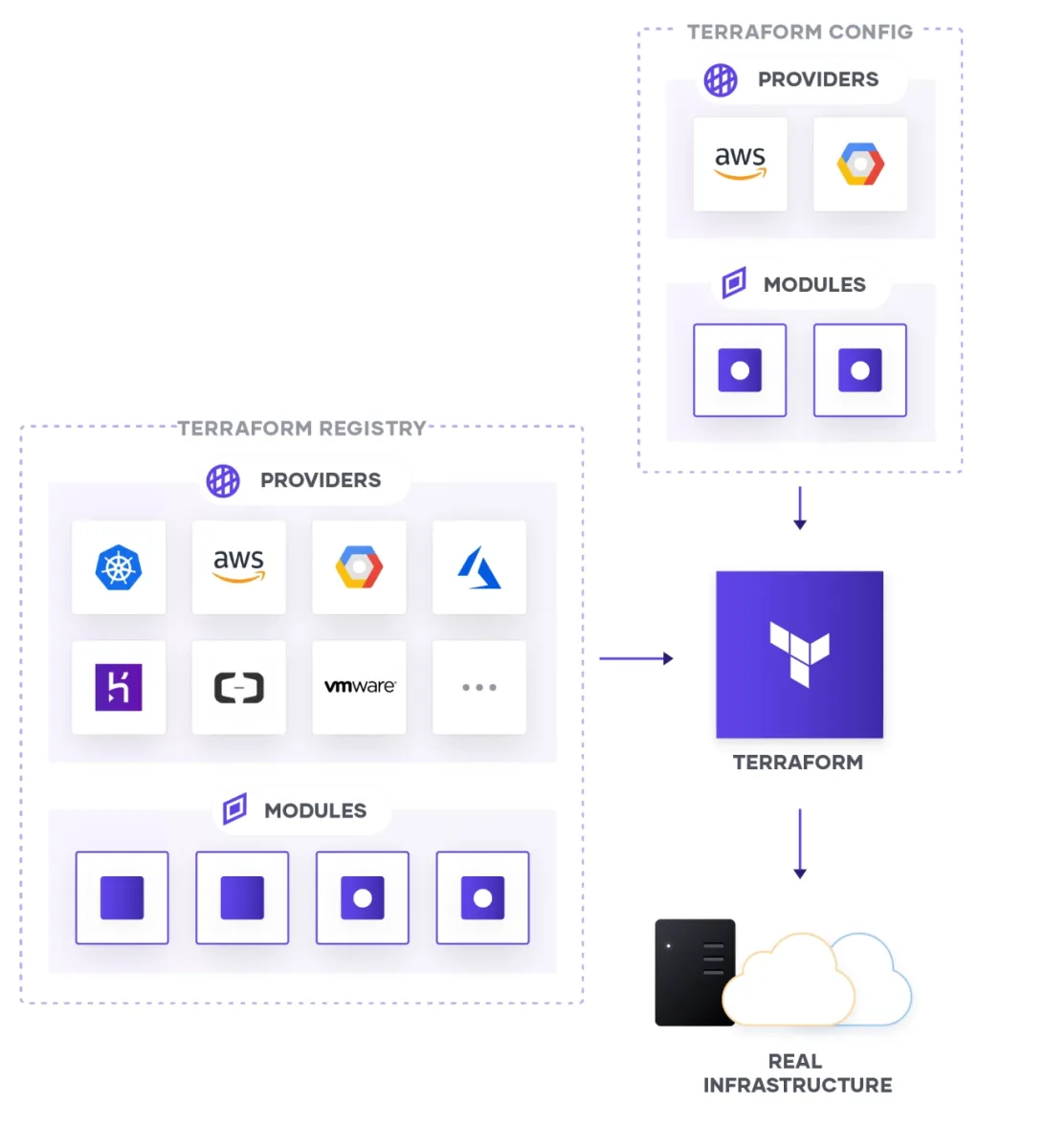
Terraform
Terraform enables infrastructure-as-code management across on-premises systems and multiple cloud platforms through declarative configuration.
Features
It features a declarative configuration language and supports a wide range of providers.
- Declarative configuration language to define infrastructure resources for consistent deployments.
- Multi-cloud provisioning to orchestrate infrastructure across multiple cloud providers and on-premises environments
- Infrastructure as Code to enable infrastructure management through code
LLM orchestration
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI systems trained on vast datasets to understand and generate human-like text. LLM orchestration involves tools that coordinate large language models with external systems, workflows, and AI components.
