Mobile applications, or mobile apps, have a great potential to boost your business because:
- The typical American uses his/her mobile device for 320 minutes every day.
However, the retention rate for mobile apps after a month is less than 3%, indicating that just a small number of apps add value for businesses.1 The top 30 mobile app use cases will be covered in this article to help organizations develop mobile apps with high retention rates. To make it easier to navigate, we divided the content into two parts:
- Industry-specific use cases, where we introduce:
- E-commerce
- Banking
- Insurance
- Hospitality
- And healthcare-specific applications.
- Business units’ specific use cases, where we introduce
- General business
- HR
- Supply chain
- Sales/marketing use cases.
Industry-Specific mobile App use cases
E-commerce use cases
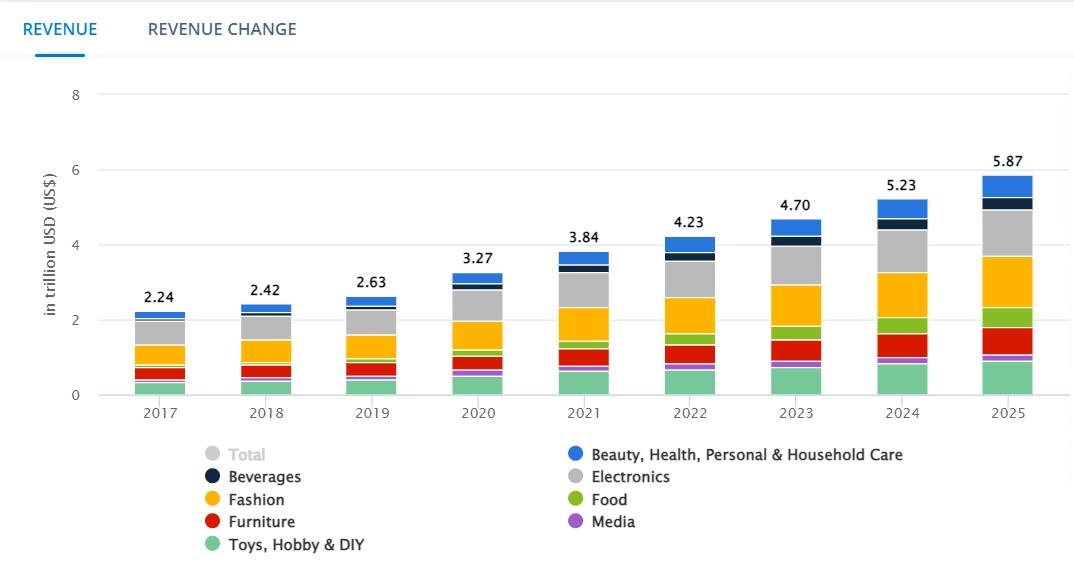
E-commerce sales reached over 4 trillion dollars in 20222 which indicates a greater economic activity than the entire UK or Canada (see Figure 1).3 And as we have already stated, mobile devices account for about 60% of online sales. As a result, AIMultiple views mobile apps as one of the most important e-commerce technologies and the development of apps that have the right capabilities as a best practice in e-commerce.
Figure 1: E-commerce sales.
Mobile app’s use cases in e-commerce include:
1. Providing an omnichannel platform
As part of their conversational commerce strategy, e-commerce firms use messaging apps such as Whatsapp and websites to engage with, and sell products to, customers.
According to McKinsey, around one-third of US consumers are happy to have the option of completing their transactions on several channels.4 And because people carry their phones everywhere, they can buy from anywhere they are. So, developing a mobile app will further strengthen your omnichannel customer engagement and boost sales.
2. Personalized sales/marketing
According to PwC,5 around one third of customers are willing to pay more for products if online sellers provide personalized sales/marketing efforts such as:
- Sending personalized notifications such as:
- Push notifications
- Delivery notifications
- Chart abandonment notifications.
- Assist clients in finding the things they seek.
- Providing users with an easy check-out by storing customer data, such as their address.
Mobile apps are suitable places for automating all these tasks since:
- You can deploy mobile app chatbots that can send personalized notifications and help customers find products in the form of sales chatbots.
- Mobile apps store personal data: Thus, e-commerce businesses can provide an easy checkout process and also can introduce products customers might like according to their previous transactions.
3. Automated customer service
Mobile app chatbots have many benefits. In customer service, since, they can:
- Work 7/24
- Engage with users in different languages
- Answer customers’ frequently asked questions
- Respond to customers simultaneously.
The result is that mobile app chatbots lower costs associated with providing customer support. For instance, the second-hand car dealer Cars 24’s chatbot has reduced call center costs by 75%.
4. Generating leads
Mobile apps capture leads. To use apps, clients need to provide personal information concerning their email, ages, addresses etc. This information can be helpful for marketing and sales teams for segmentation purposes.
Banking use cases
90% of US citizens use smartphones for financial activities, and banking and super apps have quickly gained popularity.6 Today’s banking apps can answer a wide range of customer inquiries that used to be handled in bank offices (see Figure 2).
Figure 2: An interface example of a banking app that shows key applications it.
Banking apps have the following use cases:
5. Opening accounts
Rather than visiting a bank to open a bank account, customers can now use their mobile devices to do so. Many mobile banking applications let customers to open:
- Deposit account in local and foreign currencies
- Checking accounts in local and foreign currencies.
