The insurance sector is experiencing a rapid shift towards digitalization. More than 80% of large insurance companies have either invested in or are working with insurtech companies.1 The “insurance as a service” approach is a part of such collaboration between insurtechs and established insurance companies.
Explore the insurance as a service approach, challenges, and top 7 insurance as a service companies:
Top 7 insurance as a service providers
| Provider | Rating | Focus area |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Epic | 4.3 out of 867 reviews | Accounting, customer service, document management |
| BriteCore | 4.0 out of 17 reviews | Underwriting & claims processing |
| NextAgency for Health & Life Insurance | 4.8 out of 48 reviews | Agency management |
| RiskMatch | 4.1 out of 4 reviews | Risk assessment |
| Speedy Claims | 4.7 out of 412 reviews | Claims processing |
| Virtual Claims Adjuster | 4.7 out of 33 reviews | Claims processing |
| [VRS]™ Virtual Risk Space | - out of - reviews | Underwriting & FNOL |
The abovementioned insurance platforms offer cloud computing solutions to insurers to help them digitalize their:
- Underwriting
- Risk assessment
- Claims processing
- Customer service
- Document management and so on.
Thus, these digital insurance platforms can help insurers manage a fast digital transformation process. While we were picking best insurance as a service providers we have used our lists of:
We only choose online insurance providers with ratings of at least 4. (between 0-5). While we were sorting the insurance platforms, we used user ratings since they provide different services for insurers, e.g., underwriting and claims processing.
What is insurance as a service?
The Something as a Service approach is widespread in many industries. The X as a service approach is always associated with the purchase of services from vendors on a subscription basis to increase a company’s operational efficiency. “As a service” solutions are popular because they are relatively cheap, easy to install and ensure scalability and quick upgrades.
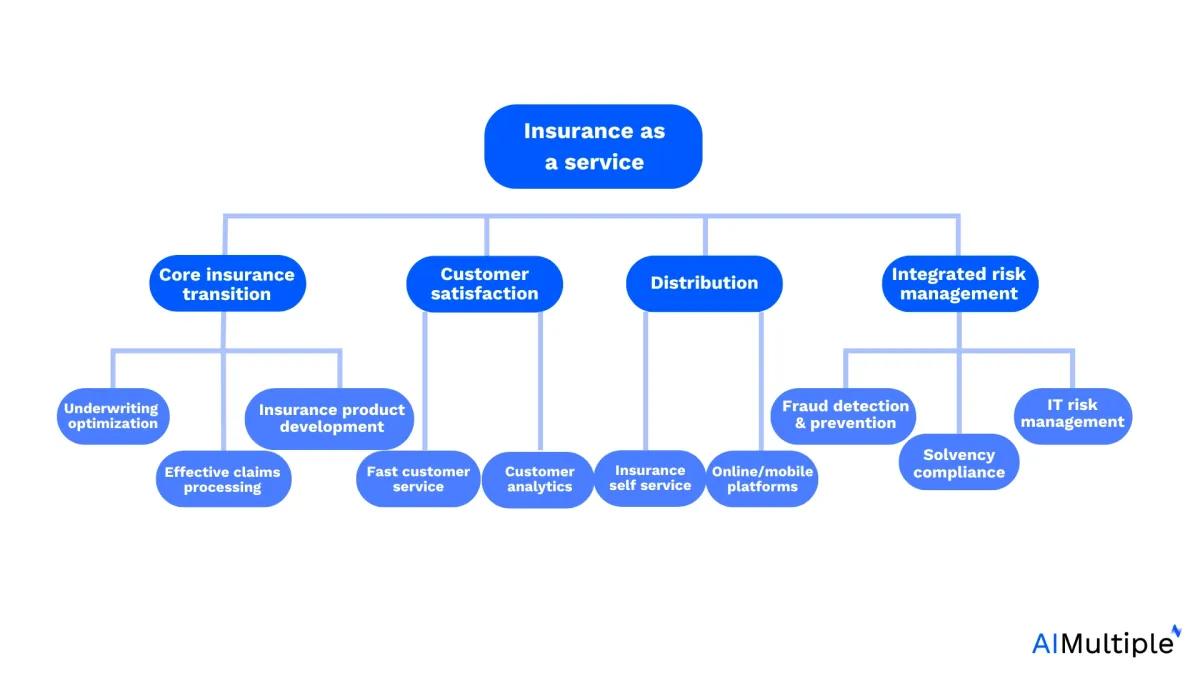
So, “insurance as a service” means that startups offer other companies the use of selected pre-built elements of the insurance value chain on a subscription basis, essentially running insurance operations for others. Such platforms are cloud-based and can help improve core insurance practices such as underwriting, claims processing, fraud detection, and customer service.
Figure 1. Insurance as a service solutions
How AI transforms insurance as a service
Transformation in the insurance industry
1. Improving customer interactions
AI-powered tools like virtual assistants and chatbots help insurers respond quickly to customer questions. These tools understand natural language, which makes conversations feel more human and less robotic.
- Customers can get help 24/7.
