The role of data has become paramount for digitally transforming enterprises. Whether it’s marketing or AI data collection, businesses have become increasingly reliant on accurate data collection to make informed decisions; it’s essential to have a clear strategy in place.
This article explores the top techniques for data collection across different sectors and use cases.
What is Data Collection?
Data collection is the process of gathering information from web sources to analyze, interpret, and act upon. The data collection process involves various methods, including crowdsourcing, web scraping, public datasets, and surveys.
What are the most common data collection methods?
- Automated data collection tools (web scrapers): Data collection tools enable users to crawl websites and extract web data automatically in a structured way.
- Primary data collection methods: Include online surveys, focus groups, interviews, and quizzes to collect primary data directly from the source. You can also leverage crowdsourcing platforms to gather large-scale human-generated datasets.
- Secondary data collection: Uses existing data sources, often called secondary data, like reports, studies, or third-party data repositories. Using web scraping tools can help gather secondary data available from online sources.
- Online survey for market research: Marketing survey tools or survey participant recruitment tools capture direct customer feedback, offering insights into preferences and potential areas for improvement in products and marketing strategies.
- Social media monitoring: This method analyzes social media interactions to gauge customer sentiment and assess the effectiveness of social media marketing strategies. Social media scraping tools can be used for this type of data.
- Web analytics: Web analytics tools track website user behavior and traffic, helping to optimize website design and online marketing strategies.
- Email tracking: Email tracking software measures the success of email campaigns by monitoring key metrics like open and click-through rates. You can also use email scrapers to gather relevant data for email marketing.
- A/B testing: A/B testing compares two marketing assets to determine which is more effective in engaging customers and driving conversions.
- Feedback forms: Companies can use feedback tools or analysis to gather direct insights from customers about their experiences, preferences, and expectations.
- Customer service interactions: Recording and analyzing all interactions with the customers, including chats, emails, and calls, can help in understanding customer issues and improving service delivery.
- Incident data: You can use incident management or response systems to document, track, and analyze incidents; encourage employees to report issues and use this data to improve risk management processes.
- Employee training and policy acknowledgment records: You can implement learning management systems to track employee training and use digital platforms for employees to acknowledge policy understanding and compliance.
- Vendor and third-party risk assessment data: For this type of data, you can employ vendor intelligence and security risk analysis tools. Data gathered from these tools can help evaluate and monitor the risk levels of external parties, ensuring that they adhere to the required compliance standards and do not present unforeseen risks.
Importance of data collection
Having access to high-quality data allows businesses to stay ahead of the curve, understand market dynamics, and create value for their stakeholders. Moreover, the success of many modern technologies also relies on the availability and accuracy of the gathered data.
Accurate data collection ensures:
- Data integrity: Ensuring the consistency and accuracy of data over its entire lifecycle.
- Data quality: Addressing issues like inaccurate data or data quality issues that can derail business objectives.
- Data consistency: Ensuring uniformity in data produced, making it easier to analyze and interpret.
Top 6 data collection use cases you need to know
This section highlights some reasons why businesses need data collection and provides some methods for collecting data for that specific purpose.
1. AI development
Data is required in the development process of AI models. This section highlights two major areas where data is needed for the AI development process. If you wish to work with a data collection service provider for your AI projects, check out this guide.
1.1. Building AI models
The evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) has necessitated an increased focus on data collection for businesses and developers worldwide. They actively accumulate vast quantities of data, vital for shaping advanced AI models.
Among these, conversational AI, like chatbots and voice assistants, stands out prominently. Such systems require high-quality, relevant data that accurately reflects human interactions, enabling them to perform tasks naturally and effectively with users.
Beyond conversational AI, the broader AI spectrum also hinges on precise data collection, such as:
- Machine learning
- Predictive or prescriptive analytics
- Generative AI
- Natural language processing (NLP), etc.
This data enables AI to recognize patterns, make predictions, and emulate tasks previously exclusive to human cognition. For any AI model to achieve its peak performance and precision, it crucially depends on the quality and volume of its training data.