6. Checking balance
Customers can check their balance and see its details (income, debts, etc.) anytime and anywhere, thanks to banking apps.
7. Transfering money
Clients can transfer money domestically or internationally using banking apps. Money transfer takes a few hours to a few days, depending on the banks and their location of them. The video below illustrates the money transferring capability of Chase’s banking app:
8. Paying bills
It is also possible for clients to pay their bills such as electricity or credit card debts by using banking apps.
9. Determining mortgage/refinancing rate
The combination of AI-driven mobile chatbots and apps can automate tasks such as determining mortgage and refinancing rates for banks. Mortgage chatbots can collect and verify personal information concerning:
- Income of the mortgage applicant
- The value of the house
- Wealth of the applicant and so on.
To determine the mortgage rate.
The video below illustrates how mobile mortgage chatbots can automate the refinancing rate determination process:
10. Financial assistant
Deploying wealth management chatbots on mobile apps can streamline the provision of investment tips for financial institutions. For instance IIFL improved user engagement with a mobile app chatbot that provides stock ideas.
To learn more about conversational banking, you can read our Conversational Banking: Everything You Need to Know article.
Insurance use cases
Mobile app development is beneficial for insurers due to its following applications:
11. Claims processing and withdrawal
Claims processing is a crucial insurance operation, as 90% of clients select their insurance provider based on their experience with the last claims processing.7 Mobile apps can automate claims processing by collecting and verifying necessary information regarding the incident. Location tracking by collecting GPS data of users helps insurers to verify claims.
AI driven insurance chatbots can be an important part of automating claims since they can act like your human insurance broker. The video below shows how insurance mobile chatbots can automate claims filing.
12. Buying an insurance policy
Some insurtech companies, such as Lemonade, sell their insurance products directly on mobile apps. AI-driven computing devices calculate risk within seconds and automate the insurance underwriting process.
13. Getting real-time incident support
In case of an unfortunate event, such as a car accident, location tracking capabilities of mobile apps help clients discover a solution provider nearby.
14. Providing loss prevention services
Insurers can advise clients on best practices aimed at preventing losses based on weather forecasts and recent events. For example, a Nat Cat insurer provider can alert policyholders of an anticipated rain storm.
Hospitality use cases
15. Making/canceling reservations
Restaurant and hospitality mobile apps enable people to make reservations or cancel them using only their mobile devices.
16. Check-in
Travelers can complete their check-in before arriving at the airport thanks to airway apps.
Healthcare use cases
17. Nutrition suggestion
Healthcare applications can recommend personalized diet tips and track their progress. By deploying healthcare chatbots, companies can make this process more engaging for the users.
18. Monitoring sleep
By integrating with smartwatches, healthcare apps can monitor and regulate users’ sleep times.
19. Managing patient calendar
Users of healthcare apps can receive reminders for their scheduled checks. Also, users can make appointments if they need additional checkups.
Business unit-specific mobile app use cases
An enterprise mobile app can be a valuable tool for monitoring and organizing various business activities across multiple departments. Enterprise mobile apps are great tools for digitalization and have the following applications.
General business use cases
20. Scheduling
Workers can enter their calendar information (such as meetings) as well as time off, thanks to apps.
21. Business travel organization
For workers, travel and planning apps offer route tracking, ticket scanning, navigation services, and general trip planning.
HR
22. Performance measurement
HR apps collect performance indicators for employees, such as working hours, and help HR staff to evaluate the performance of workers.
23. Surveying
Apps for employee feedback enable HR management to gather suggestions from staff, conduct post-surveys, and obtain feedback to improve the working environment.
Accounting
24. Expense reporting
Employees can easily address and collect travel expenses, remote working expenses etc. thanks to the accounting apps.
25. Asset management
Asset management apps assist companies in monitoring the conditions and locations of assets that are used by employees or other parties.
Supply chain
26. Inventory management
Employees can check stock levels, conduct counts, enter new inventory, and make modifications thanks to inventory management apps. Such apps can also integrate with ERP systems and can scan barcodes to monitor inventory.
27. Tracking Deliveries
Thanks to the GPS integrations via APIs, supply chain apps help companies to track the location of deliveries, thus enhancing supply chain resilience.
Sales/Marketing
28. Customer relationship management (CRM)
CRM or customer relationship management apps are critical for data-driven sales and marketing actions. With the aid of these apps, sales representatives stay current on their clients’ needs and foster strong relationships with them.
29. Tracking prices and stocks
Field service employees can use sales apps on their phones to track and view product details and customer orders from any location at any time. They are able to inform clients of prices, stock information, and projected delivery dates as a result.
30. Signature capturing
Many sales apps are built with a signature capture feature that enables the staff to obtain the customer’s digital signature after delivering the purchased item. Thus, companies can reduce the use of paper as well as monitor sales.
External Links
- 1. Same source as footnote (2).
- 2. Same source with footnote (3).
- 3. List of countries by GDP (nominal) - Wikipedia. Contributors to Wikimedia projects
- 4. “Omnichannel: The path to value”. McKinsey. (2021).
- 5. Customer experience is everything: PwC .
- 6. Same source as footnote (4).
- 7. “Claims in a digital era.” EY.




Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.