LLM orchestration help efficient integration, scalability, and enhanced functionality when deploying LLMs in complex applications or enterprise environments. Here is a list of LLM orchestration tools and their GitHub scores, sorted in alphabetical order:
| LLM Orchestration Framework | Github Stars |
|---|---|
| LangChain | 83.8k |
| AutoGen | 38.7k |
| LlamaIndex | 31.2k |
| crewAI | 25.9k |
| Semantic kernel by Microsoft | 22.9k |
| Haystack by Deepset AI | 19k |
| TaskWeaver | 5.5k |
| Agency Swarm | 3.2k |
| Microchain | 282 |
| Loft | 10 |
| IBM watsonx orchestrate | Not open-source |
Explore more on LLM orchestration applications and compare LLM orchestration frameworks in terms of features and supported languages.
Other orchestration tools
There are various orchestration tools that can be placed under the 4 major categories explained above, such as:
Process orchestration tools
Business process orchestration tools automate and coordinate workflows and processes across various systems and applications. They enable the efficient execution and management of complex business processes.
Pipefy
Pipefy is a workflow orchestration platform to standardize and manage complex processes and workflows without technical resources. Pipefy users can scheduling and monitoring workflows as directed acyclic graphs (DAGs).
Features
It provides features for task dependency management and workflow visualization, such as:
- Integrations to connect with other applications via open API or Zapier
- Pre-configured metrics to monitor process performance KPIs like productivity, lead time, and flow
- Visual management to track process stages, responsibilities, deadlines, action statuses and SLAs
- Automated alerts and real-time performance analytics
- Internal and external portals to access more intelligent solutions and improve data and process control.
Here is an example of Pipefy analytics dashboard:
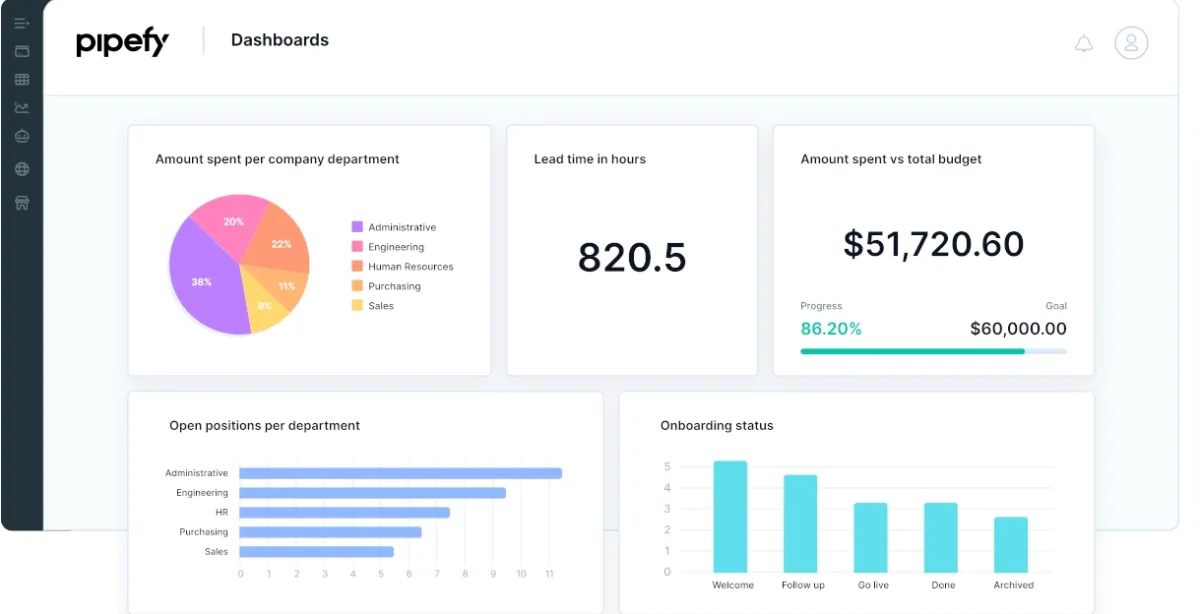
Process Street
Process Street is a business process management platform, designed to streamline operations and automate tasks.
Features
It offers a variety of features, including:
- Task dependencies to manage task dependencies
- Dynamic workflow updates to modify workflows without disrupting ongoing processes
- Automated workflow execution to Automate task execution to align with business cadence
- Data security controls to manage who has access to sensitive information within workflows
- Compliance and accountability to improve compliance with single or sequential approvals
- AI-Powered workflows to create step-by-step processes.
Cloud orchestration tools
Cloud orchestration tools automate the provisioning, configuration, and management of cloud resources and services across various cloud environments. They streamline tasks such as deploying virtual machines, managing networking, and scaling infrastructure in the cloud.