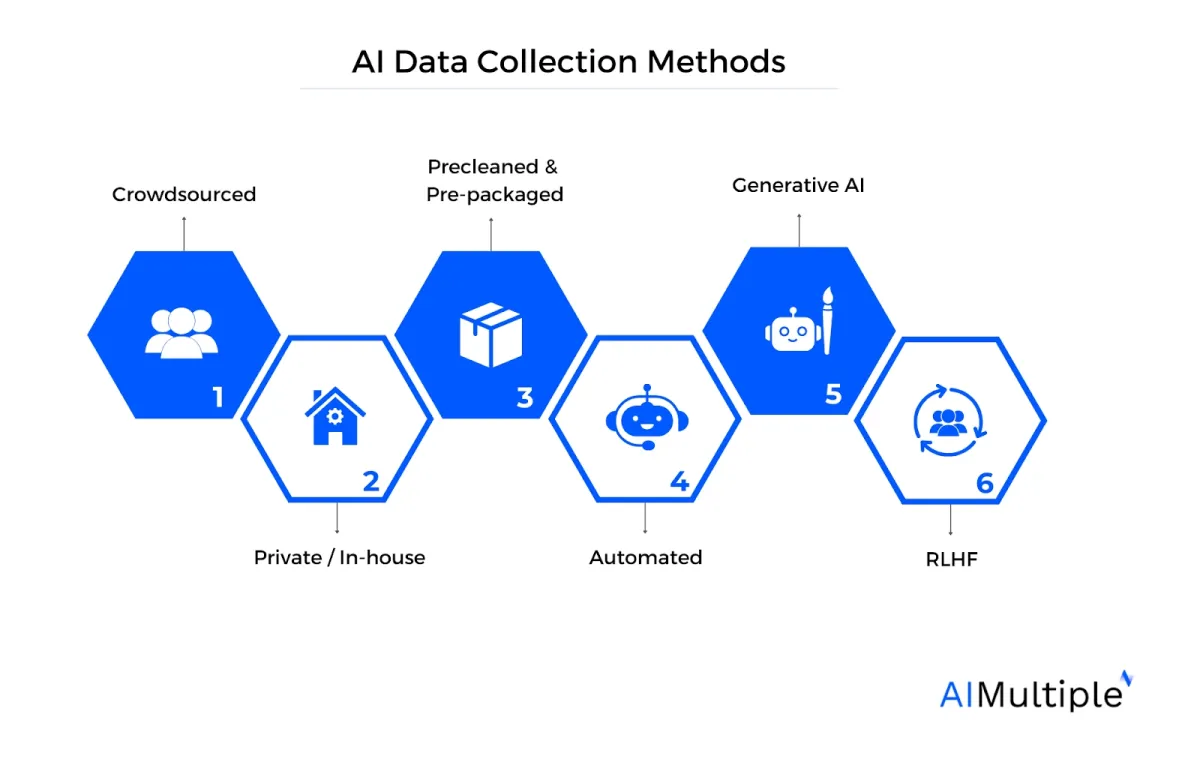
Some popular methods of collecting AI training data:
- Crowdsourcing
- Prepackaged datasets
- In-house data collection
- Automated data collection
- Web scraping
- Generative AI
- Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF)
Figure 1. AI data collection methods
1.2. Improving AI models
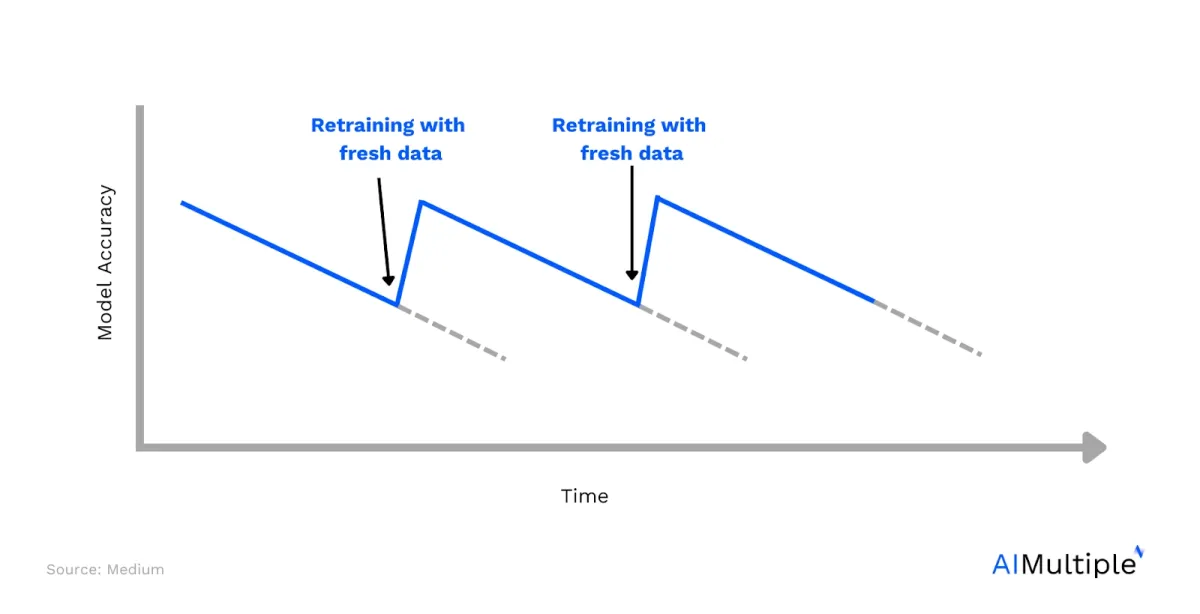
Once a machine learning model is deployed, it should be improved. For instance, a quality assurance system implemented on a conveyor belt will perform sub-optimally if the product that it is analyzing for defects changes (i.e., from apples to oranges). Similarly, if a model works effectively on a specific population, and the population changes over time, that will also impact the model’s performance.
Figure 2. A regularly retrained model with fresh data
2. Conducting research
Research, an integral component of academic, business, and scientific processes, is deeply rooted in the systematic collection of data. Whether it’s market research aimed at understanding consumer behaviors and market trends or academic studies exploring complex phenomena, the foundation of any research lies in gathering pertinent data.
This data serves as the foundation, providing insights, validating hypotheses, and ultimately helping to answer the specific research questions posed. Moreover, the quality and relevance of the data collected can significantly influence the accuracy and reliability of the research outcomes.
3. Online marketing
Companies actively collect and analyze various types of data to enhance and refine their online marketing strategies, making them more tailored and effective. By understanding consumer behavior, preferences, and feedback, businesses can design more targeted and relevant marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience. This personalized approach can help boost the overall success and return on investment of the marketing efforts.
4. Customer engagement
Companies collect data to enhance customer engagement by understanding their preferences, behaviors, and feedback, enabling more personalized and meaningful interactions. Here are some ways businesses can gather relevant data to improve customer engagement:
5. Risk management and compliance
Data helps businesses identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and promoting sound, secure business practices.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.