Business rule management can be challenging because:
- They may be hard to formalize
- When rules are stored in documents, document management has high costs
- Legacy systems may implement many poorly documented rules
Business rule mining discipline tackles this challenge by extracting, validating and implementing executable business rules. However, it is an emerging concept that has started to become popular over the last two years, as Google trends data shows (See Figure 1).
Therefore, this research will provide a comrehensive guide on business rule mining by exploring:
- What is business rule mining
- Business rule mining tools
- Applications of rule mining
- How process mining can facilitate it.
What is a business rule?
Business rules manage the systems and data sources to determine business decisions, such as activity execution and business models. These technical rules can cover financial, operational or legal rules and norms.
What is an example of a business rule?
For example, a business rule of an online retailer can state:
The customers must return the purchased goods within 30 days following their good delivery.
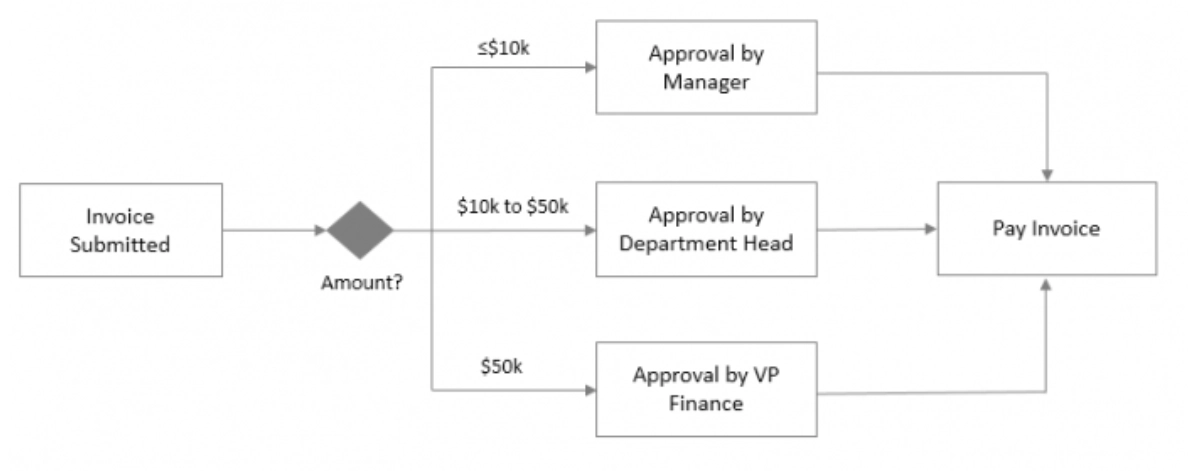
Figure 2 describes a business rule in the invoice payment process as another example. Once an invoice is submitted, the rule dictates that based on the amount, there should be different approval authorities to proceed to the payment phase.
The manager can approve invoices that are up to ten thousand dollars in value. The department head can approve $10k to $50k, while the VP of Finance can approve $50k and more.
What is business rule mining ?
Business rules mining automatically discovers and extracts underlying business rules from various sources, such as database systems, process models, contracts, and regulations. Business rule mining analyzes these sources by combining techniques from:
- Data mining
- Artificial intelligence
- Knowledge management.
Analysts leverage these extracted business rules to ensure compliance and improve and manage processes.
As Figure 3 illustrates, business rule mining can be applied in five steps:
- Access and wrangle operational data
- Extract rules from the data
- Test, analyze and simulate the data for validating rules
- Implement these rules
- Constantly monitor to ensure rule mining success.
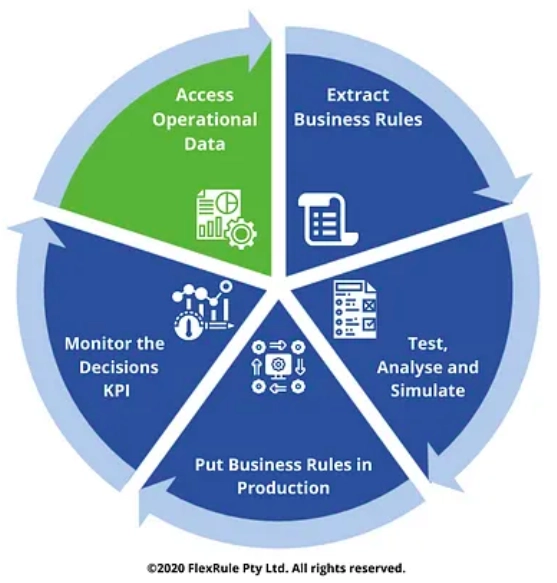
Figure 3: 5 steps to business rule mining, Source: Medium
Top 5 Business rule mining tools
Some of the most common tools for business rule mining include:
- Artificial intelligence platforms: Businesses can leverage AI platforms to develop and implement rule extraction algorithms, such as decision trees, association rule mining, and clustering algorithms.
- Data mining tools: Data science tools can be helpful for data cleaning and wrangling, pattern recognition, and knowledge discovery from large data sets.
