An IP ban is a security measure taken by website administrators and online service providers to restrict or block access from particular IP addresses, either on a temporary or permanent basis. This measure is commonly initiated due to reasons such as an unusually high number of requests from the same IP address, engagement in harmful activities, or breaches of the terms of service.
To avoid IP bans, individuals often resort to solutions like VPNs and proxy servers, which enable them to modify their IP address. Although altering your IP address is not illegal itself, the implications of bypassing IP bans legally are significant. This article explains the most effective and lawful strategies for bypassing IP bans, ensuring adherence to both legal standards and ethical practices.
Understanding IP bans
What is an IP ban?
An IP ban is a security measure implemented by the target network administrator and other online service providers that blocks incoming requests from a specific IP address.
A website or platform’s server might restrict an IP address due to several factors, like web scraping challenges, attempting to access geo-restricted content, or engaging in spam activities.
Why are IP bans implemented?
IP bans are implemented for a number of reasons to protect services and ensure a secure environment for users, including:
- Combating spam: IP ban as a security measure helps website owners mitigate the influx of unwanted comments, messages or other spam related content activities. For example, dynamic blocking systems enable websites to automatically identify the source of spam activity and add it to a blacklist. The use of shared proxy and dynamic IP addresses makes it challenging for websites to identify the spam malicious activities.
- Preventing unauthorized access: IP ban is used as an access control mechanism to restrict or block the ability of a user with a particular IP address to interact with a network.
- Limiting overuse of resources: Websites use IP ban measures to identify and block IP addresses that consume an excessive amount of a network’s resources. Activities such as downloading large files or conducting large-scale data transfers can slow down the network. IP bans enable online services to monitor usage patterns to flag IP addresses that exceed usage thresholds.
- Protecting against web scraping activities: Implementing automated anti-bot measures helps service administrators detect malicious data scraping activities and block the associated IP address.
How does an IP get banned?
IP banning or blocking is a security measure used to prevent misuse and block access from problematic sources. Sometimes, a ban might apply not just to an IP address but also to a MAC address (media access control), which is a unique identifier for network interfaces. The process starts with identifying unusual behavior, such as unexpected traffic spikes that could suggest spamming, or numerous unsuccessful login attempts.
Tools like server logs, cookies, and analytics can help in pinpointing the IP address involved. Once a site flags an activity as potentially harmful, security protocols or network administrators review it. If they confirm it violates rules, they place the IP address on a blacklist, effectively stopping any data exchange from that IP. This ensures that any attempt to connect from the blacklisted IP is either blocked or ignored, maintaining the site’s security.
IP bans may be either temporary or permanent, depending on the policies of each service provider regarding the management of infractions. Service providers might opt for temporary bans as a corrective measure for initial offenses, whereas more severe or recurrent breaches could result in a permanent ban. The nature of the violation significantly influences the length of the ban imposed.
Legal and ethical considerations
Is it legal to bypass IP bans?
Changing your IP address in itself is not typically illegal, but the legality of circumventing IP bans can differ widely based on factors like local laws and the terms of service of the specific website or service involved—also raising questions around web scraping ethics.
Engaging in illicit activities such as hacking, fraud, or sharing forbidden content under a bypass IP ban is clearly unlawful and can result in serious legal consequences. It’s crucial to reflect on the ethical considerations evading IP bans. If there’s any uncertainty regarding the legal standing in your situation, seeking legal counsel is advisable.
What are the ethical implications of circumventing IP bans?
- Violation of terms of service (ToS): ToS is a legal agreement between the user and service provider, outlining the guidelines for using the service. When they start using the service, ignoring these rules may lead to penalties for ToS violations such as permanent IP ban or legal action.
- Potential misuse: Tools used to bypass an IP ban can be misused for illegal activities such as violating privacy. For instance, VPN services can be used to gain unauthorized access to private accounts. There are many areas of concern related to potential misuse of these tools such as data theft, dark web access, or copyright infringement.
- Privacy and anonymity: The use of IP-bypassing tools like VPNs and Tor Network can lead to legal challenges in balancing privacy rights.
Tools for bypassing IP bans
1. Proxy Servers
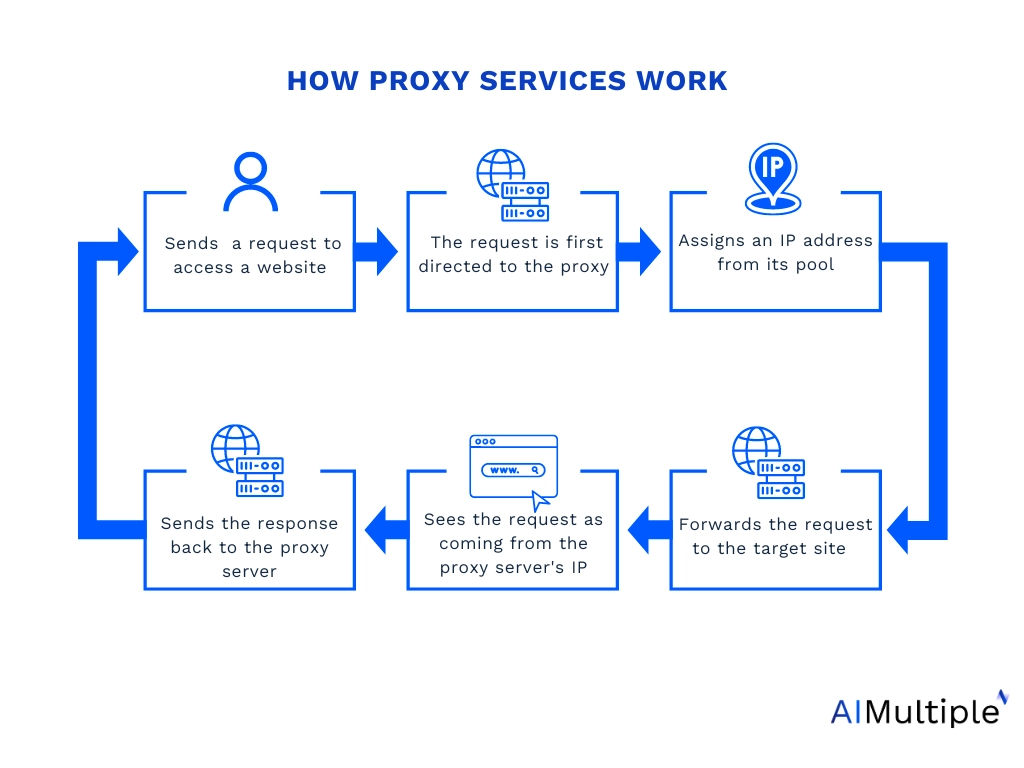
Using a proxy service to bypass IP ban can be a practical solution as it routes your internet traffic through an intermediary server. Selecting a reliable proxy provider is crucial. There are various types of proxies, including datacenter, mobile, ISP proxy server and residential proxies, each offering unique benefits and suited to different applications. For instance, residential proxies are ideal for activities that demand enhanced security and privacy.
