There are different types of proxy servers, varying by source and price. The most common are residential and datacenter proxies. Proxies can also be classified by network type (mobile, ISP), anonymity (transparent, anonymous, elite), access level (shared, semi-dedicated, dedicated), rotation (static, rotating), or cost (free, paid).
In this guide, we break down the main proxy server types, how they work, and their pros and cons.
By Network Type
Residential proxies
Residential proxies are real IP addresses assigned by ISPs to residential devices connected to the internet. These IPs come from actual household networks. Many residential proxy networks rely on people sharing their IP addresses, either willingly in exchange for free services or unknowingly by agreeing to terms buried in app or software agreements.
Imagine you install a free VPN. Buried in the terms, it states that the app can utilize your device as part of a peer-to-peer network. Your IP address might be added to a residential proxy pool and sold to someone who uses it to browse, without interfering with your normal use.
Datacenter proxies
Datacenter proxies provide IP addresses that originate from servers within data centers, rather than from individual households. Datacenter proxy providers acquire IP ranges directly from:
- Cloud hosting services (e.g., AWS, OVH, or DigitalOcean)
- ISPs offering commercial IP allocations.
- Data center operators that lease IP ranges to proxy service providers.
Since datacenter IPs are not associated with any physical residence or ISP customer, they’re often flagged by websites as suspicious. However, they are generally faster and much cheaper than residential or mobile proxies.
Mobile Proxies
Mobile proxies provide IP addresses assigned by mobile network operators. When you use a mobile proxy, your traffic appears to originate from a real mobile device connected to a cellular network. Mobile proxy networks are sourced through:
- Devices owned by the proxy company: SIM cards and mobile devices are running on real mobile networks but are controlled directly by the proxy provider.
- User-contributed devices: Users may share mobile network connections through apps or agreements.
ISP proxies
ISP proxies (also known as static residential proxies) provide IP addresses originating from Internet Service Providers (ISPs), but these addresses are hosted on servers within data centers. Instead of real user devices or peer-to-peer networks, the proxy company owns or leases the IPs.
By Trust Level
Transparent proxies
Transparent proxies (also known as non-anonymous proxies) forward your actual IP address along with the proxy IP address to the target website. The destination server knows both your IP and the fact that you’re using a proxy.
Anonymous proxies
Anonymous proxies (or anonymizer proxies) hide your real IP address from the target website, but reveal that you are using a proxy solution. Your internet traffic is routed through an anonymous proxy server, but headers indicate the use of a proxy, such as via or proxy-connection.
Elite proxies
Elite proxies (or high anonymity proxies) both hide your real IP address and do not reveal that a proxy is being used. The proxy does not add headers or signals to prevent the identification of the client’s IP address, making them suitable for web scraping and bypassing anti-bot systems.
By Cost
Free proxies
Free proxies are publicly accessible proxy servers that require no payment and are listed on free proxy websites. However, they may be slow, frequently down, or already blacklisted. You can use proxy checker apps to check if your real IP address is hidden or if the IP address listed is on spam or abuse blacklists.
Paid proxies
Paid proxies come with service-level guarantees for uptime, speed, support, and security. They offer a lower risk of IP bans, especially with reputable proxy providers. The cost of the service depends on the type of proxy, mobile and residential proxies are more expensive.
By Stability
Static proxies
Static proxies are fixed IP addresses that remain constant throughout the entire session. Every request you make through a static proxy will appear to come from the same IP address.
Datacenter proxies are generally static by default. ISP proxies are also static, providing residential IPs hosted on servers. While most residential and mobile proxies rotate by default, some providers offer static residential or mobile options at a higher price.
Rotating proxies
Rotating proxies automatically change the IP address at fixed intervals. These proxy pools can include residential, mobile, and datacenter IPs.
Rotating proxies can rotate on a per-request, per-time-period, or per-session basis. For instance, each time you make a request, the provider assigns you a different IP address from the pool.
