A few tech and retail giants dominate the eCommerce sector, which is growing at ~10%/year.1
2. Email marketing
Email marketing tools for eCommerce enable online businesses to design, automate, and deliver email campaigns directly to their consumers.
Email marketing for eCommerce involves sending customized messages, promotional content, and transactional information to targeted audiences with the aim of increasing customer engagement, driving sales, and building brand loyalty.
Real-life example:
Livrarias Curitiba, an online store in Brazil, utilized GetResponse’s customizable drag-and-drop editor to create personalized marketing emails, landing pages, and websites and boosted their revenue by 200%. Additionally, they leveraged A/B testing and email analytics tools from GetResponse to improve and optimize their email campaign performance.
3. Image search engines
Google image searches make up more than 22% of all queries, according to SemRush.2
Customers can utilize Google Images to search for products by capturing images and using reverse image search to find related photos, a feature that enhances the online shopping experience.
eCommerce businesses can leverage this technology by uploading optimized images for each item in their online stores. By adding informative titles and alt texts to these photographs, businesses ensure Google search crawlers understand the image content, improving their Google rankings and increasing customer engagement.
Integrating this strategy into mobile commerce and mobile apps can further streamline operations and support the growing number of customers preferring to shop on mobile devices.
4. Mobile apps
According to recent studies, around 60% of e-commerce sales are conducted on mobile apps, and having a custom mobile app can be highly beneficial for eCommerce technology.3
As shown in Figure 1, the general trend suggests that mobile commerce will be even more present in the near future.
Customers can interact with your brand continuously through apps, and they can learn about fresh and useful purchasing opportunities. Additionally, mobile apps provide customers a simple check-out process.
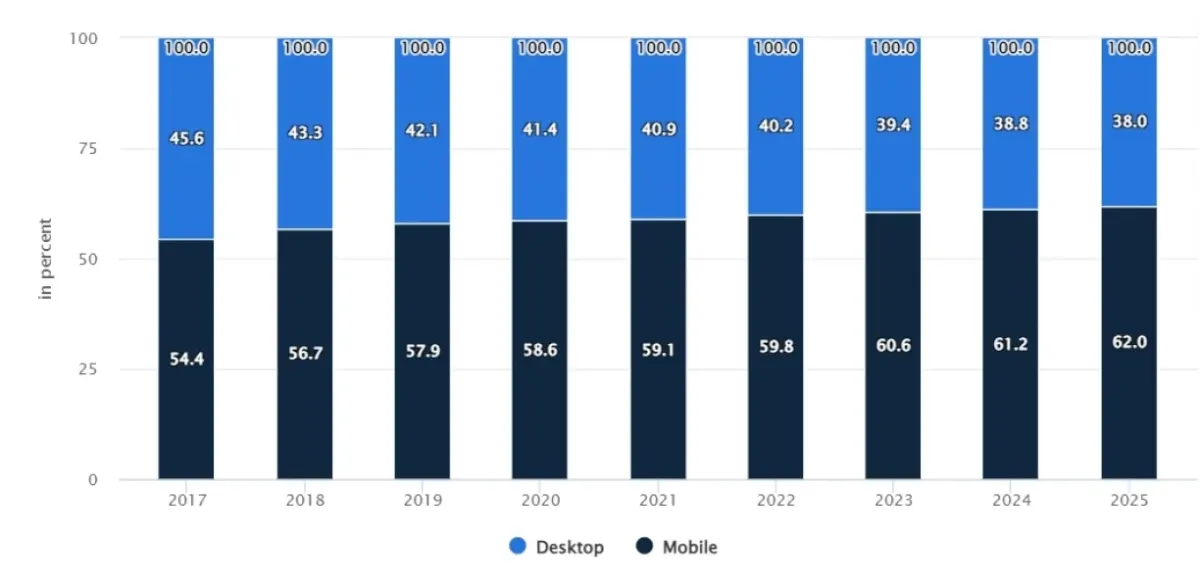
Figure 1: Sales channels mobile vs desktop comparison.4
5. Recommendation systems
Employing recommendation systems is an essential part of effective eCommerce strategies, as approximately 30% of consumers are willing to pay more for things that are suggested to them.5
The aim is to enhance customer engagement by offering personalized shopping experiences based on customer data. These systems utilize machine learning to analyze online purchases and browsing behavior, allowing e-commerce platforms to tailor marketing campaigns and increase customer satisfaction.