- Common tasks—like checking policy details or filing claims—can be done without waiting for a human agent.
- Personalized responses improve customer satisfaction.
These improvements help insurance companies meet rising customer expectations.
2. Faster claims processing
Traditionally, processing insurance claims took time and involved a lot of manual work. AI speeds up this process.
- It can review documents, images, and data automatically.
- It can detect errors or signs of fraud early.
- Agents can focus on complex claims, while AI handles routine ones.
This means faster results for customers and lower costs for companies.
3. Smarter underwriting and pricing
AI can help insurers offer fairer and more competitive pricing.
- It can analyze customer data—like age, location, and driving history—to suggest the best rate.
- It helps underwriters make decisions faster by providing insights from large amounts of data.
This makes insurance more accurate and personalized.
4. Creating new insurance models
AI supports flexible, behavior-based insurance.
- Car insurance can be based on miles driven or driving behavior.
- Health insurance can reward healthy habits.
These models make insurance more personalized and adaptable to real life.
5. Enabling Embedded Insurance
AI makes it easier to offer insurance as a built-in service. Through APIs (tools that let systems talk to each other), insurance can be added directly into other products.2
- For example, travel insurance can be offered when someone books a flight.
- This creates new ways to reach customers and offer coverage at the right time.
Users expectation from AI in Insurance-as-a-Service
One of the main AI tools driving transformation is Generative AI (GenAI). It is no longer just a trend. Many business leaders now see it as essential. According to a recent survey by Fortune and Deloitte, nearly 80% of CEOs believe GenAI will reshape their businesses in the next three years.3
Figure 2. Expectations of users of insurance as a service from AI
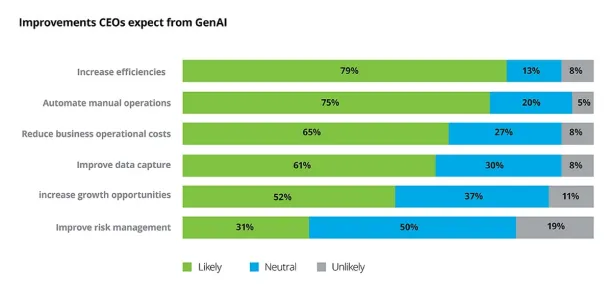
Source: Deloitte4
Why is insurance as a service important now?
Necessity to improve margins
The best price is the most effective criteria for buying business and property insurance. However, most insurance companies operate with very low or negative economic profit margins. Consequently, insurance companies need to improve their operational processes. The “insurance as a service” approach offers a relatively easy and cost friendly path to digital transformation for insurance companies and helps incumbents to remain competitive.
Figure 3. Economic profit of insurance companies
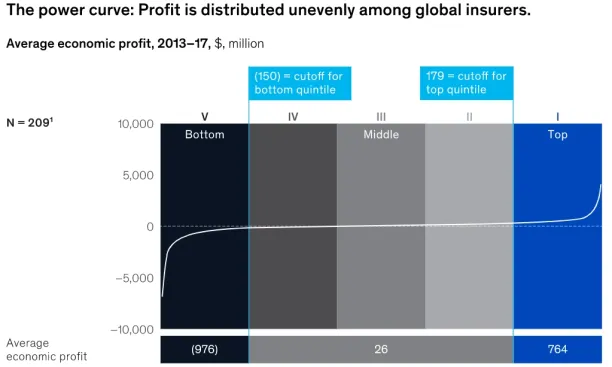
McKinsey5
Pressure to adopt new technologies fast
With deregulation and tech innovation, insurtechs are innovating fast which forces the whole industry to innovate at a faster pace. Insurer executives plan to increase their technology investments. Insurance as a service helps insurance companies adopt new technologies quickly.
Figure 4. Emerging technologies where insurance executives expected to increase spending
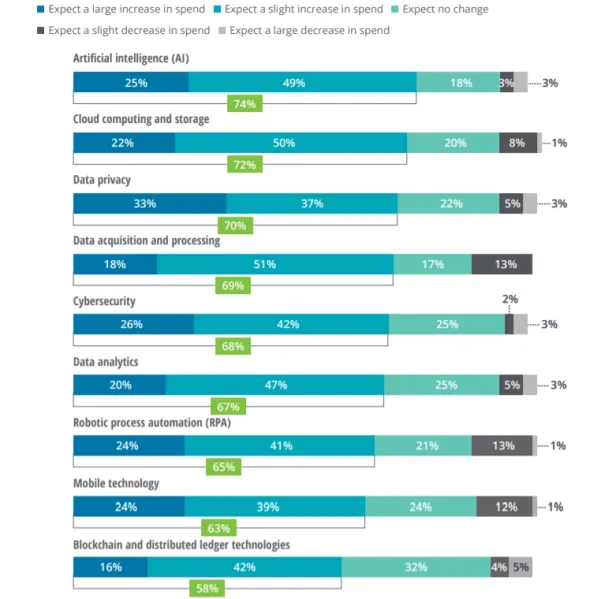
Source: Deloitte6
What are the fundamental insurance as a service models?