Proxies are typically divided into two types based on their ability to change IP addresses: rotating and static. Rotating proxies assign a new IP address for every connection request or after a certain time interval. This feature is particularly useful when a website has detected and blocked your current IP; with rotating proxies (offering dynamic IP addresses), you can obtain a fresh IP address, allowing you to circumvent advanced anti-scraping technologies.
Pros:
- Like VPNs, proxy solutions hide your original IP address, suitable for tasks such as data extraction projects, bypassing IP-based restrictions and accessing region-specific content.
- Proxy services can be found at prices more affordable than those of VPN services, offering a cost-effective option for both individuals and organizations.
Cons:
- Proxy services don’t encrypt internet traffic, your data can be vulnerable to interception on unsecured networks.
Top 7 proxy server provider
| Providers | Starting price/GB* | Traffic (GB) | PAYG** | Free trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Data | $6.30 | 1 | All proxy types | 7-day |
| Oxylabs | $9 | 11 | Residential Mobile | 7-day |
| Nimble | $150 | $8 | ❌ | 7-day |
| NetNut | $15 | 20 | ❌ | 7-day |
| Smartproxy | $7 | 2 | Residential Mobile | From $1 to free |
| PrivateProxy. | $12 | 10 | ❌ | 7-day |
| IPRoyal | $7 | 1 | ❌ | 24-hour refund |
Table notes:
Starting price*: Based on the smallest monthly subscription plan for the smallest residential package offered. In our analysis of proxy services, we focused on residential proxies due to their effectiveness in circumventing IP bans.
PAYG**: Entries in this column are available for acquisition on a pay-as-you-go basis.
2. VPNs (Virtual Private Networks)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology for creating a secure and encrypted connection between two networks. When you connect to a VPN service, all the data you send is received between remote locations over the Internet.
VPN services can hide your actual IP address by routing your internet connection in another location, making it appear as if you’re accessing the internet from another place.
Pros:
- A VPN server can mask your real IP address and encrypt web traffic. Data you send and receive from the target web server is in a coded form that can only be decrypted with the correct key. VPN services protect you from security threats on unsecured networks such as public Wi-Fi networks.
Cons:
- The web data encryption process and routing of internet traffic through VPN servers can lead to slower internet speed.
3. TOR Network
The TOR Network, also known as The Onion Router, conceals user information by encrypting data and routing it through a series of random relays. This method guarantees that both the initial data and the user’s geographical location are kept confidential, challenging online services to determine the user’s actual location.
Tor browser allows users to bypass IP bans and regain access to the target website by routing your internet traffic through multiple random nodes. It is developed using Mozilla Firefox as its base framework.
Pros:
- Tor browser is configured to not keep browsing history or cookies, enhancing users’ digital privacy.
Cons:
- Tor browser can be a complex solution for those unfamiliar with privacy tools.
- Some online services and websites may block traffic from Tor Network due to security reasons.
4. Smart DNS Services
Smart DNS services primarily help circumvent geographic content blocks. In contrast to VPNs and proxies, which redirect all internet traffic through a remote server, Smart DNS selectively alters only the DNS queries that reveal your location, effectively bypassing regional restrictions on content.
Pros:
- Smart DNS can be configured on various devices, including those that don’t support VPNs like streaming devices.
Cons:
- It doesn’t encrypt your web data, leaving your online activities exposed to ISPs.
- Smart DNS doesn’t change your IP address, your online identity can be identified by other online services.
5. Manual IP change
You can manually alter the specific IP addresses in its network settings without relying on automatic assignment methods. Most proxy service providers offer automatic IP assignment features by default. Manual IP rotation can be useful for tasks that require static IP addresses for consistent web access.
Pros:
- Manual IP change provides users complete control over when and how often your IPs rotate.
Cons:
- Changing IP addresses manually might not be effective in the long run since many websites employ strict IP bans that are strict enough to detect IP rotations.
Further reading
- 7 Web Scraping Best Practices You Must Be Aware of
- The Ultimate Guide to Avoiding CAPTCHAs in Web Scraping in
- 6 Main Web Scraping Challenges & Practical Solutions
For guidance to choose the right tool, check out data-driven list of proxy services, and reach out to us:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.