By integrating into mobile apps and progressive web apps, recommendation systems improve customer service and loyalty, driving business growth and e-commerce sales.
The overall benefit of recommendation systems is higher rates of engagement and boosted sales.
Recommendation systems can also integrate with pop-ups to alert users about discounts or unattended carts. Thus, eCommerce businesses can reduce site leakages and cart abandonment.
In this regard, AIMultiple suggests executives deploy behavioral analytics to predict their customers’ wants better.
6. Social commerce
Social commerce is the integration of eCommerce processes directly within social media platforms by enabling users to discover, engage with, and purchase products without leaving the social media app or site. With almost 19% of total online sales, social commerce has become highly significant for eCommerce businesses.6
This merging of social media and online shopping leverages the power of social networks to drive sales through social interactions, influencer collaborations, and user-generated content.
Social commerce use cases:
- Instagram shopping: Features shoppable posts, stories, and a dedicated “Shop” tab where users can browse and buy products.
- Facebook shops: Allows businesses to create customizable online stores on Facebook and Instagram, with integrated checkout.
- TikTok shopping: Enables brands to add product links to videos and partner with influencers for product promotion.
- Pinterest buyable pins: Users can purchase products directly from pins they discover on Pinterest.
7. Virtual reality
Another disadvantage of eCommerce vs. offline stores is that people cannot try or experience products before purchasing them. Virtual reality technology solves that issue by creating 3D artificial environments that users can explore and interact with. With virtual reality technology, customers can virtually try out products, arrange furniture in their homes and more.
Real-life example:
The British shirt manufacturer Thomas Pink launched Fits.me, a virtual reality online sales platform. By entering their body size, clients may use the virtual reality platform to see how well the shirt fits them. Thomas Pink observed that the program led to an increase in sales.
eCommerce technologies for operations and efficiency
8. Sustainability solutions
Sustainability solutions for eCommerce are designed to reduce the environmental impact of online retail operations.
These solutions aim to address issues such as carbon emissions, waste production, and resource depletion while promoting eco-friendly practices throughout the supply chain.
Sustainability solutions for eCommerce companies include eco-friendly packaging, carbon-neutral shipping, waste reduction initiatives, product take-back programs, and sustainable logistics such as electric and hybrid delivery vehicles.
Real-life example:
Amazon has made significant improvements in sustainable packaging by reducing single-use plastics by 11.6% in 2022 and implementing paper-based and flexible packaging solutions.
The company has also expanded its electric delivery vehicle fleet. It aims to power its operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025 as part of its commitment to reaching net-zero carbon by 2040.
These efforts have reduced material waste and carbon emissions and supported Amazon’s environmental efforts and customer engagement.7
9. Supply chain visibility software
The entire supply chain processes, from delivery to warehouses, can be managed using supply chain visibility tools. These systems automate the issuance of invoices and track inventory.
While automating supply chain operations, supply chain visibility software also helps to produce reports that can aid the decision-making process. They generate financial reports, and some supply chain management systems have the ability to calculate the corporate and product carbon footprint of the companies.
As a result, you can identify your current carbon emissions pain points and take steps to strengthen your environmental, social, and governance (ESG) posture, ultimately increasing your sales.
For instance, a PwC survey revealed that more than 75% of consumers consider firms’ ESG policies before making a purchase (see Figure 2).