It is possible to classify insurance as a service into three different categories: Full-stack digitization, digitizing process assistance, and core service digitization.
1. Full-stack digitization
Full-stack digitization is an end-to-end infrastructure for deploying digital insurance practices. In the name of full-stack digitization, insurtechs can develop a platform for an incumbent company or the companies can agree on a licensed white-label backend. Such insurtechs are examples of B2B2x where they facilitate the digital transformation of old-fashioned insurance companies. Full-stack digitization saves infrastructure costs and helps incumbents conduct technology driven insurance practices from anywhere, anytime.
2. Digitizing process assistance
Some Insurtechs are working with incumbents to redesign internal processes within a closed digital ecosystem for non-insurance practices. For example, providing effective customer service using NLP-driven chatbots is a common digital solution that offers efficiencies to businesses whether they are insurance companies or not. Automating customer service, company accounting systems, IT requirements, etc., by leveraging the “insurance as a service” model, falls into this category.
3. Core service digitization
Some Insurtech companies offer their services in a specific area of insurance, such as underwriting, claims processing, and fraud detection. Using such services can help incumbents compete with innovative insurers that can:
- Conducting an appropriate risk assessment with technology-driven underwriting processes. Therefore, they can set a lower premium, which gives them a larger market share, as price is the main criterion of insurance customers.
- Ensuring customer engagement with fast claim processing.
- Gaining a greater strategic movement area in pricing thanks to effective fraud detection.
Challenges insurance as a service companies face
1. Securing digital operations
As digital insurance becomes standard, cybersecurity has become critical to protect customer data and uphold trust. Insurance companies need robust defenses against cyber threats to avoid costly breaches and data compromise.
2. Rising consumer expectations
Today’s modern consumers demand a seamless integration of technology with their customer experience. Insurers must leverage data-driven insights and adapt to provide customer-centric digital services, including mobile apps and AI-powered support.
3. Attracting and retaining skilled talent
Securing digitally skilled professionals is crucial to support industry innovation. Insurance expertise combined with technology proficiency is essential, and companies must create an environment aligned with a tech-driven business model to retain talent.
4. Navigating regulatory changes
Meeting compliance requirements in a changing regulatory landscape requires agility. Insurance companies must balance regulatory adherence with digital innovation, making compliance a core part of their business cases.
5. Adapting to insurtech and disruptive technologies
Insurtech startups are revolutionizing the industry, challenging traditional insurers to adapt quickly to embedded insurance, IoT, and AI innovations. Embracing these changes provides new business models and revenue streams for insurers.
6. Managing climate and catastrophic risks
With rising climate-related claims, insurers need advanced risk modeling and insurance products that can mitigate the financial impact of catastrophic events, ensuring their core business can withstand future disruptions.
7. Responding to shifting demographics
With an aging population, the insurance industry must develop coverage options like long-term care policies. Adapting insurance policies to address these demographic shifts will help meet evolving customer expectations.
8. Containing healthcare costs
Rising healthcare costs challenge health insurers to provide comprehensive insurance products while keeping premiums manageable. Innovation in health models and pricing strategies is essential to balance coverage and affordability.
9. Embracing digital distribution channels
With a shift towards online channels, independent agents and brokers need to adjust. Insurers are focusing on direct-to-consumer platforms to streamline the insurance value chain and adapt their distribution models for a digital-first audience.
10. Maintaining profitability in low-interest environments
Prolonged low-interest rates impact revenue streams from investments. Insurance companies must seek alternative business cases to maintain profitability while ensuring they can meet claims obligations.
Further readings
By reading our selection of five articles, you can learn more about the latest developments in the insurance sector.
- 6 Ways IoT will Change the Insurance Sector: Smart devices have the potential to completely change the insurance sector as we know it. They monitor the environment we live in 24/7 and will thus reduce the percentage of physical losses. However, the advent of the IoT could bring more cyber risks, and soon cybersecurity insurance could be the most important insurance practice.
- Technologies that Improve Insurance Claims Processing: Claims processing includes all the steps during which the insurer checks the necessary information about the loss, policy and the event in order to calculate and pay out its liability to the policyholder. It begins with the submission of the first notice of loss (FNOL) and ends with either the rejection of the customer’s request or the transfer of the money to the customer. We analyze 7 technologies directly improve claims processing.
- Insurance Pricing: Determination & New Methods: Getting the best price is the top priority for 52% of auto insurance customers, 50% of home insurance customers, and 38% of life insurance customers. Read the determinants of insurance pricing.
External Links
- 1. The new face of insurance. IBM.
- 2. Generative AI: transforming creativity and innovation in insurance.. Charles Taylor Group
- 3. Gen AI Innovation in the Insurance Industry | Deloitte US. Deloitte
- 4. Gen AI Innovation in the Insurance Industry | Deloitte US. Deloitte
- 5. Pricing strategy for P&C insurers post COVID-19 | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 6. 2025 global insurance outlook | Deloitte Insights. Deloitte

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.