- Business process management (BPM) tools: Some BPM software can help extract and visualize business rules as business process models.
- Process intelligence tools: Process mining, task mining or process modeling solutions can automatically capture process data or user interactions to analyze and model business rules.
- Text mining tools: Business rule data requires text mining tools to understand contracts and regulations, process instruction documents, and extract the rules from these documents.
4 steps to leverage process mining for business rule mining
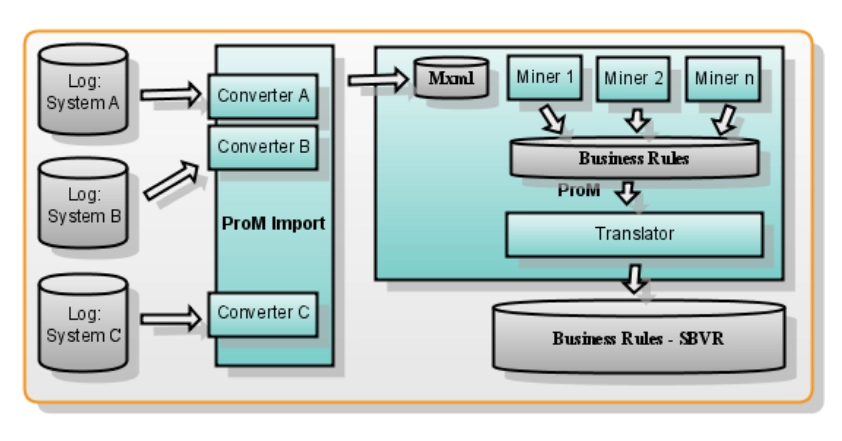
Process mining is a technology and data-driven analytical discipline to provide an end-to-end view of actual business processes. Process mining extracts, analyzes, and models event log data registered in company IT systems (See Figure 4).
Process mining can enable business rule mining with these steps:
1. Data collection
Business rule mining requires documents where the rules are written or defined and the process executions, activities where these rules are practiced and business rule management systems where these rules are managed, if applicable. However, such comprehensive data collection can be achieved with the help of software to look for the documents and capture the employee activities automatically.
Process mining integrates with business systems, such as ERP and CRM systems and automatically gathers event log data. This data includes mainly case ID, timestamp and activities.
2. Process discovery and rule extraction
As a second step in rule mining, the gathered data must be analyzed to identify business rules. An intelligent tool like process mining can do that seamlessly.
Process mining discovers and visualizes a process model by identifying patterns and relationships between activities/ process events. This helps extract business rules from the discovered model. For instance, an invoice approval process model can contain rules such as:
- Approval must be concluded in 5 days
- If not, it must be forwarded to another department.
3. Rule validation and compliance
Once the rules are extracted, analysts and experts must ensure that these rules are accurate and complete.
Process mining conformance checks can help at this stage. Conformance check, also known as analysis, compares as-is and as-if processes against each other. To assess validation levels, rule mining can compare existing business rules against documented, ideal practices.
4. Rule implementation
Once the business rule mining team is sure that the extracted and analyzed rule is valid, they must look for ways to implement these rules in the processes.
Process mining discovers processes and maps workflows, allowing the team to locate areas where they can add the rules or update the activities to include predefined constraints.
What are the business rule mining use cases?
Business rule mining helps organizations to:
1. Optimize processes
By mining rules, process analysts can identify the impact of extracted rules causing bottlenecks and inefficiencies in operations. Analysts can optimize the rule and the activities based on such insight, improving process performance.
2. Ensure compliance
Business rule mining can be useful for assessing process compliance against rules and regulations. This way, companies can avoid high costs resulting from mistakes, inefficient operations and fees related to lack of compliance.
In some cases, compliance can help protect employees. For instance, a safety rule in a construction area ensures the safety of workers.
3. Support data-driven decisions
Business rule mining can assist business leaders and executives in decision-making since it informs them about rules and standards to meet. Once done with process mining, business rules mining can promote data-driven decision-making.
4. Manage knowledge
Since rule extraction requires gathering, analyzing and storing relevant knowledge from business processes, it streamlines and improves knowledge management.
5. Mitigate risks
Identifying business rules allow business leaders to forecast potential risks that might affect their operations. With such insights, leaders can consider scenarios to prevent these risks and intervene in time.
6. Improve customer service
Business rule mining can be used to optimize customer service processes since customer service processes contain various rules that organize and manage customer relations.
Businesses can improve customer service and satisfaction by understanding these rules and enhancing them.
Further reading
Learn more on process mining use cases, benefits and case studies by reading our comprehensive guides below:
- Top 44 Process Mining Use Cases & Applications
- Unlock 11 Process Mining Benefits
- 51 Process mining case studies & project results
If you believe your business can benefit from process mining for business rule mining, check out our data-driven and comprehensive process mining vendor list to decide.
Explore other tools that can assist business rule mining by understanding and managing workflows:
- Workflow management software
- Business process management software
- Low-code/No-code development platform
- Onboarding software
If you need more questions on business rule mining, let us help you


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.