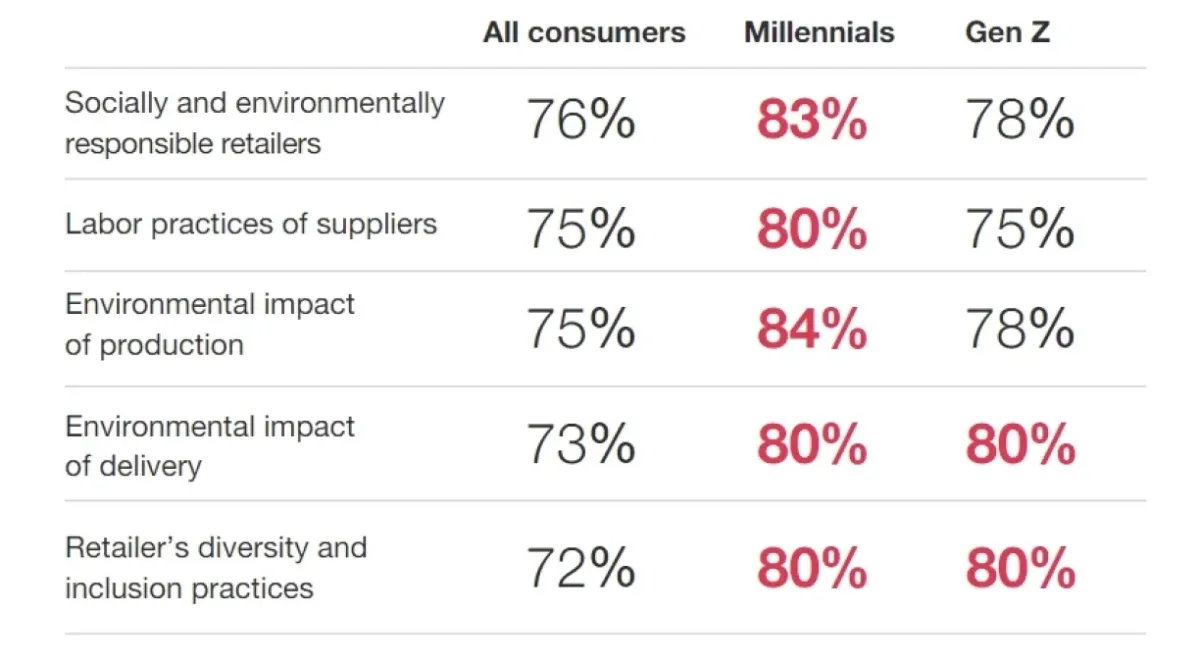
Figure 2: Shoppers that are concerned with ESG practices of businesses.8
To learn more, check out sustainable management definitions and best practices.
10. Warehouse automation technologies
Warehouse automation providesthe following benefits:
- accurate scheduling of intermediate goods and final products,
- optimal inventory management,
- easier financial/environmental reporting, and
- carbon footprint reduction.
eCommerce technology enables the automation of warehouses with the following technologies:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart lightning and HVAC systems optimize the storage conditions of the products while minimizing energy costs. Thus, you can reduce your carbon footprint up to 4% while reducing the number of waste products.
- Intelligent automation: Intelligent automation allows the combination of NLP and RPA technologies. Order processing is automated by this technology, where NLP reads, comprehends, and converts orders into machine-readable formats. Following that, RPA shares the data with inventory management software and creates a shipping label based on the data.
- Collaborative robots (Cobots): Cobots can work around the clock, package and palletize products and augment your workforce.
11. Web scraping
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites using a scraping bot or web scraping API. The technique can be advantageous for eCommerce businesses since these companies produce:
- customer data,
- product data, and
- financial data.
Leveraging web scraping initiatives can be beneficial for companies since they:
- enable price comparison with competitors to stay competitive,
- provide insights on customers’ purchase behavior and find demanded products,
- determine special users such as whales that bring significant income,
- support execution of targeted ads,
- conduct customer sentiment analysis.
Real-life example:
Bright Data’s Data Collector scrapes public data from targeted websites (see Figure 3). It allows companies to choose scraping frequency, such as real-time or scheduled. Scraped data is delivered in the desired format.
Bright Data provides datasets that do not require any programming or technical expertise for those who would rather skip data scraping and obtain the data directly (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Bright Data eCommerce services.
12. AI-driven price monitoring tools
In highly competitive marketplaces, immediately changing pricing to match those employed by rivals can also significantly impact conversion rates and it helps you pounce on the small margins.
With the use of dynamic pricing tools, you can instantly evaluate your prices by comparing them to those of your competitors, as well as your stock levels and delivery policies.
With this knowledge, it is feasible to manually adjust the sales figures or, more frequently, set up the virtual store so that prices are adjusted based on changes in the competition. These strategies help your eCommerce company to remain in competition.
eCommerce technologies for payment systems
13. Check-out free systems
eCommerce technologies and data collected regarding customers is not only optimizing online sales experience but also in-store retail experience. Check-out free systems allow customers to make in-store purchases without queuing by utilizing following technologies:
- computer vision,
- machine learning algorithms,
- smart sensors,
- e-wallets, or custom mobile apps.
Real-life example:
Amazon Go is a network of stores created by Amazon that operate without traditional cash registers. The stores utilize sensors, cameras, and AI technology to monitor what customers pick up, automatically charging their Amazon account as they exit. This system helps eliminate the need for checkout lines and enables an easier shopping experience.