Cloud orchestration can be considered as part of container or infrastructure orchestration.
Microsoft Azure Logic Apps
Microsoft Azure Logic Apps is a cloud platform to create and run automated workflows and integrate systems and services. It offers a visual designer for building workflows and supports a wide range of connectors and triggers. With Azure platform, users can fully control their workflows, including invoking other services, handling messages, and managing the flow with scopes, conditions, switch cases, and loopings.
Features
Azure logic apps capabilities include:
- Automated and integrated communication via messaging, EDI and B2B integration.
- Data wrangling
- Hybrid and cloud-native integration for enterprise application integration (EAI)
- Integration to AI services.
Here is an illustration of Azure logic apps’ integration to various connectors:
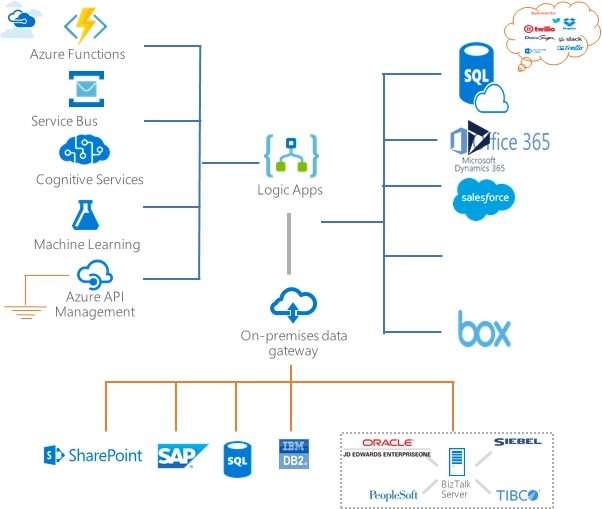
AWS Step Functions
AWS Step Functions is a visual workflow service designed to coordinate distributed applications, automate processes, orchestrate microservices, and construct data and machine learning pipelines using AWS services.
Features
Users can benefit from functionalities like:
- Orchestration and automation of extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes
- Direct integration with over 220 AWS services and 10,000+ APIs
- Built-in state management, error handling, and workflow progress tracking
- Real-time and auditable workflow execution history with monitoring and logging
- Serverless solutions that automatically scale to accommodate changing workloads
- High-volume orchestration for event processing workflows such as IoT and data ingestion.
- Visual operator dashboard for monitoring and troubleshooting workflow executions.
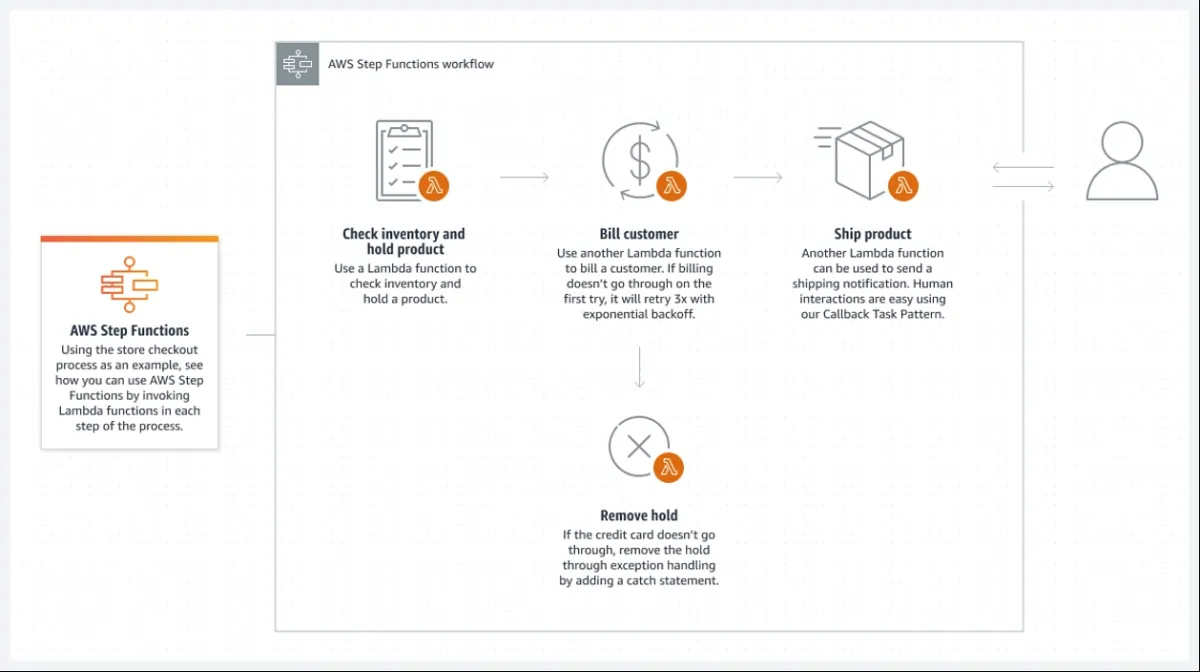
There are also orchestration tools that can overlap with more than one category like:
Data orchestration tools
Data orchestration tools are used for managing and automating workflows related to data processing, integration, and movement. They ensure efficient handling of data across different systems and environments.