By User Exclusivity
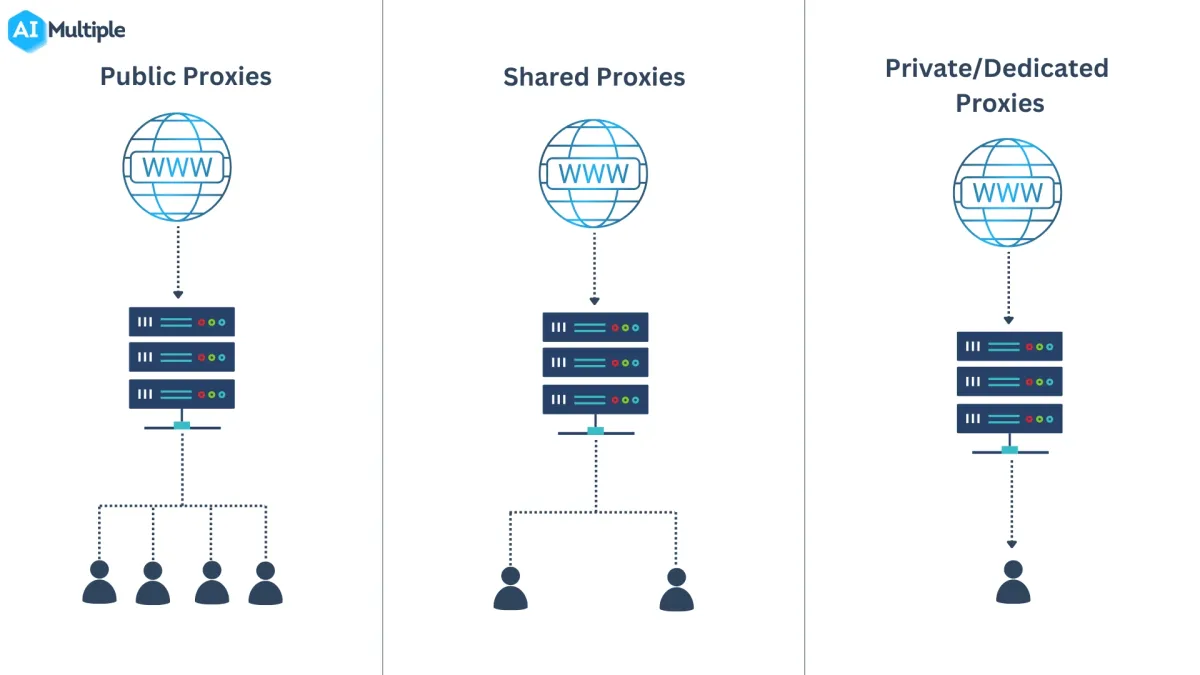
Shared proxies
Shared proxies are proxy IP addresses that are used simultaneously by multiple users. However, the performance and speed of the proxy server will decrease as the number of users increases. Since you do not have control over each activity, being blocked by websites is easier with public proxies compared to private proxies.
The cost is more affordable than that of private proxies, as many users share and utilize the same IP address.
Semi-dedicated proxies
Semi-dedicated proxies are shared between a limited group of users (usually 2 or 3). They are more stable and faster than fully shared proxies.
Dedicated proxies
A private proxy, also known as a dedicated proxy, is a type of proxy used by only one user, allowing complete control over all activities. Since a specific IP address is used solely by one user, the proxy server speed is high. If you are concerned about speed and security but not about cost, private proxies are the best option for you.
Figure 3: Proxy types based on the number of people who share an IP address
By protocol
Internet protocols enable data transmission between a client and a server through a proxy server. There are many types of proxy servers based on the Internet Protocol. The most common protocols used by proxy servers include:
- HTTP proxies
- SOCKS proxies
- SOCKS4
- SOCKS5
- SSL proxies
The two main internet protocols used by proxy servers to receive and forward client connection requests are HTTP and SOCKS. Both proxy types mask clients’ actual IP addresses, providing anonymity while browsing. However, there are circumstances where an HTTP or SOCKS proxy should not be used.
FAQs About Proxy Server Types
Which proxy type offers the highest trust level?
The proxy types with the highest anonymity level are:
Mobile proxies utilize real IP addresses assigned by mobile carriers (3G/4G/5G), allowing websites to recognize them as genuine mobile users.
Residential proxies utilize IP addresses assigned by ISPs to actual households, making them appear as legitimate home users.
Are free proxies safe?
Free proxies are not safe. These proxies may log your activity or inject ads into web pages. They are often slow or already blacklisted by many websites.
How to check proxy type?
Visiting IP-check tools (e.g. whatismyip.com, ipinfo.io) to see what kind of network it’s from (datacenter, residential, mobile, ISP).
Testing anonymity level (e.g. whoer.net, ipleak.net) to see if your real IP is hidden.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.