The video below demonstrates how Amazon Go (check-out free system of Amazon) works.
14. Cryptocurrency payments
Cryptocurrency payments utilize digital currencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, to facilitate transactions. These payments leverage blockchain technology to provide a secure, decentralized, and often faster method of transferring value compared to traditional fiat currency systems.
Typically, cryptocurrency transactions have lower fees compared to traditional payment methods, especially for international transactions.
Since all transactions are recorded publicly (blockchain), cryptocurrency payments ensure transparency and traceability.
15. E-Wallets
An “e-wallet,” or digital wallet, is connected to a person’s bank account and used for online purchases on a computer or smartphone.
The two major components of an e-wallet are software and data information:
- The software component secures and encrypts the personal information.
- The data information component includes a database that contains information that users have supplied, such as names, shipping addresses, preferred payment options, required payment amounts, and credit or debit card information.
E-wallets have three main benefits:
- enhanced security,
- support the payment process, thus reducing cart abandonment and
- ease of refund ,which takes a few seconds only.
For more on successful pricing, read mastering eCommerce price monitoring.
Conclusion
To compete effectively in the eCommerce sector, smaller businesses must adopt technologies that address key areas: customer engagement, operational efficiency, and payment systems.
Personalization tools, such as chatbots, recommendation systems, and social commerce features, help improve the customer experience and increase customer retention.
Operational technologies, including warehouse automation, supply chain visibility software, and sustainability initiatives, support cost control and align with consumer expectations on environmental responsibility.
In payment systems, innovations like checkout-free solutions, e-wallets, and cryptocurrency options respond to changing customer preferences and purchasing habits.
Together, these technologies form a practical set of solutions that businesses can implement to enhance performance, meet consumer demands, and achieve sustainable growth.
External Links
- 1. https://www.statista.com/sso/iplogin?__sso_redirect=%2Foutlook%2Femo%2Fecommerce%2Fworldwide%3Fcurrency%3Dusd/efn_note] To compete, smaller businesses should invest in tech to lower costs and increase customer satisfaction, and boost profitability.
To help businesses follow and adopt current eCommerce trends, we present the top 15 eCommerce technologies in personalization and customer engagement, operations and efficiency, and payment systems:
eCommerce technologies for personalization and customer engagement
1. Chatbots and Intelligent virtual assistants (IVAs)
Chatbots and intelligent virtual assistants (IVAs) can be effective for engaging with customers and reducing engagement costs.
By leveraging natural language processing and machine learning, these tools can handle customer inquiries in real-time, providing personalized shopping experiences and improving customer service.
Sales chatbots and IVAs can carry out the same functions on websites, mobile applications, and messaging services like WhatsApp.
Imagine making a purchase in a physical store. Salespeople inform customers about the advantages of the products, display alternatives and complementary items, and perhaps give advice to assist customers in making decisions.
Real-life example:
PrintAbout, a printer and printing supplies company, faced challenges in customer inquiries during the COVID-19 pandemic. To address the increased demand and manage customer service, they collaborated with Watermelon to implement an AI-powered chatbot named “Printy.”
Printy is designed to handle common questions about products like ink, toner, and paper. By drawing information directly from PrintAbout’s website, blogs, and FAQs, the chatbot operates 24/7.
The chatbot ensures customers receive immediate assistance, even during high-traffic periods. Its ability to recall previous conversations allows Printy to provide consistent and personalized responses over time.
The chatbot now manages approximately 90% of PrintAbout’s customer interactions, handling around 1,200 queries each month. This integration has reduced the load on traditional customer service channels like email and phone while enhancing overall response time and customer satisfaction.1https://watermelon.ai/success-story/printabout/!
- 2. Alt Text: What Is It & Why It Matters for Accessibility & SEO.
- 3. https://www.statista.com/sso/iplogin?__sso_redirect=%2Foutlook%2Fdmo%2Fecommerce%2Fworldwide
- 4. eCommerce - Worldwide | Statista Market Forecast. Statista
- 5. Customer experience is everything: PwC .
- 6. https://www.statista.com/sso/iplogin?__sso_redirect=/statistics/1251145/social-commerce-share-worldwide/
- 7. 9 takeaways from Amazon’s 2022 Sustainability Report. US About Amazon
- 8. Holiday Outlook 2024: PwC .


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.