Data orchestration tools streamline and automate the movement and transformation of data across different systems and platforms. These tools can be combined with data warehouse automation software, ETL automation tool, data validation tools, API connectors, and data pipeline management systems to streamline data integration and management.
Google Dataflow
Google Dataflow is a managed data processing service supporting both real-time and batch pipelines through a serverless model.
- Automated resource management for a fully managed service with automated provisioning and horizontal/vertical autoscaling
- Real-Time insights and AI for predictive analytics and real-time personalization with the support of NVIDIA GPUs
- Dynamic work rebalancing for constant adjustment of adjusts resource allocation
- Machine learning pipelines to train, deploy, and manage complete ML pipelines for both batch and streaming data
- Monitoring and observability to diagnose issues and track data at each step with tools.
Prefect
Prefect is a dataflow orchestration tool for building, scheduling, and monitoring complex workflows across systems.
Features
It offers various features like:
- Log retention and debugging for enhanced data traceability and troubleshooting
- Service accounts and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for secure workflow management
- Event-driven workflows that integrate with external systems for comprehensive stack visibility
- Automated flow runs initiation, deployment pausing, and custom notifications sending.
Other orchestration tools
- Cluster management tools: Cluster management tools can automate the deployment, scaling, and management of clusters of computing resources, such as containers or virtual machines. They aim to provide efficient resource utilization and high availability of applications. A cluster management tool can be considered as infrastructure orchestration.
- DevOps orchestration tools: DevOps orchestration tools automate and streamline the software development lifecycle, from code commit to deployment and operations. They facilitate continuous integration, continuous deployment, and collaboration between development and operations teams. DevOps orchestration tools can span across workflow orchestration and infrastructure orchestration categories, as they involve automating workflows related to software development and deployment processes.
- Workflow orchestration: These tools manage the automation and coordination of workflows or processes across different systems or applications. They help in defining, scheduling, and executing complex workflows involving multiple tasks, dependencies, and conditions. Users can create workflows across multiple systems.
| Type of orchestration | Main focus | Key technologies | Common use cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Container Orchestration | Managing containerized apps | Container Orchestration Tools | Scaling containerized apps, managing container clusters |
| Cloud Orchestration | Managing cloud resources | Cloud Automation Tools | Deploying cloud infrastructure, managing cloud resources |
| Data Orchestration | Coordination of data workflows | ETL tools, Workflow Orchestration | ETL processes, data pipelines, data management |
| ETL Orchestration | Extraction, transformation, loading of data | ETL Tools | Data warehousing, data transformation, data integration |
| Infrastructure Orchestration | Automation of infrastructure | Infrastructure as Code (IaC) | Automating infrastructure setup, cloud provisioning |
| IT Orchestration | Automation in IT operations | Scripts, Configuration Management | Automating IT tasks, managing IT resources |
| Process Orchestration | Workflow automation | Business Process Management (BPM) | Business process automation, task coordination |
| Security Orchestration | Automation of security tasks | Security Orchestration and Response (SOAR) | Security automation, incident response, threat intelligence |
| Service Orchestration | Coordination of services | Microservices, APIs, ESB | Integrating different services, creating service-based workflows |
Disclaimers
AIMultiple recognizes that certain tools may fall into multiple categories and that there is overlap between categories. However, to maintain precision and clarity in our analysis, AIMultiple has streamlined the categorization process and assigned each vendor to a single category only.
For open-source tools, AIMultiple choose the frameworks with the highest GitHub score.
FAQ
What are orchestration tools?
Orchestration tools automate the configuration, coordination, integration, and data management across multiple applications and systems. They streamline IT processes like server provisioning, incident management, cloud orchestration, database management, and application orchestration, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
How to choose the best orchestration tool for your business
The best way to decide which orchestration tool is the perfect fit for your company involves a systematic approach that considers several key factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide based on the provided text and best practices in workflow orchestration:
1. Understand business goals and objectives: Begin by clearly understanding your company’s business goals and objectives. Ensure that any tool you consider aligns with these strategic objectives.
2. Research business trends: Stay informed about current business trends in your industry. This knowledge can help you identify emerging technologies and tools that can enhance your business process orchestration.
3. Identify existing system gaps: Evaluate your current systems and processes to identify any gaps or inefficiencies. Consider the specific use cases across different departments such as customer service, sales, marketing, HR, and finance.
4. Assess scalability: Choose an orchestration tool that can scale according to your company’s growth and changing business needs. Ensure that it can handle increasing workload demands without compromising performance.
5. Consider security and compliance: Prioritize security and compliance by selecting a tool that aligns with your company’s security protocols and regulatory requirements. Verify that sensitive data is protected and that the tool meets industry compliance standards.
6. Evaluate flexibility: Look for a tool that offers flexibility, allowing workflows to be easily modified or updated in response to changing business dynamics and requirements.
7. Promote process transparency and collaboration: Choose a tool that promotes process transparency and encourages collaboration among stakeholders. Ensure that all team members have a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities within the orchestration workflows.
8. Regular monitoring and maintenance: Prioritize regular monitoring and maintenance of the chosen orchestration tool to ensure optimal performance and to address any issues promptly.
Orchestration vs. automation tools
Automation tools focus on streamlining repetitive tasks by executing predefined actions without manual intervention. They are designed to handle specific tasks or processes with minimal human involvement, such as software installation, file backups, or system updates. These tools operate based on predefined rules and conditions, allowing users to automate routine operations efficiently.
Orchestration tools streamline the coordination of multifaceted workflows across multiple tasks, systems, and applications. They serve as a centralized platform for integrating automated processes throughout an organization’s infrastructure. By automating end-to-end workflows—from resource provisioning to deployment—they enhance collaboration, efficiency, scalability, and reliability in IT operations.
Explore more on automation vs orchestration in our in-depth guide.
What are the benefits of IT orchestration?
Orchestration offers multiple benefits to IT teams, such as:
Centralized management: Orchestration enables IT teams to automate tasks across multiple platforms from a single point, which provides centralized monitoring and management over all IT servers, applications, and workflows.
Fast and easy integrations: Centralized coordination among IT servers and applications enables easier and faster integration of new tools and systems to the existing infrastructure.
Reduced product-release cycles: Coordinating IT workflows such as DevOps and automation testing enables faster time to release new products and applications.
Where is orchestration used?
Orchestration is used for:
1. Unified IT workflow automation
Orchestration tools enable scheduling and execution of IT jobs and workflows across multiple platforms, as well as initiating workflows at triggering events, thus, automating repetitive IT process workflows.
2. DevOps orchestration
DevOps is the set of practices that combines software development and IT operations in order to reduce software development lifecycle (SDLC). Orchestration tools enhance DevOps lifecycles by:
Automating IT processes relevant to DevOps, such as machine provisioning, system reboots, or task scheduling
Auto reporting of process errors, fails, and interruptions
Creating a product backlog and revision history for audit and compliance
3. Cloud orchestration
Cloud orchestration is the practice of automating cloud-related tasks, including:
provisioning and de-provisioning of virtual machines on multiple clouds
provisioning storage capacity
Orchestration provides enhanced management of connections and operations of workloads on private and public clouds.
Transparency statement
AIMultiple partners with multiple companies such as ActiveBatch, RunMyJobs, and Fortra’s Jams.
Further reading
Explore our detailed benchmarks and comparisons to learn more about orchestration tools across categories like process, data, and container orchestration:
- Top 10 Process Orchestration Tools based on 5,200 Reviews
- Process Orchestration: Top 5 Tools & Best Practices
External sources
- 1. Finalists and Winners | SAP Pinnacle Awards.
- 2. Application & Infrastructure Monitoring | DigitalOcean.
- 3. View observability metrics | Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) | Google Cloud.
- 4. Kubernetes | Production-Grade Container Orchestration – Cozy Systems.
- 5. OpenShift 4.3: Dashboard refinements and the new Project dashboard. Red Hat
- 6. Provision Infrastructure as Code - AWS CloudFormation - AWS.
- 7. What is Azure Resource Manager? - Azure Resource Manager | Microsoft Learn.
- 8. Puppet Enterprise: Desired State Automation for Modern Business.
- 9. Terraform Registry.
- 10. Dashboards | Pipefy. Pipefy
- 11. Azure Logic Apps Life Cycle: The Big Picture | Turbo360.
- 12. Serverless Workflow Orchestration – AWS Step Functions – Amazon Web Services.
- 13. Pythonic, Modern Workflow Orchestration For Resilient Data Platforms | Prefect.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.